Go识别IPv6的服务
IPv6 Socket连接

package main import ( "time" "fmt" "net" "regexp" "strconv" "encoding/hex" ) func main() { addr := "[fe80::3de0:b557:a1f:d123%18]:80" timeout := 1 taskSocket(addr,timeout) } // socket发送探测数据包编码 func DecodeData(s string) ([]byte, error) { sByteOrigin := []byte(s) matchRe := regexp.MustCompile(`\\(x[0-9a-fA-F]{2}|[0-7]{1,3}|[aftnrv])`) sByteDec := matchRe.ReplaceAllFunc(sByteOrigin, func(match []byte) (v []byte) { var replace []byte if isHexCode(match) { hexNum := match[2:] byteNum, _ := strconv.ParseInt(string(hexNum), 16, 32) replace = []byte{uint8(byteNum)} } if isStructCode(match) { structCodeMap := map[int][]byte{ 97: []byte{0x07}, // \a 102: []byte{0x0c}, // \f 116: []byte{0x09}, // \t 110: []byte{0x0a}, // \n 114: []byte{0x0d}, // \r 118: []byte{0x0b}, // \v } replace = structCodeMap[int(match[1])] } if isOctalCode(match) { octalNum := match[2:] byteNum, _ := strconv.ParseInt(string(octalNum), 8, 32) replace = []byte{uint8(byteNum)} } return replace }) matchRe2 := regexp.MustCompile(`\\([^\\])`) sByteDec2 := matchRe2.ReplaceAllFunc(sByteDec, func(match []byte) (v []byte) { var replace []byte if isOtherEscapeCode(match) { replace = match } else { replace = match } return replace }) return sByteDec2, nil } func isHexCode(b []byte) bool { matchRe := regexp.MustCompile(`\\x[0-9a-fA-F]{2}`) return matchRe.Match(b) } func isOctalCode(b []byte) bool { matchRe := regexp.MustCompile(`\\[0-7]{1,3}`) return matchRe.Match(b) } func isStructCode(b []byte) bool { matchRe := regexp.MustCompile(`\\[aftnrv]`) return matchRe.Match(b) } func isOtherEscapeCode(b []byte) bool { matchRe := regexp.MustCompile(`\\[^\\]`) return matchRe.Match(b) } func taskSocket(addr string,SocketTimeout int) { //1.连接端口 connTimeout := time.Duration(int64(SocketTimeout))*time.Second // 设置socket连接超时时间 //conn, errConn := net.DialTimeout("tcp", "[fe80::3de0:b557:a1f:d123%18]:80", connTimeout) /* tcp后面可以是IPv4的地址 也可以是IPv6的地址 ipv6的地址需要用中括号括起来[fe80::3de0:b557:a1f:d123%18] tcp4 只能传入ipv4地址 tcp6 只能传入ipv6地址 */ conn, errConn := net.DialTimeout("tcp6", addr, connTimeout) defer func(){ if conn != nil{ conn.Close() } }() if errConn != nil { // 连接端口失败 fmt.Println(errConn) } else { fmt.Println("Socket连接端口成功") } //2.端口发送指纹数据 conn.SetWriteDeadline(time.Now().Add(time.Second*time.Duration(int64(SocketTimeout)))) hexNum :="474554202f20485454502f312e310d0a0d0a" data1, _ :=hex.DecodeString(hexNum) //数组形式 datastr := string(data1) //这里是乱码,导致响应的结果也是乱码 fmt.Println(datastr) data_byte, err := DecodeData(datastr) if err != nil { fmt.Println(err) } _, errWrite := conn.Write(data_byte) if errWrite != nil { fmt.Println(errWrite) } else { fmt.Println("端口发送指纹数据成功") } //3.接收端口响应指纹数据 var response []byte // 保存响应的结果 conn.SetReadDeadline(time.Now().Add(time.Second*time.Duration(int64(SocketTimeout)))) for true { buff := make([]byte, 4096) n, errRead := conn.Read(buff) if errRead != nil { if len(response) > 0 { break } else { fmt.Println(errRead) } } if n > 0 { response = append(response, buff[:n]...) } } fmt.Println(response) //数组形式 fmt.Println(string(response)) }

Socket连接超时问题
外网地址连接socket的时间比内网地址连接socket的时间要长,所以按照内网的标准连接外网就会导致socket连接超时,socket超时就会导致端口指纹识别失败
内网设置的超时时间可以是毫秒级time.Duration(timeout)*time.Millisecond,但是外网地址必须以秒级为超时时间单位time.Duration(timeout)*time.Second

