D. GukiZ and Binary Operations(矩阵+二进制)
D. GukiZ and Binary Operations
We all know that GukiZ often plays with arrays.
Now he is thinking about this problem: how many arrays a, of length n, with non-negative elements strictly less then 2l meet the following condition: 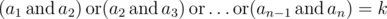 ? Here operation
? Here operation  means bitwise AND (in Pascal it is equivalent to and, in C/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to &), operation
means bitwise AND (in Pascal it is equivalent to and, in C/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to &), operation  means bitwise OR (in Pascal it is equivalent to
means bitwise OR (in Pascal it is equivalent to  , inC/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to |).
, inC/C++/Java/Python it is equivalent to |).
Because the answer can be quite large, calculate it modulo m. This time GukiZ hasn't come up with solution, and needs you to help him!
First and the only line of input contains four integers n, k, l, m (2 ≤ n ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ k ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ l ≤ 64, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109 + 7).
In the single line print the number of arrays satisfying the condition above modulo m.
2 1 2 10
3
2 1 1 3
1
3 3 2 10
9
In the first sample, satisfying arrays are {1, 1}, {3, 1}, {1, 3}.
In the second sample, only satisfying array is {1, 1}.
In the third sample, satisfying arrays are{0, 3, 3}, {1, 3, 2}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 3, 1}, {2, 3, 3}, {3, 3, 0}, {3, 3, 1}, {3, 3, 2}, {3, 3, 3}.
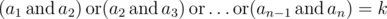 ,两两取与再取或的方式最后答案为k,问你有多少种方案数,答案取余m
,两两取与再取或的方式最后答案为k,问你有多少种方案数,答案取余m注意l=64的时候,要特别注意一下
我用了无符号的long long 各种错。。。最后还是long long 过的。
不知道是不是我编译器坏了。
转载请注明出处: 寻找&星空の孩子
寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/551/problem/D
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #define LL long long 5 using namespace std;//unsigned 6 struct matrix 7 { 8 LL mat[2][2]; 9 }; 10 LL mod; 11 12 matrix multiply(matrix a,matrix b) 13 { 14 matrix c; 15 memset(c.mat,0,sizeof(c.mat)); 16 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) 17 { 18 for(int j=0;j<2;j++) 19 { 20 if(a.mat[i][j]==0)continue; 21 for(int k=0;k<2;k++) 22 { 23 if(b.mat[j][k]==0)continue; 24 c.mat[i][k]+=a.mat[i][j]*b.mat[j][k]%mod; 25 // c.mat[i][k]%=mod; 26 if(c.mat[i][k]>mod) c.mat[i][k]-=mod; 27 else if(c.mat[i][k]<0) c.mat[i][k]+=mod; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 return c; 32 } 33 34 matrix quicklymod(matrix a,LL n) 35 { 36 matrix res; 37 memset(res.mat,0,sizeof(res.mat)); 38 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) res.mat[i][i]=1; 39 while(n) 40 { 41 if(n&1) 42 res=multiply(a,res); 43 a=multiply(a,a); 44 n>>=1; 45 } 46 return res; 47 } 48 49 LL ppow(LL a,LL b) 50 { 51 LL c=1; 52 while(b) 53 { 54 if(b&1) c=c*a%mod; 55 b>>=1; 56 a=a*a%mod; 57 } 58 return c; 59 } 60 61 62 int main() 63 { 64 LL n,k,l,m; 65 scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&k,&l,&mod); 66 if(l!