6、什么是跨域?跨域解决方案?
2021-08-03 20:30 石吴玉 阅读(206) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38128179/article/details/84956552
一、为什么会出现跨域问题
出于浏览器的同源策略限制。同源策略(Sameoriginpolicy)是一种约定,它是浏览器最核心也最基本的安全功能,如果缺少了同源策略,则浏览器的正常功能可能都会受到影响。可以说Web是构建在同源策略基础之上的,浏览器只是针对同源策略的一种实现。同源策略会阻止一个域的javascript脚本和另外一个域的内容进行交互。所谓同源(即指在同一个域)就是两个页面具有相同的协议(protocol),主机(host)和端口号(port)。
二、什么是跨域
当一个请求url的协议、域名、端口三者之间任意一个与当前页面url不同即为跨域
| 当前页面url | 被请求页面url | 是否跨域 | 原因 |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.test.com/index.html | 否 | 同源(协议、域名、端口号相同) |
| http://www.test.com/ | https://www.test.com/index.html | 跨域 | 协议不同(http/https) |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.baidu.com/ | 跨域 | 主域名不同(test/baidu) |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://blog.test.com/ | 跨域 | 子域名不同(www/blog) |
| http://www.test.com:8080/ | http://www.test.com:7001/ | 跨域 | 端口号不同(8080/7001) |
三、非同源限制
(1)无法读取非同源网页的 Cookie、LocalStorage 和 IndexedDB
(2)无法接触非同源网页的 DOM
(3)无法向非同源地址发送 AJAX 请求
四、服务端的跨域解决方案
1、JSONP
JSONP 是服务器与客户端跨源通信的常用方法。最大的特点是简单适用,兼容性好(兼容低版本IE),缺点是只支持 Get 请求,不支持 Post 请求。
核心思想:网页通过添加一个 <script> 元素,向服务器请求JSON数据、服务器接收到请求后,将数据放在一个指定名字的回调函数的参数位置传回来。
前端代码

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>JSONP</title>
<script src="https://css.ssl.q1.com/jquery/jquery-1.11.1.min.js?v=2018051103"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="btn">请求接口</div>
<script>
$('#btn').click(() => {
$.ajax({
async: true,
url: "http://xxxxxx.dev.q1op.com/home/test",
type: "GET",
dataType: "jsonp", // 返回的数据类型,设置为JSONP方式
jsonp: 'callback', //指定一个查询参数名称来覆盖默认的 jsonp 回调参数名 callback
jsonpCallback: 'handleResponse', //设置回调函数名
data: {
q: "javascript",
count: 1
},
success: function (response, status, xhr) {
console.log('状态为:' + status + ',状态是:' + xhr.statusText);
console.log(response);
}
});
});
function handleResponse()
{
console.log('回调');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
后端代码:

namespace CorsTest.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class HomeController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("test")]
public IActionResult Test(string callback)
{
return Content($"{callback}(ok)");
}
}
}
执行结果:

2、CORS
CORS是跨域资源分享(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)的缩写,他是W3C标准,属于跨源AJAX请求的根本解决方法。
(1) 普通跨域请求:只需服务器端设置 Access-Control-Allow-Origin
(2)带cookie跨域请求,前后端都需要进行设置。
一个错误的案例
在服务端代码中 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) 定义跨域解决方案
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CorsAllowAll", (builder) =>
{
builder.AllowAnyOrigin() // 允许任意来源的主机访问
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowCredentials();//处理 Cookie
});
});
在 public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) 中 use上述方案(注 "CorsAllowAll" 可以定义为任何值,但需要上下一致)
app.UseCors("CorsAllowAll");
上述方案启动服务时会报错:
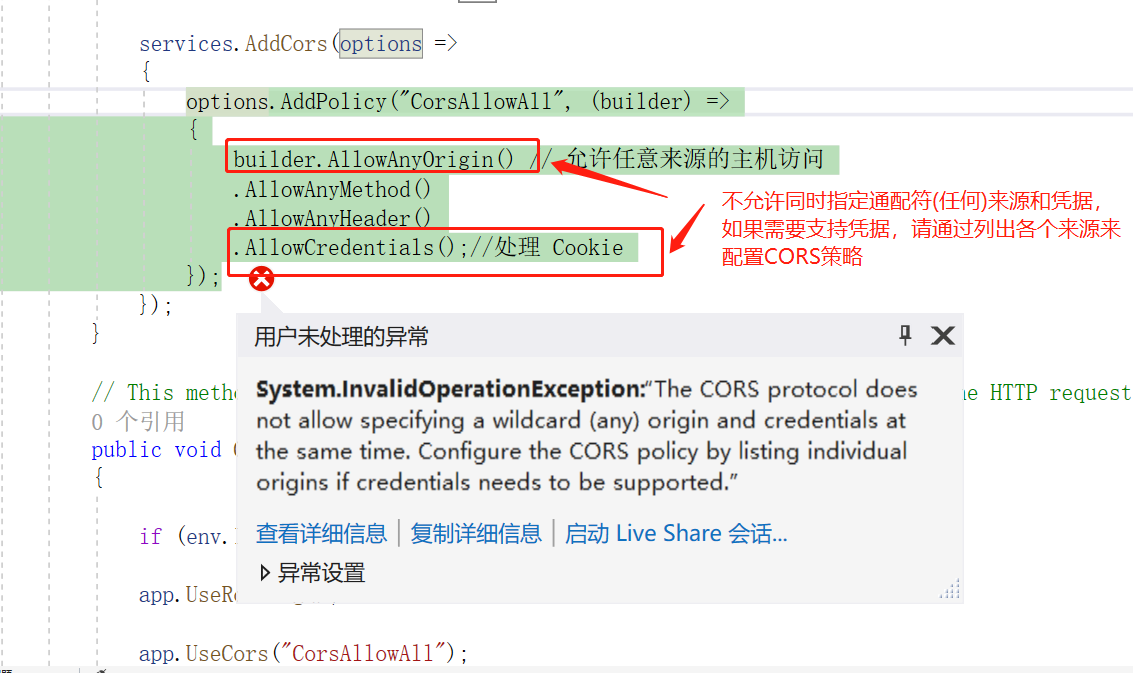
解决方案:
根据请求是否需要携带Cookie来修改跨域方案配置。
(1)请求设置不携带 Cookie
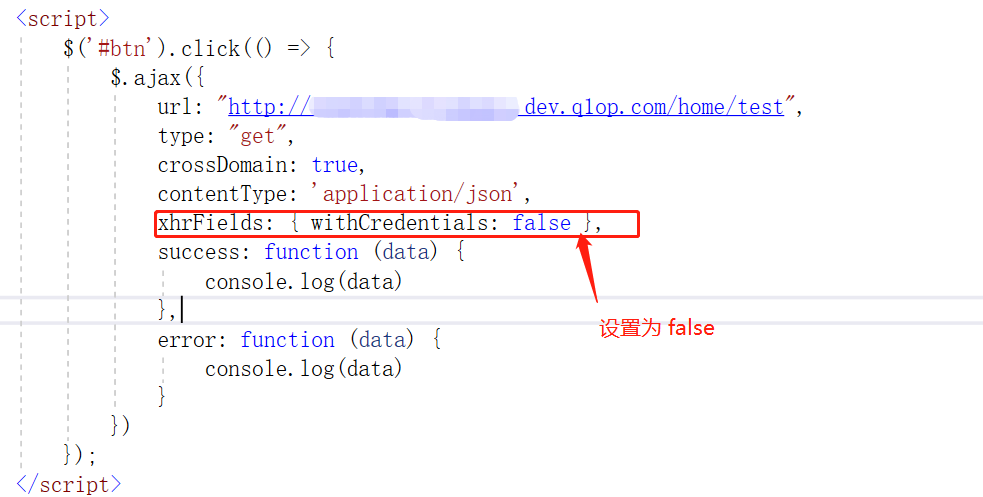
此时,服务端无需设置 AllowCredentials()
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CorsAllowAll", (builder) =>
{
builder.AllowAnyOrigin() // 允许任意来源的主机访问
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader();
//.AllowCredentials();//处理 Cookie (当前端的 xhrFields: { withCredentials: false } 参数设置为false时,无需处理 Cookie)
});
});
(2)请求设置携带 Cookie
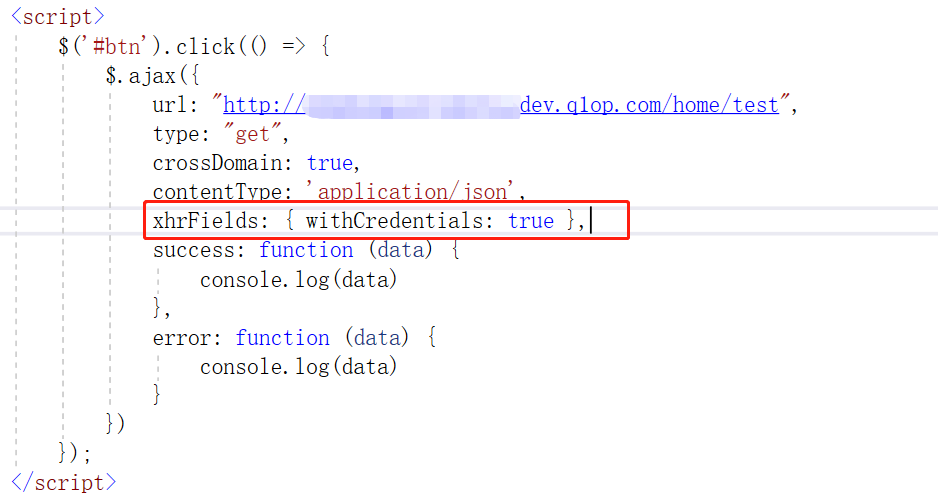
此时,服务端需要 配置 AllowAnyOrigin()
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CorsAllowAll", (builder) =>
{
//这段解决 AllowAnyOrigin() 不能跟 AllowCredentials() 共用的问题
builder = builder.SetIsOriginAllowed((host) => true);
builder.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowCredentials();//处理 Cookie (当前端的 xhrFields: { withCredentials: false } 参数设置为false时,无需处理 Cookie)
});
});
此案例前端完整代码:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>CORS</title>
<script src="https://css.ssl.q1.com/jquery/jquery-1.11.1.min.js?v=2018051103"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="btn">请求接口</div>
<script>
$('#btn').click(() => {
$.ajax({
url: "http://xxxxxxx.dev.q1op.com/home/test",
type: "get",
crossDomain: true,
contentType: 'application/json',
xhrFields: { withCredentials: true },
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
},
error: function (data) {
console.log(data)
}
})
});
</script>
</body>
</html>




