Codeforces 831D Office Keys - 贪心 - 二分答案 - 动态规划
There are n people and k keys on a straight line. Every person wants to get to the office which is located on the line as well. To do that, he needs to reach some point with a key, take the key and then go to the office. Once a key is taken by somebody, it couldn't be taken by anybody else.
You are to determine the minimum time needed for all n people to get to the office with keys. Assume that people move a unit distance per 1 second. If two people reach a key at the same time, only one of them can take the key. A person can pass through a point with a key without taking it.
The first line contains three integers n, k and p (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, n ≤ k ≤ 2 000, 1 ≤ p ≤ 109) — the number of people, the number of keys and the office location.
The second line contains n distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — positions in which people are located initially. The positions are given in arbitrary order.
The third line contains k distinct integers b1, b2, ..., bk (1 ≤ bj ≤ 109) — positions of the keys. The positions are given in arbitrary order.
Note that there can't be more than one person or more than one key in the same point. A person and a key can be located in the same point.
Print the minimum time (in seconds) needed for all n to reach the office with keys.
2 4 50
20 100
60 10 40 80
50
1 2 10
11
15 7
7
In the first example the person located at point 20 should take the key located at point 40 and go with it to the office located at point 50. He spends 30 seconds. The person located at point 100 can take the key located at point 80 and go to the office with it. He spends 50 seconds. Thus, after 50 seconds everybody is in office with keys.
题目大意 一个走廊里有n个人和k个钥匙,办公室在位置p,假定每个人每秒走一米,问至少要到少时间才能使得所有人到达办公室(进入办公室必须要钥匙,并且拿到了钥匙就不能给别人)。
Solution 1 (Slower Binary Search)
题目要求最大值最小,十有八九都是二分答案,因此,求值问题被转化成判定问题,给定时间mid,判断是否能够使得所有人进入办公室。
首先可以把每个人可以拿钥匙的区间求出来,然后按左端点排一道序(因为就算先将人按位置排序,也不能保证区间的长度一样,即不能保证左端点的单调性),接着开始贪心,让每个人尽量拿靠左的钥匙(当然你按右端点排序,让每个人拿尽量靠右的钥匙也可以),中间判断一下是否可行。所以,先要按钥匙的位置排一次序。
另外注意一点,二分的左端点应从0开始,比如,只有一个人1把钥匙,人站在办公室门口,钥匙在办公室门口。
Code

1 /** 2 * Codeforces 3 * Problem#831D 4 * Accepted 5 * Time:15ms 6 * Memory:2100k 7 */ 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <cstdio> 10 #include <ctime> 11 #include <cmath> 12 #include <cctype> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include <cstdlib> 15 #include <fstream> 16 #include <sstream> 17 #include <algorithm> 18 #include <map> 19 #include <set> 20 #include <stack> 21 #include <queue> 22 #include <vector> 23 #include <stack> 24 #include <cassert> 25 #ifndef WIN32 26 #define Auto "%lld" 27 #else 28 #define Auto "%I64d" 29 #endif 30 using namespace std; 31 typedef bool boolean; 32 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 33 const signed long long llf = (signed long long)((1ull << 61) - 1); 34 const double eps = 1e-6; 35 const int binary_limit = 128; 36 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 37 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 38 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 39 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 40 template<typename T> 41 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 42 char x; 43 int aFlag = 1; 44 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -1); 45 if(x == -1) { 46 ungetc(x, stdin); 47 return false; 48 } 49 if(x == '-'){ 50 x = getchar(); 51 aFlag = -1; 52 } 53 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - '0'); 54 ungetc(x, stdin); 55 u *= aFlag; 56 return true; 57 } 58 59 int n, m, p; 60 int *ps, *ks; 61 62 inline void init() { 63 readInteger(n); 64 readInteger(m); 65 readInteger(p); 66 ps = new int[(n + 1)]; 67 ks = new int[(m + 1)]; 68 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 69 readInteger(ps[i]); 70 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 71 readInteger(ks[i]); 72 } 73 74 pair<int, int>* ls; 75 boolean check(int mid) { 76 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 77 int dis = abs(ps[i] - p); 78 if(dis > mid) return false; 79 dis = (mid - dis) >> 1; 80 int l = ps[i], r = p; 81 if(l > r) swap(l, r); 82 l -= dis, r += dis; 83 ls[i] = pair<int, int>(l, r); 84 } 85 // cout << mid << " " << ls[1].first << " " << ls[1].second << endl; 86 sort(ls + 1, ls + n + 1); 87 int i, fin; 88 for(i = 1, fin = 1; i <= n; i++, fin++) { 89 while(fin <= m && ks[fin] < ls[i].first) fin++; 90 if((ls[i].second < ks[fin]) || fin > m) 91 return false; 92 } 93 return true; 94 } 95 96 inline void solve() { 97 sort(ks + 1, ks + m + 1); 98 // sort(ps + 1, ps + n + 1); 99 ls = new pair<int, int>[n + 1]; 100 int l = 0, r = 2e9; 101 while(l <= r) { 102 int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1); 103 if(check(mid)) r = mid - 1; 104 else l = mid + 1; 105 } 106 printf("%d", r + 1); 107 } 108 109 int main() { 110 init(); 111 solve(); 112 return 0; 113 }
