Hessian的使用以及理解
官网
http://hessian.caucho.com/
Hessian的使用以及理解
Hessian版本:3.1.5
将包括如下的内容:
Hessian的基本使用
Hessian的原理
Hessian和Spring 的结合使用
扩展
简单说来,Hessian是一个轻量级的RPC框架(RPC是什么?请参考这里https://www.zhihu.com/question/25536695)。
它基于HTTP协议传输,使用Hessian二进制序列化,对于数据包比较大的情况比较友好。
但是它的参数和返回值都需要实现Serializable接口。
简单实现一个Hessian的例子:
创建接口和实现类
1 2 3 | public interface Basic {String sayHello(String name);} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | public class BasicImpl implements Basic{public String sayHello(String name) {return "This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. " + name;}} |
配置HessianServlet, web.xml中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | <servlet><servlet-name>HessianServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>service-class</param-name><param-value>example.impl.BasicImpl</param-value></init-param></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>HessianServlet</servlet-name><url-pattern>/hessian</url-pattern></servlet-mapping> |
我们将会把Servlet部署在Tomcat上,端口8080。
编写客户端代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public class BasicClient {public static void main(String[] args) {try {String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}} |
创建HessianProxyFactory对象,创建Basic “对象”,然后调用sayHello()方法。
整个过程感觉很简单,并没有什么配置。
启动Tomcat,运行Client。
输出如下:
This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. SW
可见是调用成功了。
等等,这个过程到底发生了些什么?
我们先从服务端说起,主要是有这几个步骤:
编写接口和实现类
在web.xml中声明HessianServlet,并且将上一步的实现类设置为Servlet的[service-class]属性值
将Servlet部署在Tomcat容器中
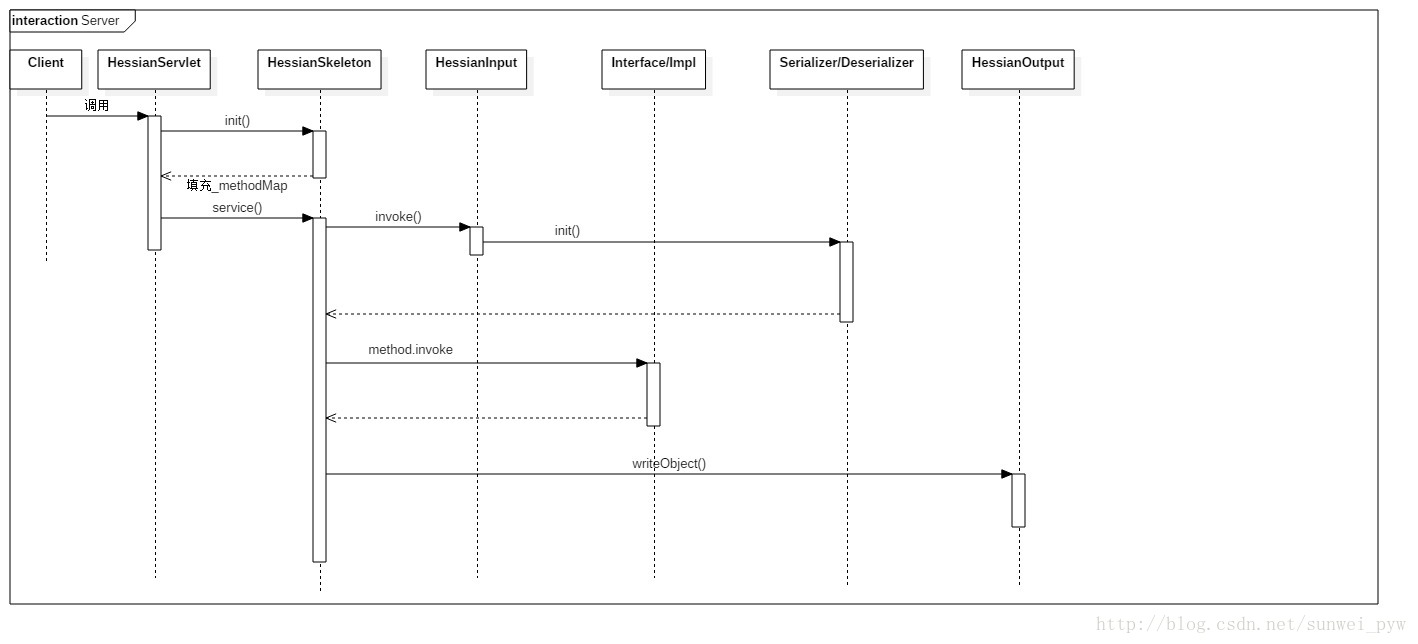
可见我们所有的工作都围绕在HessianServlet在展开。该Servlet中有两个比较重要的方法:init()、service();
init方法初始化服务和服务对象,主要分为3步:
通过home-class或者service-class创建服务端的实现类实例;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | if (_homeImpl != null) {}else if (getInitParameter("home-class") != null) {String className = getInitParameter("home-class");Class homeClass = loadClass(className);_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();init(_homeImpl);}else if (getInitParameter("service-class") != null) {String className = getInitParameter("service-class");Class homeClass = loadClass(className);_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();init(_homeImpl);}else {if (getClass().equals(HessianServlet.class))throw new ServletException("server must extend HessianServlet");_homeImpl = this;} |
通过home-api或者api-class加载实现类的接口对象;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | if (_homeAPI != null) {}else if (getInitParameter("home-api") != null) {String className = getInitParameter("home-api");_homeAPI = loadClass(className);}else if (getInitParameter("api-class") != null) {String className = getInitParameter("api-class");_homeAPI = loadClass(className);}else if (_homeImpl != null)_homeAPI = _homeImpl.getClass(); |
init方法还会创建HessianSkeleton对象,这是Hessian服务端的核心功能部分。
