一些搜索总结
双向BFS
我们在BFS时,要从起点,搜遍整颗搜索树,然后找到终点,整个过程大概是一个如下的结构
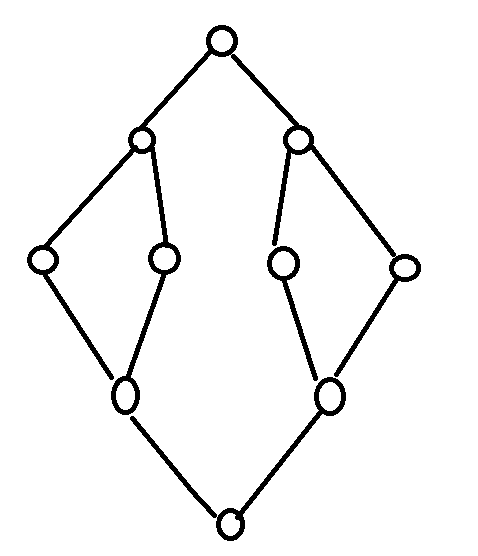
我比较懒,所以图非常简陋。
最上面的节点表示起点,最下面的点表示终点。
我们正常的BFS是从起点一路向下搜到终点,这样要扩展不少的状态,耗费不少的时间。
这样我们想我们其实可以从起点和终点同时开始搜,起点和终点同时向外扩展一步,当两个搜索路径交会时,结束搜索。
这样我们可以省去一半的时间。
我们用两个队列分别表示起点的扩展和终点的扩展
例题:
常见的迷宫问题,0表示有障碍,1表示无障碍,假设没有无法走到的情况,求最少需要多少步
非常显然的BFS

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn = 3030; 4 struct node { 5 int x, y; 6 }q1[maxn], q2[maxn]; 7 //int stx, sty, edx, edy; 8 int a[maxn][maxn]; 9 int n, m; 10 int tail1 = 0, head1 = 1, tail2 = 0, head2 = 1; 11 //int dx[9] = {-1, -1, 1, 1, -2, -2, 2, 2}; 12 //int dy[9] = {2, -2, 2, -2, -1, 1, -1, 1}; 13 //int vis[maxn][maxn]; 14 int dx[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[5] = {0, -1, 0, 1}; 15 int st[maxn][maxn], ed[maxn][maxn]; 16 int stept[maxn][maxn], stepe[maxn][maxn]; 17 bool flag = 0; 18 int ans = 0; 19 20 inline int read() { 21 int x = 0, y = 1; 22 char ch = getchar(); 23 while(!isdigit(ch)) { 24 if(ch == '-') y = -1; 25 ch = getchar(); 26 } 27 while(isdigit(ch)) { 28 x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0'; 29 ch = getchar(); 30 } 31 return x * y; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 memset(st, 0, sizeof(st)); 36 memset(ed, 0, sizeof(ed)); 37 memset(a, -1, sizeof(a)); 38 n = read(), m = read(); 39 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 40 for(int j = 1; j <= m;++j) 41 a[i][j] = read(); 42 q1[++tail1].x = 1, q1[tail1].y = 1; 43 q2[++tail2].x = n, q2[tail2].y = m; 44 for(head1 = 1, head2 = 1; head1 <= tail1 || head2 <= tail2; head1++, head2++) { 45 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { 46 int xx = q1[head1].x + dx[i]; 47 int yy = q1[head1].y + dy[i]; 48 if(a[xx][yy] == -1) continue; 49 if(!st[xx][yy] && a[xx][yy]) { 50 stept[xx][yy] = stept[q1[head1].x][q1[head1].y] + 1; 51 if(ed[xx][yy]) { 52 flag = 1; 53 ans = stept[xx][yy] + stepe[xx][yy]; 54 break; 55 } 56 st[xx][yy] = 1; 57 q1[++tail1].x = xx; 58 q1[tail1].y = yy; 59 } 60 } 61 if(flag == 1) break; 62 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { 63 int xx = q2[head2].x + dx[i]; 64 int yy = q2[head2].y + dy[i]; 65 if(a[xx][yy] == -1) continue; 66 if(!ed[xx][yy] && a[xx][yy]) { 67 stepe[xx][yy] = stepe[q2[head2].x][q2[head2].y] + 1; 68 if(st[xx][yy]) { 69 flag = 1; 70 ans = stepe[xx][yy] + stept[xx][yy]; 71 break; 72 } 73 ed[xx][yy] = 1; 74 q2[++tail2].x = xx; 75 q2[tail2].y = yy; 76 } 77 } 78 if(flag == 1) break; 79 } 80 cout << ans << '\n'; 81 return 0; 82 }
迭代加深搜索
在一些需要搜索的情况下,使用DFS会因为搜索树的深度太深,加上结果比较靠后,而导致耗费巨大的时间,而如果使用BFS,则会因为要存储大量状态而耗费大量的空间
这个时候我们可以使用迭代加深搜索。
简而言之就是我们人为规定一个搜索深度,每次到限定的搜索深度时停止。
比如说第一次我们规定搜索深度为1,我们搜索一层,结束
第二次我们规定搜索深度为2,我们搜索两层,结束
.......
