Java-Shiro(七):Shiro认证、授权信息缓存
声明:本证项目基于《Java-Shiro(六):Shiro Realm讲解(三)Realm的自定义及应用》构建项目为基础。
本文代码:《https://github.com/478632418/springmv_without_web_xml/tree/master/mybaits-test-dynamic-sql-02》
Shiro内部提供了对认证信息和授权信息的缓存,但是shiro默认是关闭认证信息缓存,对于授权信息的缓存shiro默认开启的。一般情况下,使用shiro缓存时,只需要关注授权信息缓存,因为认证信息只是一次验证查询,而授权信息需要在每次认证都会执行(访问量大),且一般情况下授权的数据量大。
但是,当用户信息被修改时,我们希望理解看到认证信息也被同步时,需要关注认证信息清空同步问题。
Shiro授权缓存的使用
配置
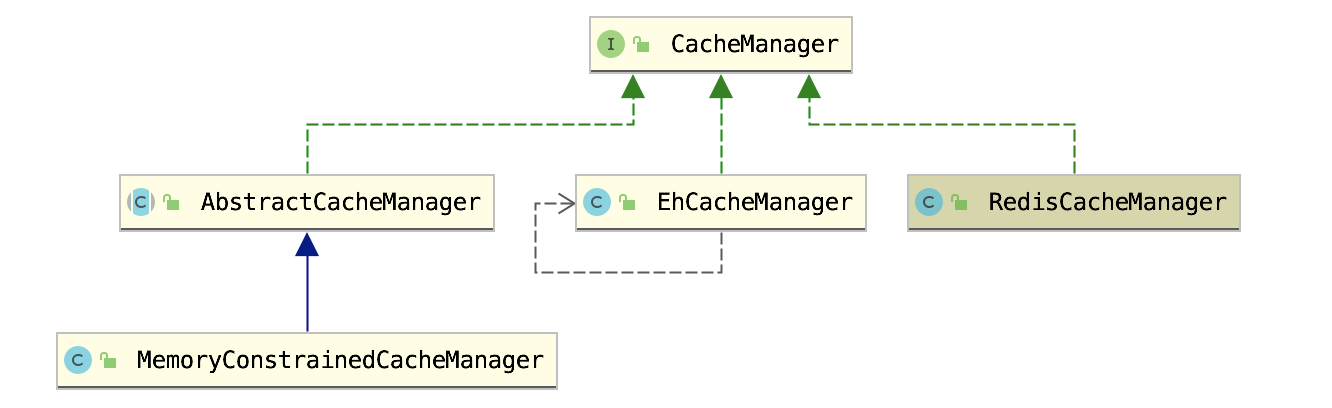
在授权信息缓存的方案包含以下三种:
1)使用Ehcache(系统混合缓存方案);
2)使用本地内存缓存方案;
3)自定义CacheManager(比如Redis用来作为缓存)。
1)使用Ehcache(系统混合缓存方案)
1)在pom.xml中引入shiro-ehcache依赖;
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId> <version>${shiro.version}</version> </dependency>
2)在applicationContext-shiro.xml中添加ehcache配置并被securityManager的cacheManage引用:
<!--cacheManager--> <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManagerConfigFile" value="classpath:shiro-ehcache.xml"/> </bean> <!-- securityManager安全管理器 --> <bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="realm" ref="myRealm"></property> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"></property> </bean>
3)在src/main/resources下添加shiro-ehcache.xml ehcache配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache> <!-- 数据缓存地址,如,F:/develop/ehcache --> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir/shiro-spring-sample"/> <!-- name="authorizationCache" //缓存名称 maxEntriesLocalHeap="2000" //缓存最大条目数 eternal="false" //对象是否永久有效,true则timeout失效 timeToIdleSeconds="3600" //对象在失效前的闲置时间(单位:s),仅eternal=false时有效;默认为0,即可闲置时间无穷大。 timeToLiveSeconds="0" //缓存数据的生成时间(单位:s),介于创建时间和失效时间之间;仅eternal=false有效;默认为0,即对象存活时间无穷大。 overflowToDisk="false" //内存中对象数量达到maxElementInMemory时,是否将对象写到磁盘 diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:设置diskStore磁盘缓存的缓存区大小,默认30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓存区。 maxElementOnDisk:磁盘最大缓存个数。 diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据,默认false。 diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds: 磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认120s。 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:达到maxElementInMemory时,Ehcache将会根据此策略去清理内存,默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用),可设为FIFO(先进先出)或LFU(较少使用)。 clearOnFlush: 内存数量最大时是否清除。 --> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" /> <cache name="shiro-activeSessionCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="true" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="600"/> <cache name="org.apache.shiro.realm.SimpleAccountRealm.authorization" maxElementsInMemory="100" eternal="false" timeToLiveSeconds="600" overflowToDisk="false"/> </ehcache>
备注:ehcache中cache标签属性意义:
name="authorizationCache" //缓存名称
maxEntriesLocalHeap="2000" //缓存最大条目数
eternal="false" //对象是否永久有效,true则timeout失效
timeToIdleSeconds="3600" //对象在失效前的闲置时间(单位:s),仅eternal=false时有效;默认为0,即可闲置时间无穷大。
timeToLiveSeconds="0" //缓存数据的生成时间(单位:s),介于创建时间和失效时间之间;仅eternal=false有效;默认为0,即对象存活时间无穷大。
overflowToDisk="false" //内存中对象数量达到maxElementInMemory时,是否将对象写到磁盘
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:设置diskStore磁盘缓存的缓存区大小,默认30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓存区。
