基于Django rest framework 和Vue实现简单的在线教育平台
一、基于api前端显示课程详细信息
1、调整Course.vue模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
<template> <div> <h1>课程列表</h1> <div v-for="row in courseList"> <div style="width:350px;float: left;"> <!--<img src="" alt=""/>--> <h3><router-link :to="{name:'detail', params:{id:row.id}}">{{row.title}}</router-link></h3> <p>{{row.level}}</p> </div> </div> </div></template><script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { courseList: [] } }, mounted: function () { // vue页面刚加载时自动执行 this.initCourse() }, methods: { initCourse: function () { /* this.courseList = [ {id:1,title:'Python全栈'}, {id:2,title:'Linux运维'}, {id:3,title:'金融分析'}, ] */ // 通过ajax向接口发送请求,并获取课程列表 // axios 发送ajax请求 // npm install axios --save // 第一步:在main.js中配置 // 第二步:使用axios发送请求 var that = this; this.$axios.request({ url: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/course/', method: "GET" }).then(function (ret) { // ajax请求发送成功后,获取的响应内容 console.log(ret.data); if (ret.data.code === 1000) { // 注意这里的this已经不再是之前的this that.courseList = ret.data.data }else{ alert("获取数据失败"); } }).catch(function (ret) { // ajax请求失败之后,获取响应的内容 }) } } }</script><style scoped></style> |
显示效果:
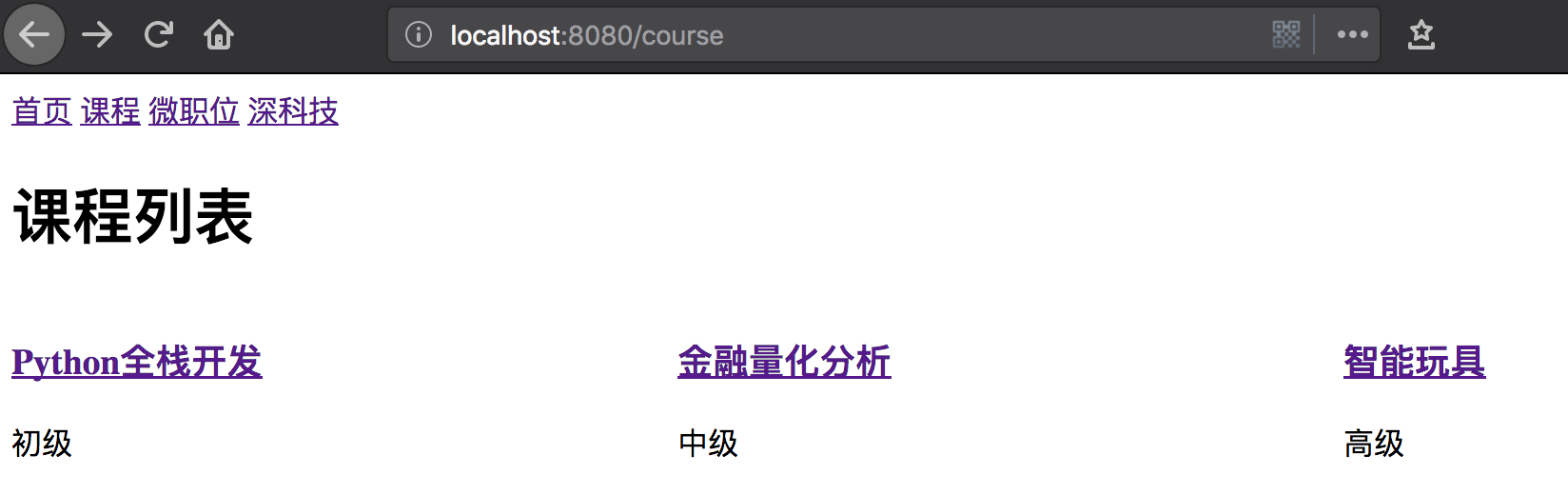
2、调整Detail.vue模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
<template> <div> <h1>课程详细页面</h1> <div> <p>{{detail.course}}</p> <p>{{detail.img}}</p> <p>{{detail.level}}</p> <p>{{detail.slogon}}</p> <p>{{detail.title}}</p> <p>{{detail.why}}</p> <div> <ul v-for="item in detail.chapter"> <li>{{item.name}}</li> </ul> </div> <div> <ul v-for="item in detail.recommends"> <li>{{item.title}}</li> </ul> </div> </div> </div></template><script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { detail: { // 定义字典和相关的key course: null, img: null, level: null, slogon: null, title: null, why: null, chapter: [], recommends: [], } } }, mounted() { this.initDetail() }, methods: { initDetail() { var nid = this.$route.params.id; // 获取当前id值(用于拼接url) var that = this; this.$axios.request({ // 发送axios请求 url: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/course/' + nid + '/', method: 'GET' }).then(function (arg) { // arg是返回的值:{code:1000, data:{...}} // 将拿到的值赋值给detail if (arg.data.code === 1000) { that.detail = arg.data.data // 注意这里的this已经不是原来的this } else { alert(arg.data.error) } }) } } }</script><style scoped></style> |
显示效果:
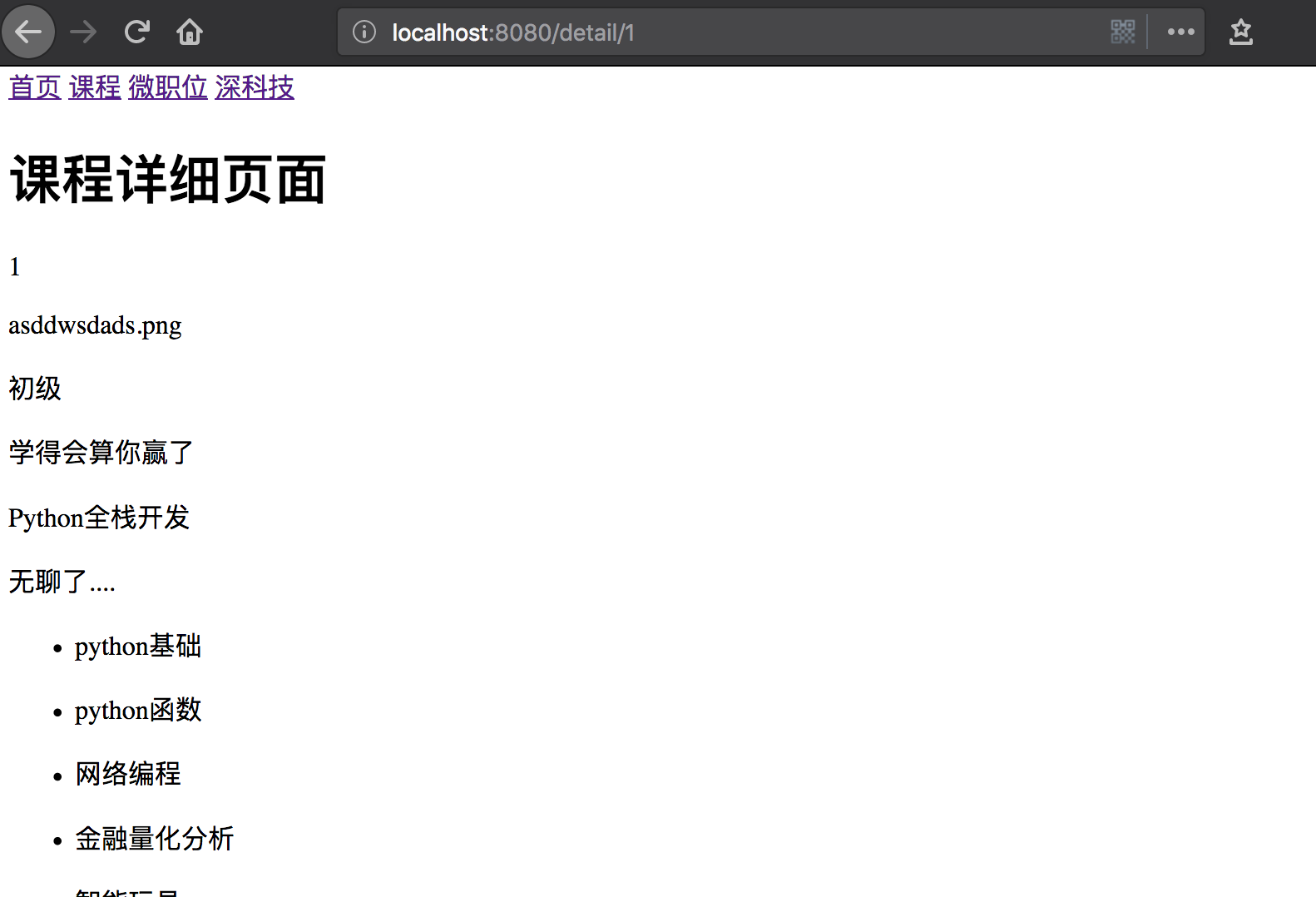
二、推荐课程切换及详情展示
1、测试使用router-link是否合适
