Linux之命令进阶
Linux系统的启动过程
1.开机自检 BIOS
2.MBR引导
3.GRUB菜单
4.加载内核
5.运行init进程
6.从/etc/inittab读取运行级别
7.根据/etc/rc.sysinit 初始化系统(设置主机名 设置ip)
8.根据运行级别启动对应的软件(开机自启动软件)
9.运行mingetty显示登录界面

PATH环境变量
什么是环境变量
1、大写
2、在系统大部分地方都可以使用,含义相同
3、常见的环境变量
LANG PATH PS1
PATH含义
路径-存放的是Linux命令的位置/路径
[root@luffy_boy-001 ~]# echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
# 用冒号分割 [root@luffy_boy-001 ~]# echo $LANG en_US.UTF-8
linux下面运行命令过程
1、输入命令
2、在PATH里面 进行查找
3、找到了就运行,找不到就提示:command not found
查看目录
如何过滤出已知当前目录下oldboy中的所有一级目录(提示:不包含oldboy目录下面目录的子目录及隐藏目录,即只能是第一级目录)?
##创建环境 mkdir /oldboy -p cd /oldboy mkdir ext/oldboy test xiaodong xiaofan xingfujie -p touch jeacen oldboy wodi.gz yingsui.gz
##方法1-tree yum install tree -y [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# tree -Ld 1 . ├── ext ├── test ├── xiaodong ├── xiaofan └── xingfujie 5 directories ##方法2-find [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# find -maxdepth 1 -type d 把-maxdepth放在前面,否则会有警告信息 . ./xingfujie ./test ./xiaodong ./xiaofan ./ext [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# find -maxdepth 1 -type d -name "." . [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# find -maxdepth 1 -type d ! -name "." ./xingfujie ./test ./xiaodong ./xiaofan ./ext ##方法3-grep [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# ls -l |grep "以d开头的行" [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# ls -l |grep "^d" drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 ext drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Dec 11 21:22 test drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xiaodong drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xiaofan drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xingfujie ^ 高级货色(三剑客使用) 正则表达式 以.....开头的行 ##方法4-awk [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# ls -l |awk '第2列大于1' awk: 第2列大于1 awk: ^ invalid char '奠in expression [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# ls -l |awk '$2>1' total 32 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 ext drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Dec 11 21:22 test drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xiaodong drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xiaofan drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 15 00:26 xingfujie 这种方法其实是不准确的,了解一下 ##方法5-ls [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# ls -F|grep "/" ext/ test/ xiaodong/ xiaofan/ xingfujie/ [root@oldboyedu43-lnb oldboy]# #-F 给不通类型的文件 加上不通的标记/尾巴 ##方法6-ls ls -ld */
## 查看某个软件包里面有什么 [root@luffy_boy-001 oldboy]# rpm -ql tree /usr/bin/tree /usr/share/doc/tree-1.5.3 /usr/share/doc/tree-1.5.3/LICENSE /usr/share/doc/tree-1.5.3/README /usr/share/man/man1/tree.1.gz
查看某个软件是否安装
rpm -qa |grep tree
跳转目录
如何快速的回到 上一次所在的位置/目录
cd - 快速回到上一次的位置。- 相当于 环境变量
cd - #cd $OLDPWD cd - #如何快速的回到 上一次所在的位置 cd . #当前目录 复制/移动 cd .. #进入当前目录的上级目录 cd ~ #进入当前目录的家目录 回老家 cd #进入当前目录的家目录 回老家
查找最近跟新的文件
一个目录中有很多文件(ls查-看时好多屏),想最快速度查看到最近更新的文件。如何看?
[root@luffy_boy-001 etc]# ls -lrt
t 按时间排序
r 逆序
实时查看日志内容的实时跟新
调试系统服务时,希望能实时查看系统日志/var/log/messages 的更新,如何做?
#1、重新打开一个窗口 [root@luffy_boy-001 etc]# tail -f /var/log/messages
tailf ==== tail -f 一样的
查找文件内容以及行号
三剑客sed、grep、awk都能过滤,但是在过滤方面还是grep的比较快一些
sed跟擅长替换,修改文本内容
awk擅长取行,取列
打印配置文件nginx.conf的内容的行号以及内容,该如何做?