maxElementOnDisk:磁盘最大缓存个数。
diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据,默认false。
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds: 磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认120s。
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:达到maxElementInMemory时,Ehcache将会根据此策略去清理内存,默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用),可设为FIFO(先进先出)或LFU(较少使用)。
clearOnFlush: 内存数量最大时是否清除。
2)使用本地内存缓存方案
applicationContext-shiro.xml中配置cacheManager,该cacheManager并被securityManager引用。
<!-- // 采用本地内存方式缓存 --> <bean id="cacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.MemoryConstrainedCacheManager"/> <!-- securityManager安全管理器 --> <bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="realm" ref="myRealm"></property> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"></property> </bean>
其他不需要配置即可。
3)自定义CacheManager
比如Redis用来作为缓存。
1)需要添加redis依赖到pom.xml
<!-- redis依赖包 --> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.data/spring-data-redis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> <version>2.2.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
2)在src/main/resources下新建applicaitonContext-redis.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 加载配置文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jedis.properties" ignore-unresolvable="true" /> <!-- 连接池配置 --> <bean id="jedisPoolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <!-- 最大连接数 --> <property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}" /> <!-- 最大空闲连接数 --> <property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}" /> <!-- 每次释放连接的最大数目 --> <property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="${redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun}" /> <!-- 释放连接的扫描间隔(毫秒) --> <property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="${redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis}" /> <!-- 连接最小空闲时间 --> <property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" /> <!-- 连接空闲多久后释放, 当空闲时间>该值 且 空闲连接>最大空闲连接数 时直接释放 --> <property name="softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="${redis.softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis}" /> <!-- 获取连接时的最大等待毫秒数,小于零:阻塞不确定的时间,默认-1 --> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}" /> <!-- 在获取连接的时候检查有效性, 默认false --> <property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}" /> <!-- 在空闲时检查有效性, 默认false --> <property name="testWhileIdle" value="${redis.testWhileIdle}" /> <!-- 连接耗尽时是否阻塞, false报异常,ture阻塞直到超时, 默认true --> <property name="blockWhenExhausted" value="${redis.blockWhenExhausted}" /> </bean> <bean id="jedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool"> <constructor-arg name="host" value="${redis.host}"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="port" value="${redis.port}"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPoolConfig"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 需要密码 --> <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory" p:host-name="${redis.host}" p:port="${redis.port}" p:password="${redis.pass}" p:pool-config-ref="jedisPoolConfig"/> <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory" /> <property name="keySerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer" /> </property> <property name="valueSerializer"> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer" /> </property> </bean> </beans>
