推箱子 (hdu1254)(bfs双重广搜)
推箱子
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4593 Accepted Submission(s):
1298
Problem Description
推箱子是一个很经典的游戏.今天我们来玩一个简单版本.在一个M*N的房间里有一个箱子和一个搬运工,搬运工的工作就是把箱子推到指定的位置,注意,搬运工只能推箱子而不能拉箱子,因此如果箱子被推到一个角上(如图2)那么箱子就不能再被移动了,如果箱子被推到一面墙上,那么箱子只能沿着墙移动.
现在给定房间的结构,箱子的位置,搬运工的位置和箱子要被推去的位置,请你计算出搬运工至少要推动箱子多少格.
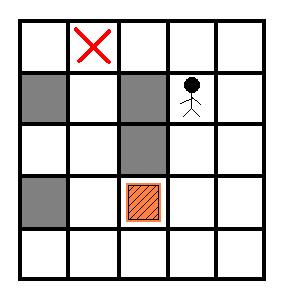
现在给定房间的结构,箱子的位置,搬运工的位置和箱子要被推去的位置,请你计算出搬运工至少要推动箱子多少格.

Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数T(1<=T<=20),代表测试数据的数量.然后是T组测试数据,每组测试数据的第一行是两个正整数M,N(2<=M,N<=7),代表房间的大小,然后是一个M行N列的矩阵,代表房间的布局,其中0代表空的地板,1代表墙,2代表箱子的起始位置,3代表箱子要被推去的位置,4代表搬运工的起始位置.
Output
对于每组测试数据,输出搬运工最少需要推动箱子多少格才能帮箱子推到指定位置,如果不能推到指定位置则输出-1.
Sample Input
1
5 5
5 5
0 3 0 0 0
1 0 1 4 0
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 2 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
Sample Output
4
一开始没考虑到人的初始情况,就是能不能到箱子的后面所以代码很快就写好了。。。
后来发现的,写起来好挺多的,貌似有128行。
思路是:先移动箱子,然后考虑能否退一步的位置,人能不能到,能到,则,进行下一步同时更新地图,不能到,就重新移动箱子。
双重搜索!!!
详见代码
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> using namespace std; int n,m,T; int dir[4][2]={{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; int str[10][10]; struct Node { int x,y,step; int mmap[10][10]; bool check() { if(x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m) return true; return false; } }s,e,u,v,ss,ee,uu,vv; bool bfs_people(Node n1) { //搜索人是否能到达指定位置 int i; queue<Node>que; ss=n1; bool flag[10][10]; memset(flag,false,sizeof(flag)); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { //找到人的起点 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { if(n1.mmap[i][j]==4) { ss.x=i; ss.y=j; ss.step=0; } } } if(ss.x==ee.x&&ss.y==ee.y) return true; que.push(ss); flag[ss.x][ss.y]=true; while(!que.empty()) { uu=que.front(); que.pop(); for(i=0;i<4;i++) { vv=uu; vv.step++; vv.x+=dir[i][0]; vv.y+=dir[i][1]; if(vv.check()&&flag[vv.x][vv.y]==false&&(n1.mmap[vv.x][vv.y]!=1&&n1.mmap[vv.x][vv.y]!=2)) { //目标点不是墙也不是箱子 flag[vv.x][vv.y]=true; if(vv.x==ee.x&&vv.y==ee.y) return true; que.push(vv); } } } return false; } int bfs_box() { //搜索箱子 int flag[10][10][4]; queue<Node>Q; Q.push(s); memset(flag,false,sizeof(flag)); while(!Q.empty()) { u=Q.front(); Q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { v=u; v.x+=dir[i][0]; v.y+=dir[i][1]; v.step++; if(v.check()&&str[v.x][v.y]!=1&&flag[v.x][v.y][i]==false) { //人的目标位置 ee.x=u.x-dir[i][0]; ee.y=u.y-dir[i][1]; if(ee.check()==false) continue; if(bfs_people(v)) { //更新地图,箱子和人的位置 swap(v.mmap[v.x][v.y],v.mmap[u.x][u.y]); swap(v.mmap[ee.x][ee.y],v.mmap[ss.x][ss.y]); flag[v.x][v.y][i]=true; if(str[v.x][v.y]==3) return v.step; Q.push(v); } } } } return -1; } int main() { int T,i,j; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { for(j=0;j<m;j++) { scanf("%d",&str[i][j]); s.mmap[i][j]=str[i][j]; if(str[i][j]==2) { //标注箱子起点 s.x=i; s.y=j; s.step=0; } } } printf("%d\n",bfs_box()); } return 0; } /* 60 3 1 3 2 4 3 3 3 0 0 2 0 0 4 0 0 3 3 3 0 1 1 2 1 4 0 1 3 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 4 0 3 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 3 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 3 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 4 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 4 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 4 3 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 5 7 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 4 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 Ans:1 Ans:1 Ans:-1 Ans:5 Ans:-1 Ans:3 Ans:-1 Ans:-1 Ans:4 Ans:4 */
之前的代码先存着,可以当模板。。。

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> using namespace std; const int maxn=10; bool vst[maxn][maxn],t; int map[maxn][maxn]; int dir[4][2]={-1,0,1,0,0,-1,0,1} ; int m,n,fx,fy; struct state { int x,y; int step; }; int check(int x, int y) { if(x<0 || x>=m || y<0 || y>=n) return 0; else return 1; } void bfs() { queue<state>Q; state now,next; now.x=fx; now.y=fy; now.step=0; t=0; Q.push(now); vst[now.x][now.y]=1 ; while(!Q.empty()) { now=Q.front(); Q.pop(); if(map[now.x][now.y]==3) { printf("%d\n",now.step);//找到第一个就输出了 t=1; return ;//结束bfs,返回。,不写的话,会等全部输出之后才停下来的 } /* if(map[now.x][now.y]=='x') { map[now.x][now.y] = '.'; now.step+= 1; Q.push(now); continue; } */ else for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { next.x=now.x+dir[i][0]; next.y=now.y+dir[i][1]; if(vst[next.x][next.y] || map[next.x][next.y]==1 || !check(next.x,next.y)||map[now.x-dir[i][0]][now.y-dir[i][1]]==1) continue; next.step=now.step+1; Q.push(next); vst[next.x][next.y]=1; } } } int main() { int i,j,T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); // getchar(); //用scanf,就要先吸收回车;用cin就没必要了 for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<n;j++) { cin>>map[i][j];//scanf("%c",&map[i][j]);为什么最后一列输不进来? if(map[i][j]==2) {fx=i;fy=j;} } // getchar();//用scanf,就要先吸收回车;用cin就没必要了 } /* for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<n;j++) { printf("%d",map[i][j]); } puts(""); } */ memset(vst,0,sizeof(vst)); t=0; bfs(); if(!t) cout <<-1<< endl; } return 0; } /* 5 5 5 0 3 0 0 0 1 0 1 4 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 5 0 3 0 0 0 0 1 1 4 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 5 0 3 0 0 1 0 1 1 4 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 5 0 3 0 1 0 0 1 1 4 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 2 3 1 1 4 1 1 */
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuyixingkong/
自己命运的掌控着!