打造环境
echo stu{01..10} |xargs -n1 >nginx.conf
###方法1 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# cat -n nginx.conf 1 stu1 2 stu2 3 stu3 4 stu4 5 stu5 ###方法2 vi /vim :set nu #显示行号 :set nonu #取消显示行号 ###方法3 grep [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# grep -n "." nginx.conf 1:stu1 2:stu2 3:stu3 4:stu4 5:stu5 ####. 正则表达式里面的 表示任意一个字符 ###方法4 sed [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# sed '=' nginx.conf |xargs -n2 1 stu1 2 stu2 3 stu3 4 stu4 5 stu5 ###方法5 awk [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# awk '显示行号' nginx.conf awk: 显示行号 awk: ^ invalid char '?in expression [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# awk '{print NR}' nginx.conf 1 2 3 4 5 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# awk '{print NR,$0}' nginx.conf 1 stu1 2 stu2 3 stu3 4 stu4 5 stu5 ###方法6 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb oldboy]# nl nginx.conf 1 stu1 2 stu2 3 stu3 4 stu4 5 stu5
文件处理(日志仅保留7天)
已知apache/nginx服务的访问日志按天记录在服务器本地目录/app/logs下,由于磁盘空间紧张,现在要求只能保留最近7天访问日志!请问如何解决? 请给出解决办法或配置或处理命令。(提示:可以从apache服务配置上着手,也可以从生成出来的日志上着手。)
# 创建环境 mkdir -p /app/logs cd /app/logs for time in {01..20};do date -s "201705$time"; touch access_www_$(date +%F).log ;done date -s "20170520" 修改系统时间
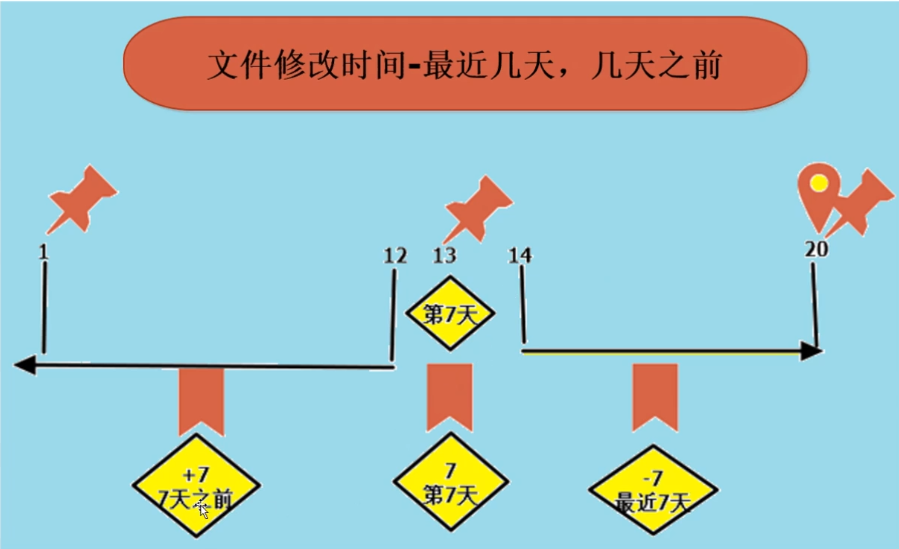
# 前第七天 [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# find -type f -name '*.log' -mtime 7 ./access_www_2017-05-13.log # 7天之前 [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# find -type f -name '*.log' -mtime +7 ./access_www_2017-05-11.log ./access_www_2017-05-12.log ./access_www_2017-05-10.log ./access_www_2017-05-08.log ./access_www_2017-05-09.log ./access_www_2017-05-01.log ./access_www_2017-05-02.log ./access_www_2017-05-03.log ./access_www_2017-05-06.log ./access_www_2017-05-07.log ./access_www_2017-05-05.log ./access_www_2017-05-04.log # 最近7天 [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# find -type f -name '*.log' -mtime -7 ./access_www_2017-05-18.log ./access_www_2017-05-15.log ./access_www_2017-05-20.log ./access_www_2017-05-16.log ./access_www_2017-05-19.log ./access_www_2017-05-17.log ./access_www_2017-05-14.log
找出/app/logs下面以.log结尾的并且修改时间是7天之前的文件并删除(ls -l) find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7 #find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7|xargs ls -l #ls -l $(find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7) #find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -exec ls -l {} \; 通过系统软件对日志进行切割。 补充find命令相关题目: 查找/oldboy 下所有以log 结尾的大于1M 的文件复制到/tmp [root@oldboyedu43-lnb logs]# cat /etc/services /etc/services > 1m.log [root@oldboyedu43-lnb logs]# ls -lh 1m.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.3M Dec 12 00:14 1m.log find /oldboy -type f -name "*.log" -size +1M -size +1M -size +100k find /oldboy -type f -name "*.log" mkdir -p /tmp/a /tmp/b /tmp/c /tmp/d 方法1 find+$() #cp 次处是find命令的结果 /tmp/a/ cp $(find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log") /tmp/a/ 方法2 find + -exec find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" -exec cp {} /tmp/b/ \; 方法3 find + |xargs find /app/logs/ -type f -name "*.log" |xargs cp -t /tmp/c
设置服务的开启级别
装完系统后,希望让网络文件共享服务NFS(iptables),仅在3级别上开机自启动,应该怎么做?