对Detail.vue修改如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<template> <div> <h1>课程详细页面</h1> <div> <p>{{detail.course}}</p> <p>{{detail.img}}</p> <p>{{detail.level}}</p> <p>{{detail.slogon}}</p> <p>{{detail.title}}</p> <p>{{detail.why}}</p> <div> <ul v-for="item in detail.chapter"> <li>{{item.name}}</li> </ul> </div> <div> <h3>推荐课程</h3> <ul v-for="item in detail.recommends"> <li><router-link :to="{name:'detail',params:{id:item.id}}">{{item.title}}</router-link></li> </ul> </div> </div> </div></template> |
给推荐课程添加链接地址,点击可以实现url切换,但是由于组件没有重新加载,this.initDetail()没有执行。
因此页面的内容并不会发生切换。此方法不合适。
2、添加点击事件处理推荐课程点击切换
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
<template> <div> <h1>课程详细页面</h1> <div> <p>{{detail.course}}</p> <p>{{detail.img}}</p> <p>{{detail.level}}</p> <p>{{detail.slogon}}</p> <p>{{detail.title}}</p> <p>{{detail.why}}</p> <div> <ul v-for="item in detail.chapter"> <li>{{item.name}}</li> </ul> </div> <div> <h3>推荐课程</h3> <ul v-for="item in detail.recommends"> <!--为推荐课程添加点击事件--> <li @click="changeDetail(item.id)">{{item.title}}</li> </ul> </div> </div> </div></template><script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { detail: { // 定义字典和相关的key course: null, img: null, level: null, slogon: null, title: null, why: null, chapter: [], recommends: [], } } }, mounted() { var id = this.$route.params.id; // 获取当前id值(用于拼接url) this.initDetail(id) }, methods: { initDetail(nid) { var that = this; this.$axios.request({ // 发送axios请求 url: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/course/' + nid + '/', method: 'GET' }).then(function (arg) { // arg是返回的值:{code:1000, data:{...}} // 将拿到的值赋值给detail if (arg.data.code === 1000) { that.detail = arg.data.data // 注意这里的this已经不是原来的this } else { alert(arg.data.error) } }) }, changeDetail(id){ // click拿到课程id重新加载就可以渲染成功了 this.initDetail(id); // 切换页面显示 this.$router.push({name: 'detail', params: {id:id}}); // 修改url地址 } } }</script><style scoped></style> |
注意:这里将var id = this.$route.params.id; 操作提到了vue生命周期mounted方法中。因此initDetail(nid)函数接收的nid,有可能是从mounted中传递过来的id也可以是changeDetail传递的id。
在 Vue 实例内部,你可以通过 $router 访问路由实例。因此你可以调用 this.$router.push。
|
1
|
this.$router.push({name: 'detail', params: {id:id}}); // 命名的路由 |
显示效果如下所示:
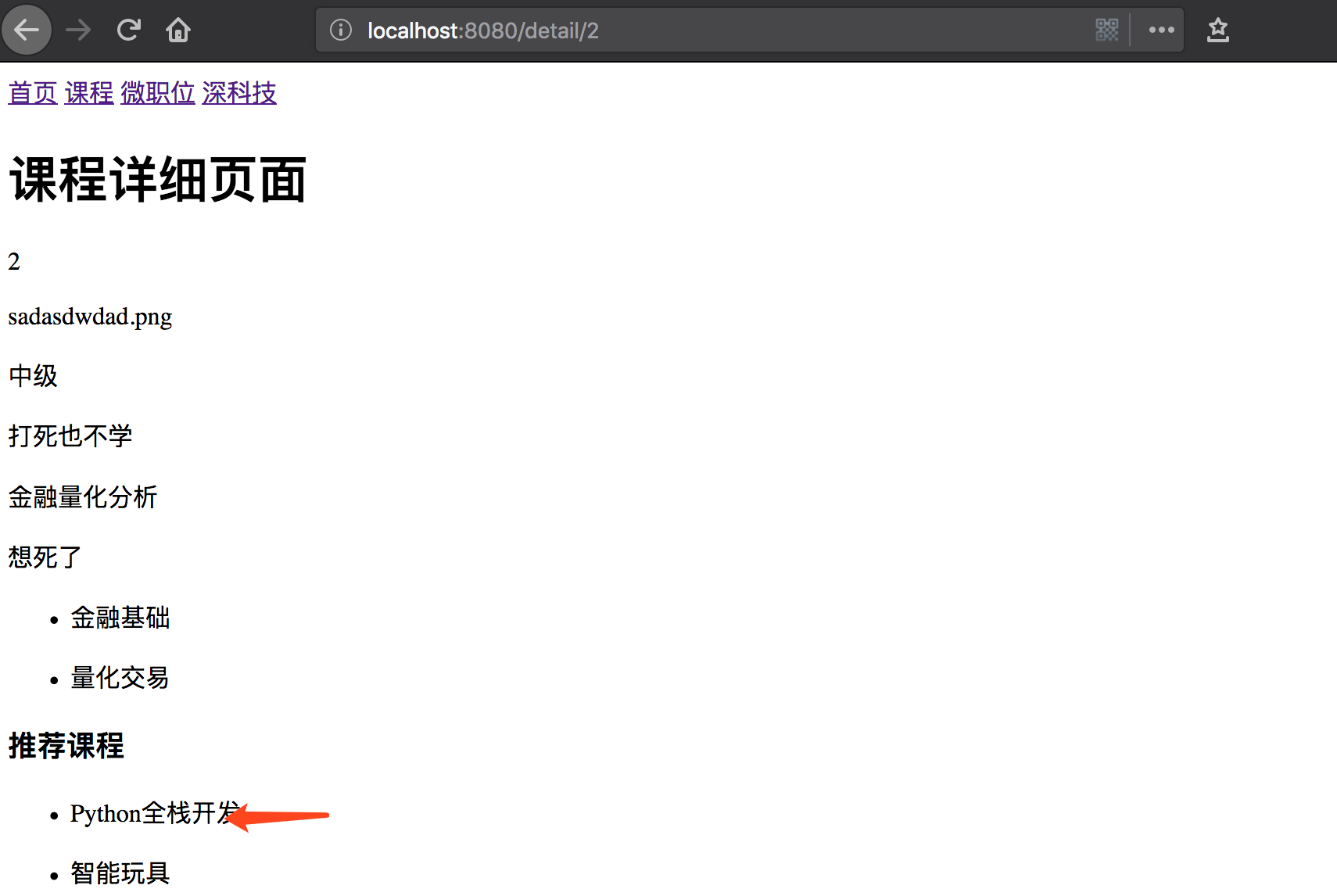
点击推荐课程可以自由切换页面路径和页面显示。
三、用户登录功能实现
1、前端添加Login.vue模块
(1)App.vue和index.js添加Login模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
############# App.vue ###############<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/index">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> <router-link to="/micro">微职位</router-link> <router-link to="/news">深科技</router-link> <div> <router-link to="/login">登录</router-link> </div> <router-view/> </div></template>############# index.js ###############import Login from '../components/Login'Vue.use(Router);export default new Router({ routes: [ // 其他代码省略 { path: '/login', name: 'login', component: Login }, ]}) |