配置中需要依赖资源文件jedis.properties
redis.maxTotal=2000
redis.maxIdle=50
redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun=1024
redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=30000
redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=1800000
redis.softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis=10000
redis.maxWaitMillis=15000
redis.testOnBorrow=false
redis.testWhileIdle=false
redis.testOnReturn=false
redis.blockWhenExhausted=true
redis.host=127.0.0.1
redis.port=6379
redis.pass=
3)修改web.xml,ContextLoaderListener加载文件添加applicationContext-redis.xml,修改后为:
<!-- 加载spring容器 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> classpath:applicationContext-redis.xml, classpath:applicationContext-shiro.xml, classpath:applicationContext-mybatis.xml </param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
4)新建redis缓存管理类RedisCache.java和RedisCacheManager.java
RedisCache.java

public class RedisCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; private Logger logger; private String keyPrefix; public String getKeyPrefix() { return this.keyPrefix; } public void setKeyPrefix(String keyPrefix) { this.keyPrefix = keyPrefix; } public RedisCache(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) { this.logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); this.keyPrefix = "shiro_redis_cache:"; this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate; } public RedisCache(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, String prefix) { this(redisTemplate); this.keyPrefix = prefix; } /** * 获得byte[]型的key * * @param key * @return */ private byte[] getByteKey(Object key) { if (key instanceof String) { String preKey = this.keyPrefix + key; return preKey.getBytes(); } else { return SerializeUtils.serialize((Serializable) key); } } private RedisConnection getRedisConnect() { return redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection(); } @Override public Object get(Object key) throws CacheException { byte[] bytes = getByteKey(key); byte[] value = getRedisConnect().get(bytes); if (value == null) { return null; } return SerializeUtils.deserialize(value); } /** * 将shiro的缓存保存到redis中 */ @Override public Object put(Object key, Object value) throws CacheException { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); byte[] bytesKey = getByteKey(key); byte[] bytesValue = SerializeUtils.serialize((Serializable) value); redisConnection.set(bytesKey, bytesValue); byte[] bytes = redisConnection.get(getByteKey(key)); Object object = SerializeUtils.deserialize(bytes); return object; } @Override public Object remove(Object key) throws CacheException { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); byte[] bytes = redisConnection.get(getByteKey(key)); redisConnection.del(getByteKey(key)); return SerializeUtils.deserialize(bytes); } /** * 清空所有缓存 */ @Override public void clear() throws CacheException { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); redisConnection.flushDb(); } /** * 缓存的个数 */ @Override public int size() { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); Long size = redisConnection.dbSize(); return size.intValue(); } /** * 获取所有的key */ @Override public Set keys() { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); Set<byte[]> keys = redisConnection.keys(new String("*").getBytes()); Set<Object> set = new HashSet<Object>(); for (byte[] bs : keys) { set.add(SerializeUtils.deserialize(bs)); } return set; } /** * 获取所有的value */ @Override public Collection values() { RedisConnection redisConnection = getRedisConnect(); Set keys = this.keys(); List<Object> values = new ArrayList<Object>(); for (Object key : keys) { byte[] bytes = redisConnection.get(getByteKey(key)); values.add(SerializeUtils.deserialize(bytes)); } return values; } }
RedisCacheManager.java
public class RedisCacheManager implements CacheManager { @Resource private RedisTemplate<Serializable, Object> redisTemplate; @Override public <K, V> Cache<K, V> getCache(String name) throws CacheException { return new RedisCache<K, V>(redisTemplate); } }
5)修改applicationContext-shiro.xml配置文件,配置securityManager的cacheManager对象。
<!-- 自定义cacheManager --> <bean id="cacheManager" class="com.dx.test.shiro.RedisCacheManager"/> <!-- securityManager安全管理器 --> <bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="realm" ref="myRealm"></property> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"></property> <property name="sessionManager" ref="sessionManager"></property> </bean>
执行效果
执行效果:
1)进入登录页面http://localhost:8080/mybaits-test-dynamic-sql/login/,填写用户&密码点击登录按钮,用户认证通过;
2)该用户第一次授权,调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库。
3)该用户第二次授权,不调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库,直接从缓存中取出授权信息(授权标识符)。
清除缓存
如果用户正常退出,缓存自动清空;
如果用户非正常退出,缓存也自动清空;
如果修改了用户权限,而用户不退出系统,修改的权限无法立即生效。需要开发者变成实现:
1)在权限修改后,调用MyRealm的clearCache方法清除缓存。
在MyRealm类方法最下边添加方法clearCache方法:
/** * 清空已经放入缓存的授权信息。 * */ public void clearCache() { PrincipalCollection principals=SecurityUtils.getSubject().getPrincipals(); super.clearCache(principals); }
2)添加模拟编辑角色SysRoleController.java类:
@Controller @RequestMapping(value = "/role") public class SysRoleController { @Autowired private MyRealm myRealm; @RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String updateRole(SysRole sysRole, Map<String, Object> map) { BaseResult baseResult = null; ResultEnum enu = null; // 模拟:在这里做了以下业务: // 1)修改了角色下的资源信息; // 2)删除了角色; // 3)修改了用户的角色信息。 myRealm.clearCache(); enu = ResultEnum.Success; baseResult = new BaseResult(enu.getCode(), enu.getMessage(), enu.getDesc()); map.put("result", baseResult); return "role/list.jsp"; } }
备注:
1)上边代码只是模拟测试代码,模拟修改了授权信息,实际上做了以下操作都会修改授权信息:
1.1)修改了角色下的资源信息;
1.2)删除了角色;
1.3)修改了用户的角色信息。
2)思考:如果修改了授权信息,实际系统已经修改了,但是认证的用户授权已经被缓存到了缓存中,假设不再修改授权信息的地方清理授权缓存,什么时候用户会获取修改后的授权信?
