2020系统综合实践 第7次实践作业——23组
在树莓派中安装opencv库
安装依赖
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev libtiff5-dev libjasper-dev libpng12-dev
sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libv4l-dev
sudo apt-get install libxvidcore-dev libx264-dev
sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev libgtk-3-dev
sudo apt-get install libatlas-base-dev
sudo apt install libqt4-test
sudo apt install libqtgui4
下载解压OpenCV源码
cd ~
wget -O opencv.zip https://github.com/Itseez/opencv/archive/4.1.2.zip
unzip opencv.zip
wget -O opencv_contrib.zip https://github.com/Itseez/opencv_contrib/archive/4.1.2.zip
unzip opencv_contrib.zip
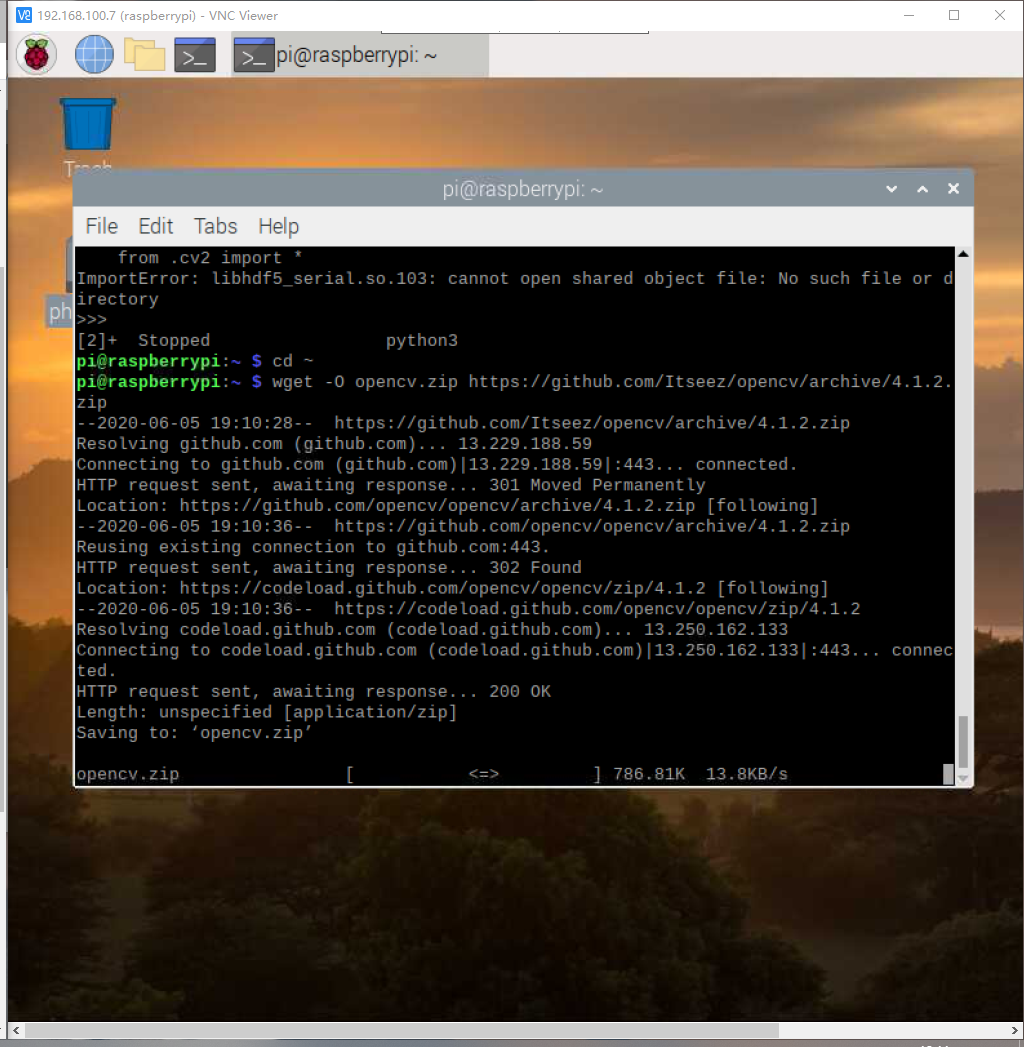
安装Python虚拟机
sudo pip install virtualenv virtualenvwrapper
sudo rm -rf ~/.cache/pip

配置profile
export WORKON_HOME=$HOME/.virtualenvs
export VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3
export VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_VIRTUALENV=/usr/local/bin/virtualenv
source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh
export VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_ENV_BIN_DIR=bin
安装numpy
pip3 install numpy
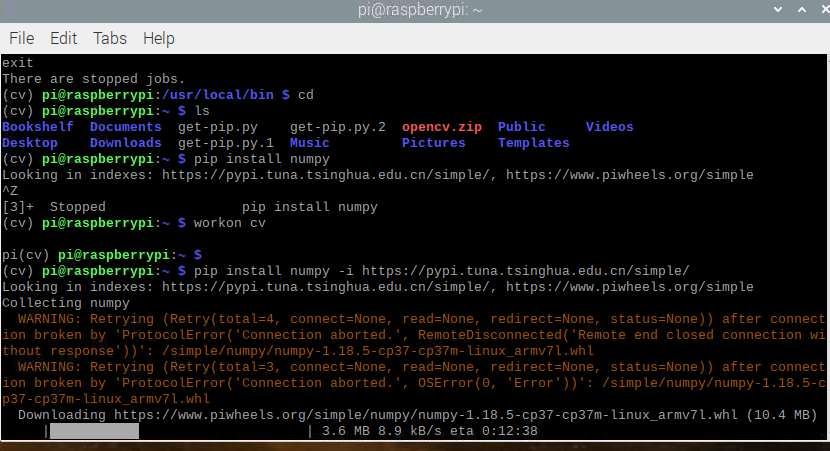
编译OpenCV
cd ~/opencv-4.1.2/
mkdir build
cd build
# 设置CMake构建选项
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local \
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=~/opencv_contrib-4.1.2/modules \
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON
教程中说这个需要1-2h来执行,我们组执行途中出现很多问题,索性放弃了这种方式,直接利用python安装
遇到的问题在最后
利用python3安装opencv
pip3 install opencv-python
安装好以后依次输入
python3
import cv2
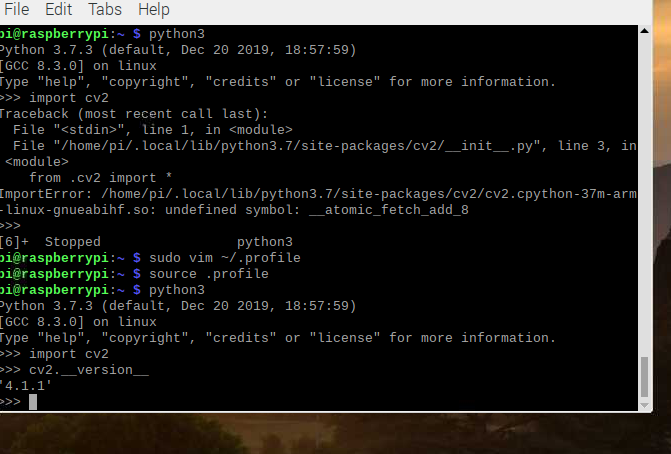
