Struts(十二):异常处理:exception-mapping元素
- 配置当前action的声明异常处理
1、exception-mapping元素中有2个属性
exception:指定需要捕获的异常类型
result:指定一个响应结果,该结果将在捕获到异常时被执行。即可以来自当前action的声明,也可以来自global-results声明。2、可以在视图上通过<s:property>标签显示异常消息。
基于上几个章节的例子开始往下写,修改save函数:
public String save(){ System.out.println("save"); int val=10/0; return "success"; }
此时访问http://localhost:8080/Struts_01/,输入信息点击“提交”按钮跳转到details.jsp,当访问save函数时,就跑出了异常信息:
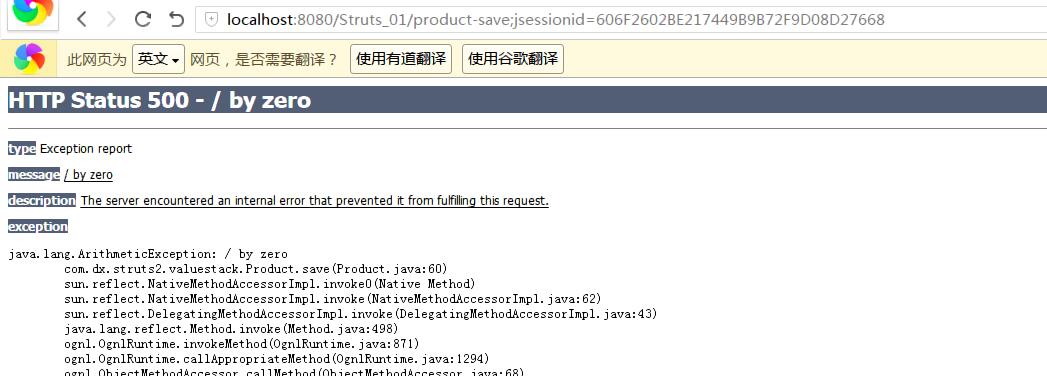
此时,我们发现异常信息并没有被合理的处理掉,比如出错了,我们让页面跳转到error.jsp该多好,其实struts2中通过配置struts.xml是可以实现的。
修改struts.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <!-- <constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action" /> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> --> <constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true" /> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="false" /> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="product-save" class="com.dx.struts2.valuestack.Product" method="save"> <exception-mapping result="error" exception="java.lang.ArithmeticException"></exception-mapping> <result name="error">/error.jsp</result> <result>/details.jsp</result> </action> </package> <!-- Add packages here --> </struts>
添加在WebContent下添加error.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> error </body> </html>
重启服务,重新访问页面,并提交参数,发现页面自动跳转到了error.jsp: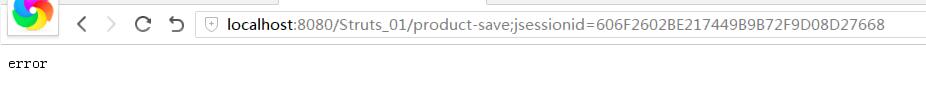
如果光跳转过来不太完美,如果可以显示错误信息不是更好,实际上通过EL或者s:property标签是可以实现的,修改error.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> error<br/> <s:debug/> <s:property value="exception" /><br/> ${exception}<br/> ${exception.message}<br/> <s:property value="exception.message"/><br/> <s:property value="exceptionStack"/><br/> ${exceptionStack} </body> </html>
显示信息: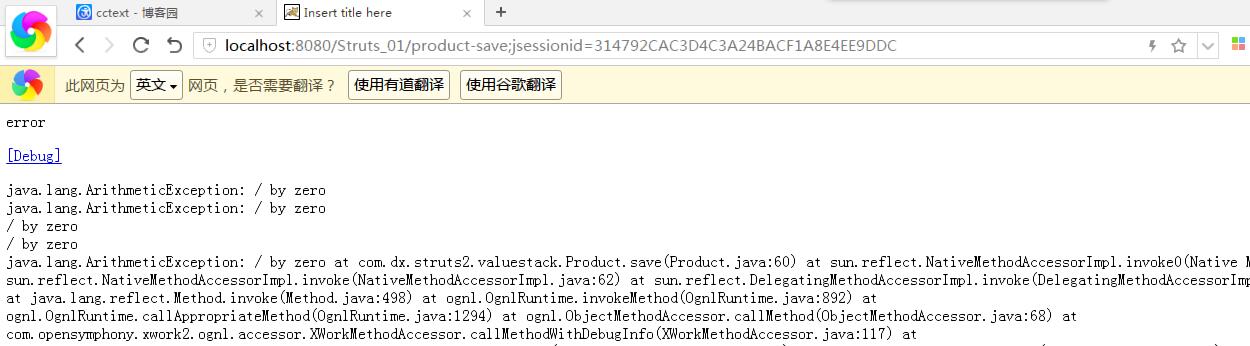
s:debug第一个元素类型为:com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExceptionHolder
元素包含两个属性:exception和exceptionStack
- 可以通过global-exception-mappings元素为应用程序提供一个全局性的异常捕获映射。
1、但在global-exception-mappings元素下声明任何exception-mapping元素只能引用在global-results元素下声明的某个result元素。
只需要修改struts.xml即可,其他不需要变动:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <!-- <constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action" /> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> --> <constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true" /> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="false" /> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <global-results> <result name="error">/error.jsp</result> </global-results> <global-exception-mappings> <exception-mapping result="error" exception="java.lang.ArithmeticException"></exception-mapping> </global-exception-mappings> <action name="product-save" class="com.dx.struts2.valuestack.Product" method="save"> <!-- <exception-mapping result="error" exception="java.lang.ArithmeticException"></exception-mapping> <result name="error">/error.jsp</result> --> <result>/details.jsp</result> </action> </package> <!-- Add packages here --> </struts>
重新访问即可,其他内容不影响显示。
- 声明式异常处理机制由ExceptionMappingInterceptor拦截器负责处理。
1、当某个exception-mapping元素声明的异常被捕获到是,ExceptionMappingInterceptor拦截器就会向ValueStack中添加两个对象:
exception:表示被捕获异常的Exception对象
exceptionStack:包含着被捕获异常的栈2、什么地方注册这个拦截器?
