Angular4学习笔记(五)- 数据绑定、响应式编程和管道
概念
Angular中的数据绑定指的是同一组件中控制器文件(.ts)与视图文件(.html)之间的数据传递。
分类
流向
单向绑定
它的意思是要么是ts文件为html文件赋值,要么相反。
ts->html
<div>
<img src="{{imgUrl}}">
<img [src]="imgUrl">
</div>
html->ts
<input (keyup)="press($event)">
小结:ts->html使用插值表达式{{value}}或[attr],html->ts使用(event)。ts->html较为常用。
双向绑定
ts文件与html文件中绑定的值同时改变。
下列代码表示当HTML文件输入框内容改变时,ts文件的属性name的值同时改变。
<input [(ngModel)]="name">
它的作用等于:
html
<input [value]="name" (input)="doOnInput($event)">
ts
doOnInput(event: any) {
this.name = event.target.value;
}
目标
Dom属性
首先看看Dom属性和HTML属性的关系:

<!--Dom属性绑定-->
<input value="Yan" (input)="doOnInput($event)">
HTML属性
上面已经提到,colspan没有对应的Dom属性,只能使用HTML属性绑定:
<!--html属性绑定-->
<table border="solid">
<tr>
<!-- 以下表达式会报错:colspan不是td的属性
<td [colspan]="colspanSize">hello</td>
-->
<td [attr.colspan]="colspanSize" align="center">hello</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>嘻嘻</td>
<td>哈哈</td>
</tr>
</table>
protected colspanSize: number = 2;
类绑定
<!--单一类的控制-->
<div class="a b" [class.c]="isBig">判定是否有c类:{{isBig}}</div>
<!--多个类的控制-->
<div [ngClass]="divClasses">是否有类a:{{divClasses.a}}、b:{{divClasses.b}}和c:{{divClasses.c}}</div>
<!--以下两种方式效果相同,均为divClass的值'fontRedClass'-->
<div [class]="divClass">红色字体</div>
<div class="{{divClass}}">红色字体</div>
protected divClass = 'fontRedClass';
protected divClasses: any = {
a: Math.random() < 0.5,
b: Math.random() < 0.5,
c: Math.random() < 0.5
};
.fontRedClass {
color:red;
}
.a {
background: yellowgreen;
}
.b {
font-family: 华文隶书;
}
.c {
font-size: 20px;
}
样式绑定
<!--单一样式绑定-->
<div [style.color]="isRed?'red':'green'">单一样式绑定</div>
<!--多个样式绑定-->
<div [ngStyle]="divStyles">多个样式绑定</div>
protected isRed = Math.random() < 0.5;
protected divStyles: any = {
color: 'red',
background: 'yellowgreen'
};
响应式编程
响应式编程主要是通过观察者模式实现,在Angular中的Rxjs即是它的具体实现,它们的关系如下:
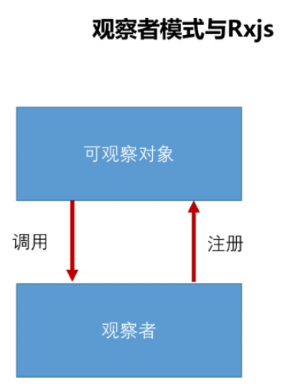
在Rxjs中,观察者模式的基本实现如下:

Observable类似于java中的Stream。
上图只是简单的数组流,实际上,万物皆可用流处理,比如页面上的按钮点击事件:
import {Observable} from 'rxjs/';
let button = document.querySelector('button');
Observable.fromEvent(button,'click');
使用formControl来监听输入的值,并用流的方式处理(打印):
<!--响应式编程-->
<input [formControl]="formControl">
注意:要使用[formControl]需要在app.module.ts中引入模块ReactiveFormsModule。
import {FormControl} from '@angular/forms';
protected formControl: FormControl = new FormControl();
constructor() {
this.formControl.valueChanges
.debounceTime(500).subscribe(bookname => this.print(bookname));
}
模板变量
模板变量是在html标签上使用#开头来定义的变量,它代表html元素本身。
<input (keyup)="onKeyUp($event)">
<input #iValue (keyup)="onKeyUp(iValue.value)">
onKeyUp(param: any) {
let iInput;
try {
iInput = param.target.value;
} catch (e) {
iInput = param;
}
console.log(iInput);
}
管道
管道是用来对输入的数据进行处理,如大小写转换、数值和日期格式化等。

基础知识不再赘述,请看推荐博客:
Demo:
- 生成组件
ng g component pipe - html
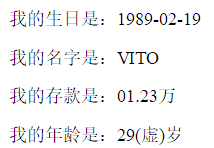
<p>我的生日是:{{birthday | date:'yyyy-MM-dd'}}</p>
<p>我的名字是:{{name | uppercase}}</p>
<p>我的存款是:{{deposit | number:'2.2-2'}}万</p>
- ts
protected birthday:Date = new Date(1989,1,19);
protected name:string = 'Vito';
protected deposit:number = 1.23456;
- 自定义管道
age:ng g pipe pipe/age
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'age'
})
export class AgePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, args?: any): any {
let year: number = new Date().getFullYear();
let res:string;
if (args)
{
res = (year- value.getFullYear()+ 1) +'(虚)';
} else {
res = year- value.getFullYear() +'';
}
return res;
}
}
- html中新增
<p>我的年龄是:{{birthday | age:true}}岁</p>
- 效果
Demo
God, Grant me the SERENITY, to accept the things I cannot change,
COURAGE to change the things I can, and the WISDOM to know the difference.
标签:
angular



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
2016-10-31 MyEclipse安装EGit插件方法