如果没有报错则说明安装成功
我们安装时遇到了
Python 3.7.3 (default, Apr 3 2019, 05:39:12)
[GCC 8.2.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import cv2
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/home/pi/cv2/__init__.py", line 3, in <module>
from .cv2 import *
ImportError: /home/pi/cv2/cv2.cpython-37m-arm-linux-gnueabihf.so: undefined symbol: __atomic_fetch_add_8
参考这里:http://www.yoyojacky.com/?m=201911
得以解决,至此安装好了opencv
使用opencv和python控制树莓派的摄像头
拍照
# import the necessary packages
from picamera.array import PiRGBArray
from picamera import PiCamera
import time
import cv2
# initialize the camera and grab a reference to the raw camera capture
camera = PiCamera()
rawCapture = PiRGBArray(camera)
# allow the camera to warmup
time.sleep(2)
# grab an image from the camera
camera.capture(rawCapture, format="bgr")
image = rawCapture.array
# display the image on screen and wait for a keypress
cv2.imshow("Image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
录像
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while(1):
ret, frame = cap.read()
cv2.imshow("capture", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
利用树莓派的摄像头实现人脸识别
安装face_recognition
pip3 install face_recognition
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44310603/article/details/104962026
由于安装速度太慢,采用离线下载的办法,文件我上传到了百度云如下:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/10WhHrz3yBJR2bBVt0xMNEQ
提取码:892w
下载完以后利用VNC文件传输传到/home/pi
python3 -m pip install face_recognition_models-0.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
python3 -m pip install face_recognition-1.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