2.1)用户退出系统时会清理缓存,重新后在第一次授权时,会调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库,将最新的授权信息缓存;
2.2)缓存过期,在shiro-ehcache.xml配置的cache标签项中有配置自动过期时间,当然如果配置为0,永不过期。
3)测试
认证后,访问授权,然后修改授权信息,重新授权是否调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库。
备注:
1)认证:访问登录页面,输入账户密码点击‘登录’按钮,登录后台;
2)授权(url拦截、访问<shiro:标签>、@RequiresPermission、@RequiresRole等):访问后台页面,第一次会调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库,然后ehcache会缓存该授权吸信息到缓存中。第二次以后都不会再调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库;
3)修改授权信息,访问修改授权页面(http://localhost:8080/mybaits-test-dynamic-sql/role/update)
执行了以下三种操作都可能修改授权信息:
- 1)修改了角色下的资源信息;
- 2)删除了角色;
- 3)修改了用户的角色信息。
4)重新访问授权(url拦截、访问<shiro:标签>、@RequiresPermission、@RequiresRole等)信息:访问后台页面,如果缓存被情况的情况下会再次调用realm#doGetAuthorizationInfo(...)方法查询数据库,然后ehcache会缓存该授权信息到缓存中。
遇到问题:java.io.NotSerializableException: org.apache.shiro.util.SimpleByteSource
在使用Redis作为Shiro的缓存管理器的时候,在将SimpleAuthenticationInfo信息进行序列化的时候报异常:java.io.NotSerializableException: org.apache.shiro.util.SimpleByteSource
原因是:SimpleByteSource没有实现Serializable接口
解决办法:
1)重新定义SimpleByteSource(MySimpleByteSource.java)

/** * 解决:shiro 使用缓存时出现:java.io.NotSerializableException: org.apache.shiro.util.SimpleByteSource * 序列化后,无法反序列化的问题 */ public class MySimpleByteSource implements ByteSource, Serializable { private byte[] bytes; private String cachedHex; private String cachedBase64; public MySimpleByteSource() { } public MySimpleByteSource(byte[] bytes) { this.bytes = bytes; } public MySimpleByteSource(char[] chars) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(chars); } public MySimpleByteSource(String string) { this.bytes = CodecSupport.toBytes(string); } public MySimpleByteSource(ByteSource source) { this.bytes = source.getBytes(); } public MySimpleByteSource(File file) { this.bytes = (new MySimpleByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(file); } public MySimpleByteSource(InputStream stream) { this.bytes = (new MySimpleByteSource.BytesHelper()).getBytes(stream); } public static boolean isCompatible(Object o) { return o instanceof byte[] || o instanceof char[] || o instanceof String || o instanceof ByteSource || o instanceof File || o instanceof InputStream; } public void setBytes(byte[] bytes) { this.bytes = bytes; } @Override public byte[] getBytes() { return this.bytes; } @Override public String toHex() { if (this.cachedHex == null) { this.cachedHex = Hex.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedHex; } @Override public String toBase64() { if (this.cachedBase64 == null) { this.cachedBase64 = Base64.encodeToString(this.getBytes()); } return this.cachedBase64; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return this.bytes == null || this.bytes.length == 0; } @Override public String toString() { return this.toBase64(); } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.bytes != null && this.bytes.length != 0 ? Arrays.hashCode(this.bytes) : 0; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (o instanceof ByteSource) { ByteSource bs = (ByteSource) o; return Arrays.equals(this.getBytes(), bs.getBytes()); } else { return false; } } private static final class BytesHelper extends CodecSupport { private BytesHelper() { } public byte[] getBytes(File file) { return this.toBytes(file); } public byte[] getBytes(InputStream stream) { return this.toBytes(stream); } } }
