Linux之磁盘管理
一、Raid卡之初识
又叫磁盘冗余阵列,阵列卡。他的主要作用有三点
1、获取更高的容量
2、获取更高的性能
3、获取更强的安全性
raid卡按支持的raid级别不同和raid卡的缓存容量不同,分为基础raid卡和高级raid卡

左边是raid基础卡,右边是高级卡。
基础卡只支持raid0和raid1
高级卡支持0、1、3、5、10、11或者更多
常见的raid级别
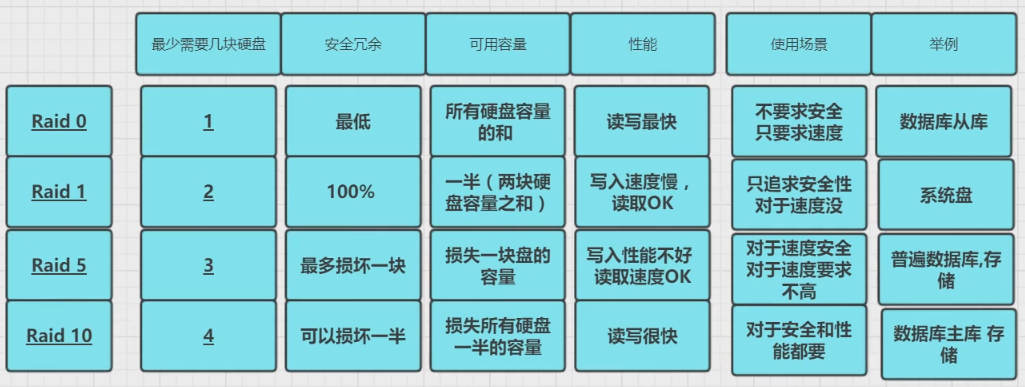
raid0
主要是为了应对不做raid用不了的情况。
硬盘不做raid,识别不了硬盘。所以如果只有一块硬盘,就做个raid0吧。
安全性最低,其中一个硬盘坏掉了,所有数据都会报废。
用于安全性需求低的数据,不怕丢失的数据。优点就是读写快
raid1
只能有两块硬盘
算是个鸡肋,因为只能同时给两个硬盘做raid1。
raid5
最少需要3块硬盘,在写入之前有一个校验的过程。有一块硬盘用来做校验,用来保护数据的安全性,当其中一块硬盘坏了,就可以使用校验数据恢复丢失的数据。
可以在添加一块热位盘(RAID5 + spare),当坏了一块硬盘之后,可以启动热位盘来替换坏的硬盘。
三个有点都占一点,在并发量不高的时候,可以使用
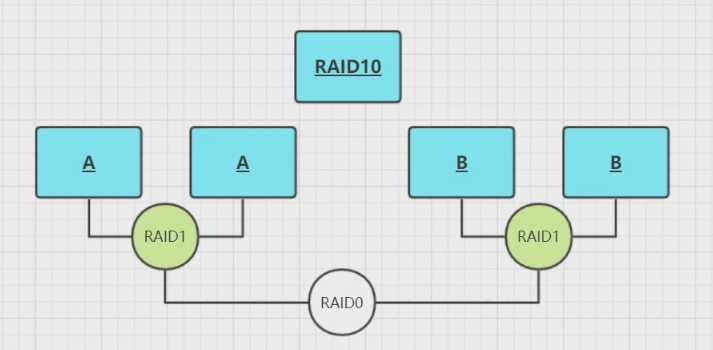
raid10
读取速度和安全性都很高,但是很奢侈,并发量很大的时候可以使用
raid10的基本原理如下:
二、磁盘分区
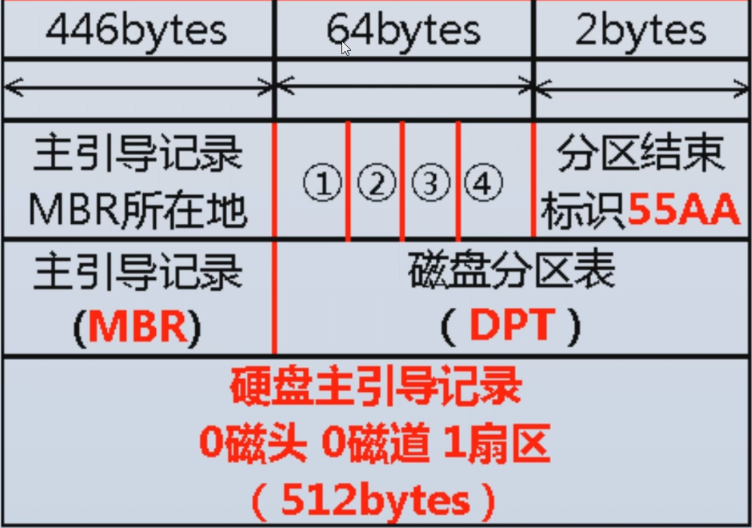
磁盘分区表
所在位置:0磁头0磁道1扇区的秘密
我们已经知道一个扇区的大小是512字节,那么这512字节是如何划分的呢?