[root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# chkconfig |grep ipt iptables 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# chkconfig --level 3 iptables off [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# chkconfig |grep ipt iptables 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:off 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# chkconfig --level 35 iptables off [root@luffy_boy-001 logs]# chkconfig |grep ipt iptables 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:off 4:on 5:off 6:off
备份一堆文件-打包tar
/etc/目录是linux系统默认的配置文件以及服务启动命令的目录
a、请用tar打包/etc整个目录(打包以及压缩)
b、请把a点命令的压缩包,解压到/tmp 指定目录下(最好用tar命令实现)
c、请用tar打包/etc整个目录(打包及压缩,但需要排除/etc/services文件)
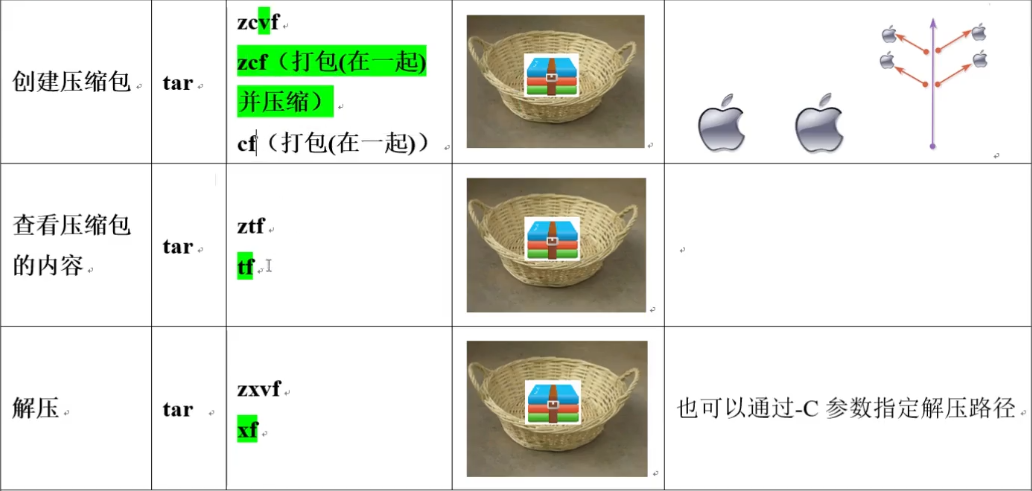
tar - 创建查看解压 压缩包
####创建一个压缩包 #tar zcvf /tmp/etc.tar.gz /etc/ #z----压缩工具---gzip 最常用一种 压缩之后我们一般给 压缩包命名位 xxxx.tar.gz #c----创建-------create #v----显示压缩/解压过程 #f----file------指定压缩包的名字 ###查看压缩包里面的内容 tar ztf /tmp/etc.tar.gz #t---list------列表 显示 ###解压----解压到当前目录 # cd /tmp/ # pwd /tmp # tar zxvf /tmp/etc.tar.gz #x-----extract 解压
提示的是什么?:
[root@luffy_boy-001 etc]# tar zcf /etc/haha.tar.gz /etc/ tar: Removing leading `/' from member names tar: Removing leading `/' from hard link targets tar: /etc: file changed as we read it ###问题:"创建压缩包"的时候会提示 tar: Removing leading `/' from member names tar:把每个文件开头的/删除掉了。 /etc/hosts ------> etc/hosts tar命令提示你:我在创建压缩包的时候 把压缩包中的文件 绝对路径----->相对路径 tar: Removing leading `/' from hard link targets 打包的时候使用相对路径,就不会出现提示了 ###小结:核心 为了安全----tar命令 把你使用的绝对路径----变化为-----相对路径
b和c的答案:
b.请用tar打包/etc整个目录(打包及压缩,但需要排除/etc/services文件)。 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar zcf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz /etc/ --exclude=services ###排除所有文件名叫services的文件 tar: Removing leading `/' from member names tar: Removing leading `/' from hard link targets [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar tf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz |grep services etc/init/readahead-disable-services.conf [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar tf /tmp/etc.tar.gz |grep services etc/services etc/init/readahead-disable-services.conf ##排除---精确版本 加上位置 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar zcf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz /etc/ --exclude=etc/services tar: Removing leading `/' from member names tar: Removing leading `/' from hard link targets [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar tf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz |grep services etc/sysconfig/services etc/init/readahead-disable-services.conf #把你要排除的名单写到一个文件中 /tmp/paichu.txt(了解) #tar zcf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz /etc/ --exclude-from=/tmp/paichu.txt c.请把a点命令的压缩包,解压到/tmp指定目录下(最好只用tar命令实现)。 tar xf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz -C /opt 把/etc/hosts /etc/sysconfig/network /etc/sysconfig/i18n /etc/init.d/ 打包压缩 /tmp/conf.tar.gz 解压到/opt目录 [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar zcf /tmp/conf.tar.gz /etc/hosts /etc/sysconfig/network /etc/sysconfig/i18n /etc/init.d/ tar: Removing leading `/' from member names [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar tf /tmp/conf.tar.gz etc/hosts etc/sysconfig/network etc/sysconfig/i18n etc/init.d [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# tar xf /tmp/conf.tar.gz -C /opt/ [root@oldboyedu-39-nb /]# ls /opt/ etc rh