2)修改MyRealm#doGetAuthenticationInfo()中使用salt代码:
@Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("‘MyRealm’执行认证操作:"); if (token == null) { throw new UnsupportedTokenException(); } UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; if (userToken == null) { throw new UnsupportedTokenException(); } // 获取当前需要登录的用户 String username = userToken.getUsername(); String userPwd = String.valueOf(userToken.getPassword()); if (StringUtils.isBlank(username) || userPwd == null) { throw new IncorrectCredentialsException("用户名或密码不正确"); } SysUser sysUser = this.sysUserMapper.getByUsername(username); if (sysUser == null) { throw new UnknownAccountException("用户名不存在"); } Byte locked = Byte.valueOf("1"); if (sysUser.getStatus().equals(locked)) { throw new LockedAccountException("用户已锁定"); } Date now = new Date(); if (sysUser.getExpireTime().before(now)) { throw new ExpiredCredentialsException("用户过期"); } // 从数据库中取出密码,密码是加过盐的 String password = sysUser.getPassword(); // 从数据库中取出盐 String salt=sysUser.getSalt(); SysUser simpleSysUser=new SysUser(); simpleSysUser.setUserName(sysUser.getUsername()); simpleSysUser.setEmail(sysUser.getEmail()); simpleSysUser.setPhone(sysUser.getPhone()); simpleSysUser.setNickName(sysUser.getNickName()); simpleSysUser.setSignature(sysUser.getSignature()); // 该信息会提交给SecurityManager,在SecurityManager内部会进行验证: // 用户输入的password+salt+md5+hashIterations 是否等于 db password? 等于则通过认证,否则不通过认证。 SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( simpleSysUser, password.toCharArray(), new MySimpleByteSource(salt), this.getName()); return authenticationInfo; }
配置认证缓存
指定缓存认证的缓存对象,以及是否开启缓存,这些配置都需要在realm属性上配置。
1)自定义缓存对象:
1)首先,开启realm的缓存控制开关属性;
2)其次,需要指定 realm.authenticationCache 属性(也即是指定缓存类对象)。
配置
主要两种实现方式:
1)采用自定义authenticationCache的cache对象;
2)集成ehcache,在ehcache中配置authenticationCache对象。
1)自定义缓存类对象
<!-- 配置自定义Realm --> <bean id="myRealm" class="com.dx.test.shiro.MyRealm"> <!-- 将凭证匹配器设置到realm中,realm按照凭证匹配器的要求进行散列 --> <property name="credentialsMatcher" ref="credentialsMatcher"></property> <!--启用缓存,默认SimpleAccountRealm关闭,默认AuthenticatingRealm、AuthorizingRealm、CachingRealm开启--> <property name="cachingEnabled" value="true"/> <!--启用身份验证缓存,即缓存AuthenticationInfo,默认false--> <property name="authenticationCachingEnabled" value="true"/> <!--启用授权缓存,即缓存AuthorizationInfo的信息,默认为true--> <property name="authorizationCachingEnabled" value="true"/> <property name="authenticationCache" ref="redisCache"></property> </bean> <bean id="redisCache" class="com.dx.test.shiro.RedisCache"> <constructor-arg ref="redisTemplate"></constructor-arg> </bean>
备注:
1)其中RedisCache需要依赖redisTemplate bean,因此需要在ContextLoaderListener中添加applicationContext-redis.xml(上边有提过)。
2)cachingEnabled:启用缓存,默认SimpleAccountRealm关闭,默认AuthenticatingRealm、AuthorizingRealm、CachingRealm开启;
3)authenticationCachingEnabled:启用身份验证(认证)缓存,即缓存AuthenticationInfo,默认false;