前446字节:mbr主引导记录
64字节:分区表,分区一创建,表便生成
55AA:表示结束标记
主分区-扩展分区-逻辑分区的关系
系统的主分区最多有4个。
因为一个主分区一旦创立,就要在64字节的分区表中占用16个字节。
鉴于此,就有了扩展分区。
所以,扩展分区就是为了解决主分区只有4个的问题。
主分区+扩展分区最多也就是4个。
扩展分区是没法直接使用的。
要想使用,需要在扩展分区下面创建逻辑分区。
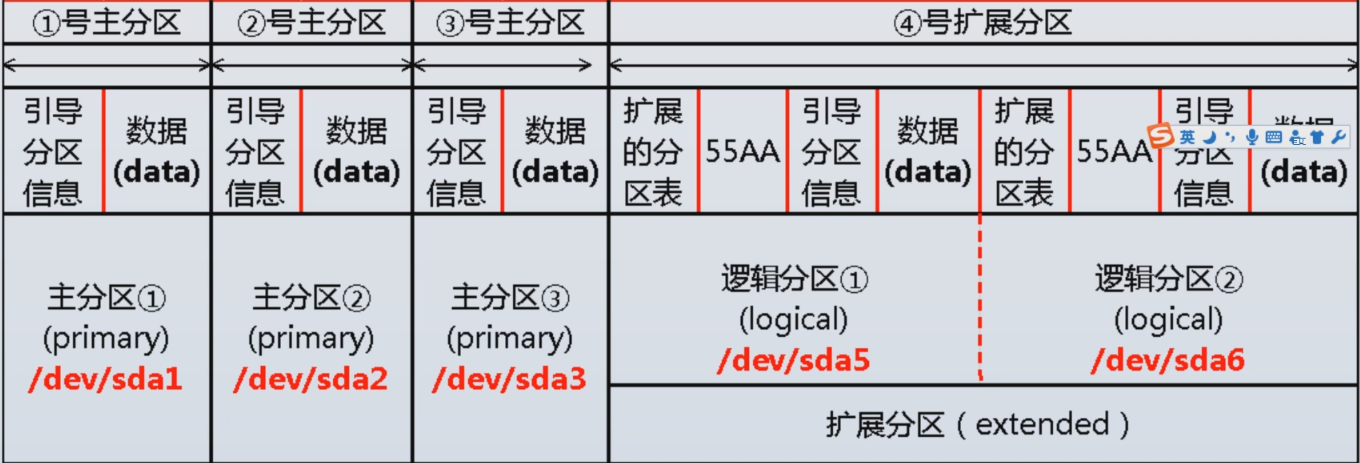
主分区
存放数据分区,最多有4个
扩展分区
无法直接使用
最多只能有一个
必须要在扩展分区中创建逻辑分区
逻辑分区
存放数据
在功能上和主分区没有什么区别
硬盘分区命令规则
硬盘命名
sas/sata/scsi接口,以sd开头sd?
