深度学习之强化学习Q-Learning
1、知识点
""" 1、强化学习:学习系统没有像很多其他形式的机器学习方法一样被告知应该做什么行为, 必须在尝试之后才能发现哪些行为会导致奖励的最大化,当前的行为可能不仅仅会影响即时奖励, 还会影响下一步奖励以及后续的所有奖励 2、机制:奖励和惩罚机制 3、名词:智能体,即操控的目标 状态:所处的环境 行为:执行动作 奖励:达到所需的目标,给与奖励 策略:Q-learning,bellman 4、过程:观察-->行动-->观察-->行动-->观察(不断循环) 5、马尔可夫决策要求: 1、能够检测到理想的状态 2、可以多次尝试 3、系统的下个状态只与当前状态信息有关,而与更早之前的状态无关,在决策过程中还和当前采取的动作有关 6、马尔科夫决策过程由5个元素构成: S:表示状态集(states) A:表示一组动作(actions) P:表示状态转移概率 𝑃𝑠𝑎表示在当前s ∈ S状态下,经过a ∈ A作用后,会转移到的其他状态的概率分布情况 在状态s下执行动作a,转移到s’的概率可以表示为p(s’|s,a) R: 奖励函数(reward function)表示 agent 采取某个动作后的即时奖励 y:折扣系数意味着当下的 reward 比未来反馈的 reward 更重要 7、Bellman方程: 当前状态的价值和下一步的价值及当前的奖励(Reward)有关 价值函数分解为当前的奖励和下一步的价值两部分 Q-learning: """
2、Bellman优化目标
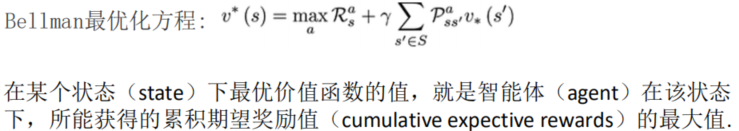
3、bellman案例,gridworld.py和ValueIteration.py

import numpy as np import sys from gym.envs.toy_text import discrete UP = 0 RIGHT = 1 DOWN = 2 LEFT = 3 class GridworldEnv(discrete.DiscreteEnv): """ Grid World environment from Sutton's Reinforcement Learning book chapter 4. You are an agent on an MxN grid and your goal is to reach the terminal state at the top left or the bottom right corner. For example, a 4x4 grid looks as follows: T o o o o x o o o o o o o o o T x is your position and T are the two terminal states. You can take actions in each direction (UP=0, RIGHT=1, DOWN=2, LEFT=3). Actions going off the edge leave you in your current state. You receive a reward of -1 at each step until you reach a terminal state. """ metadata = {'render.modes': ['human', 'ansi']} def __init__(self, shape=[4,4]): if not isinstance(shape, (list, tuple)) or not len(shape) == 2: raise ValueError('shape argument must be a list/tuple of length 2') self.shape = shape nS = np.prod(shape) nA = 4 MAX_Y = shape[0] MAX_X = shape[1] P = {} grid = np.arange(nS).reshape(shape) it = np.nditer(grid, flags=['multi_index']) while not it.finished: s = it.iterindex y, x = it.multi_index P[s] = {a : [] for a in range(nA)} is_done = lambda s: s == 0 or s == (nS - 1) reward = 0.0 if is_done(s) else -1.0 # We're stuck in a terminal state if is_done(s): P[s][UP] = [(1.0, s, reward, True)] P[s][RIGHT] = [(1.0, s, reward, True)] P[s][DOWN] = [(1.0, s, reward, True)] P[s][LEFT] = [(1.0, s, reward, True)] # Not a terminal state else: ns_up = s if y == 0 else s - MAX_X ns_right = s if x == (MAX_X - 1) else s + 1 ns_down = s if y == (MAX_Y - 1) else s + MAX_X ns_left = s if x == 0 else s - 1 P[s][UP] = [(1.0, ns_up, reward, is_done(ns_up))] P[s][RIGHT] = [(1.0, ns_right, reward, is_done(ns_right))] P[s][DOWN] = [(1.0, ns_down, reward, is_done(ns_down))] P[s][LEFT] = [(1.0, ns_left, reward, is_done(ns_left))] it.iternext() # Initial state distribution is uniform isd = np.ones(nS) / nS # We expose the model of the environment for educational purposes # This should not be used in any model-free learning algorithm self.P = P super(GridworldEnv, self).__init__(nS, nA, P, isd) def _render(self, mode='human', close=False): if close: return outfile = StringIO() if mode == 'ansi' else sys.stdout grid = np.arange(self.nS).reshape(self.shape) it = np.nditer(grid, flags=['multi_index']) while not it.finished: s = it.iterindex y, x = it.multi_index if self.s == s: output = " x " elif s == 0 or s == self.nS - 1: output = " T " else: output = " o " if x == 0: output = output.lstrip() if x == self.shape[1] - 1: output = output.rstrip() outfile.write(output) if x == self.shape[1] - 1: outfile.write("\n") it.iternext()

import numpy as np from gridworld import GridworldEnv env = GridworldEnv() def value_iteration(env, theta=0.0001, discount_factor=1.0): """ Value Iteration Algorithm. Args: env: OpenAI environment. env.P represents the transition probabilities of the environment. theta: Stopping threshold. If the value of all states changes less than theta in one iteration we are done. discount_factor: lambda time discount factor. Returns: A tuple (policy, V) of the optimal policy and the optimal value function. """ def one_step_lookahead(state, V): """ Helper function to calculate the value for all action in a given state. Args: state: The state to consider (int) V: The value to use as an estimator, Vector of length env.nS Returns: A vector of length env.nA containing the expected value of each action. """ A = np.zeros(env.nA) for a in range(env.nA): for prob, next_state, reward, done in env.P[state][a]: A[a] += prob * (reward + discount_factor * V[next_state]) return A V = np.zeros(env.nS) while True: # Stopping condition delta = 0 # Update each state... for s in range(env.nS): # Do a one-step lookahead to find the best action A = one_step_lookahead(s, V) best_action_value = np.max(A) # Calculate delta across all states seen so far delta = max(delta, np.abs(best_action_value - V[s])) # Update the value function V[s] = best_action_value # Check if we can stop if delta < theta: break # Create a deterministic policy using the optimal value function policy = np.zeros([env.nS, env.nA]) for s in range(env.nS): # One step lookahead to find the best action for this state A = one_step_lookahead(s, V) best_action = np.argmax(A) # Always take the best action policy[s, best_action] = 1.0 return policy, V policy, v = value_iteration(env) print("Policy Probability Distribution:") print(policy) print("") print("Reshaped Grid Policy (0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left):") print(np.reshape(np.argmax(policy, axis=1), env.shape)) print("")
4、认识Q-Learning
a) 算法步骤

b) reward矩阵

5、Q-learning案例看文件
本文来自博客园,作者:小白啊小白,Fighting,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ywjfx/p/11045027.html