/* 端口探活方式1 此方式资源消耗较高 */ func (N *NmapProbe)ConnectPort(host string, port string, timeout int) bool{ //addr2 := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", host, port) //这里一定要注意port是int类型还是string类型 //如果是string类型就只能用%s,如果是数字就只能用%d if (IsIPv6 == false) { addr := host+":"+port // _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Millisecond) //Millisecond时间周期探测内网地址可以,但是探测外网地址超时 //超时时间必须设置为Second _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Second) if err != nil { //N.Writefile("端口关闭列表.txt",addr+"\r\n") return false } } else { addr := "["+host+"]:"+port //connTimeout := time.Duration(2*time.Second) //connTimeout2 := time.Duration(2*time.Millisecond) //ipv6的连接时间比ipv4花的时间要长,所有socket的超时时间不能和ipv4一样 _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp6", addr, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Second) //conn, errConn := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, connTimeout) //fmt.Println(err) if err != nil { //N.Writefile("端口关闭列表.txt",addr+"\r\n") return false } } return true } //先进行端口探活 /* 在探针探测之前先判断端口是否存活,如果端口不能连接 则不要继续执行后面的代码提高探测效率 尽量探测存活的端口,不存活的端口就不需要再去进行探测 */ cres := N.ConnectPort(host,port,STimeout) //先判断端口是否存活 if cres == false { fmt.Println("远程Socket连接失败",host,port) return false } //只做端口探活,不进行服务指纹检查 if NocheckSrv { //执行到这里可以确定端口一定是活的 tasktmp := Task{} tasktmp.Addr = GetAddress(host, port) resultChan <- &tasktmp return true }
Ping IPV6地址

package ping6 import ( "bytes" "errors" "net" "os" "time" "fmt" ) const ( icmpv4EchoRequest = 8 icmpv4EchoReply = 0 icmpv6EchoRequest = 128 icmpv6EchoReply = 129 ) type icmpMessage struct { Type int // type Code int // code Checksum int // checksum Body icmpMessageBody // body } type icmpMessageBody interface { Len() int Marshal() ([]byte, error) } // Marshal returns the binary enconding of the ICMP echo request or // reply message m. func (m *icmpMessage) Marshal() ([]byte, error) { b := []byte{byte(m.Type), byte(m.Code), 0, 0} if m.Body != nil && m.Body.Len() != 0 { mb, err := m.Body.Marshal() if err != nil { return nil, err } b = append(b, mb...) } switch m.Type { case icmpv6EchoRequest, icmpv6EchoReply: return b, nil } csumcv := len(b) - 1 // checksum coverage s := uint32(0) for i := 0; i < csumcv; i += 2 { s += uint32(b[i+1])<<8 | uint32(b[i]) } if csumcv&1 == 0 { s += uint32(b[csumcv]) } s = s>>16 + s&0xffff s = s + s>>16 // Place checksum back in header; using ^= avoids the // assumption the checksum bytes are zero. b[2] ^= byte(^s & 0xff) b[3] ^= byte(^s >> 8) return b, nil } // parseICMPMessage parses b as an ICMP message. func parseICMPMessage(b []byte) (*icmpMessage, error) { msglen := len(b) if msglen < 4 { return nil, errors.New("message too short") } m := &icmpMessage{Type: int(b[0]), Code: int(b[1]), Checksum: int(b[2])<<8 | int(b[3])} if msglen > 4 { var err error switch m.Type { case icmpv4EchoRequest, icmpv4EchoReply, icmpv6EchoRequest, icmpv6EchoReply: m.Body, err = parseICMPEcho(b[4:]) if err != nil { return nil, err } } } return m, nil } // imcpEcho represenets an ICMP echo request or reply message body. type icmpEcho struct { ID int // identifier Seq int // sequence number Data []byte // data } func (p *icmpEcho) Len() int { if p == nil { return 0 } return 4 + len(p.Data) } // Marshal returns the binary enconding of the ICMP echo request or // reply message body p. func (p *icmpEcho) Marshal() ([]byte, error) { b := make([]byte, 4+len(p.Data)) b[0], b[1] = byte(p.ID>>8), byte(p.ID&0xff) b[2], b[3] = byte(p.Seq>>8), byte(p.Seq&0xff) copy(b[4:], p.Data) return b, nil } // parseICMPEcho parses b as an ICMP echo request or reply message body. func parseICMPEcho(b []byte) (*icmpEcho, error) { bodylen := len(b) p := &icmpEcho{ID: int(b[0])<<8 | int(b[1]), Seq: int(b[2])<<8 | int(b[3])} if bodylen > 4 { p.Data = make([]byte, bodylen-4) copy(p.Data, b[4:]) } return p, nil } func Ping(address string, timeout int) (alive bool,err error,timedelay int64) { t1:=time.Now().UnixNano() err = Pinger(address, timeout) t2:=time.Now().UnixNano() alive = err == nil return alive,err,t2-t1 } func Pinger(address string, timeout int) (err error) { //c, err := net.Dial("ip4:icmp", address) c, err := net.Dial("ip6:ipv6-icmp", address) if err != nil { fmt.Println("error ",err) return } c.SetDeadline(time.Now().Add(time.Duration(timeout) * time.Millisecond)) //时延ms单位 defer c.Close() //typ := icmpv4EchoRequest typ := icmpv6EchoRequest xid, xseq := os.Getpid()&0xffff, 1 wb, err := (&icmpMessage{ Type: typ, Code: 0, Body: &icmpEcho{ ID: xid, Seq: xseq, Data: bytes.Repeat([]byte("Go Go Gadget Ping!!!"), 3), }, }).Marshal() if err != nil { return } if _, err = c.Write(wb); err != nil { return } var m *icmpMessage rb := make([]byte, 20+len(wb)) for { if _, err = c.Read(rb); err != nil { return } //if net == "ip4" { //only for ipv4 // rb = ipv4Payload(rb) //} if m, err = parseICMPMessage(rb); err != nil { return } switch m.Type { case icmpv4EchoRequest, icmpv6EchoRequest: //fmt.Println("type ",m.Type) continue } break } return } func ipv4Payload(b []byte) []byte { if len(b) < 20 { return b } hdrlen := int(b[0]&0x0f) << 2 fmt.Println("hdrlen ",hdrlen) //ipv4的时候为20 return b[hdrlen:] }