(2)Login.vue构建
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
<template> <div> <h2>用户登录</h2> <div> <p> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" v-model="username"> </p> <p> <input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" v-model="password"> </p> <input type="button" value="登录" @click="doLogin"> </div> </div></template><script> export default { data(){ return { // 通过v-model双向绑定用户名和密码 username:'', password:'' } }, methods: { doLogin(){ this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/', method:'POST', data:{ user:this.username, pwd:this.password }, headers:{ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } }).then(function (arg) { // 拿回结果 console.log(arg) }).catch(function (arg) { // 拿到错误信息 console.log("发生错误") }) } } }</script><style scoped></style> |
注意:这里是通过v-model双向绑定用户名和密码,并以此通过post请求来发送username和password。
2、django后台auth接口配置
(1)路由配置api/urls.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
urlpatterns = [ """代码省略""" url(r'^(?P<version>[v1|v2]+)/auth/$', account.AuthView.as_view()),] |
(2)视图配置api/view/account.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responseclass AuthView(APIView): def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print(request.data) return Response('...') |
(3)在前台页面尝试登陆

可以看到虽然配置的是post请求,但实际却发送的是OPTIONS请求。
3、跨域问题处理
(1)简单请求和非简单请求
浏览器将CORS请求分成两类:简单请求(simple request)和非简单请求(not-so-simple request)。
只要同时满足以下两大条件,就属于简单请求。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
(1) 请求方法是以下三种方法之一:HEADGETPOST(2)HTTP的头信息不超出以下几种字段:AcceptAccept-LanguageContent-LanguageLast-Event-IDContent-Type:只限于三个值application/x-www-form-urlencoded、multipart/form-data、text/plain |
凡是不同时满足上面两个条件,就属于非简单请求。
如果是复杂请求,会先用options请求进行预检,通过之后才能发送post请求。
(2)配置修改account.py,添加options请求处理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
from rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responsefrom django.shortcuts import HttpResponseclass AuthView(APIView): def options(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # 进行预检 obj = HttpResponse('') obj["Access-Control-Allow-Origin"] = "*" # 允许你的域名来获取我的数据 obj['Access-Control-Allow-Headers'] = "Content-Type" # 允许你携带Content-Type请求头 return obj def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): print(request.data) # 同源策略禁止读取位于 http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/ 的远程资源。(原因:CORS 头缺少 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin') obj = Response("...") obj["Access-Control-Allow-Origin"] = "*" # 允许你的域名来获取我的数据 return obj # 返回值再加上一个响应头 |
再次访问登录页面,尝试登录操作,可以看到OPTIONS请求通过后,发送POST请求,python后端也打印出request.data中的数据。
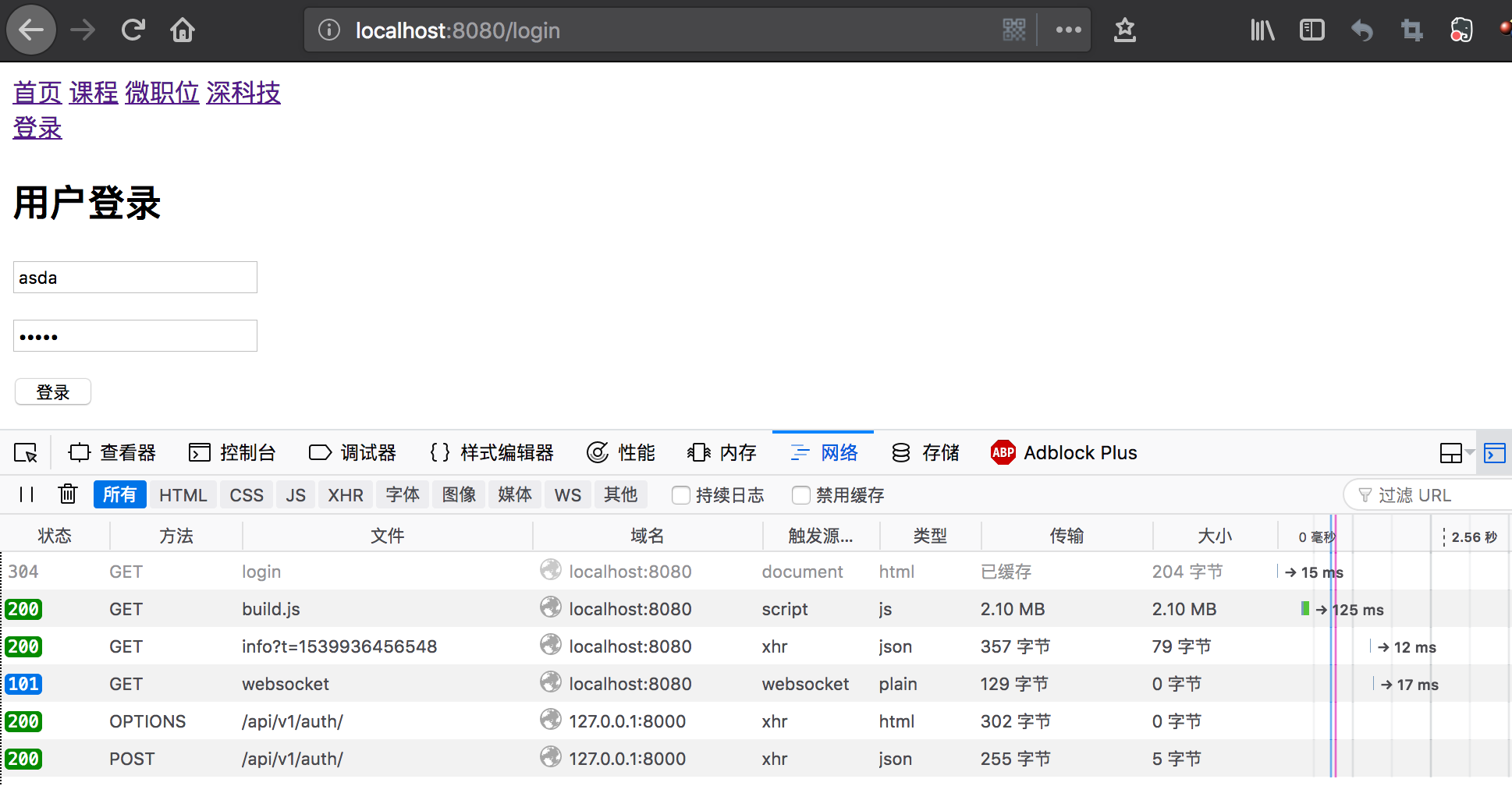
(3)用中间件来处理跨域问题
上面这种方式过于麻烦了,一般还是交给中间件来处理跨域问题,为所有请求都设置头。