完成后测试安装是否成功
python3
import face_recognition
示例
# This is a demo of running face recognition on a Raspberry Pi.
# This program will print out the names of anyone it recognizes to the console.
# To run this, you need a Raspberry Pi 2 (or greater) with face_recognition and
# the picamera[array] module installed.
# You can follow this installation instructions to get your RPi set up:
# https://gist.github.com/ageitgey/1ac8dbe8572f3f533df6269dab35df65
import face_recognition
import picamera
import numpy as np
# Get a reference to the Raspberry Pi camera.
# If this fails, make sure you have a camera connected to the RPi and that you
# enabled your camera in raspi-config and rebooted first.
camera = picamera.PiCamera()
camera.resolution = (320, 240)
output = np.empty((240, 320, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
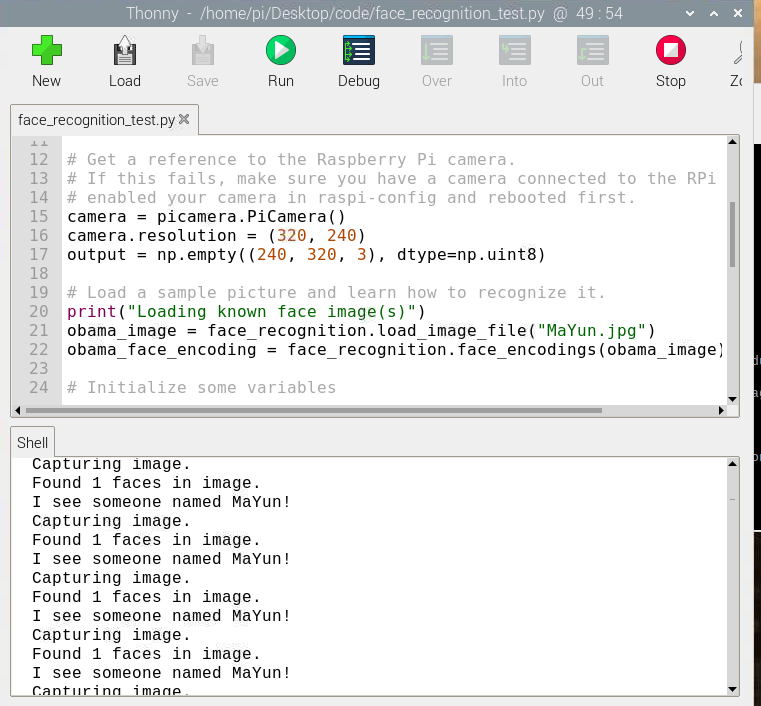
print("Loading known face image(s)")
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("Biden.jpg")
obama_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
while True:
print("Capturing image.")
# Grab a single frame of video from the RPi camera as a numpy array
camera.capture(output, format="rgb")
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(output)