第一块sas硬盘,取名sda
第三块sas硬盘,取名sdc
分区命名
主分区/扩展分区,1-4,如sda1
逻辑分区,从5开始
例子
第一块SAS硬盘的第一个主分区
/dev/sda1
第二块SAS硬盘的第二个扩展分区
/dev/sdc6
第四块SATA硬盘的第一个扩展分区
/dev/sdd5
fdisk进行磁盘分区详解
首先创建环境
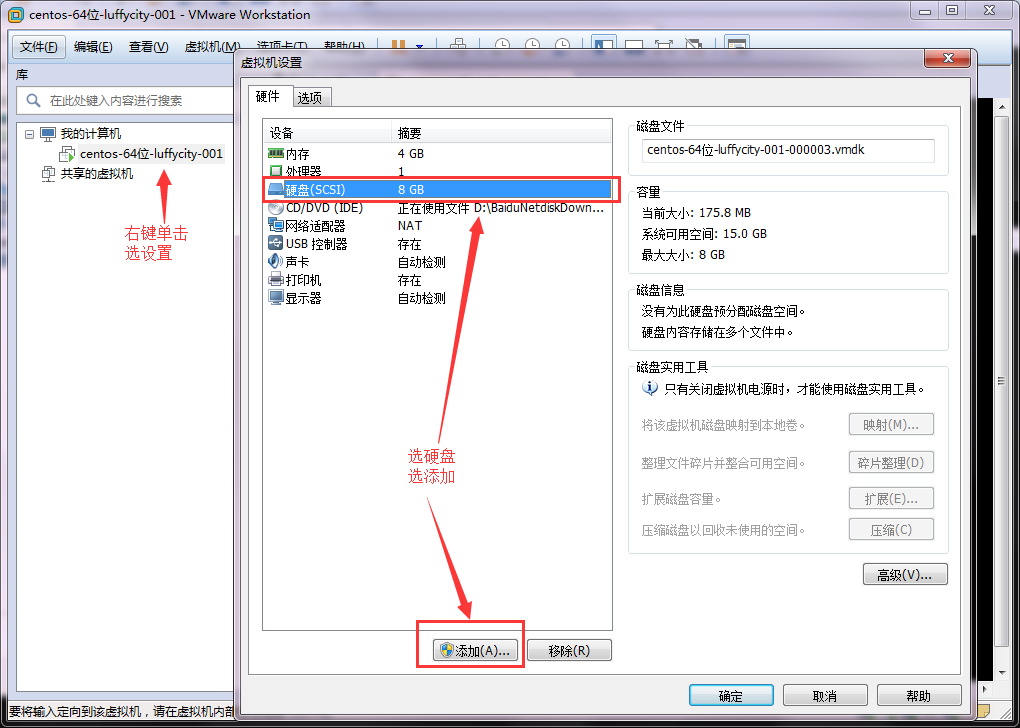
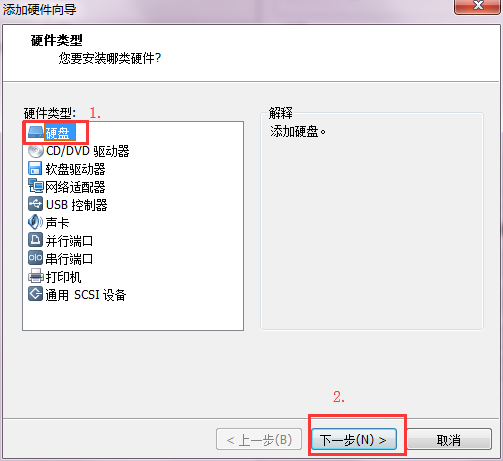
一直点下一步
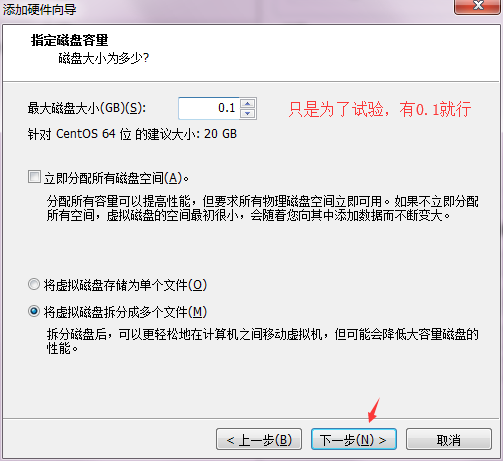
创建2-3个新硬盘
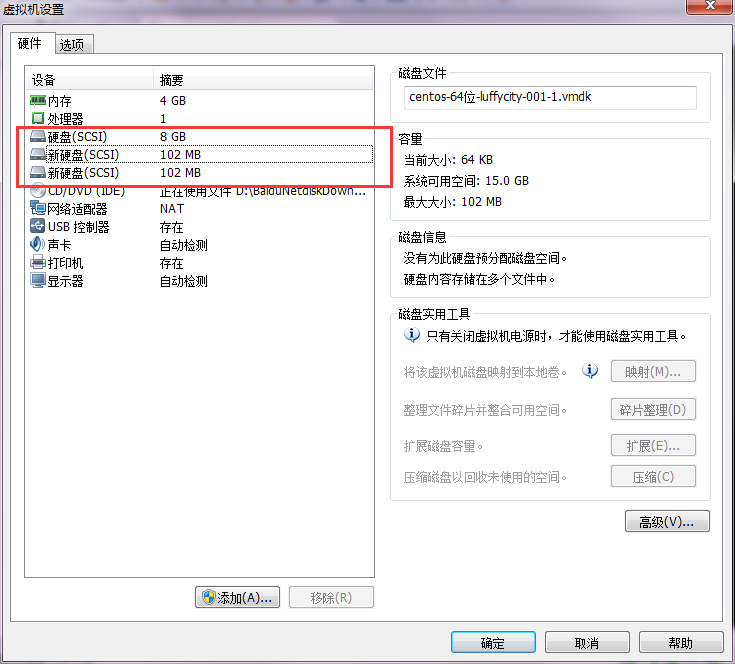
最后点确定
reboot
重启了查看一下
[root@luffy-001 ~]# fdisk -l|grep 'sd[a-d]:'
Disk /dev/sda: 8589 MB, 8589934592 bytes
Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes
Disk /dev/sdc: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes
Disk /dev/sdd: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes
分区工具的使用
小于2个T的使用fdiak,大于2T就使用parted
fdisk支持MBR
题目:创建一个100M分区,把他挂载到/mnt上面
[root@luffy-001 ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb # 首先是警告信息:磁盘没有分区表 Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xfed34d83. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) # 有一个模式已经过时了,你可以关掉。默认磁盘在分区或者是进行读写的时候,是按照扇区,柱面,还是磁道来进行的... # 然后,告诉了我们两个参数c和u WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): m # 按下m显示帮助信息 [: unknown command Command action a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag # 关闭DOS的兼容模式 d delete a partition # 删除 l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition # 表示创建一个分区 o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table # 显示分区信息 q quit without saving changes # 退出不保存 s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition's system id u change display/entry units # 按照扇区进行磁盘分区 v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit # 退出并保存 x extra functionality (experts only)
100M的分区,30M的主分区,30M的逻辑分区
## 加上推荐的参数cu [root@luffy-001 ~]# fdisk -cu /dev/sdb Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x1bbbfcff. Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable. Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite) ## p显示分区信息: Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System ## 添加主分区30M: Command (m for help): n Command action e extended # 扩展分区 p primary partition (1-4) # 主分区 p Partition number (1-4): 1 # 编号 First sector (2048-208895, default 2048): # 不填就是默认的2048 Using default value 2048 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-208895, default 208895): +30M ## 显示分区信息,已经创建好了 Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 63487 30720 83 Linux Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) e Partition number (1-4): 2 First sector (63488-208895, default 63488): Using default value 63488 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (63488-208895, default 208895): Using default value 208895 Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 63487 30720 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 63488 208895 72704 5 Extended ## 再创建 30M扩展分区 Command (m for help): n Command action l logical (5 or over) p primary partition (1-4) l First sector (65536-208895, default 65536): Using default value 65536 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (65536-208895, default 208895): +30M Command (m for help): P Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 63487 30720 83 Linux /dev/sdb2 63488 208895 72704 5 Extended /dev/sdb5 65536 126975 30720 83 Linux Command (m for help): ## 此时,并没有在系统中生效,改变只是暂时放在内存中 Command (m for help): w # 按w保存并退出 The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disk
在w之前,检查一次,是不是在新的磁盘上创建分区。无误之后再按回车键,否则会发生无法挽回的错误。