/api/cors.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixinclass CORSMiddleware(MiddlewareMixin): """自定义中间件""" def process_response(self, request, response): # 添加响应头 # 允许你的域名来获取我的数据 response['Access-Control-Allow-Origin'] = "*" # 允许你携带Content-Type请求头,这里不能写* # response['Access-Control-Allow-Headers'] = "Content-Type" # 允许你发送GET/POST/DELETE/PUT # response['Access-Control-Allow-Methods'] = "GET, POST" if request.method == "OPTIONS": response["Access-Control-Allow-Headers"] = "Content-Type" return response |
4、rest-framework登录验证
(1)给models.py添加User和Token模型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class UserInfo(models.Model): user = models.CharField(max_length=32) pwd = models.CharField(max_length=64)class UserToken(models.Model): user = models.OneToOneField(to="UserInfo", on_delete=models.CASCADE) token = models.CharField(max_length=64) # 不仅可以配置token,还可以配置超时时间 |
利用makemigrations和migrate完成数据迁移操作。在UserInfo表添加用户和密码。
(2)后端处理登录信息,更新并创建token信息
重写/api/views/account.py如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
from rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responsefrom django.shortcuts import HttpResponsefrom api import modelsimport uuid # 网卡和时间生成的随机字符串class AuthView(APIView): def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ 用户登录认证 :param request: :param args: :param kwargs: :return: """ print(request.data) ret = {'code': 1000} # 用get方法取的话,不存在即为Null user = request.data.get("user") pwd = request.data.get("pwd") user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(user=user, pwd=pwd).first() if not user: ret['code'] = 1001 ret['error'] = "用户名或密码错误" else: uid = str(uuid.uuid4()) # 将生成的随机对象转化为随机字符串 models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=user, defaults={"token":uid}) ret["token"] = uid return Response(ret) |
(3)登录验证
在vue前端登录,显示信息如下:
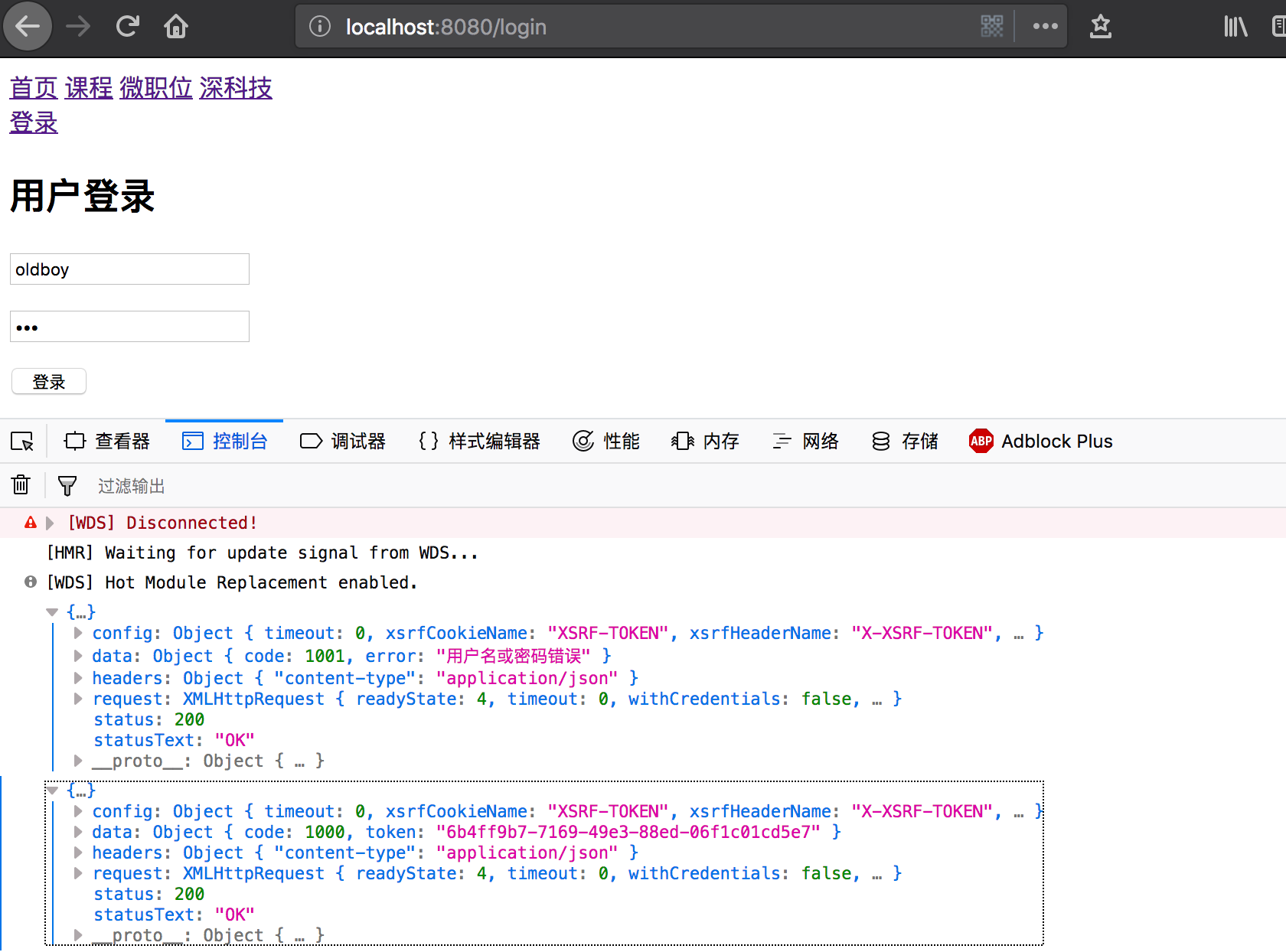
在python后台打印request.data信息:{'user': 'asdw', 'pwd': 'asdw131'}、{'user': 'oldboy', 'pwd': '123'}。
5、用vuex实现在各个组件中共享值
(1)全局变量配置
1)创建/src/store文件夹,创建并编写store.js文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'// import Cookie from 'vue-cookies'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({ // 组件中通过 this.$store.state.username 调用 state: { username: null, token: null, },}) |
组件中通过 this.$store.state.username 调用。
2)在main.js中引入store,并放入实例化组件中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App'import router from './router'import axios from 'axios'import store from './store/store'// 在vue的全局变量中设置了 $axios=axios// 以后每个组件使用时:this.$axiosVue.prototype.$axios = axios;Vue.config.productionTip = false;/* eslint-disable no-new */new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, // 放入实例化中 components: {App}, template: '<App/>'}) |