print("Found {} faces in image.".format(len(face_locations)))
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(output, face_locations)
# Loop over each face found in the frame to see if it's someone we know.
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
match = face_recognition.compare_faces([obama_face_encoding], face_encoding)
name = "<Unknown Person>"
if match[0]:
name = "Biden"
print("I see someone named {}!".format(name))
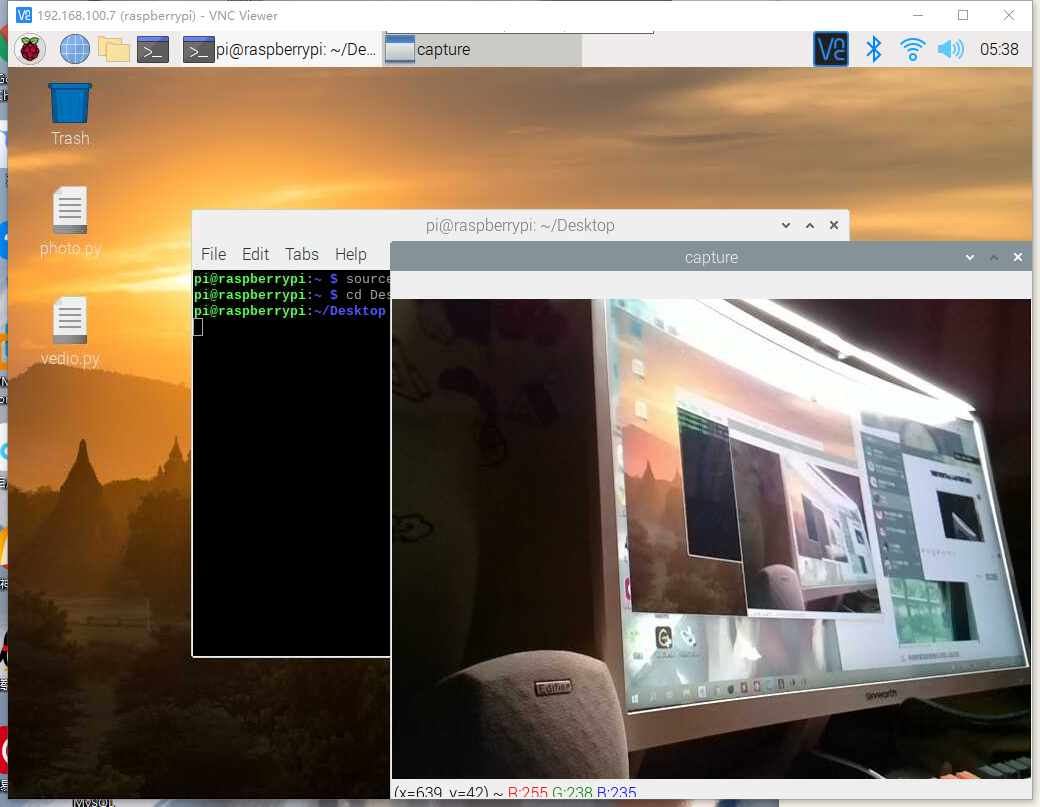
代码中的参数自行修改,需要在代码目录中放入相应图片,此处选用马云的图片,代码运行如下
示例2
代码如下:
import face_recognition
import cv2
import numpy as np
# This is a demo of running face recognition on live video from your webcam. It's a little more complicated than the
# other example, but it includes some basic performance tweaks to make things run a lot faster:
# 1. Process each video frame at 1/4 resolution (though still display it at full resolution)
# 2. Only detect faces in every other frame of video.
# PLEASE NOTE: This example requires OpenCV (the `cv2` library) to be installed only to read from your webcam.
# OpenCV is *not* required to use the face_recognition library. It's only required if you want to run this
# specific demo. If you have trouble installing it, try any of the other demos that don't require it instead.
# Get a reference to webcam #0 (the default one)
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("Obama.jpg")