在系统中已经可以查看创建的分区了
[root@luffy-001 ~]# ls -l /dev/sdb* brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 16 Feb 17 17:00 /dev/sdb brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 17 Feb 17 17:00 /dev/sdb1 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 18 Feb 17 17:00 /dev/sdb2 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 21 Feb 17 17:00 /dev/sdb5
磁盘分区--格式化--挂载流程
[root@luffy-001 ~]# fdisk -cu /dev/sdb # 第一次的提示信息已经没有了 ## 工作中一般怎么用? 创建一个100M分区,把他挂载到/mnt上面 ### 1、分区 ## 先删除之前的分区 Command (m for help): d Partition number (1-5): 1 Command (m for help): d Partition number (1-5): 2 Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System Command (m for help): n Command action e extended p primary partition (1-4) p Partition number (1-4): 1 First sector (2048-208895, default 2048): # 把空间全部分给一个分区,直接回车 Using default value 2048 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-208895, default 208895): # 直接回车 Using default value 208895 Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 106 MB, 106954752 bytes 64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 102 cylinders, total 208896 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x1bbbfcff Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdb1 2048 208895 103424 83 Linux Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. ### 2、通知系统,/dev/sdb硬盘的磁盘分区表变化了 [root@luffy-001 ~]# partprobe /dev/sdb [root@luffy-001 ~]# # 默认没有任何反应 ### 3、格式化创建文件系统make filesystem [root@luffy-001 ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=1024 (log=0) Fragment size=1024 (log=0) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 25896 inodes, 103424 blocks # 诞生了inode和block 5171 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=1 Maximum filesystem blocks=67371008 13 block groups 8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group 1992 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 8193, 24577, 40961, 57345, 73729 Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (4096 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done ## 下面这段话,主要意思是讲磁盘会定期自动检查,在下一步可以关闭它,提示中已经给出了命令 This filesystem will be automatically checked every 20 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override. [root@luffy-001 ~]# ### 4、关闭磁盘分区的自动检查功能 [root@luffy-001 ~]# tune2fs -c 0 -i 0 /dev/sdb1 tune2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Setting maximal mount count to -1 Setting interval between checks to 0 seconds -c 0 count # 关闭每挂载多少次进行磁盘检查的功能 -i 0 interval # 关闭每180天进行磁盘检查功能 ### 5、使用mount进行磁盘分区挂载 ## 先检查是不是在使用 [root@luffy-001 ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 6.9G 1.9G 4.7G 29% / tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot ## 如果在使用可以用umount 切掉 ## 使用mount 挂载 [root@luffy-001 ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/ [root@luffy-001 ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 6.9G 1.9G 4.7G 29% / tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot /dev/sdb1 94M 1.6M 88M 2% /mnt