(2)在所有组件中使用全局变量
Login.vue:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
<script> export default { data(){ return { // 通过v-model双向绑定用户名和密码 username:'', password:'' } }, methods: { doLogin(){ var that = this; this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/', method:'POST', data:{ user:this.username, pwd:this.password }, headers:{ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } }).then(function (arg) { // 拿回结果 if (arg.data.code === 1000){ // 成功的情况下 that.$store.state.token = arg.data.token; that.$store.state.username = that.username; }else { alert(arg.data.error) } }).catch(function (arg) { // 拿到错误信息 console.log("发生错误") }) } } }</script> |
App.vue:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/index">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> <router-link to="/micro">微职位</router-link> <router-link to="/news">深科技</router-link> <div v-if="this.$store.state.token"> <a href="">{{this.$store.state.username}}</a> </div> <div v-else> <router-link to="/login">登录</router-link> </div> <router-view/> </div></template><script> export default { name: 'App' }</script> |
如此就可以通过获取全局变量实现用户登录效果:
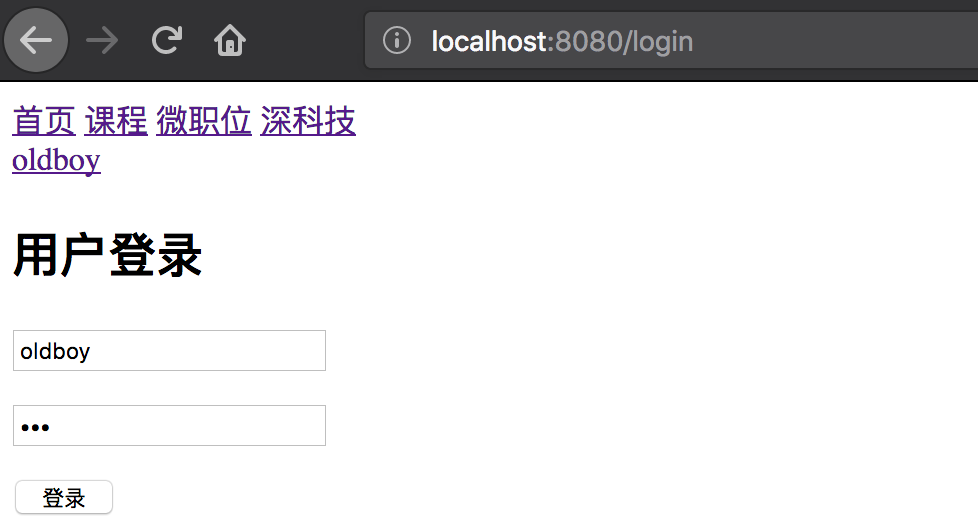
但是这种登录状态,只要浏览器一刷新,登录状态就消失了,因此登录成功不仅要设置到全局变量,还要在cookie中放一份全局变量。
6、vue-cookies应用
(1)store.js
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'import Cookie from 'vue-cookies' // 引入cookie,npm install vue-cookies --saveVue.use(Vuex);export default new Vuex.Store({ // 组件中通过 this.$store.state.username 调用 state: { // 默认去cookie中取值 username: Cookie.get("username"), token: Cookie.get("token"), }, mutations: { // 组件中通过this.$store.commit(函数名, 参数)调用 saveToken: function (state, userToken) { state.username = userToken.username; state.token = userToken.token; Cookie.set("username", userToken.username, "20min"); Cookie.set("token", userToken.token, "20min"); }, }}) |
1)注意引入cookie的方法;
2)注意mutations方法。更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。
3)组件中通过this.$store.commit(函数名, 参数)调用。
(2)Login.vue修改
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
<script> export default { data(){ return { // 通过v-model双向绑定用户名和密码 username:'', password:'' } }, methods: { doLogin(){ var that = this; this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/', method:'POST', data:{ user:this.username, pwd:this.password }, headers:{ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } }).then(function (arg) { // 拿回结果 if (arg.data.code === 1000){ // 成功的情况下 // that.$store.state.token = arg.data.token; // that.$store.state.username = that.username; that.$store.commit('saveToken',{token: arg.data.token, username: that.username}); }else { alert(arg.data.error) } }).catch(function (arg) { // 拿到错误信息 console.log("发生错误") }) } } }</script> |