HessianSkeleton继承自AbstractSkeleton,其构造方法,将会从实现类中抽取方法和方法的Method对象,并且存储到_methodMap中。
对于一个Servlet来说其service方法是对外提供服务的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | /*** Execute a request. The path-info of the request selects the bean.* Once the bean's selected, it will be applied.*/public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)throws IOException, ServletException{HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;if (! req.getMethod().equals("POST")) {res.setStatus(500, "Hessian Requires POST");PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();res.setContentType("text/html");out.println("<h1>Hessian Requires POST</h1>");return;}String serviceId = req.getPathInfo();String objectId = req.getParameter("id");if (objectId == null)objectId = req.getParameter("ejbid");ServiceContext.begin(req, serviceId, objectId);try {InputStream is = request.getInputStream();OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();HessianInput in = new HessianInput(is);HessianOutput out = new HessianOutput(os);if (objectId != null)_objectSkeleton.invoke(in, out);else_homeSkeleton.invoke(in, out);} catch (RuntimeException e) {throw e;} catch (ServletException e) {throw e;} catch (Throwable e) {throw new ServletException(e);} finally {ServiceContext.end();}} |
最主要的是调用HessianSkeleton对象的invoke方法。注意,Servlet实例中有两个HessianSkeleton变量,分别是:_objectSkeleton和 _homeSkeleton,调用谁,是由objectid决定的。此处还有不明白的地方。
invoke方法:
首先从HessianInput对象中获取到Method信息,获取到真正的service对象。
根据反射机制,调用service对象的invoke方法,获取到返回值。
最后调用HessianOutput对象将结果写回到调用方。
客户端代码
Hessian原生API编写客户端HessianClient:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | public class BasicClient {public static void main(String[] args) {try {String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}} |
创建HessianProxyFacotry,创建接口Basic的代理对象,然后调用sayHello()方法。
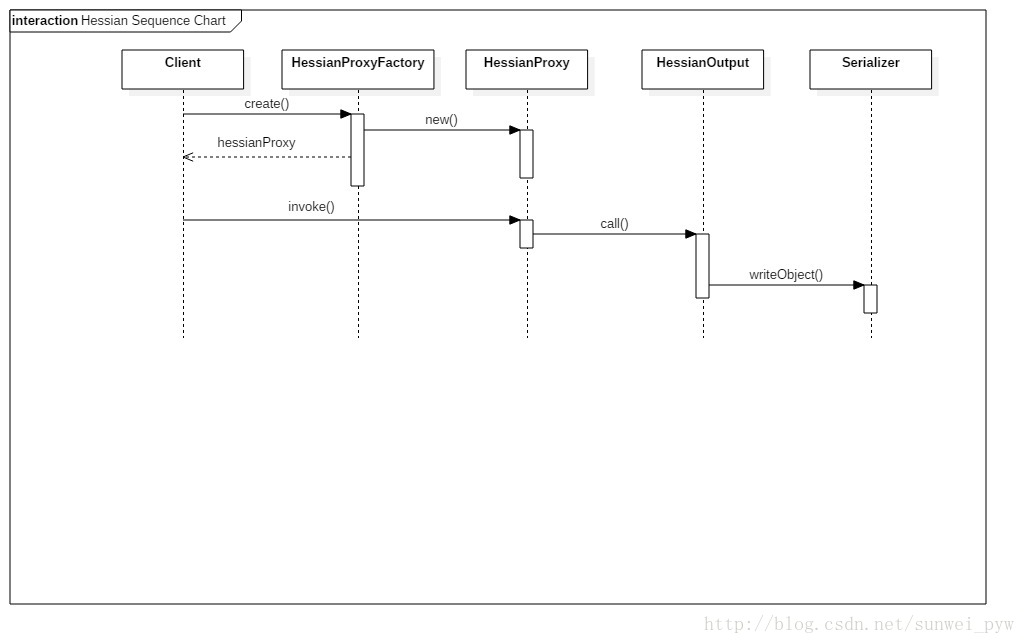
那么重点就在于创建代理对象,首先创建HessianProxyFacotry对象,构造方法中创建了一个HessianProxyResolver对象,这个对象的lookup方法将用来查找远程服务。此外HessianProxyFacotry还有包括权限验证方面的支持。
创建了factory之后,接下来就是通过Class对象和远程服务的URL创建代理对象了。
HessianProxyFactory使用HessianProxy对象作为代理的Handler,也就是说,我们对代理对象的所有操作,都会由这个handler来处理。handler的invoke方法,在进行一些方法名和参数的确认之后,创建HttpURLConnection对象,调用sendRequest方法,将方法名和参数用HessianOutput对象(设置序列化的方式)的call方法,写入到服务端。
主要代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | protected URLConnection sendRequest(String methodName, Object []args)throws IOException{URLConnection conn = null;conn = _factory.openConnection(_url);// Used chunked mode when available, i.e. JDK 1.5.if (_factory.isChunkedPost() && conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {try {HttpURLConnection httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;httpConn.setChunkedStreamingMode(8 * 1024);} catch (Throwable e) {}}addRequestHeaders(conn);OutputStream os = null;try {os = conn.getOutputStream();} catch (Exception e) {throw new HessianRuntimeException(e);}try {if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINEST)) {PrintWriter dbg = new PrintWriter(new LogWriter(log));os = new HessianDebugOutputStream(os, dbg);}AbstractHessianOutput out = _factory.getHessianOutput(os);out.call(methodName, args);out.flush();return conn;} catch (IOException e) {if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect();throw e;} catch (RuntimeException e) {if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect();throw e;}} |
服务端拿到请求,进行反序列化,然后将方法调用,再将结果序列化之后写回到connection。所以,客户端在sendRequest之后,所要做的就是将返回的结果进行解析,看返回的code是不是200:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | conn = sendRequest(mangleName, args);if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;int code = 500;try {code = httpConn.getResponseCode();} catch (Exception e) {}parseResponseHeaders(conn);if (code != 200) {StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();int ch;.....AbstractHessianInput in = _factory.getHessianInput(is);in.startReply();Object value = in.readObject(method.getReturnType());if (value instanceof InputStream) {value = new ResultInputStream(httpConn, is, in, (InputStream) value);is = null;httpConn = null;}elsein.completeReply();return value; |
解析HessianInput对象,并且从中读取到结果返回。
至此,服务端和客户端的交互过程已经简单地介绍完毕。
Spring也为Hessian提供了很友好的支持,通过使用spring-remoting包,我们可以很方便地发布和调用服务。
这部分提供一个简单的实现例子:
在web.xml中,我们配置SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | <servlet><servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name><url-pattern>/remote/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping> |
applicationContext.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"default-lazy-init="true"><bean id = "basicService" class="example.impl.BasicImpl"/><bean name="/basicHessianService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter"><property name="service" ref="basicService"/><property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/></bean></beans> |
这里,我们使用了org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter来发布服务。将程序部署在tomcat中。
客户端,使用org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean来代理请求:
client.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"default-lazy-init="true"><bean id="basicService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean"><property name="serviceUrl" value="http://localhost:8080/remote/basicHessianService"/><property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/></bean></beans> |
编写客户端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public class SpringClient {public static void main(String[] args) {ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"classpath:client.xml"});Basic basic = (Basic)context.getBean("basicService");System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SUNWEI"));}} |