如何进行开机自动挂载
重启服务器后,我挂载的磁盘不见了,这可如何是好?
[root@luffy-001 ~]# reboot [root@luffy-001 ~]# Broadcast message from root@luffy-001 (/dev/pts/0) at 17:42 ... The system is going down for reboot NOW! Connection closing...Socket close. Connection closed by foreign host. Disconnected from remote host(study_luffy001) at 09:49:19. Type `help' to learn how to use Xshell prompt. [D:\~]$ Connecting to 10.0.0.200:22... Connection established. To escape to local shell, press 'Ctrl+Alt+]'. WARNING! The remote SSH server rejected X11 forwarding request. Last login: Sun Feb 17 17:43:57 2019 [root@luffy-001 ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 6.9G 1.9G 4.7G 29% / tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 190M 40M 141M 22% /boot [root@luffy-001 ~]#
自动挂载的方法
1、/etc/rc.local
开机自启动的目录
将命令/bin/mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/ 放在 /etc/rc.local 里面
2、/etc/fstab
开机自动挂载的目录
[root@luffy-001 ~]# cat /etc/fstab # # /etc/fstab # Created by anaconda on Thu Jan 10 14:45:14 2019 # # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk' # See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info # 我们可以使用 man fstab 得到这些信息
设备或者磁盘的名字 入口/挂载点 磁盘分区的类型 挂载参数 是否备份 开机是否检查 UUID=30ef1485-38f4-4bac-80c9-1812eddcb1f1 / ext4 defaults 1 1 UUID=94102f2f-e731-4636-81bc-7cb023db0068 /boot ext4 defaults 1 2 UUID=fac5852c-baa7-425c-b513-591de82cdb14 swap swap defaults 0 0 tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0 devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0 sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0 proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
按照上面的格式将我们要挂载的磁盘写进去
vim /etc/fstab
加入:
/dev/sdb1 /mnt ext4 defaults 0 0
卸载磁盘
[root@luffy-001 ~]# umount /mnt
磁盘分区工具parted和GPT分区表
parted主要是给磁盘大于2TB的进行分区,当然2TB一下的也是可以使用的。
还有一点就是,parted是基于GPT分区表
GPT与MBR兼容,支持的容量级别是ZB
Parted
[root@luffy-001 ~]# parted GNU Parted 2.1 Using /dev/sda Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. (parted) help # 查看帮助 align-check TYPE N check partition N for TYPE(min|opt) alignment check NUMBER do a simple check on the file system cp [FROM-DEVICE] FROM-NUMBER TO-NUMBER copy file system to another partition help [COMMAND] print general help, or help on COMMAND mklabel,mktable LABEL-TYPE create a new disklabel (partition table) # 创建磁盘分区表 mkfs NUMBER FS-TYPE make a FS-TYPE file system on partition NUMBER mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition # 创建分区 mkpartfs PART-TYPE FS-TYPE START END make a partition with a file system move NUMBER START END move partition NUMBER name NUMBER NAME name partition NUMBER as NAME print [devices|free|list,all|NUMBER] display the partition table, available devices, free space, all found partitions, or