(3)刷新仍在全局显示登录用户
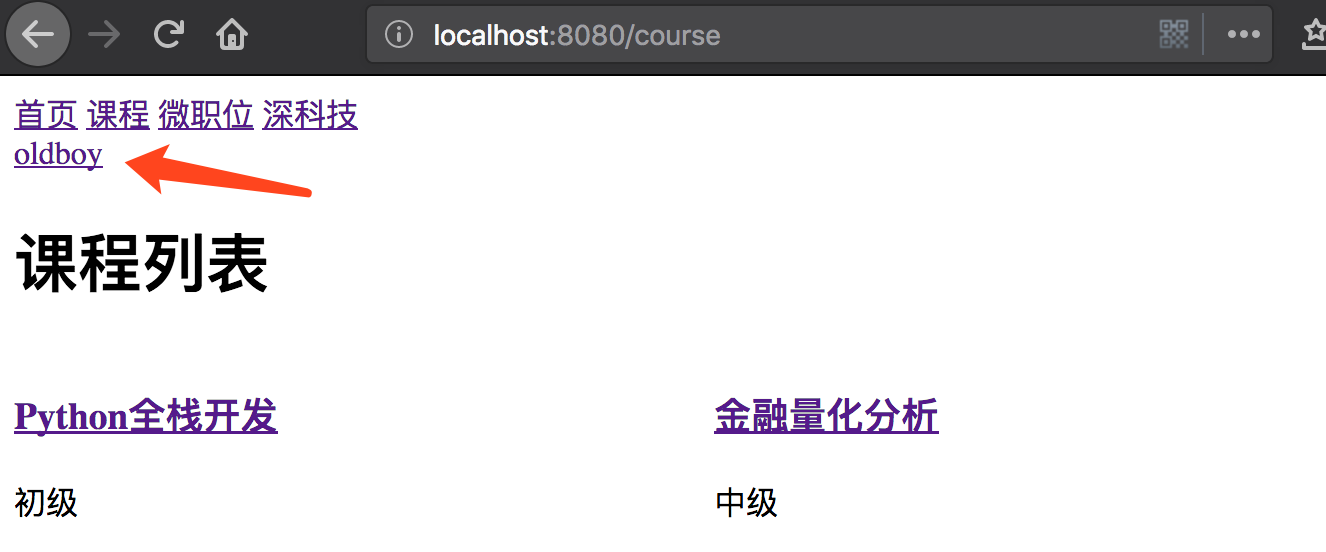
(4)添加登出注销操作
App.vue:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/index">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/course">课程</router-link> <router-link to="/micro">微职位</router-link> <router-link to="/news">深科技</router-link> <div v-if="this.$store.state.token"> <a href="">{{this.$store.state.username}}</a> <a @click="logout">注销</a> </div> <div v-else> <router-link to="/login">登录</router-link> </div> <router-view/> </div></template><script> export default { name: 'App', methods:{ logout(){ // 注销 this.$store.commit('clearToken'); } } }</script> |
store.js:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'import Cookie from 'vue-cookies' // 引入cookie,npm install vue-cookies --saveVue.use(Vuex);export default new Vuex.Store({ // 组件中通过 this.$store.state.username 调用 state: { // 默认去cookie中取值 username: Cookie.get("username"), token: Cookie.get("token"), }, mutations: { // 组件中通过this.$store.commit(函数名, 参数)调用 saveToken: function (state, userToken) { state.username = userToken.username; state.token = userToken.token; Cookie.set("username", userToken.username, "20min"); Cookie.set("token", userToken.token, "20min"); }, clearToken: function (state) { state.username = null; state.token = null; Cookie.remove("username"); Cookie.remove("token"); } }}) |
登出效果如下所示:
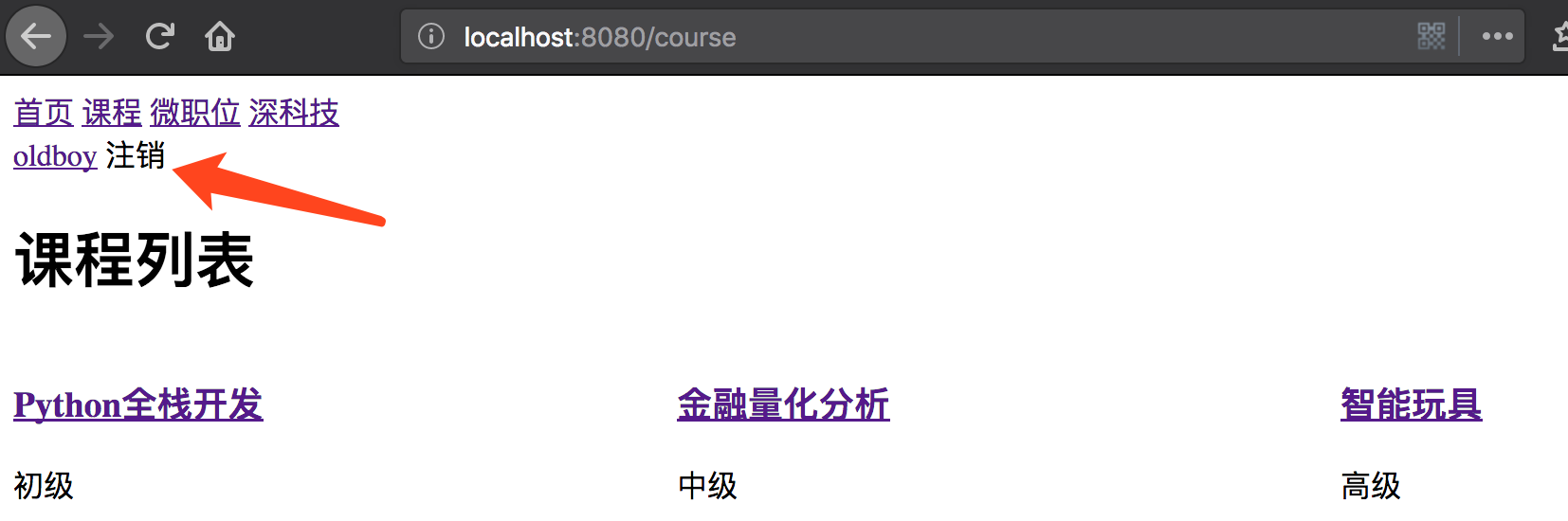
点击注销后显示效果:
四、拦截器
有些页面登录了才能访问,有些页面不需要登录即可访问。
1、页面访问登录判断
这里以micro模块为例,给模块添加登录判断,用户未登录时访问微职业,直接跳转到登录页面。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<template> <div> <h1>LuffyX学位</h1> </div></template><script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { } }, mounted(){ // 刚加载即执行 if(!this.$store.state.token){ // 重定向返回登录页面 this.$router.push({name:"login"}) } } }</script><style scoped></style> |
但是对于组件很多的网站却不能这么处理,而是应该使用vue自带的拦截器来处理。
2、添加拦截器
(1)在路由控制中给需要拦截的路由配置meta字段
index.js:给需要拦截的路由配置meta字段
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: '/index', name: 'index', component: Index, }, { path: '/course', name: 'course', component: Course }, { path: '/detail/:id', // 动态接收名字为id的值 name: 'detail', component: Detail }, { path: '/micro', name: 'micro', component: Micro, meta:{ requireAuth:true // 表示必须要登录 } }, { path: '/news', name: 'news', component: News, meta:{ requireAuth:true // 表示必须要登录 } }, { path: '/login', name: 'login', component: Login }, ], mode: 'history'}) |
(2)添加配置拦截器
main.js:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
