git 的 pull、fetch、merge
1.pull = fetch + merge
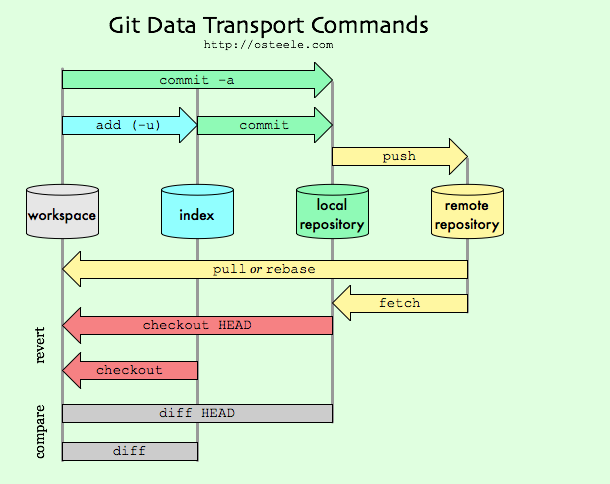
In the simplest terms, git pull does a git fetch followed by a git merge.
You can do a git fetch at any time to update your remote-tracking branches under refs/remotes/<remote>/. This operation never
changes any of your own local branches under refs/heads, and is safe to do without changing your working copy. I have even heard
of people running git fetch periodically in a cron job in the background (although I wouldn't recommend doing this).
A git pull is what you would do to bring a local branch up-to-date with its remote version, while also updating your other
remote-tracking branches.
2. merge VS rebase
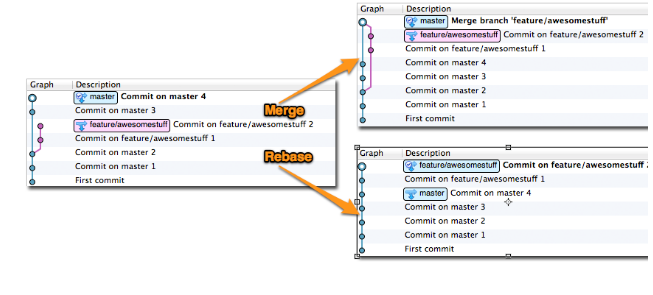
2.1、merge命令
把origin分支上的修改拉下来并且和你的修改合并;产生一个合并的提交(merge commit):
2.2、rebase命令
把你的分支里的每个提交(commit)取消掉,并且把它们临时保存为补丁(patch)(.git/rebase目录),然后把你的分支更新到最新的origin分支,
最后把保存的这些补丁应用到你的分支上。在rebase的过程中,也许会出现冲突(conflict),Git会停止rebase并会让你去解决 冲突;在解决完冲突后,
用"git-add"命令去更新这些内容的索引(index), 然后,你无需执行 git-commit,只要执行:
$ git rebase --continue
这样git会继续应用(apply)余下的补丁。在任何时候,你可以用--abort参数来终止rebase的行动,你的分支会回到rebase开始前的状态。
$ git rebase --abort
3. git merge VS git merge --no-ff
git merge 在没有冲突的时候不会生成新的commit。
如果想在没有冲突的情况下也自动生成一个commit,记录此次合并就可以用:git merge --no-ff命令。



