Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) -----CF546
C. Soldier and Cards
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it's possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a "war"-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent's card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player's stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won't end.
First line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier's cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier's cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
If somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won't end and will continue forever output - 1.
4
2 1 3
2 4 2
6 2
3
1 2
2 1 3
-1
First sample:
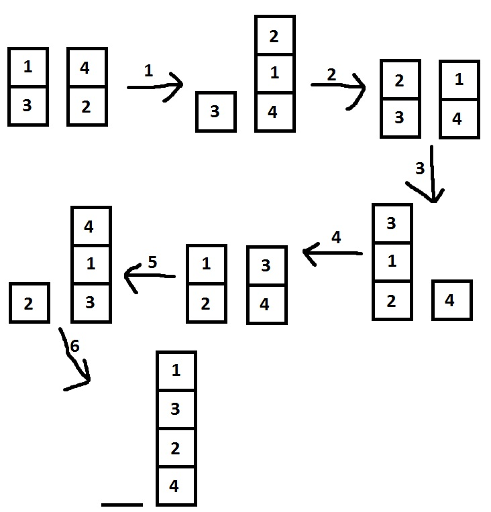
Second sample:
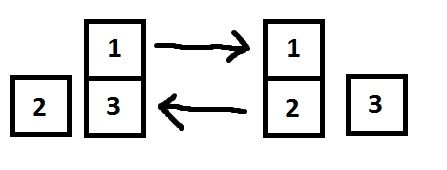
题意:给一个n(<=10)表示两人手中共有n张牌,接下来一行表示第1个人有k1张牌,k1 v1[1] v1[2]......v1[k1], v1[i]表示第i 张牌的大小,第三行表示第2个人有k2张牌,k2 v2[1] v2[2]......v2[k2], v2[i]表示第i 张牌的大小。每一轮,两人从牌顶部各出一张,谁出的牌大则两张牌归谁,放入到自己牌的底部,直到其中一个人手中没有牌出,则那个人输了。问需要多少轮,哪个人赢了。如果没有解则输出-1.
思路:(模拟题)直接模拟一下过程,主要是标记一下两个人手中牌的状态,用map<string,map<string,bool> >vist 标记一下。
转载请注明出处:寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/C
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <bitset> 12 #include <list> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 #include <climits> 15 using namespace std; 16 17 #define lson 2*i 18 #define rson 2*i+1 19 #define LS l,mid,lson 20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson 21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++) 22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--) 23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) 24 #define W(a) while(a) 25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b) 26 #define LL long long 27 #define N 5000005 28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 29 #define EXP 1e-8 30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x) 31 const int mod = 1e9+7; 32 33 map<string,map<string,int> > vis; 34 int n; 35 int k1,k2; 36 int a[15],b[15],c[15]; 37 char s1[15],s2[15]; 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 int i,j,k; 42 scanf("%d",&n); 43 scanf("%d",&k1); 44 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 45 { 46 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 47 c[i] = a[i]; 48 } 49 scanf("%d",&k2); 50 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 51 { 52 scanf("%d",&b[i]); 53 c[k1+i] = b[i]; 54 } 55 sort(c,c+k1+k2); 56 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 57 { 58 for(j = 0; j<k1+k2; j++) 59 { 60 if(a[i]==c[j]) 61 s1[i] = j+'0'; 62 } 63 } 64 s1[k1] = '\0'; 65 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 66 { 67 for(j = 0; j<k1+k2; j++) 68 { 69 if(b[i]==c[j]) 70 s2[i] = j+'0'; 71 } 72 } 73 s2[k2] = '\0'; 74 vis[s1][s2] = 1; 75 int ans = 0; 76 while(k1&&k2) 77 { 78 int p1 = s1[0],p2 = s2[0]; 79 // printf("[%d %d %d %d]\n",p1,p2,k1,k2); 80 81 /* printf("(1):"); 82 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 83 printf("%c ",s1[i]); 84 printf("\n"); 85 printf("(2):"); 86 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 87 printf("%c ",s2[i]); 88 printf("\n");*/ 89 if(p1>p2) 90 { 91 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 92 s2[i] = s2[i+1]; 93 k2--; 94 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 95 s1[i] = s1[i+1]; 96 s1[k1-1] = p2; 97 s1[k1] = p1; 98 k1++; 99 s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0'; 100 } 101 else 102 { 103 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 104 s1[i] = s1[i+1]; 105 k1--; 106 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 107 s2[i] = s2[i+1]; 108 s2[k2-1] = p1; 109 s2[k2] = p2; 110 k2++; 111 s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0'; 112 } 113 /* printf("(1):"); 114 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++) 115 printf("%c ",s1[i]); 116 printf("\n"); 117 printf("(2):"); 118 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++) 119 printf("%c ",s2[i]); 120 printf("\n");*/ 121 if(vis[s1][s2]) 122 { 123 ans = -1; 124 break; 125 } 126 //printf("%d %d\n",k1,k2); 127 ans++; 128 vis[s1][s2] = 1; 129 } 130 printf("%d",ans); 131 if(ans!