a particular partition # 显示磁盘分区表信息 quit exit program # 退出不保存 rescue START END rescue a lost partition near START and END resize NUMBER START END resize partition NUMBER and its file system rm NUMBER delete partition NUMBER # 删除分区 select DEVICE choose the device to edit set NUMBER FLAG STATE change the FLAG on partition NUMBER toggle [NUMBER [FLAG]] toggle the state of FLAG on partition NUMBER unit UNIT set the default unit to UNIT version display the version number and copyright information of GNU Parted (parted)
创建 30M 30M (因为gpt支持很多主分区,一百多个,所以扩展和逻辑分区就没用了
[root@luffy-001 ~]# parted /dev/sdc # 给sdc做分区 GNU Parted 2.1 Using /dev/sdc Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. (parted) p # P也可以使用 Error: /dev/sdc: unrecognised disk label (parted) print Error: /dev/sdc: unrecognised disk label (parted) mklabel New disk label type? gpt #支持两种格式====>gpt和msdos(mbr) (parted) p #可以查看分区了 Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdc: 107MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags ## 创建分区30M,默认单位就是MB (parted) mkpart primary 0 30 Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance. Ignore/Cancel? I # I表示忽略 (parted) print Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdc: 107MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 30.0MB 30.0MB primary ## 创建下一个30M分区 (parted) mkpart primary 30 60 (parted) p Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdc: 107MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 30.0MB 30.0MB primary 2 30.4MB 59.8MB 29.4MB primary ## 使用parted的时候,是实时生效的,所以没有保存并退出的命令 (parted) q Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. [root@luffy-001 ~]# ls -l /dev/sdc* brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 32 Feb 17 18:23 /dev/sdc brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 33 Feb 17 18:22 /dev/sdc1 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 34 Feb 17 18:22 /dev/sdc2 ##parted命令在命令行中也能显示和使用 [root@luffy-001 ~]# parted /dev/sdc mklabel gpt Warning: The existing disk label on /dev/sdc will be destroyed and all data on this disk will be lost. Do you want to continue? Yes/No? y Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. [root@luffy-001 ~]# parted /dev/sdc mkpart primary 0 30 Ignore Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance. Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. [root@luffy-001 ~]# parted /dev/sdc mkpart primary 30 60 Warning: You requested a partition from 30.0MB to 60.0MB. The closest location we can manage is 30.0MB to 30.4MB. Is this still acceptable to you? Yes/No? y Warning: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance. Ignore/Cancel? I Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. [root@luffy-001 ~]# parted /dev/sdc p Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi) Disk /dev/sdc: 107MB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 30.0MB 30.0MB primary 3 30.0MB 30.4MB 409kB primary 2 30.4MB 59.8MB 29.4MB primary ## fsdisk也可以这么使用(非交互式应用),只是比较麻烦,可以了解一下
故障案例:java环境内存不足大量使用swap