obama_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("Biden.jpg")
biden_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Create arrays of known face encodings and their names
known_face_encodings = [
obama_face_encoding,
biden_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Barack Obama",
"Joe Biden"
]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
# Grab a single frame of video
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
# Only process every other frame of video to save time
if process_this_frame:
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
# # If a match was found in known_face_encodings, just use the first one.
# if True in matches:
# first_match_index = matches.index(True)
# name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
# Or instead, use the known face with the smallest distance to the new face
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
# Display the results
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
# Draw a box around the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Draw a label with a name below the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# Display the resulting image
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
# Hit 'q' on the keyboard to quit!
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release handle to the webcam
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
代码中的参数自行替换,此处用的马云以及马化腾的图片,需放在代码目录下,运行结果如图
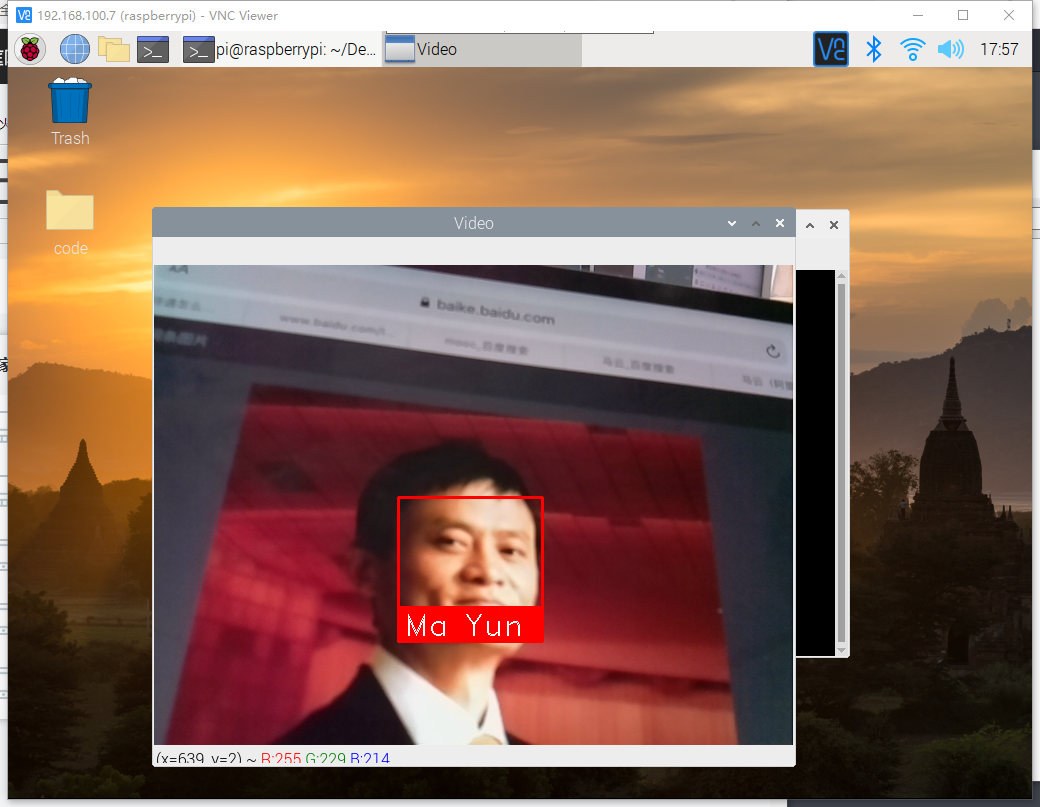
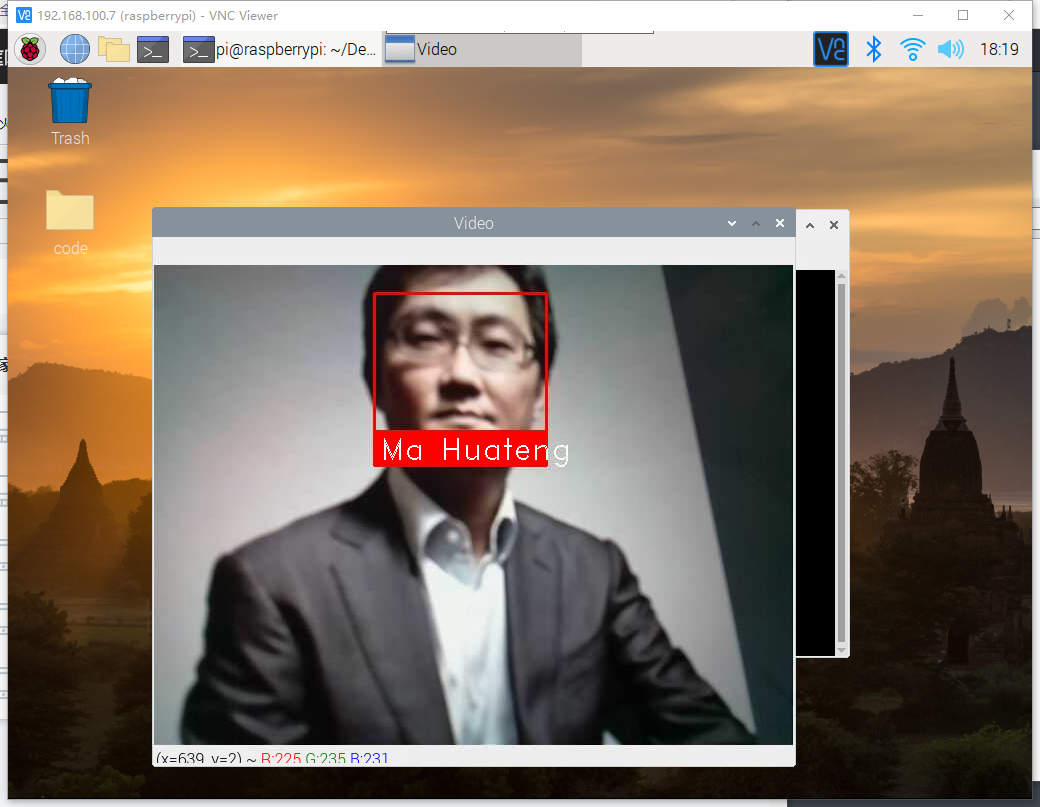
结合微服务的进阶任务
安装docker
下载安装脚本
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
执行安装脚本
sh get-docker.sh --mirror Aliyun
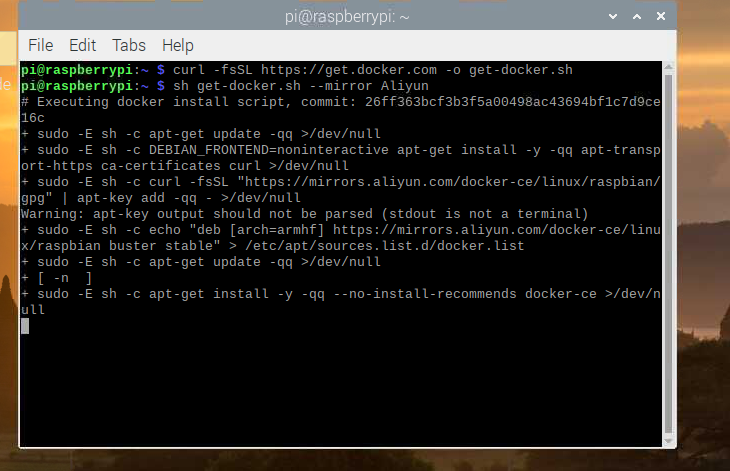
docker换源
cd /etc/docker/
sudo vi daemon.json
在文件中写入如下,此处用的中科大源,但后来发现中科大源一直timeout,遂换了网易源:http://hub-mirror.c.163.com
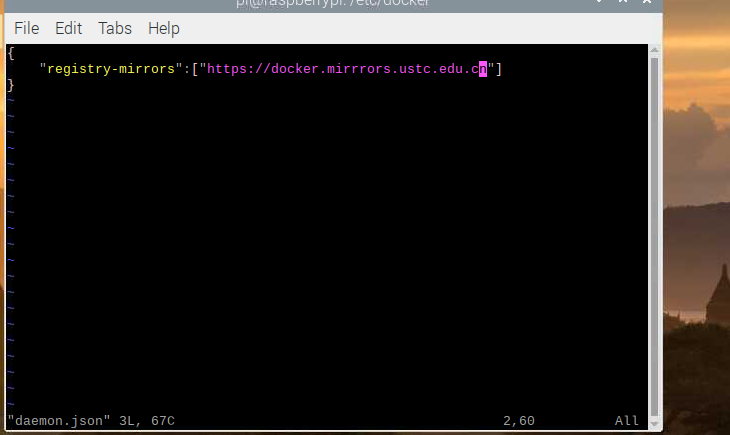
保存后重启docker service
service docker restart
拉取镜像
docker pull sixsq/opencv-python
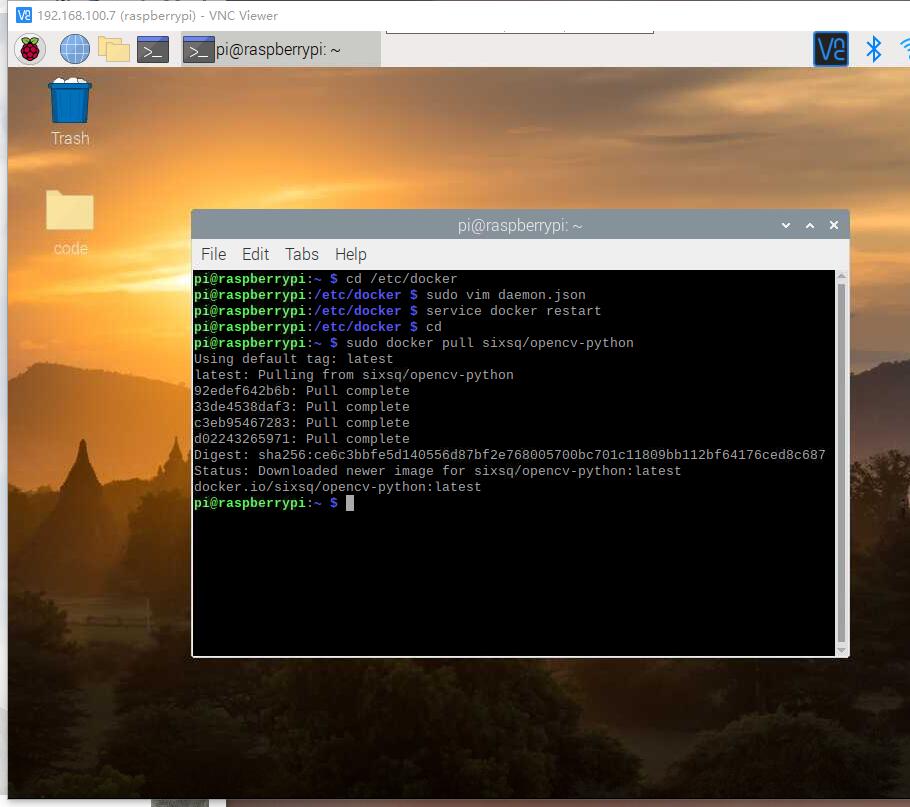
运行镜像
docker run -it sixsq/opencv-python /bin/bash
进入镜像以后安装numpy dlib face_recognition,安装方法同上
由于安装速度太慢,一直timeout,选择把文件传进去再安装
cd +刚才传入的face_recognition的位置
sudo docker cp xxx.whl + 容器ID:+文件要储存的位置
传好以后还是按照刚才的方法安装,最后commit
Build镜像
文件夹结构如下:

Dockerfile
FROM opencv2
RUN mkdir /myapp
WORKDIR /myapp
COPY myapp .