import Vue from 'vue'import App from './App'import router from './router'import axios from 'axios'import store from './store/store'// 在vue的全局变量中设置了 $axios=axios// 以后每个组件使用时:this.$axiosVue.prototype.$axios = axios;Vue.config.productionTip = false;/* eslint-disable no-new */new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, // 放入实例化中 components: {App}, template: '<App/>'});// 拦截器 to:要去哪 next:去跳转 from:从哪来router.beforeEach(function (to, from, next) { if (to.meta.requireAuth) { // 当前要去的url只有登录后才能访问 if (store.state.token) { // token为true表示可以继续访问 next() } else { // token不为true跳转到登录页面 next({path:'/login',}) } } else { // url不需要访问即可以访问 next() }}); |
3、登录后直接显示登录前页面
比如在访问微职业时,由于没有登录跳转到了登录页面,输入账户密码登录后,显示的内容应该是微职业的内容。
(1)修改main.js中的拦截器
在url地址中添加返回的url:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// 拦截器 to:要去哪 next:去跳转 from:从哪来router.beforeEach(function (to, from, next) { if (to.meta.requireAuth) { // 当前要去的url只有登录后才能访问 if (store.state.token) { // token为true表示可以继续访问 next() } else { // token不为true跳转到登录页面 next({path:'/login', query:{backUrl: to.fullPath}}) } } else { // url不需要访问即可以访问 next() }}); |
(2)Login.vue中修改登录操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
<script> export default { data(){ return { // 通过v-model双向绑定用户名和密码 username:'', password:'' } }, methods: { doLogin(){ var that = this; this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/', method:'POST', data:{ user:this.username, pwd:this.password }, headers:{ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } }).then(function (arg) { // 拿回结果 if (arg.data.code === 1000){ // 成功的情况下 that.$store.commit('saveToken',{token: arg.data.token, username: that.username}); var url = that.$route.query.backUrl; if (url) { that.$router.push({path:url}) } else { that.$router.push({path:'/index'}) } }else { alert(arg.data.error) } }).catch(function (arg) { // 拿到错误信息 console.log("发生错误") }) } } }</script> |
(3)登录验证
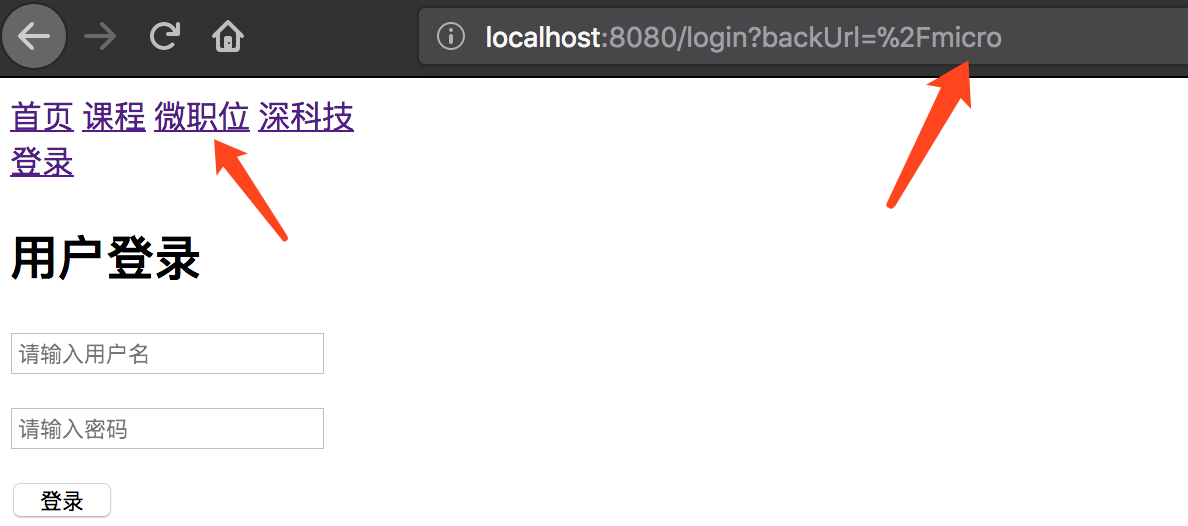
登录成功后显示效果:
五、用户认证
1、通过token进行用户认证
(1)配置micro的url和视图
api/urls.py:
|
1
2
3
4
|
urlpatterns = [ """省略""" url(r'^(?P<version>[v1|v2]+)/micro/$', course.MicroView.as_view()),] |
Couse.py添加MicroView视图:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
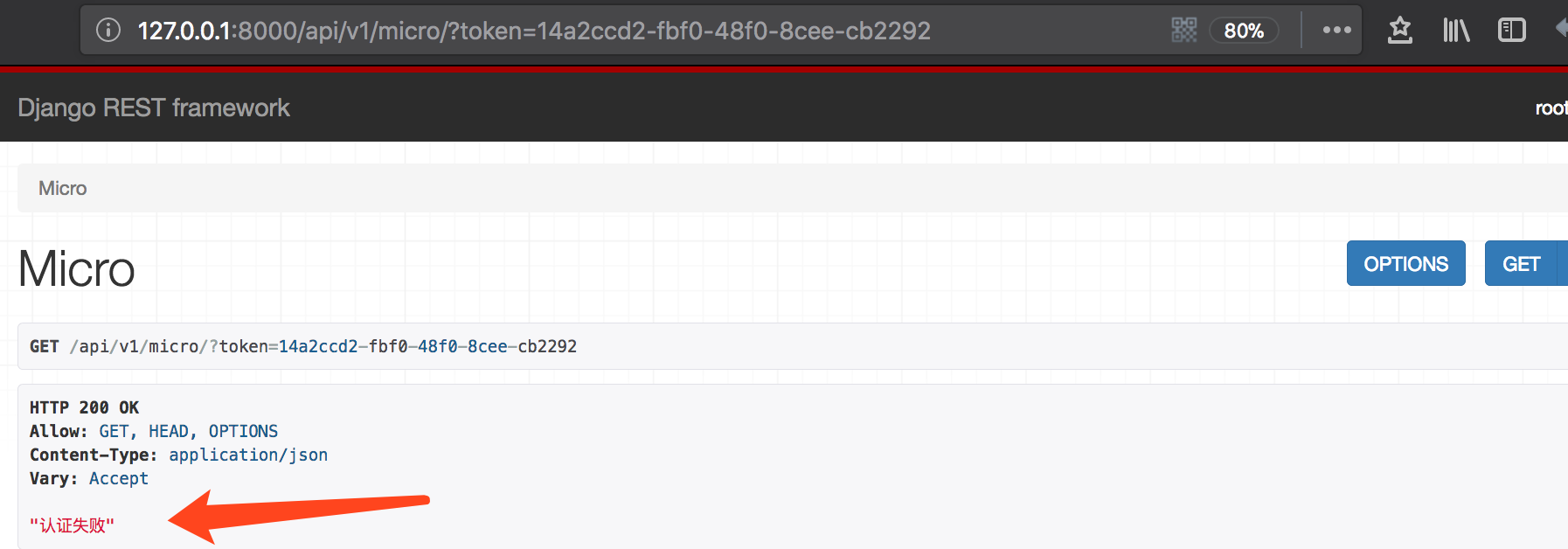
class MicroView(APIView): def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): token = request.query_params.get('token') # 获取到token obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token) # 与数据库中token检验 if not obj: return Response("认证失败") return Response("微职位") |
(2)配置Micro.vue向后端发送GET请求
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
<script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { title:null } }, mounted(){ // 刚加载即执行 this.initMicro() }, methods:{ initMicro(){ this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/micro/', // 这个地址如果被盗,任何人都可以获取数据 method:"GET", params:{ token:this.$store.state.token } }).then(function (arg) { console.log(arg); }) } } }</script> |