struts-core.jar 下的struts-default.xml中<default-interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<interceptor name="exception" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExceptionMappingInterceptor"/>
com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExceptionMappingInterceptor怎么向ValueStack中写入异常信息?
package com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.config.entities.ExceptionMappingConfig; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.Logger; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.logging.LoggerFactory; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * @author Matthew E. Porter (matthew dot porter at metissian dot com) * @author Claus Ibsen */ public class ExceptionMappingInterceptor extends AbstractInterceptor { protected static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionMappingInterceptor.class); protected Logger categoryLogger; protected boolean logEnabled = false; protected String logCategory; protected String logLevel; public boolean isLogEnabled() { return logEnabled; } public void setLogEnabled(boolean logEnabled) { this.logEnabled = logEnabled; } public String getLogCategory() { return logCategory; } public void setLogCategory(String logCatgory) { this.logCategory = logCatgory; } public String getLogLevel() { return logLevel; } public void setLogLevel(String logLevel) { this.logLevel = logLevel; } @Override public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { String result; try { result = invocation.invoke(); } catch (Exception e) { if (isLogEnabled()) { handleLogging(e); } List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings = invocation.getProxy().getConfig().getExceptionMappings(); ExceptionMappingConfig mappingConfig = this.findMappingFromExceptions(exceptionMappings, e); if (mappingConfig != null && mappingConfig.getResult()!=null) { Map parameterMap = mappingConfig.getParams(); // create a mutable HashMap since some interceptors will remove parameters, and parameterMap is immutable invocation.getInvocationContext().setParameters(new HashMap<String, Object>(parameterMap)); result = mappingConfig.getResult(); publishException(invocation, new ExceptionHolder(e)); } else { throw e; } } return result; } /** * Handles the logging of the exception. * * @param e the exception to log. */ protected void handleLogging(Exception e) { if (logCategory != null) { if (categoryLogger == null) { // init category logger categoryLogger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(logCategory); } doLog(categoryLogger, e); } else { doLog(LOG, e); } } /** * Performs the actual logging. * * @param logger the provided logger to use. * @param e the exception to log. */ protected void doLog(Logger logger, Exception e) { if (logLevel == null) { logger.debug(e.getMessage(), e); return; } if ("trace".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.trace(e.getMessage(), e); } else if ("debug".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.debug(e.getMessage(), e); } else if ("info".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.info(e.getMessage(), e); } else if ("warn".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); } else if ("error".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } else if ("fatal".equalsIgnoreCase(logLevel)) { logger.fatal(e.getMessage(), e); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("LogLevel [" + logLevel + "] is not supported"); } } /** * @deprecated since 2.3.15 please use #findMappingFromExceptions directly instead */ protected String findResultFromExceptions(List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings, Throwable t) { ExceptionMappingConfig result = findMappingFromExceptions(exceptionMappings, t); return result==null?null:result.getResult(); } /** * Try to find appropriate {@link ExceptionMappingConfig} based on provided Throwable * * @param exceptionMappings list of defined exception mappings * @param t caught exception * @return appropriate mapping or null */ protected ExceptionMappingConfig findMappingFromExceptions(List<ExceptionMappingConfig> exceptionMappings, Throwable t) { ExceptionMappingConfig config = null; // Check for specific exception mappings. if (exceptionMappings != null) { int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (Object exceptionMapping : exceptionMappings) { ExceptionMappingConfig exceptionMappingConfig = (ExceptionMappingConfig) exceptionMapping; int depth = getDepth(exceptionMappingConfig.getExceptionClassName(), t); if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) { deepest = depth; config = exceptionMappingConfig; } } } return config; } /** * Return the depth to the superclass matching. 0 means ex matches exactly. Returns -1 if there's no match. * Otherwise, returns depth. Lowest depth wins. * * @param exceptionMapping the mapping classname * @param t the cause * @return the depth, if not found -1 is returned. */ public int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Throwable t) { return getDepth(exceptionMapping, t.getClass(), 0); } private int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Class exceptionClass, int depth) { if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(exceptionMapping)) { // Found it! return depth; } // If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it... if (exceptionClass.equals(Throwable.class)) { return -1; } return getDepth(exceptionMapping, exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1); } /** * Default implementation to handle ExceptionHolder publishing. Pushes given ExceptionHolder on the stack. * Subclasses may override this to customize publishing. * * @param invocation The invocation to publish Exception for. * @param exceptionHolder The exceptionHolder wrapping the Exception to publish. */ protected void publishException(ActionInvocation invocation, ExceptionHolder exceptionHolder) { invocation.getStack().push(exceptionHolder); } }
基础才是编程人员应该深入研究的问题,比如:
1)List/Set/Map内部组成原理|区别
2)mysql索引存储结构&如何调优/b-tree特点、计算复杂度及影响复杂度的因素。。。
3)JVM运行组成与原理及调优
4)Java类加载器运行原理
5)Java中GC过程原理|使用的回收算法原理
6)Redis中hash一致性实现及与hash其他区别
7)Java多线程、线程池开发、管理Lock与Synchroined区别
8)Spring IOC/AOP 原理;加载过程的。。。
【+加关注】。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号