build镜像
docker build -t opencv_test .
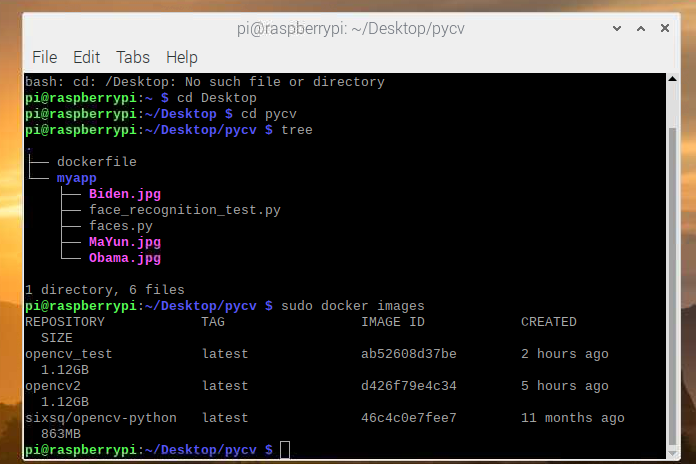
运行代码
运行容器执行face_recognition_test.py
docker run -it --device=/dev/vchiq --device=/dev/video0 --name facerec opencv_test
python3 facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py
结果如下
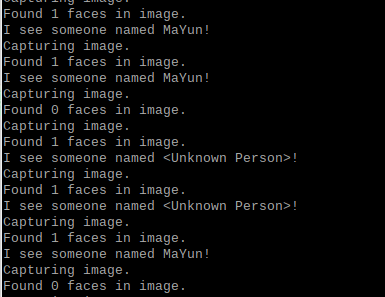
附加选做:opencv的docker容器中运行facerec_from_webcam_faster.py
先安装Xming和Putty,官网安装即可
检查树莓派的ssh配置中的X11是否开启
cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config
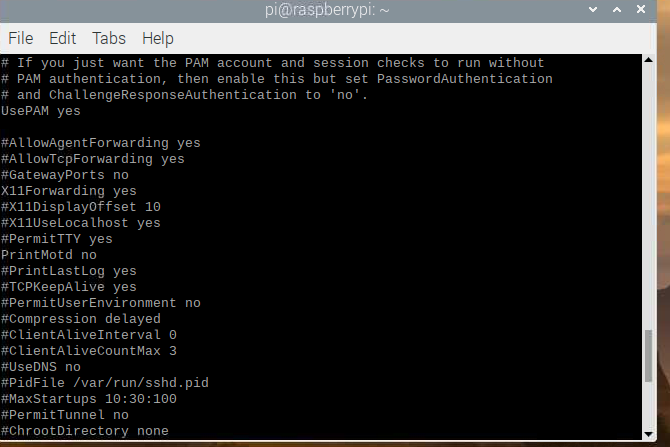
X11Forwarding yes即可
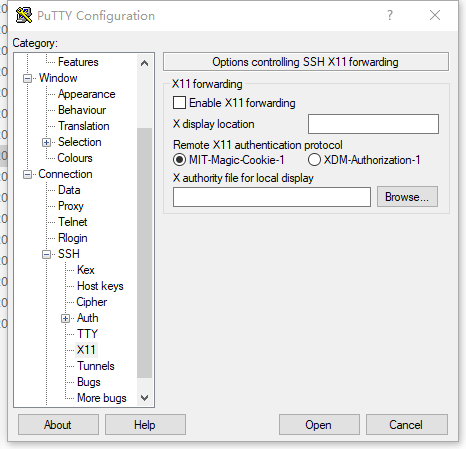
打开putty,选择ssh/x11,Enable X11 Forwarding勾上
回到session,填入树莓派的ip地址
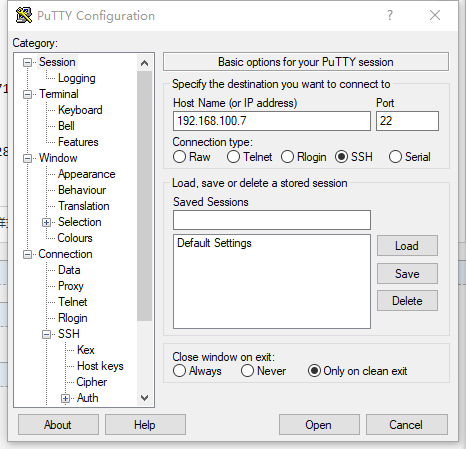
点击open,登录使用user:pi pwd:raspberry
输入printenv
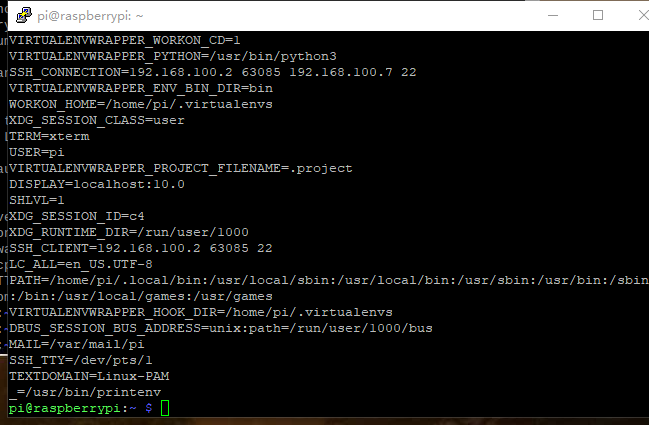
记录DISPLAY=localhost:10.0,回到树莓派,编写启动脚本,首先安装x11-xserver-utils
桌面新建run.sh,内容如下
xhost +
docker run -it \
--net=host \
