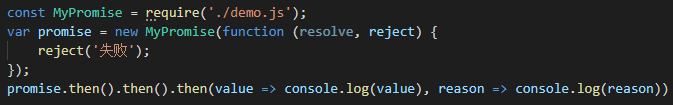
手写Promise2
Promise的then方法是可以被链式调用的, 后面then方法的回调函数拿到值的是上一个then方法的回调函数的返回值。
要实现then方法的链式调用,首先需要保存每一个then方法都返回一个Promise对象:
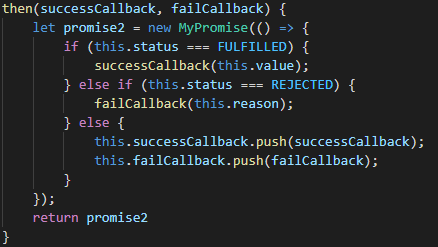
然后将拿到的上一个then方法的返回值,传递给下一个then方法的回调函数:
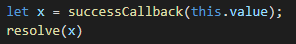
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while(this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while(this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolve(x) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { failCallback(this.reason); } else { this.successCallback.push(successCallback); this.failCallback.push(failCallback); } }); return promise2 } } module.exports = MyPromise;
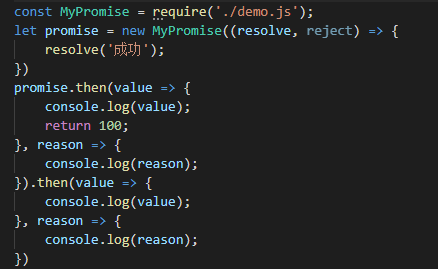

再上面的链式调用中,我们的then方法返回的是一个普通值。如果返回的是一个Promise对象,则需要先判断该对象的状态,然后根据状态来决定调用resolve 还是调用reject。这里将这个过程提取为一个公共方法resolvePromise():
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while(this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while(this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(x, resolve, reject) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(x, resolve, reject) } else { this.successCallback.push(successCallback); this.failCallback.push(failCallback); } }); return promise2 } } function resolvePromise (x, resolve, reject) { if (x instanceof MyPromise) { // X是promise对象 查看promsie对象返回的结果,再根据promise对象返回的结果 决定调用resolve 还是调用reject x.then(resolve, reject); } else { // X是普通值 直接调用resolve resolve(x); } } module.exports = MyPromise;
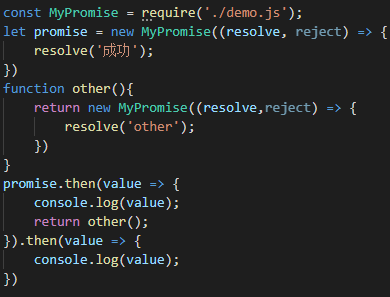

then方法链式调用识别Promise对象自返回
虽然在then方法的回调函数中可以返回Promise对象,但是存在一种例外情况:在then的回调函数中,不能返回当前这个then方法它所返回的Promise对象,否则会发生Promise的循环调用。
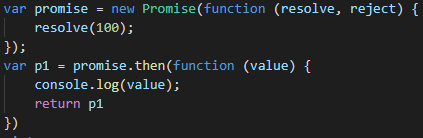
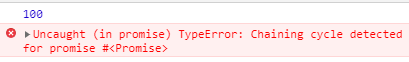

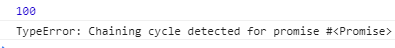
也就是说,在系统的Promise对象中,是可以判断出这种循环调用并捕获的。为了在我们自己的代码中实现这种功能,需要再添加一个判断:
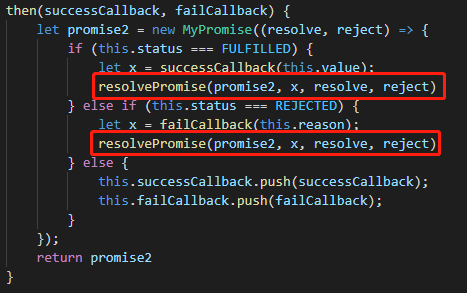