这里需要注意不能只配置Url,这个地址如果被盗,则任何人都可以向后端发送请求获取数据。
因此配置params参数,在url地址后拼接token参数来发送请求:
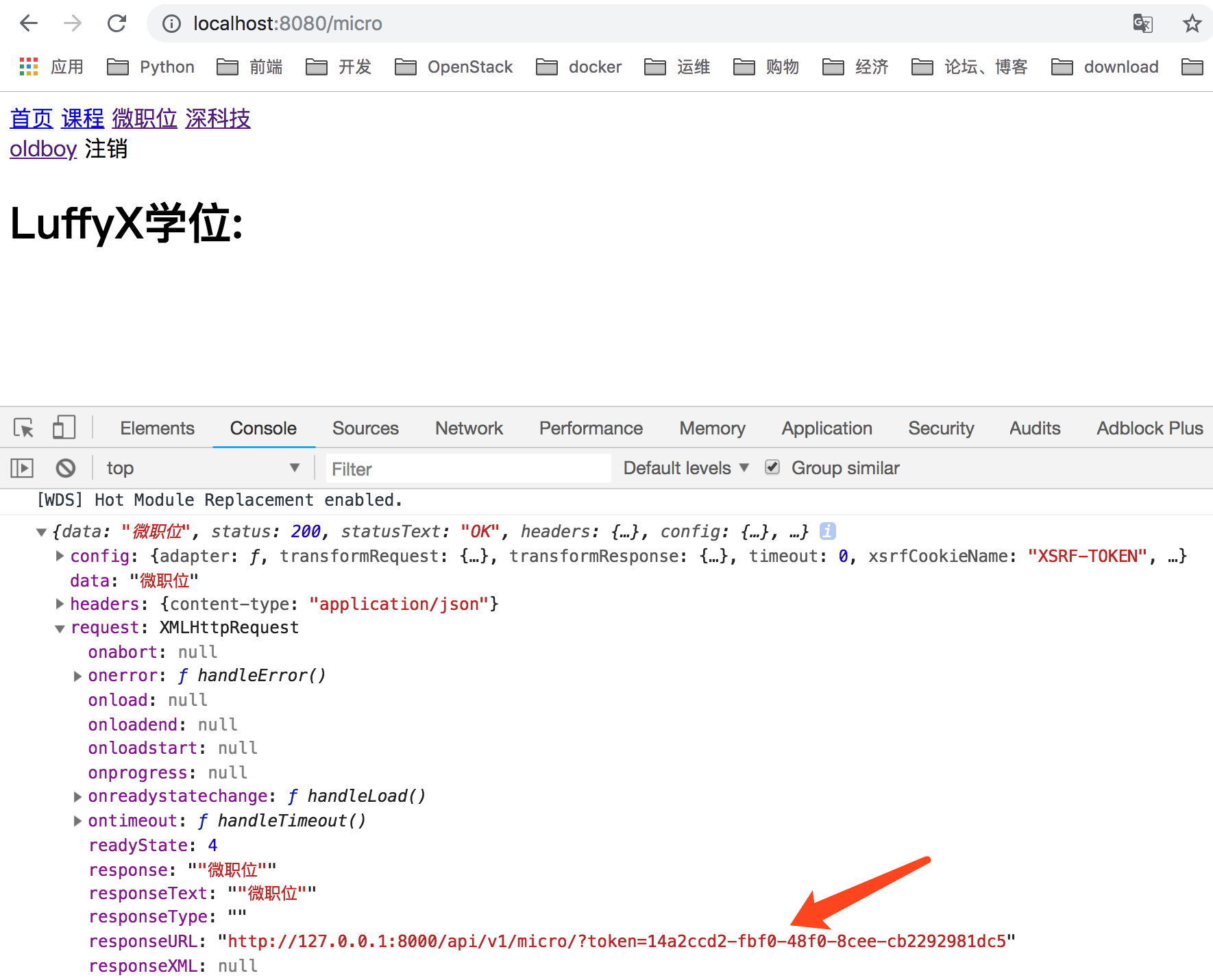
(3)django访问检验
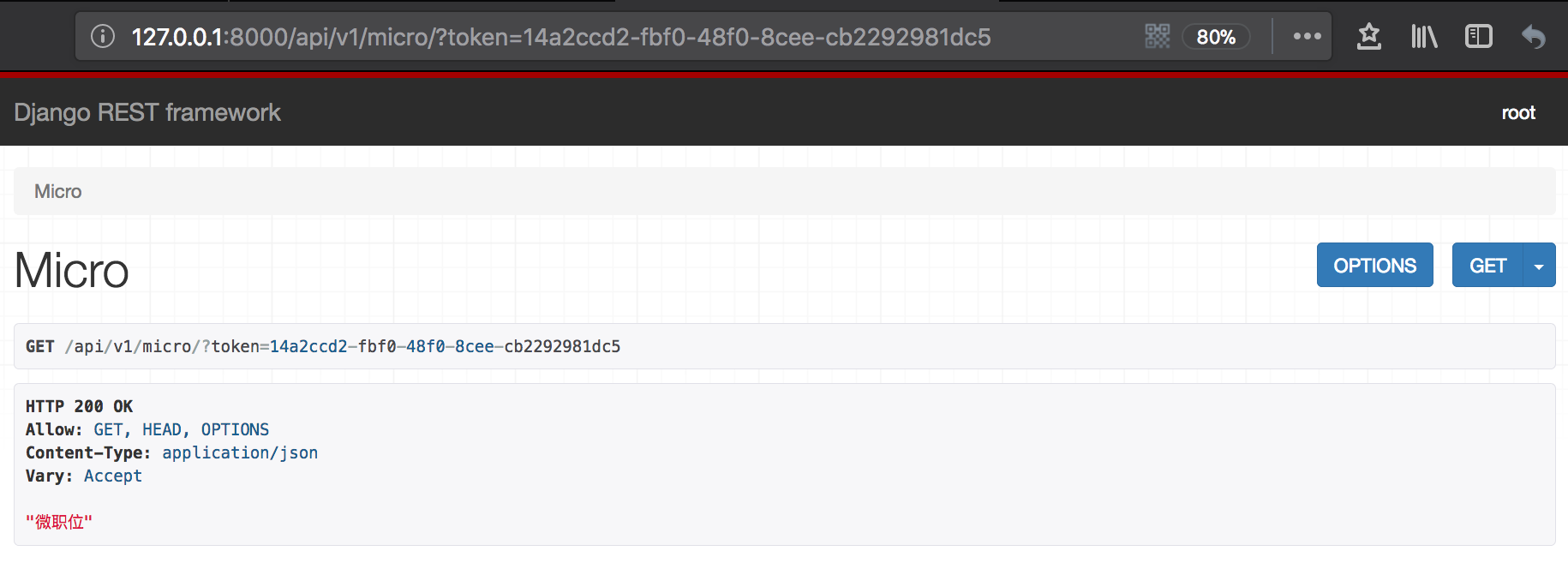
当token不正确时:
2、通过rest认证组件实现用户认证
(1) 在应用api下添加文件夹auth,添加auth.py文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthenticationfrom rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailedfrom api import modelsclass LuffyAuth(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): token = request.query_params.get("token") obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first() if not obj: raise AuthenticationFailed({"code":1001, "error": "认证失败"}) return (obj.user.user, obj) # 返回用户名和token对象 |
(2)在MicroVIew视图类中添加认证组件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
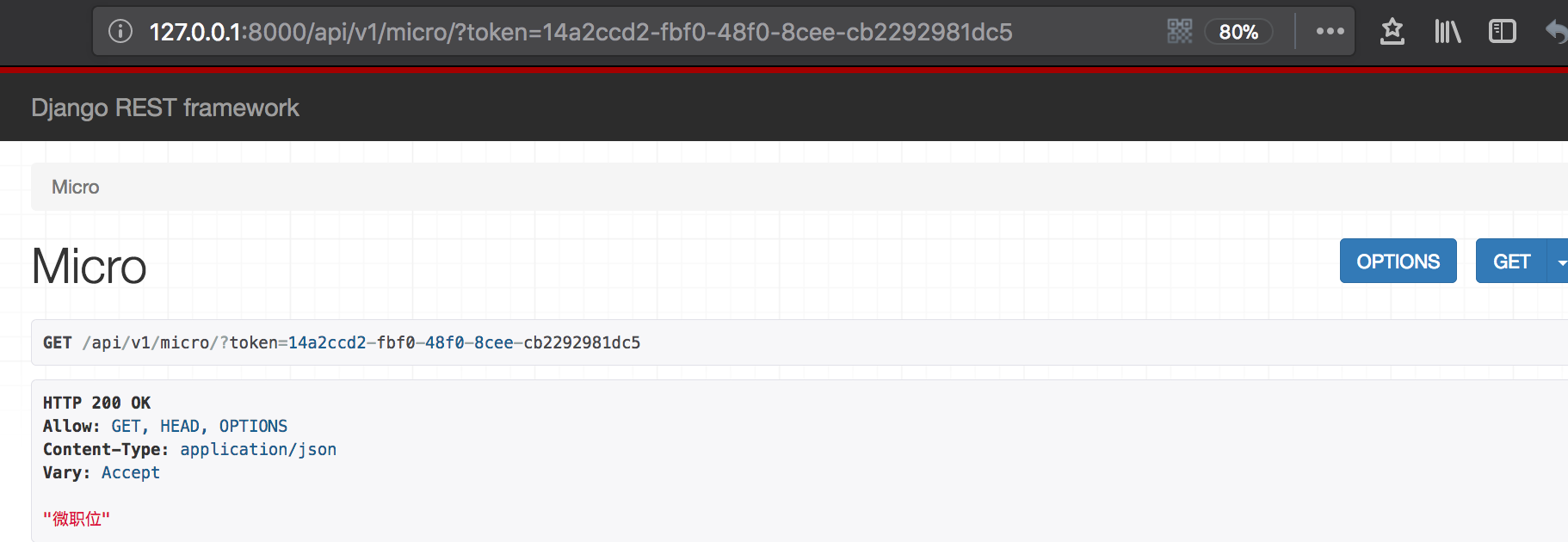
from api.auth.auth import LuffyAuthclass MicroView(APIView): authentication_classes = [LuffyAuth] def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): ret = {"code":1000, "title":"微职位"} return Response(ret) |
访问django页面验证:
(3)前端vue处理后端返回的数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
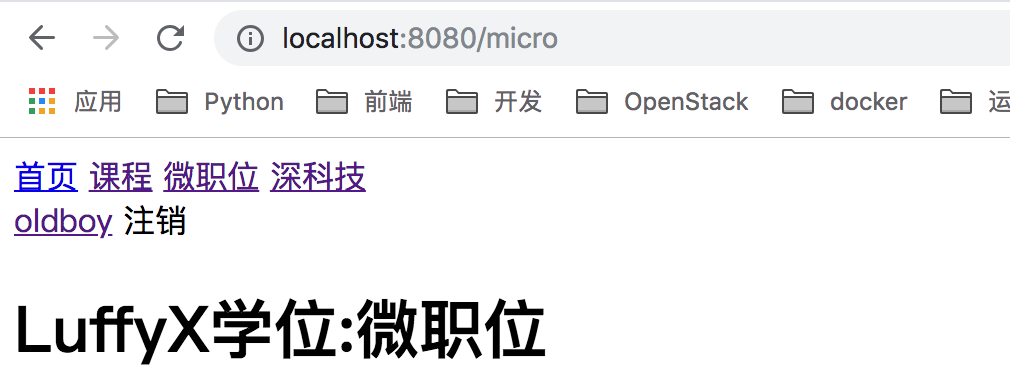
<template> <div> <h1>LuffyX学位:{{title}}</h1> </div></template><script> export default { name: "index", data() { return { title:null } }, mounted(){ // 刚加载即执行 this.initMicro() }, methods:{ initMicro(){ var that = this; this.$axios.request({ url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/micro/', // 这个地址如果被盗,任何人都可以获取数据 method:"GET", params:{ token:this.$store.state.token } }).then(function (arg) { if (arg.data.code === 1000) { that.title = arg.data.title } }) } } }</script> |
访问http://localhost:8080/micro,效果如下所示:
六、vue接口归总
1、在vuex中设置apiList字段归总所有rest接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'import Cookie from 'vue-cookies' // 引入cookie,npm install vue-cookies --saveVue.use(Vuex);export default new Vuex.Store({ // 组件中通过 this.$store.state.username 调用 state: { // 默认去cookie中取值 username: Cookie.get("username"), token: Cookie.get("token"), apiList: { // 所有的接口 course: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/course/', courseDetail: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/course/', auth: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/auth/', micro: "http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/micro/", } }, mutations: { /* 代码省略*/ }}) |
2、替换各个模块中的url地址
均按照如下方法替换:
|
1
2
3
4
|
url: this.store.state.apiList.micro,url: this.store.state.apiList.course,url: this.store.state.apiList.course + nid + '/',url: this.store.state.apiList.auth, |