这样我们会发现我们绝对会出现大量的重复计算,但是这对于我们直接进行DFS在搜索树上跑所需要的时间来说,是少得多的,这样这个算法就显得优秀了
例题1:
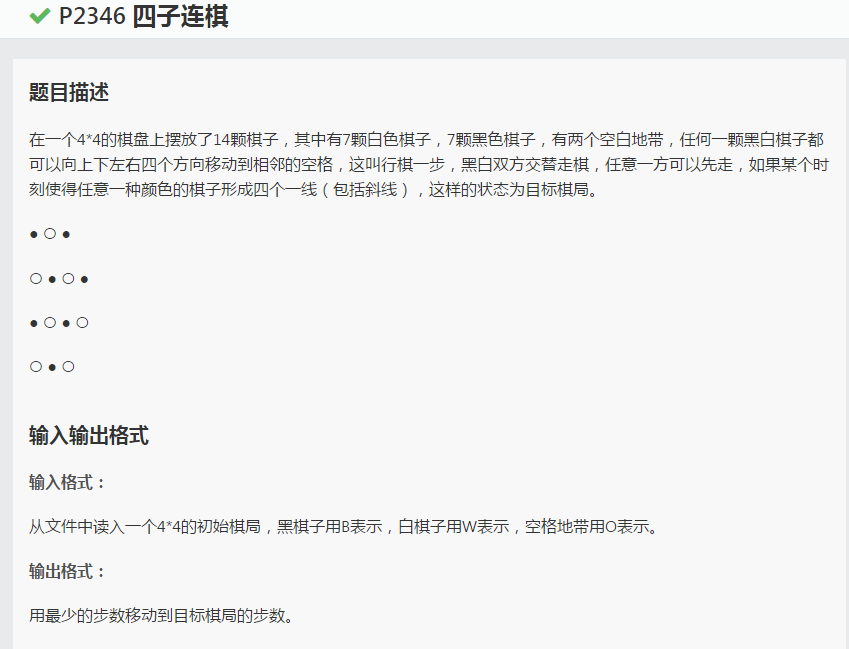
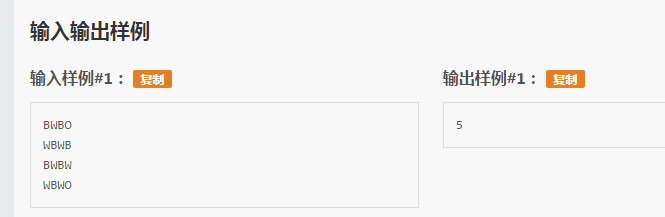
这题我们可以发现直接DFS我们似乎无法下手,我们可以脑洞一下,构造出一颗搜索树(当然我在口胡)
我们可以发现从第一个分叉向下扩展,可能会扩展的非常深都没有找到答案。用BFS我们固然可写,但是会耗费不小的空间。
这样我们就可以迭代加深搜索。
需要注意的是黑白棋是交替下的,而且题面并没有明确说是黑棋先下还是白棋先下
我们需要对黑先和白先分别进行计算

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn = 6; 4 const int deep = 1000000000; 5 int ox1, oy1, ox2, oy2;//分别记录两个空白地带的坐标 6 char ch[maxn]; 7 char a[maxn][maxn]; 8 bool flag = 0; 9 int dx[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; 10 int ans = 0; 11 12 inline bool check() { 13 for(int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i) { 14 if(a[1][i] == a[2][i] && a[1][i] == a[3][i] && a[1][i] == a[4][i]) return 1;//判断是否存在竖着的四子连棋 15 if(a[i][1] == a[i][2] && a[i][1] == a[i][3] && a[i][1] == a[i][4]) return 1;//判断是否存在横着的四子连棋 16 } 17 if(a[1][1] == a[2][2] && a[1][1] == a[3][3] && a[1][1] == a[4][4]) return 1;//判断是否存在由左上到右下角的四子连棋 18 if(a[1][4] == a[2][3] && a[1][4] == a[3][2] && a[1][4] == a[4][1]) return 1;//判断是否存在由右上到左下角的四子连棋 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 inline bool able(int x, int y, int dad) { 23 return x >= 1 && x <= 4 && y >= 1 && y <= 4 && a[x][y] != dad;} 24 25 bool deepdfs(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, char pre, int begin) { 26 if(begin == ans) { 27 if(check()) return 1; 28 else return 0; 29 } 30 for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { 31 int xx = x1 + dx[i]; 32 int yy = y1 + dy[i]; 33 if(able(xx, yy, pre)) { 34 swap(a[x1][y1], a[xx][yy]); 35 if(deepdfs(xx, yy, x2, y2, (pre == 'W' ? 'B' : 'W'), begin + 1)) return 1; 36 swap(a[x1][y1], a[xx][yy]); 37 } 38 xx = x2 + dx[i]; 39 yy = y2 + dy[i]; 40 if(able(xx, yy, pre)) { 41 swap(a[x2][y2], a[xx][yy]); 42 if(deepdfs(x1, y1, xx, yy, (pre == 'W' ? 'B' : 'W'), begin + 1)) return 1; 43 swap(a[x2][y2], a[xx][yy]); 44 } 45 } 46 return 0; 47 } 48 49 int main() { 50 //memset(a, -1, sizeof(a)); 51 for(int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i) { 52 cin >> ch + 1; 53 for(int j = 1; j <= 4; ++j) { 54 if(ch[j] == 'B') a[i][j] = 'B'; 55 else if(ch[j] == 'W') a[i][j] = 'W'; 56 if(ch[j] == 'O') { 57 a[i][j] = 'O'; 58 if(!flag) {ox1 = i, oy1 = j;flag = 1;} 59 else if(flag) ox2 = i, oy2 = j; 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 /*for(uint i = 1; i <= 4; ++i) { 64 for(uint j = 1; j <= 4; ++j) 65 cout << a[i][j] << ' '; 66 cout << '\n'; 67 }*/ 68 for(ans = 1; ans <= deep; ++ans) {//迭代加深搜索枚举搜索限定深度 69 if(deepdfs(ox1, oy1, ox2, oy2, 'B', 0)) 70 break; 71 if(deepdfs(ox1, oy1, ox2, oy2, 'W', 0)) 72 break; 73 } 74 cout << ans << '\n'; 75 return 0; 76 }