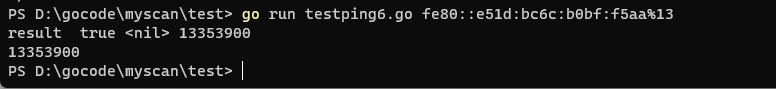
package main import ( "ping6" "fmt" "time" "os" ) func main() { //1.输入参数处理.这里使用os而非flag var host string if len(os.Args) != 2 { //fmt.Println("Usage: ", os.Args[0], "host") host="::1" //os.Exit(1) }else{ host = os.Args[1] //目标域名 } t1:=time.Now().UnixNano() alive,err,timedelay:=ping6.Ping(host,1000) fmt.Println("result ",alive,err,timedelay) t2:=time.Now().UnixNano() fmt.Println(t2-t1); }
net.Dial用法
函数调用方法很简单,源码注释中直接有例子
Dial("tcp", "golang.org:http")
Dial("tcp", "192.0.2.1:http")
Dial("tcp", "198.51.100.1:80")
Dial("udp", "[2001:db8::1]:domain")
Dial("udp", "[fe80::1%lo0]:53")
Dial("tcp", ":80")
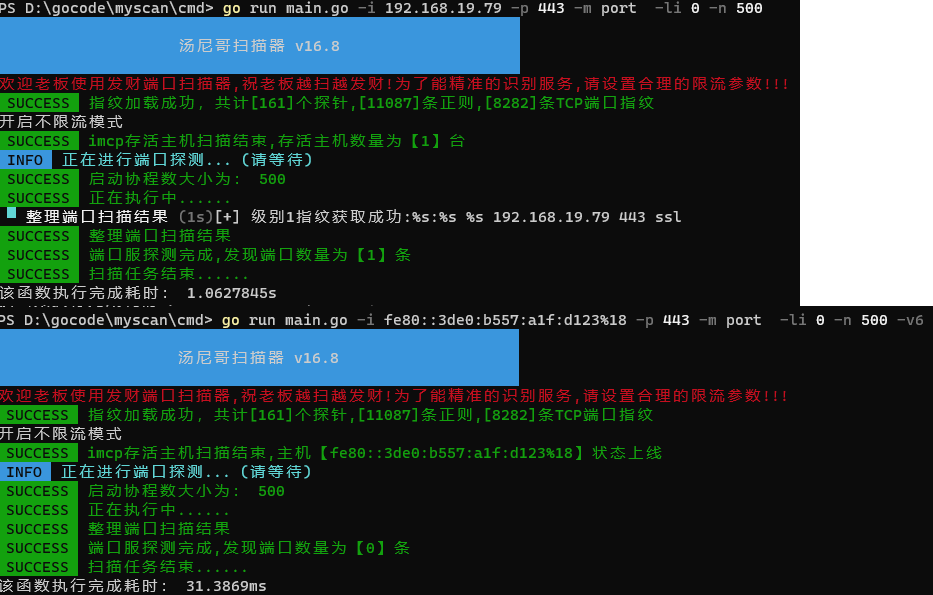
IPv6端口探活超时

