手写Promise1
Promise就是一个类,在执行这个类的时候,需要传递一个执行器进去,执行器会立即执行。
new Promise(()=>{ })
这个回调函数接收两个参数:resolve和reject,这两个函数参数是用来改变状态的:
- resolve: fulfilled
- reject: rejected
Promise 中有三种状态,分别为:成功(fulfilled) ,失败 (rejected) 和等待(pending)
- pending -> fulfilled
- pending -> rejected
const PENDING = 'pending'; // 等待 const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; // 成功 const REJECTED = 'rejected'; // 失败 class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) //立即执行的执行器 } // promsie 状态默认为等待 status = PENDING; resolve = () => { // 将状态更改为成功 this.status = FULFILLED; } reject = () => { // 将状态更改为失败 this.status = REJECTED; } }
由于Promise一旦状态确定就不可更改。此时,当我们调用了resolve将状态改为成功后,继续调用reject,还是可以将状态改为失败,所以在状态改变前,需要添加判断,如果状态不是等待,则阻止程序向下执行:
const PENDING = 'pending'; // 等待 const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; // 成功 const REJECTED = 'rejected'; // 失败 class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; resolve = () => { // 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行 if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; } reject = () => { // 如果状态不是等待 阻止程序向下执行 if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; } }
在Promise中,then方法内部做的事情就判断状态:如果状态是成功 ,调用成功的回调函数;如果状态是失败,调用失败回调函数。then方法是被定义在原型对象中的。
then (successCallback, failCallback) { //判断状态 if (this.status === FULFILLED) { successCallback(); }else if(this.status === REJECTED){ failCallback(); } }
then成功回调有一个参数,表示成功之后的值; then失败回调有一个参数,表示失败后的原因:
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; // 成功之后的值 reason = undefined; // 失败后的原因 resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; } then (successCallback, failCallback) { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { successCallback(this.value); }else if(this.status === REJECTED){ failCallback(this.reason); } } } module.exports = MyPromise;
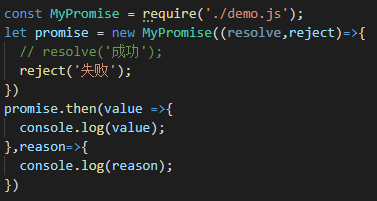
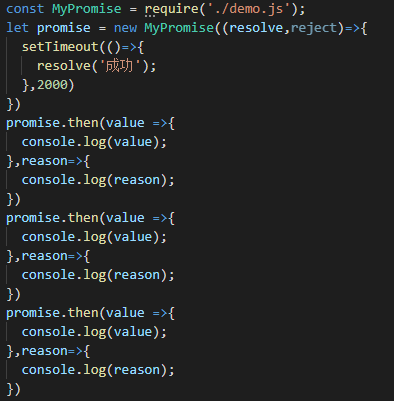
在Promise中加入异步逻辑
修改上面的代码,在代码中添加一个延时器


在代码执行过程中,当代码执行到第二行,Promise中的执行器会立即执行。此时,虽然发现了异步代码,但是总线程并不会等待异步代码的执行,而是等主线程的代码执行完毕后再去执行改异步代码,也就是会跳过异步代码,直接执行下面的then方法,此时由于异步的原因,状态并没有立即改变,还是之前的等待状态,所以,还需要在状态判断中,添加一个等待的情况:在等待状态,并不知道将来会是成功还是失败,因此需要临时存储成功和失败的回调,等异步结束后,才能知道是成功还是失败。
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; // 成功回调 failCallback = []; // 失败回调 resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; // 判断成功回调是否存在 如果存在 调用 this.successCallback && this.successCallback(this.value); } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; // 判断失败回调是否存在 如果存在 调用 this.failCallback && this.failCallback(this.reason); } then(successCallback, failCallback) { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { successCallback(this.value); } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { failCallback(this.reason); } else { //等待状态 //将成功回调和失败回调存储起来 this.successCallback = successCallback; this.failCallback = failCallback; } } } module.exports = MyPromise;
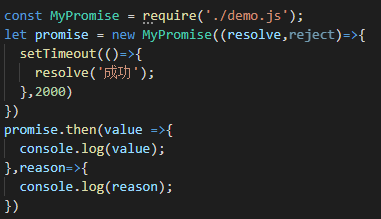

Promise实现then方法多次调用
同一个Promise下的then方法是可以被多次调用的,当then方法被多次调用的时候,每一个then方法传递的回调函数都是要被执行的。当多次调用为同步方法时,可以直接调用回调函数就可以了;但是如果时异步的,我们则需要将每一个then方法的回调存储起来,当状态变成成功或者失败后,再依次调用回调函数。
const PENDING = 'pending'; const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'; const REJECTED = 'rejected'; class MyPromise { constructor(executor) { executor(this.resolve, this.reject) } status = PENDING; value = undefined; reason = undefined; successCallback = []; failCallback = []; resolve = value => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = FULFILLED; this.value = value; while(this.successCallback.length) this.successCallback.shift()(this.value) } reject = reason => { if (this.status !== PENDING) return; this.status = REJECTED; this.reason = reason; while(this.failCallback.length) this.failCallback.shift()(this.reason) } then(successCallback, failCallback) { if (this.status === FULFILLED) { successCallback(this.value); } else if (this.status === REJECTED) { failCallback(this.reason); } else { this.successCallback.push(successCallback); this.failCallback.push(failCallback); } } } module.exports = MyPromise;