=-1) 132 { 133 if(k1) 134 printf(" 1"); 135 else 136 printf(" 2"); 137 } 138 printf("\n"); 139 140 return 0; 141 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <bitset> 12 #include <list> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 #include <climits> 15 using namespace std; 16 17 #define lson 2*i 18 #define rson 2*i+1 19 #define LS l,mid,lson 20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson 21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++) 22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--) 23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) 24 #define W(a) while(a) 25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b) 26 #define LL long long 27 #define N 5000005 28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 29 #define EXP 1e-8 30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x) 31 const int mod = 1e9+7; 32 int p[N]; 33 int a[N]; 34 int prime[700]; 35 LL sum[N]; 36 void init() 37 { 38 39 for(int i=0; i<700; ++i) 40 prime[i] = INF; 41 prime[0] = 2; 42 int num = 0; 43 for(int i=3; i<5005; ++i) 44 { 45 int x = 0; 46 while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x; 47 if( !(i%prime[x]) ) 48 a[i] = prime[x]; 49 else 50 { 51 prime[++num] = i; 52 a[i] = i; 53 } 54 } 55 a[2] =2; 56 for(int i=5005; i< N; ++i) 57 { 58 int x = 0; 59 while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x; 60 if( !(i%prime[x]) ) 61 a[i] = prime[x]; 62 else 63 a[i] = i; 64 } 65 p[2] = 1; 66 for(int i=3; i <N; ++i) 67 p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + 1; 68 } 69 int main() 70 { 71 int i,j,k; 72 init(); 73 sum[1] = 0; 74 // printf("%d\n",p[4]); 75 for(i = 2; i<=5000000; i++) 76 { 77 sum[i] = sum[i-1]+p[i]; 78 // printf("%d %I64d\n",i,sum[i]); 79 } 80 int t; 81 scanf("%d",&t); 82 while(t--) 83 { 84 scanf("%d%d",&i,&j); 85 // printf("%d %d %I64d %I64d\n",i,j+1,sum[i],sum[j+1]); 86 if(i == j) 87 printf("0\n"); 88 else 89 printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]); 90 } 91 92 return 0; 93 }
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <bitset> 12 #include <list> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 #include <climits> 15 using namespace std; 16 17 #define lson 2*i 18 #define rson 2*i+1 19 #define LS l,mid,lson 20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson 21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++) 22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--) 23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) 24 #define W(a) while(a) 25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b) 26 #define LL long long 27 #define N 5000005 28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 29 #define EXP 1e-8 30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x) 31 const int mod = 1e9+7; 32 int p[N]; 33 bool v[N]; 34 int a[N]; 35 int prime[N/10]; 36 LL sum[N]; 37 void init() 38 { 39 for(int i=2; i<N; ++i) 40 a[i] = i; 41 int num=-1; 42 for(int i=2; i<N; ++i) 43 { 44 if(!v[i]) prime[++num] = i; 45 for(int j=0; j<=num && i*prime[j] < N; ++j) 46 { 47 int t = i*prime[j]; 48 v[t] =1; 49 if(a[t] > prime[j]) a[t] = prime[j]; 50 if(i%prime[j] == 0) break; 51 } 52 } 53 p[2] = 1; 54 for(int i=3; i <N; ++i) 55 p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + 1; 56 } 57 int main() 58 { 59 int i,j,k; 60 init(); 61 sum[1] = 0; 62 for(i = 2; i<=5000000; i++) 63 { 64 sum[i] = sum[i-1]+p[i]; 65 } 66 int t; 67 scanf("%d",&t); 68 while(t--) 69 { 70 scanf("%d%d",&i,&j); 71 if(i == j) 72 printf("0\n"); 73 else 74 printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]); 75 } 76 77 return 0; 78 }