这样,服务端/客户端的代码都已经编写完成。
最原始的实现,我们的服务是通过Servlet来绑定的,而Spring的实现,我们使用了SpringMVC的加载时机,将配置文件加载。HessianServiceExporter
1 2 | public class HessianServiceExporter extends RemoteExporter implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {.... |
这个类实现了InitializingBean接口,这是spring-beans包中很重要的一个扩展接口。
这个接口的说明如下:
1 2 3 | Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all theirproperties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custominitialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set. |
也就是说,它会随着Spring容器(此处为Spring MVC容器)的启动而被加载。看看HessianServiceExporter的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | public void prepare() {HessianSkeleton skeleton = null;try {try {Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object, class$java$lang$Class == null?(class$java$lang$Class = class$("java.lang.Class")):class$java$lang$Class});this.checkService();this.checkServiceInterface();skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService(), this.getServiceInterface()});} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object});skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService()});}} catch (Throwable var5) {throw new BeanInitializationException("Hessian skeleton initialization failed", var5);}if(hessian2Available) {this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian2SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);} else {this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian1SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);}}public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {Assert.notNull(this.skeletonInvoker, "HessianServiceExporter has not been initialized");if(!"POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("POST", "HessianServiceExporter only supports POST requests");} else {try {this.skeletonInvoker.invoke(request.getInputStream(), response.getOutputStream());} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new NestedServletException("Hessian skeleton invocation failed", var4);}}} |
在prepare方法中,获取service和serviceInterface的配置,创建HessianSkeleton对象。
同时,还实现了HttpRequestHandler,spring-web中的接口。
又因为实现了HttpRequestHandler接口,所以在handleRequest方法中,可以像HessianServlet的service方法一样,调用Hessian2SkeletonInvoker的invoke方法进行实际的方法调用。
最后一点尾巴
定义一个自己的HttpRequestHandler对象,配置在applicationContext.xml中,然后通过页面访问:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class MyHandler implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {System.out.println("初始化 MyHandler");}public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("执行 MyHandler");}} |
配置在applicationContext.xml中:
1 | <bean id = "/myHandler" class="client.MyHandler"/> |
通过Spring MVC的上下文加载该Handler,启动Tomcat的时候,可以看到控制台输出:
初始化 MyHandler
在浏览器中访问:http://localhost:8080/remote/myHandler
将触发执行:执行 MyHandler




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理