-v $HOME/.Xauthority:/root/.Xauthority \
-e DISPLAY=:10.0 \
-e QT_X11_NO_MITSHM=1 \
--device=/dev/vchiq \
--device=/dev/video0 \
--name facerecgui \
opencv_test \
python3 faces.py
启动时间比较慢,而且画面会出现卡顿,最后结果如图

以小组为单位,发表一篇博客,记录遇到的问题和解决方法
遇到的问题
首先是编译中出现缺少文件的情况,如图所示(网图,忘记截图了
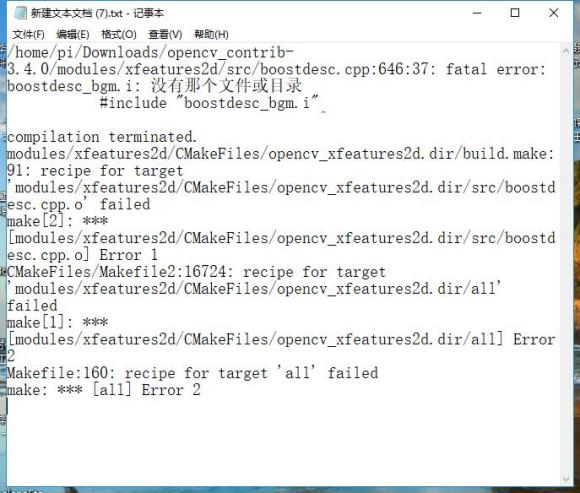
最后查阅资料得知需要重新下载"boostdesc_bgm_i"文件,再放入到/home/pi/opencv/opencv_contrib-3.3.0/modules/xfeatures2d/src目录即可继续编译
引入opencv出现undefined symbol: __atomic_fetch_add_8
提示找到不到cv2.cpython-37m-arm-linux-gnueabihf.so 一个未定义的__atomic_fetch_add_8, 这个是一个bug, 其实只需要加载一下一个库文件就好了。
sudo vi ~/.profile
添加:export LD_PRELOAD=/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libatomic.so.1
source .profile即可
face_recognition安装太慢
方法一:pip3换源,但发现并没有什么用
方法二:离线安装,文件已经上传百度云,详细看第二部即可
小组协作
| 学号 | 姓名 | 分工 |
|---|---|---|
| 031702145 | 马连政 | 操作查阅资料修改代码 |
| 031702142 | 林德辉 | 查阅资料检查修改代码 |
| 031702108 | 叶心言 | 查阅资料检查修改代码 |