内存不足的一种解决方法是增加内存,但是增加内存需要关机,另一种方法就是使用swap。
一般服务器会有swap空间,以防止内存使用不足。
但是有些服务器没有设置swap,比如云服务器。
这时候,需要我们临时增加swap。
1、创建一个文件块
[root@luffy-001 ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/100m bs=1M count=100 100+0 records in 100+0 records out 104857600 bytes (105 MB) copied, 0.317705 s, 330 MB/s # dd 创建一个文件块 # if 输入文件,从哪里获取数据 # of 输出文件,数据放在哪里 # bs 每次复制多少数据 # count 复制多少次 ## 查看文件类型 [root@luffy-001 ~]# file /tmp/100m /tmp/100m: data
2、变成swap
[root@luffy-001 ~]# mkswap /tmp/100m mkswap: /tmp/100m: warning: don't erase bootbits sectors on whole disk. Use -f to force. Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 102396 KiB no label, UUID=36c6f74c-ff57-4746-be67-b9c98b575ee3 [root@luffy-001 ~]# file /tmp/100m /tmp/100m: Linux/i386 swap file (new style) 1 (4K pages) size 25599 pages
3、查看swap使用情况
[root@luffy-001 ~]# free -h total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3.7G 284M 3.4G 252K 12M 155M -/+ buffers/cache: 116M 3.6G Swap: 767M 0B 767M # 如果之前查看过,就知道,这次更该并没有生效
4、swap生效
[root@luffy-001 ~]# swapon /tmp/100m [root@luffy-001 ~]# free -h total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3.7G 284M 3.4G 252K 12M 155M -/+ buffers/cache: 116M 3.6G Swap: 867M 0B 867M
5、查看swap组成
[root@luffy-001 ~]# swapon -s Filename Type Size Used Priority /dev/sda2 partition 786428 0 -1 /tmp/100m file 102396 0 -2
6、swap永久生效
## 方法一、/etc/rc.local swapon /tmp/100m ## 方法二、/etc/fstab /tmp/100m swap swap defaults 0 0
Linux把我的内存吃了
linux特点:会把使用过的命令和数据临时存放在内存中 (cache和buffer)
以方便在下次使用的时候可以更快,提升效率
[root@luffy-001 ~]# free -h total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 3.7G 284M 3.4G 252K 12M 155M -/+ buffers/cache: 116M 3.6G # 这是减去buffer和cache的容量 Swap: 867M 0B 867M
www.linuxatemyram.com 尝试阅读并翻译
三、Linux文件系统
分区就是给房子打隔断,创建文件系统就是给房子装修,文件系统的类型就是装修风格,
文件在磁盘上面怎么放。
文件系统就是一种存储和组织计算机数据文件袋额机制或者方法。
之前已经说过了,我们很容易理解,通过fdisk命令对一个磁盘进行分区后,并不能直接挂在目录存放数据实体,还需要格式化操作,才可以进行挂载并存放数据。
为什么需要格式化呢?这是因为磁盘分区在没有格式化之前,操作系统是无法识别系统上磁盘分区格式的,也就无法存取文件目录属性和权限等内容,把分区格式化成操作系统支持的某个文件系统后,再存放数据,系统就会根据这个文件系统的格式化进行存取文件了。
文件系统细节
我们都知道,操作系统中的数据分为文件内容和文件属性两部分,其中文件内容就是文件的实体数据(block里),而文件属性就是文件类型、权限、属主、修改时间等信息。操作系统会将上述文件的属性内容放入磁盘文件系统的inode中,而把文件的实体数据存放在对应的block中。除了inode和block信息外,操作系统还会记录文件系统的整体信息于superblock中,这个superblock包括整个文件系统的inode和block的总的数量,已经使用的数量,剩余数量等(称之为metadata元数据)。
文件系统的每一个inode和block都有对应且唯一的数字编号,而superblock则存在于整个文件系统的最前面,它负责管理记录整个文件系统的相关信息,例如:上述的整个文件系统的inode和block的总数量,已经使用的数量,剩余数量等。
有关文件系统的inode和block知识,在linux文件属性一节,软链接和硬链接属性章节
查看文件系统的内部细节
[root@luffy-001 ~]# dumpe2fs -h /dev/sda1 dumpe2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem volume name: <none> Last mounted on: /boot Filesystem UUID: 94102f2f-e731-4636-81bc-7cb023db0068 Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53 Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic) Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype needs_recovery extent flex_bg sparse_super huge_file uninit_bg dir_nlink extra_isize Filesystem flags: signed_directory_hash Default mount options: user_xattr acl Filesystem state: clean Errors behavior: Continue Filesystem OS type: Linux Inode count: 51200 Block count: 204800 Reserved block count: 10240 Free blocks: 154246 Free inodes: 51161 First block: 1 Block size: 1024 Fragment size: 1024 Reserved GDT blocks: 256 Blocks per group: 8192 Fragments per group: 8192 Inodes per group: 2048 Inode blocks per group: 256 Flex block group size: 16 Filesystem created: Thu Jan 10 14:42:18 2019 Last mount time: Sun Feb 17 17:43:30 2019 Last write time: Sun Feb 17 17:43:30 2019 Mount count: 11 Maximum mount count: -1 Last checked: Thu Jan 10 14:42:18 2019 Check interval: 0 (<none>) Lifetime writes: 43 MB Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root) Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root) First inode: 11 Inode size: 128 Journal inode: 8 Default directory hash: half_md4 Directory Hash Seed: cbc9b2e9-0a58-4fbe-b35e-7118e5eafd96 Journal backup: inode blocks Journal features: (none) Journal size: 4096k Journal length: 4096 Journal sequence: 0x00000034 Journal start: 0
一块硬盘在文件系统角度的名词解释

常见的文件系统
openSUSE linux 的默认文件系统 ReiserFS 文件系统
IBM 的AIX使用的 jfs 日志文件系统
Centos7 采用 XFS 文件系统
Centos6 采用 ext4 文件系统
Centos5 采用 ext3 文件系统
文件系统的小结
1、文件系统是对一个存储设备上的数据和元数据进行组织的一种机制
2、分区必须格式化创建文件系统才能存放数据
3、一个分区只能有一种文件系统
4、linux下常见的文件系统ext2、ext3、ext4、zfs、xfs(centos7)和Reiserfs(单独安装)。
windos下常见的额文件系统:NTFS、FAT32、exFAT
文件系统选型简单介绍
1、SAS/SATA硬盘文件系统选择
- reiserfs 大量小文件业务首选reiserfs(100k以内),如果是Centos需要单独安装
- xfs 有的门户的数据库MySQL 业务会选择xfs,最数据库的支持比较好
- ext4 视频下载,流媒体,数据库,小文件业务也OK,默认的,通用的
- ext2 没有日志(丢失了数据无法恢复,但是数据的读写速度回提高),蓝汛的cache业务,CDN网站加速服务(相当于缓存)
常规应用:
对于 Centos5.x 系列,常规应用就选默认的 ext3 文件系统即可
对于 Centos6.x 系列,常规应用就选默认的 ext4 文件系统即可
对于 Centos7.x 系列,常规应用就选默认的 xfs 文件系统即可
注意:如果服务器数量少,怎么选择都可以
如果是海量服务器,考虑维护成本和性能,选择其中一个折中。
选择小结:
- Centos 默认的文件系统都是比较优秀的。
- xfs、reiserfs 需要单独安装,默认不支持的。
- 海量服务器使用多种文件系统维护可能不方便
- 大并发做磁盘系统的优化是一方面,但更多的还是在网站前端增加缓存服务器(squid、varnish),存储数据库的前端增加缓存(memcache、redis),这是架构师的能力。
2、SSD固态文件系统的选择
Ext4、Reiserfs可以作为SSD文件系统,但未对SSD做优化,不能充分发挥SSD的性能,影响SSD的使用时间。
Btrfs对SSD做了优化,mount通过参数启用。但Btrfs仍处于试验阶段,生产环境谨慎使用。
JEFS2/Nilfs2/YAFFS是常用的 flash file system,在嵌入式环境(手机、智能电器)广泛应用,建议使用。性能目前还未做测试评估。
在Linux中制作文件系统
看系统默认是否支持,如果支持就直接用对用命令格式化即可
磁盘部分总结与磁盘命令总结
磁盘知识体系
磁盘结构
raid
磁盘分区
磁盘格式化
文件系统
命令
1 fdisk:磁盘分区工具 ★★★★☆ 2 parted:磁盘分区工具 ★★★★☆ 3 partprobe:通知系统磁盘的分区信息变化 更新内核的硬盘分区表信息 ★★★☆☆ 4 tune2fs:调整ext2/ext3/ext4文件系统参数 ★★☆☆☆ 5 -c 0 count 关闭每挂载多少次进行磁盘检查 6 -i 0 interval 关闭每个多久进行磁盘检查 7 关闭磁盘分区的自动检查 8 mkfs:make filesystem 创建Linux文件系统 ★★★☆☆ 9 -t 指定文件系统类型 10 mkfs.ext4 == mkfs -t ext4 11 dumpe2fs:显示文件系统信息 ★★☆☆☆ 12 resize2fs:调整ext2/ext3/ext4文件系统大小 ★★☆☆☆ 会影响业务 13 fsck:检查并修复Linux文件系统 ★★★☆☆ 硬盘没问题不要用 14 -a 15 dd:转换或复制文件 ★★★☆☆ 16 od 查看二进制文件的内容 17 -xa 18 dd if=/dev/sda of=/tmp/512.bin bs=512 count=1 19 20 od -xa /tmp/512.bin 21 22 mount:挂载文件系统 ★★★★★ 23 umount:卸载文件系统 ★★★☆☆ 24 umount /mnt 25 df:报告文件系统磁盘空间的使用情况 ★★★★★ 26 mkswap:创建交换分区 ★★☆☆☆ 27 swapon:激活交换分区 ★★☆☆☆ 28 swapoff:关闭交换分区 ★★★☆☆ 29 sync:刷新文件系统缓冲区 ★★☆☆☆ 30 top :查看系统性能信息 31 iotop 查看系统的磁盘读写速度 显示出进程使用swap的情况 32 io input/output 输入/输出 读写 33 htop top升级版 34 iftop 查询网卡流量情况 35 -i 指定监视网卡


