手写Promise3
Promise.all()
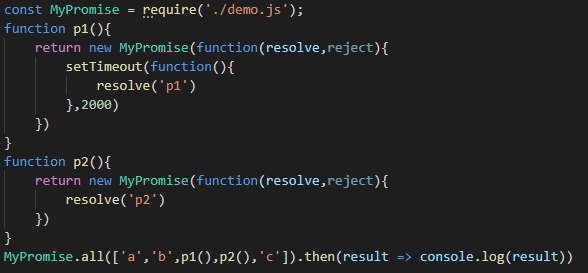
Promise.all()允许我们按照异步代码调用的顺序,得到异步代码执行的结果:

在上面的代码中,虽然p1中的有一个延时器,但是按照Promise.all的原理,我们先执行了p1,就一定会先得到p1的执行结果。
要在我们的MyPromise中实现all方法,首先需要观察其使用方式Promise.all,说明这是一个静态方法,需要使用static关键字进行声明:
static all(array) { let result = []; let index = 0; return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { function addData(key, value) { result[key] = value; index++; if (index === array.length) { resolve(result); } } for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { let current = array[i]; if (current instanceof MyPromise) { // promise 对象 current.then(value => addData(i, value), reason => reject(reason)) } else { // 普通值 addData(i, array[i]); } } }) }
Promise.resolve
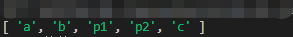
Promise.resolve用于将给定的值转换为Promise对象。
要实现Promise.resolve方法,需要判断传入的值是一个普通值还是一个Promise对象,如果是一个Promise对象,可以直接返回;如果不是Promise对象,则需要创建一个Promise对象,然后将传入的值包裹在这个对象中。
static resolve(value) { if (value instanceof MyPromise) return value; return new MyPromise(resolve => resolve(value)); }
Promise.finally
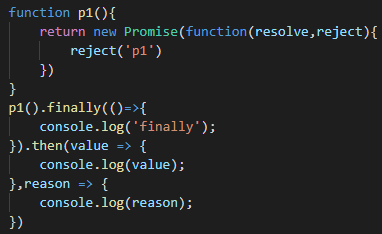
Promise.finally主要有两大特点:
- 在Promise中,不管当前的Promise的最终状态是成功还是失败,Promise.finally当中的回调函数都会被执行;
- 在Promise.finally方法的后面,我们可以链式调用then方法拿到当前Promise对象最终返回的结果
finally(callback) { return this.then(value => { return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value); }, reason => { return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => { throw reason }) }) }
Catch方法
Catch用于处理当前Promise的最终状态为失败的情况,要实现catch方法,只需要在catch方法内部调用then方法,成功传入undefined,失败传入回调函数就可以了

catch(failCallback) { return this.then(undefined, failCallback) }
完整代码
const PENDING = 'pending'; // 等待 const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; // 成功 const REJECTED = 'rejected'; // 失败 class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { try { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } catch (e) { this.reject(e); } } // promsie 状态 status = PENDING; // 成功之后的值 value = undefined; // 失败后的原因 reason = undefined; // 成功回调 successCallback = []; // 失败回调 failCallback = []; resolve = value => { // 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行 if (this.status !== PENDING) return; // 将状态更改为成功 this.status = FULFILLED; // 保存成功之后的值 this.value = value; // 判断成功回调是否存在 如果存在 调用 // this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value); while (this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()() } reject = reason => { // 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行 if (this.status !== PENDING) return; // 将状态更改为失败 this.status = REJECTED; // 保存失败后的原因 this.reason = reason; // 判断失败回调是否存在 如果存在 调用 // this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason); while (this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()() } then(successCallback, failCallback) { // 参数可选 successCallback = successCallback ? successCallback : value => value; // 参数可选 failCallback = failCallback ? failCallback : reason => { throw reason }; let promsie2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { // 判断状态 if (this.status === FULFILLED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else { // 等待 // 将成功回调和失败回调存储起来 this.successCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); this.failCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); } }); return promsie2; } finally(callback) { return this.then(value => { return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value); }, reason => { return MyPromise.resolve(callback()).then(() => { throw reason }) }) } catch(failCallback) { return this.then(undefined, failCallback) } static all(array) { let result = []; let index = 0; return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { function addData(key, value) { result[key] = value; index++; if (index === array.length) { resolve(result); } } for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { let current = array[i]; if (current instanceof MyPromise) { // promise 对象 current.then(value => addData(i, value), reason => reject(reason)) } else { // 普通值 addData(i, array[i]); } } }) } static resolve(value) { if (value instanceof MyPromise) return value; return new MyPromise(resolve => resolve(value)); } } function resolvePromise(promsie2, x, resolve, reject) { // 判断 x 的值是普通值还是promise对象 // 如果是普通值 直接调用resolve // 如果是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果 // 再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject if (promsie2 === x) { return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>')) } if (x instanceof MyPromise) { // promise 对象 // x.then(value => resolve(value), reason => reject(reason)); x.then(resolve, reject); } else { // 普通值 resolve(x); } } module.exports = MyPromise;