=64&&k>=(unsigned long long )(1ULL<<l)){printf("0\n");return 0;} 67 matrix ans; 68 ans.mat[0][0]=1;ans.mat[0][1]=1; 69 ans.mat[1][0]=1;ans.mat[1][1]=0; 70 ans=quicklymod(ans,n); 71 //相邻没有连续两个1 72 LL x=(ans.mat[0][0]+ans.mat[0][1])%mod; 73 //至少有一个连续两个1 74 LL y=((ppow(2,n)-x)%mod+mod)%mod; 75 // printf("x=%I64d\ty=%I64d\n",x,y); 76 LL sum=1; 77 for(LL i=0;i<l;i++) 78 { 79 if(k&(1LL<<i)) sum=(sum*y)%mod; 80 else sum=sum*x%mod; 81 } 82 printf("%I64d\n",sum%mod); 83 return 0; 84 }
别人的 无符号过的。。。


1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<vector> 6 #include<cmath> 7 #include<queue> 8 #include<stack> 9 #include<map> 10 #include<set> 11 #include<algorithm> 12 using namespace std; 13 typedef unsigned long long LL; 14 LL N,K,L,MOD; 15 struct Matrix 16 { 17 LL mat[2][2]; 18 Matrix(){memset(mat,0,sizeof(mat));} 19 Matrix operator*(Matrix A) 20 { 21 Matrix res; 22 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) 23 for(int j=0;j<2;j++) 24 for(int k=0;k<2;k++) 25 res.mat[i][j]=(res.mat[i][j]+mat[i][k]*A.mat[j][k]%MOD)%MOD; 26 return res; 27 } 28 }; 29 LL pow_mul(LL x,LL n) 30 { 31 LL res=1; 32 while(n) 33 { 34 if(n&1)res=(res*x)%MOD; 35 x=(x*x)%MOD; 36 n>>=1; 37 } 38 return res; 39 } 40 Matrix matrix_pow_mul(Matrix A,LL n) 41 { 42 Matrix res; 43 for(int i=0;i<2;i++)res.mat[i][i]=1; 44 while(n) 45 { 46 if(n&1)res=res*A; 47 A=A*A; 48 n>>=1; 49 } 50 return res; 51 } 52 int main() 53 { 54 while(cin>>N>>K>>L>>MOD) 55 { 56 if(L!=64&&K>=(1ULL<<L)){printf("0\n");continue;} 57 Matrix A,B; 58 A.mat[0][0]=A.mat[0][1]=A.mat[1][0]=1; 59 A=matrix_pow_mul(A,N-2); 60 B.mat[0][0]=3; 61 B.mat[0][1]=2; 62 A=A*B; 63 LL ans=1; 64 LL sum=pow_mul(2,N); 65 for(LL i=0;i<L;i++) 66 { 67 if(K&(1LL<<i))ans=(ans*((sum-A.mat[0][0]+MOD)%MOD))%MOD; 68 else ans=(ans*A.mat[0][0])%MOD; 69 } 70 cout<<ans%MOD<<endl; 71 } 72 return 0; 73 }


我用dp[i][j]表示有i个数,j表示最后一个数为0还是为1时满足没有相邻为1的方案数,因为n>=2,所以i只有大于2才有意义。首先dp[1][0]=1,dp[1][1]=1 , dp[2][0]=dp[1][0]+dp[1][1],dp[2][1]=dp[1][0] ………… 通项公式就是dp[n][0]=dp[n-1][0]+dp[n-1][1],dp[n][1]=dp[n-1][0] ,意思是当你长度为n最后一个数字为0时,你可以在长度为n-1最后一个数字为0或为1后面补0,这样不存在相邻为1的方案,若最后一位要为1,就只能在n-1最后一位为0的时候补1,这样才不会有相邻的1。最后你要计算的是all[n]=dp[n][0]+dp[n][1],其中dp[n][0]==all[n-1],dp[n][1]==dp[n-1][0]==all[n-2],推出all[n]=all[n-1]+all[n-2],这就是斐波那契数列。但这初始值有些不同,all[n] = fib[n+1] ,fib第0个元素跟第1个元素为1. 算出不相邻的方案之后,只要算出总的方案数2^n(每一位取0或取1)减去不相邻的方案,即为相邻的方案。你也可以用dp去推一下,我稍微提一下,我用c[n]表示长度为n时具有相邻1的方案数,c[2]=1 , c[3]=c[2]*2+dp[2][1]………… c[n]=c[n-1]*2+dp[n-1][1]=c[n-1]*2+all[n-3]这里的dp是上面求的不存在相邻的1,由于c[n-1]具有相邻的1所以下一位任意,dp[n-1][1]是长度为n-1最后一位为1,我们补1让它有相邻的1. 得出是斐波那契数列之后,我们可以用矩阵快速幂求解斐波那契数,也可以用矩阵快速幂求c 注意:这道题wa点挺多的,首先是unsigned long long在判断是否越界的时候用,还有快速幂的次数是long long,枚举l位时候,第63位已经暴了10^18,所以需要特判。最后输出结果要%mod,不然它有mod为1且l=0的样例