func (N *NmapProbe)ConnectPort(host string, port string, timeout int) bool{ //addr2 := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", host, port) //这里一定要注意port是int类型还是string类型 //如果是string类型就只能用%s,如果是数字就只能用%d if (IsIPv6 == false) { addr := host+":"+port _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Millisecond) if err != nil { //N.Writefile("端口关闭列表.txt",addr+"\r\n") return false } } else { addr := "["+host+"]:"+port //connTimeout := time.Duration(2*time.Second) //connTimeout2 := time.Duration(2*time.Millisecond) //ipv6的连接时间比ipv4花的时间要长,所有socket的超时时间不能和ipv4一样 _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp6", addr, 5*time.Second) //conn, errConn := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, connTimeout) //fmt.Println(err) if err != nil { //N.Writefile("端口关闭列表.txt",addr+"\r\n") return false } } return true }
IPv6指纹识别失效
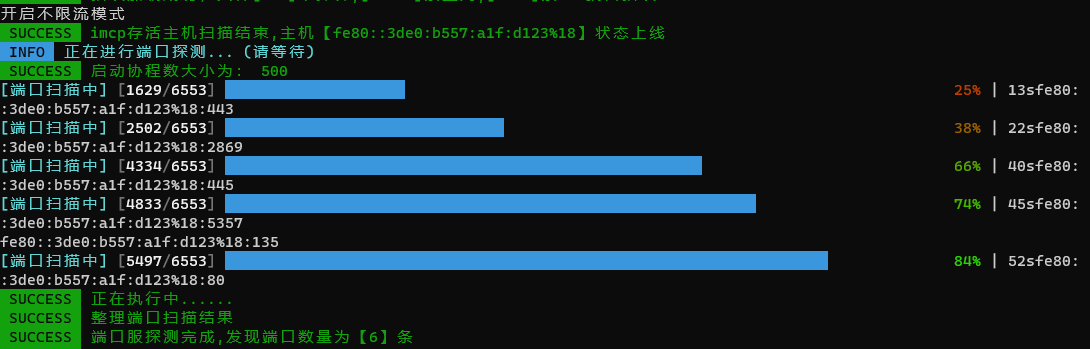
能ping通ipv6主机,能探活ipv6端口,但是不能识别ipv6端口上的服务
修改请求地址格式