4)authorizationCachingEnabled:启用授权缓存,即缓存AuthorizationInfo的信息,默认为true;
5)authenticationCache:进行认证信息缓存使用的缓存类对象。
根据上边配置中注释,我们可以得知:
当我们的自定义 MyRealm 继承自 AuthorizingRealm 时,cachingEnabled 属性值一定为 true。那么,主要控制是否开启认证的开关是 authenticationCachingEnabled。
2)集成ehcache实现认证缓存
除了上边自定义方式,实际上还可以集成Ehcache实现认证、授权缓存。这种方式,不仅仅可以配置认证缓存,对授权缓存也可以采用该方案。
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="realm" ref="myRealm"/> <property name="cacheManager" ref="ehCacheManager"/> </bean> <bean id="ehCacheManager" class="org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManagerConfigFile" value="classpath:ehcache.xml"/> <bean/> <bean id="myRealm" class="com.dx.test.shiro.MyRealm"> <property name="credentialsMatcher" ref="credentialsMatcher"/> <property name="cachingEnabled" value="true"/> <property name="authenticationCachingEnabled" value="true"/> <property name="authenticationCacheName" value="authenticationCache"/> <property name="authorizationCachingEnabled" value="true"/> <property name="authorizationCacheName" value="authorizationCache"/> </bean>
ehcache.xml配置内容:
<cache name="authorizationCache" maxEntriesLocalHeap="2000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="3600" timeToLiveSeconds="0" overflowToDisk="false" statistics="true"> </cache> <cache name="authenticationCache" maxEntriesLocalHeap="2000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="3600" timeToLiveSeconds="0" overflowToDisk="false" statistics="true"> </cache>
测试
主要针对自定authenticationCache方案进行测试:
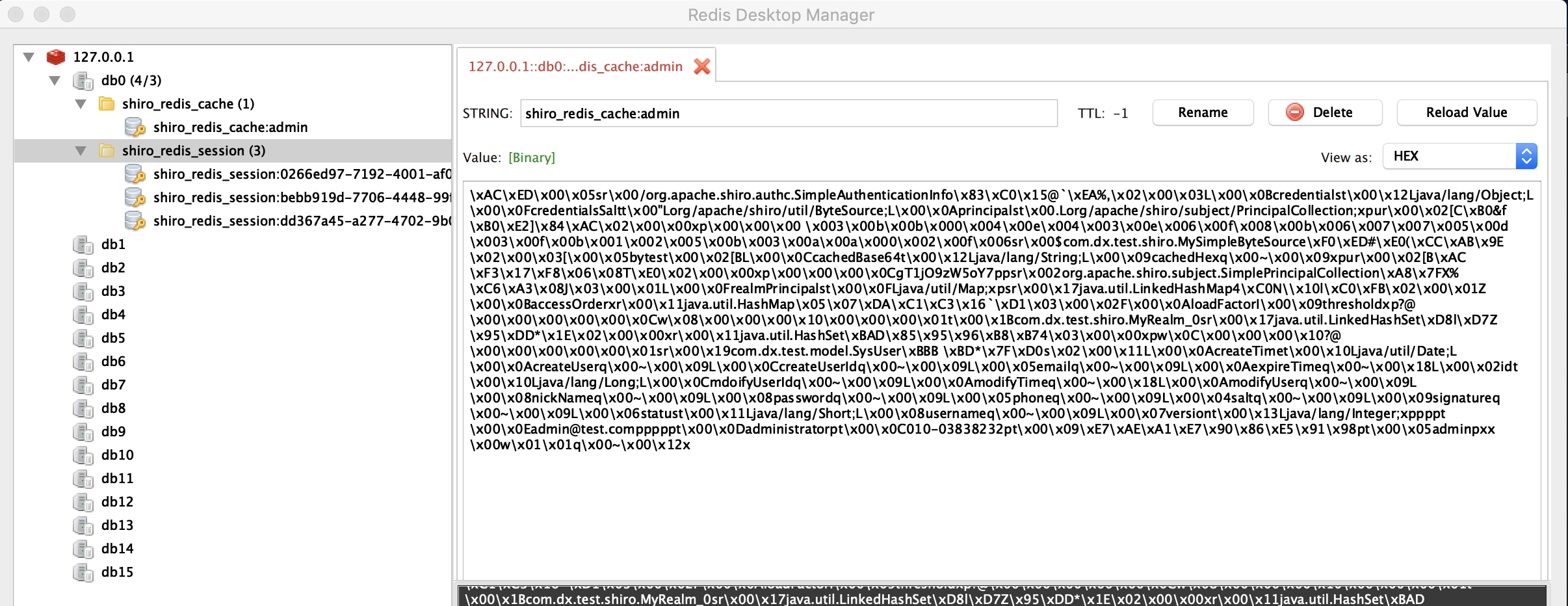
1)进入登录页面,输入账户密码,点击登录;
2)此时会发现redis中多了一条redis_cache:信息。
清除缓存
如果账户正常退出,会自动清空redis中缓存;
如果非正常退出,不会自动清空redis中缓存。(因此,这也是不推荐配置的一个原因);
当修改了用户基本信息时,如果强制执行清空认证信息,需要在MyRealm中定义clearXXX先关类。
MyRealm.java清空认证、授权信息方法定义:
//重写以下方法并改为public,否则测试无法调用这些Protected的方法 @Override public void clearCachedAuthenticationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { super.clearCachedAuthenticationInfo(principals); } @Override public void clearCachedAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) { super.clearCachedAuthorizationInfo(principals); } @Override public void clearCache(PrincipalCollection principals) { //同时调用以上俩方法,清空两个Info super.clearCache(principals); } public void clearAllCachedAuthorizationInfo(){ getAuthorizationCache().clear(); } public void clearAllCachedAuthenticationInfo() { getAuthenticationCache().clear(); } public void clearAllCache() { clearAllCachedAuthenticationInfo(); clearAllCachedAuthorizationInfo(); }
注意:
1)如果采用了redis缓存认证方案,当执行clearAllCachedAuthenticationInfo()方法,会清退所有在线用户,用户需要重新登录才能继续操作;
2)如果采用ehcache缓存认证方案,当执行clearAllCachedAuthenticationInfo()方法,不会清空任何在线用户,用户不需要重新登录;
3)不管采用什么缓存授权信息,当执行了clearAllCachedAuthorizationInfo()方法,都会清空授权信息,用户再次操作调用授权时,会重新执行MyRealm#doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法。这就有缺点,也许只修改涉及到授权改变的用户授权缓存清空才合理,以下清空所有用户有点粗暴。
基础才是编程人员应该深入研究的问题,比如:
1)List/Set/Map内部组成原理|区别
2)mysql索引存储结构&如何调优/b-tree特点、计算复杂度及影响复杂度的因素。。。
3)JVM运行组成与原理及调优
4)Java类加载器运行原理
5)Java中GC过程原理|使用的回收算法原理
6)Redis中hash一致性实现及与hash其他区别
7)Java多线程、线程池开发、管理Lock与Synchroined区别
8)Spring IOC/AOP 原理;加载过程的。。。
【+加关注】。