为了实现功能,我们再判断状态时,需要将当前的prosmise2当作参数传递给封装的方法中。但是在上面的代码中,需要new MyPromise执行完成后,才会存在prosmise2,所以在执行过程中时无法获取prosmise2的,所以需要将上面的代码改造成异步代码:
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while (this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while (this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { setTimeout(() => { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) }, 0) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { setTimeout(() => { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) }, 0) } else { this.successCallback.push(successCallback); this.failCallback.push(failCallback); } }); return promise2 } } function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) { if (promise2 === x) { return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>')) } if (x instanceof MyPromise) { x.then(resolve, reject); } else { resolve(x); } } module.exports = MyPromise;
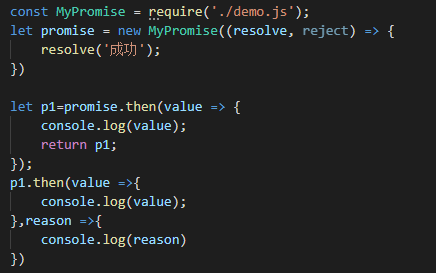
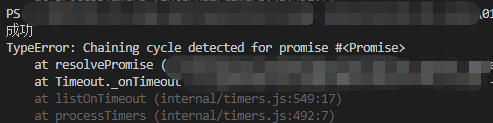
Promise捕获错误
当执行器当中的代码在执行的过程中发生错误的时候,需要让Promise的状态变为失败的状态。为了能在then方法的第二个参数处捕获到错误,需要在构造函数(调用执行器)中捕获错误。
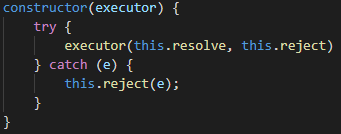
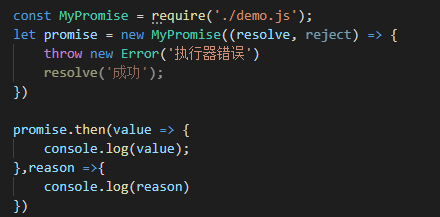
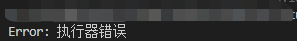
如果是then方法的回调函数在执行过程中报错了,则需要在then方法中捕获错误:
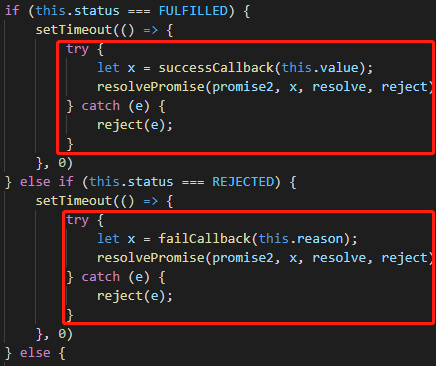
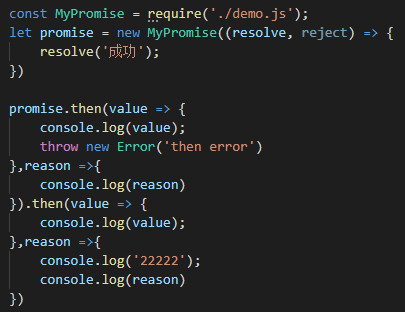
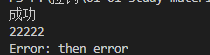
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { try { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } catch (e) { this.reject(e); } } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while (this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while (this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else { this.successCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); this.failCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); } }); return promise2 } } function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) { if (promise2 === x) { return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>')) } if (x instanceof MyPromise) { x.then(resolve, reject); } else { resolve(x); } } module.exports = MyPromise;
将then方法的参数变成可选参数
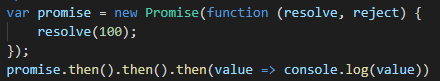
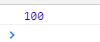
在系统的Promise对象中,即使在then方法中将参数进行省略,依旧能够向下传递状态。其效果等同于:
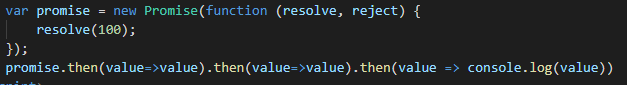
为了在我们自己的MyPromise中实现这个功能,我们需要在then方法中判断回调函数是否存在,如果存在,则直接调用,若不存在,则添加一个上面的函数:

const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { try { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } catch (e) { this.reject(e); } } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while (this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while (this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { // 参数可选 successCallback = successCallback ? successCallback : value => value; failCallback = failCallback ? failCallback: reason => { throw reason }; let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) } else { this.successCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = successCallback(this.value); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); this.failCallback.push(() => { setTimeout(() => { try { let x = failCallback(this.reason); resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) } catch (e) { reject(e); } }, 0) }); } }); return promise2 } } function resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject) { if (promise2 === x) { return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>')) } if (x instanceof MyPromise) { x.then(resolve, reject); } else { resolve(x); } } module.exports = MyPromise;