func GetAddress(ip, port string)string{ if (IsIPv6 == false) { return ip + ":" + port } else { return "["+ip+"]:"+port } } if len(defaultProbe) > 0 { //如果在nmap.txt的Probe组中定义的ports中包含当前port则优先发送probe对应的data wg := sync.WaitGroup{} chanTask := make(chan *Task, len(defaultProbe)) for _,i := range defaultProbe{ wg.Add(1) go func(v int){ defer wg.Done() N.taskSocket(GetAddress(host, port), v, SocketTimeout, chanTask) }(i) } wg.Wait() close(chanTask) } } func (N *NmapProbe)taskSocket(address string, Indexes, SocketTimeout int, taskChan chan *Task){ responeData,err := N.grabResponse(address, Indexes, SocketTimeout) /* grabResponse if len(N.Probes[Indexes].Data) > 0 { _, errWrite := conn.Write(N.Probes[Indexes].Data) } */ if err != nil { //发送指纹失败 //N.Writefile("发送失败.txt",address+"\r\n") return } ok,extras := N.regxRespone(responeData, N.Probes[Indexes].Matchs, N.Probes[Indexes].Fallback) if !ok{ //指纹识别失败 //N.Writefile("识别失败.txt",address+"\r\n") return } //发送和接收异常的情况都会被提取return //只有发送指纹成功和接收端口数据成功的探测才会被丢入到taskChan中 //所以最后只需要遍历taskChan即可获取探测结果 /* 前面的探测都是失败后直接return 打印最终探测成功的probe 如果被打印出来说明肯定是成功的 */ taskChan <- &Task{ Addr: address, ServiceNmae: extras.ServiceNmae, ProbeName: N.Probes[Indexes].Name, VendorProduct: extras.VendorProduct, Version: extras.Version, } }
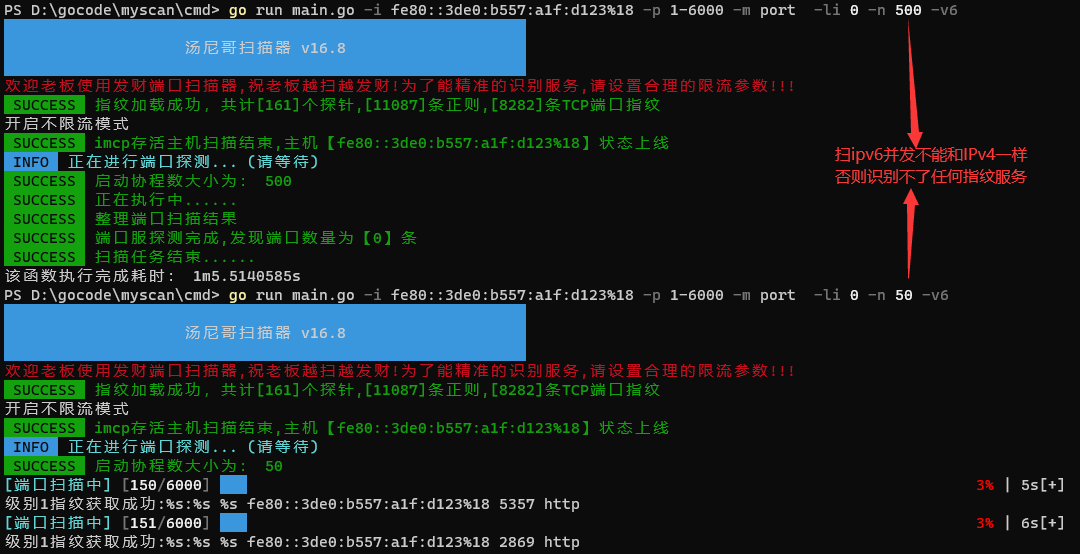
1.ipv6的并发不能和ipv4一样大
2.ipv6的socket超时时间不能和ipv4一样短
3.ipv6的ip格式和ipv4的ip格式不一样
内外网连接超时设置
内网连接在毫秒级别超时
外网连接在秒级别超时
1.设置选项参数

flag.BoolVar(&outnet, "on", false, "outer net scanner") flag.Float64Var(&tout, "t", 0.5, "scan port tcp connect time out default 0.5/50 second/millisecond") mynmap.STimeout = e.Options.Tout mynmap.IsIPv6 = e.Options.IP6 mynmap.IsDebug =e.Options.Debug mynmap.IsOutnet = e.Options.Outnet fmt.Println("是否开启调试模式:",mynmap.IsDebug) if mynmap.IsOutnet { fmt.Println("扫描的是外网地址,超时时间单位为:"+strconv.FormatFloat(mynmap.STimeout,'f', -1, 32)+" second") } else { if e.Options.Tout < 2 { e.Options.Tout = 2 //内网扫描超时时间最短为2毫秒 mynmap.STimeout = e.Options.Tout } fmt.Println("扫描的是内网地址,超时时间单位为:"+strconv.FormatFloat(mynmap.STimeout,'f', -1, 32)+" millisecond") }
2.计算连接时间

func (N *NmapProbe)ConnectPort(host string, port string, timeout float64) bool{ //addr2 := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", host, port) //这里一定要注意port是int类型还是string类型 //如果是string类型就只能用%s,如果是数字就只能用%d if (IsIPv6 == false) { addr := host+":"+port // _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, time.Duration(timeout)*time.Millisecond) //Millisecond时间周期探测内网地址可以,但是探测外网地址超时 //超时时间必须设置为Second _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, CalTimeOut(timeout)) if err != nil { if IsDebug { fmt.Println(err) } return false } } else { addr := "["+host+"]:"+port //connTimeout := time.Duration(2*time.Second) //connTimeout2 := time.Duration(2*time.Millisecond) //ipv6的连接时间比ipv4花的时间要长,所有socket的超时时间不能和ipv4一样 _, err := net.DialTimeout("tcp6", addr, CalTimeOut(timeout)) //conn, errConn := net.DialTimeout("tcp", addr, connTimeout) //fmt.Println(err) if err != nil { //N.Writefile("端口关闭列表.txt",addr+"\r\n") if IsDebug { fmt.Println(err) } return false } } return true } //返回socket连接的超时时间 func CalTimeOut(stime float64) time.Duration{ if IsOutnet { return time.Duration(2*time.Second) } else { return time.Duration(2*time.Millisecond) } }
3.这样可以使在扫内外网的时候分别设置最合适的参数
本文来自博客园,作者:不懂123,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yxh168/p/16848984.html