小结:
#1.创建压缩包 tar zcf /tmp/oldboy.tar.gz /oldboy #2.查看压缩包中的内容 tar tf /tmp/oldboy.tar.gz #3.解压---解压到当前目录 tar xf /tmp/oldboy.tar.gz tar xf /tmp/oldboy.tar.gz -C /opt #4.创建压缩包的时候 排除 tar zcf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz /etc/ --exclude=etc/services
tar zcf /tmp/etc-pai.tar.gz /etc/ --exclude-from=/tmp/paichu.txt
sed和awk筛选出文件中的指定内容
已知如下命令及结果:
mkdir -p /oldboy
echo "I am oldboy,myqq is 31333741">/oldboy/oldboy.txt
a.现在需要从文件中过滤出“oldboy”和“31333741”字符串,请给出命令.
b.如果需要从文件中过滤出“oldboy,31333741”字符串,请再给出命令.
a.现在需要从文件中过滤出“oldboy”和“31333741”字符串,请给出命令. 方法1-sed-sed [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# sed 's#I am ##g' oldboy.txt |sed 's#,myqq is##g' oldboy 31333741
方法2-sed/tr+awk [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# sed 's#,# #g' oldboy.txt |awk '{print $3,$6}' oldboy 31333741 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# tr "," " " <oldboy.txt |awk '{print $3,$6}' oldboy 31333741 方法3-awk指定多个分隔符号 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# cat oldboy.txt I am oldboy,myqq is 31333741 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "," '{print $1}' oldboy.txt I am oldboy [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "[, ]" '{print $3,$6}' oldboy.txt oldboy 31333741 -F "[, ]" 表示以逗号或者空格作为菜刀 分隔符 b.如果需要从文件中过滤出“oldboy,31333741”字符串,请再给出命令. [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "[, ]" '{print $3,$6}' oldboy.txt oldboy 31333741 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "[, ]" '{print $3","$6}' oldboy.txt oldboy,31333741 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "[, ]" '{print $3"$1"$6}' oldboy.txt oldboy$131333741 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# awk -F "[, ]" '{print $3" $1 "$6}' oldboy.txt oldboy $1 31333741 小结: 1.tr命令 2.awk指定分隔符 指定多个分隔符
awk分割列的方式

统计文件信息 wc -l
可以统计文件有多少行,有多少单词,多大等
如何查看/etc/services文件的有多少行?
[root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# wc -l /etc/services 10774 /etc/services
查看程序是否运行 ps -ef
屌丝去洗浴中心之路
3.
1)查看22端口是否开启 telnet
2)sshd远程连接进程是否在运行******
ps -ef
[root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# ps -ef |grep "sshd" root 1509 1 0 17:51 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd root 1669 1509 0 17:51 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/0 root 1795 1509 0 18:17 ? 00:00:00 sshd: root@pts/1 root 1813 1671 0 18:17 pts/0 00:00:00 grep sshd [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# ps -ef |grep "/sshd" root 1509 1 0 17:51 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd root 1817 1671 0 18:19 pts/0 00:00:00 grep /sshd [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# ps -ef |grep "/sshd"|wc -l 得到数字 2
过滤指定内容所在行的内容 egrep
过滤出/etc/services 文件包含3306或1521两数字所在的行的内容。
[root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# egrep "3306|1521" /etc/services mysql 3306/tcp # MySQL mysql 3306/udp # MySQL ncube-lm 1521/tcp # nCube License Manager ncube-lm 1521/udp # nCube License Manager [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# #egrep === grep -E 支持高级正则(公鸡里的战斗机)
命令行及shell中加单引号和加双引号的区别
单引号 所见即所得 吃啥吐啥 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# echo 'hello lls $LANG $(hostname) `pwd`' hello lls $LANG $(hostname) `pwd` 双引号 里面的特殊符号会被解析 [root@oldboyedu01-nb oldboy]# echo "hello lls $LANG $(hostname) `pwd`" hello lls en_US.UTF-8 oldboyedu01-nb /oldboy


