反射四(动态代理)
1.动态代理
(1)Proxy提供用于创建动态代理类和代理对象的静态方法,它是所有动态代理类的父亲
(2)Proxy提供了两个方法来创建动态代理类和动态代理实例
2.使用动态代理实现AOP(面向切面编程)
代理设计模式的原理:使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后用该代理对象取代原始对象,任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理。代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。
3.实现
/**
* 动态代理
*/
@Test
public void testProxy(){
final ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl();//final防止该对象被提前回收
/**
* Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,Class<?>[],InvocationHandler
* classLoader由动态代理产生的对象由那个类加载其加载,通常情况下和被代理对象使用一样的类加载器
* Class<?>[]:由动态代理产生的对象必须需要实现的接口的Class数组,数组中必须是接口对应的class
* InvocationHandler:当具体调用代理对象的方法时,将产生什么行为
*/
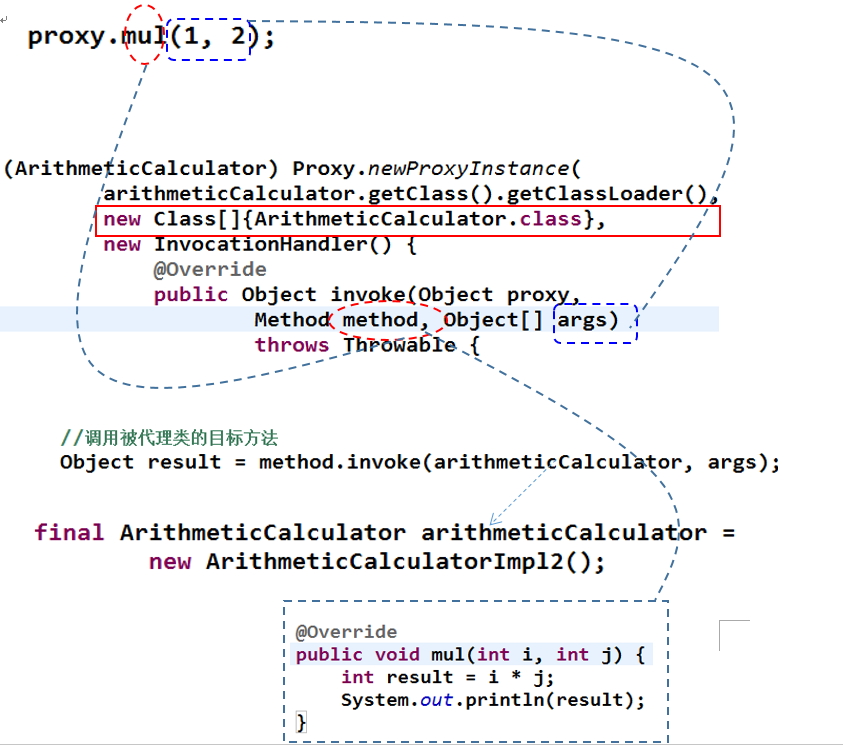
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(arithmeticCalculator.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculator.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
/**
*
* @param proxy
* @param method:正在被调用的方法
* @param args:调用方法传入的参数
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//调用被代理的目标方法,真正执行目标方法
System.out.println("方法执行前操作");
Object result = method.invoke(arithmeticCalculator,args);
System.out.println("方法执行后操作");
return result;
}
});
//调用的是上边的invoke方法
int result = proxy.add(2,5);
System.out.println(result);
result = proxy.mul(1,2);
System.out.print(result);
}
/**
* 接口定义,接口实现省略
*/
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i,int j);
int sub(int i,int j);
int mul(int i,int j);
int div(int i,int j);
}
4.代码调用