Solution 2 (Faster Binary Search)
虽然可以O(nlogn)进行二分的check,但是有个更傻逼的贪心check可以做到线性。
就是从第一个钥匙开始for,找到第一个满足条件的钥匙(满足条件是指第一个人拿这个钥匙)给第一个人,第二个符合条件的钥匙给第二个人。。像这样安排下去,如果钥匙不够就说明不行,否则当前二分值可行。
Code

1 /** 2 * Codeforces 3 * Problem#831D 4 * Accepted 5 * Time: 15ms 6 * Memory: 12k 7 */ 8 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 9 using namespace std; 10 typedef bool boolean; 11 const signed int inf = (signed)(~0u >> 1); 12 13 int n, m, p; 14 int *as, *bs; 15 16 inline void init() { 17 scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &p); 18 as = new int[(n + 1)]; 19 bs = new int[(m + 1)]; 20 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 21 scanf("%d", as + i); 22 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 23 scanf("%d", bs + i); 24 } 25 26 boolean check(int mid) { 27 int j = 1; 28 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++, j++) { 29 while(j <= m && abs(as[i] - bs[j]) + abs(bs[j] - p) > mid) 30 j++; 31 if(j > m) 32 return false; 33 } 34 return true; 35 } 36 37 inline void solve() { 38 sort(as + 1, as + n + 1); 39 sort(bs + 1, bs + m + 1); 40 int l = 0, r = inf - 1; 41 while(l <= r) { 42 int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1); 43 // cerr << mid << endl; 44 if(check(mid)) r = mid - 1; 45 else l = mid + 1; 46 } 47 printf("%d", r + 1); 48 } 49 50 int main() { 51 init(); 52 solve(); 53 return 0; 54 }
Solution 3 (dp)
仔细分析题目,可以发现当i < j,x < y时,第i个人去拿第y把钥匙肯定,第j个人去拿第x把钥匙肯定没有第i个人去拿第x把钥匙,第j个人去拿第y把钥匙更优。
所以有了两种设计状态的方法
1)用f[i][j]表示第i个人拿第j把钥匙最少消耗的最大时间。
转移从f[i - 1][i]到f[i - 1][j]取个最小值,然后和第i个人去拿第j把钥匙的时间取最大值。
但是这么做会T掉,所以考虑用一个变量维护最小值,不断更新即可。
注意f[i][j]的边界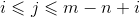 。(虽然不注意就只是慢了点)
。(虽然不注意就只是慢了点)
2)用f[i][j]表示考虑到第i把钥匙,已经有j个人拿到了钥匙的最少消耗的最大时间。
f[i][j]通过f[i - 1][j]或者f[i - 1][j - 1]转移。
我写的是第一种设计状态的dp做法。
Code
1 /** 2 * Codeforces 3 * Problem#831D 4 * Accepted 5 * Time: 15ms 6 * Memory: 7856k 7 */ 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <fstream> 10 #include <sstream> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <cstdlib> 13 #include <cstring> 14 #include <ctime> 15 #include <cmath> 16 #include <cctype> 17 #include <algorithm> 18 #include <map> 19 #include <set> 20 #include <queue> 21 #include <stack> 22 #include <vector> 23 #include <bitset> 24 #ifdef WIN22 25 #define Auto "%I64d" 26 #else 27 #define Auto "%lld" 28 #endif 29 using namespace std; 30 typedef bool boolean; 31 #define ll int 32 #define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b) 33 #define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b) 34 const signed int inf = (signed) (~0u >> 1); 35 const signed ll llf = (signed ll) (~0ull >> 1); 36 37 template<typename T> 38 inline void readInteger(T& u) { 39 static char x; 40 while(!isdigit(x = getchar())); 41 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit(x = getchar()); u = u * 10 + x - '0'); 42 } 43 44 template<typename T> 45 class Matrix { 46 public: 47 T* p; 48 int row; 49 int col; 50 Matrix():p(NULL) { } 51 Matrix(int row, int col):row(row), col(col) { 52 p = new T[(row * col)]; 53 } 54 55 T* operator [] (int pos) { 56 return p + (pos * col); 57 } 58 }; 59 #define matset(a, i, s) memset(a.p, i, s * a.row * a.col) 60 61 int n, m, s; 62 int *ps, *qs; 63 Matrix<ll> f; 64 65 inline void init() { 66 readInteger(n); 67 readInteger(m); 68 readInteger(s); 69 ps = new int[(n + 1)]; 70 qs = new int[(m + 1)]; 71 f = Matrix<ll>(n + 1, m + 1); 72 matset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(ll)); 73 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 74 readInteger(ps[i]); 75 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 76 readInteger(qs[i]); 77 } 78 79 inline void solve() { 80 sort(ps + 1, ps + n + 1); 81 sort(qs + 1, qs + m + 1); 82 f[0][0] = 0; 83 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 84 ll minv = f[i - 1][i - 1]; 85 for(int j = i; j <= m - n + i; j++) { 86 f[i][j] = max(minv, abs(ps[i] - qs[j]) + abs(qs[j] - s)); 87 smin(minv, f[i - 1][j]); 88 } 89 } 90 ll res = inf; 91 for(int i = n; i <= m; i++) 92 smin(res, f[n][i]); 93 printf("%d", res); 94 } 95 96 int main() { 97 init(); 98 solve(); 99 return 0; 100 }


