感知机算法python实现
感知机算法(Perceptron Learning Algorithm)是一个很容易实现的算法。本文对PLA 算法做了一个简单的实验,在数据集线性可分时,可以证明PLA算法最终会收敛。
生成数据
首先随机生成数据点,然后随机生成目标函数 \(f\) 的权重 \(weights\)。
def generate_data(num_of_data, num_of_features):
"""Generate random data and weight vector.
Keyword arguments:
num_of_data -- The number of datapoints
num_of_features -- The number of features
Returns:
X - The features of datapoints
y - The labels of datapoints
weights - Random weights
"""
X = np.ones((num_of_data, num_of_features + 1))
# generate random features
X[:, 1:] = np.random.randint(-1000, 1000, (num_of_data, num_of_features))
weights = np.random.randint(-1000, 1000, num_of_features + 1)
weights = weights.reshape(-1, 1)
print(weights.shape)
y = np.dot(X, weights)
y[y>=0] = 1
y[y<0] = -1
return X, y, weights
PLA 算法
PLA 算法的更新规则是:循环检测数据点是否能够被正确分类,如果分类错误,则: \(\boldsymbol{w}_{t+1}=\boldsymbol{w}_t+y_{t}\boldsymbol{x}(t)\),其中\((\boldsymbol{x}_t, y_{t})\)是被分类错误的数据点。
def sign(x):
if x >= 0:
return 1
else:
return -1
class PLA:
"""Perceptron Learning Algorithm"""
def __init__(self):
self.w = None
def train(self, X, y, shuffle=False):
num_of_data, num_of_features = X.shape
# initialize weights
w = np.zeros(num_of_features)
cycle_index = [index for index in range(num_of_data)]
# shuffle the order of datapoints
i, num_of_iter = 0, 0
while i < num_of_data:
if shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(cycle_index)
if sign(np.sum(X[cycle_index[i]]*w)) != y[cycle_index[i]]:
w += y[cycle_index[i]] * X[cycle_index[i]]
i = 0
num_of_iter += 1
i += 1
self.w = w
return w, num_of_iter
def test(self, x):
return sign(np.dot(x, self.w))
实验操作
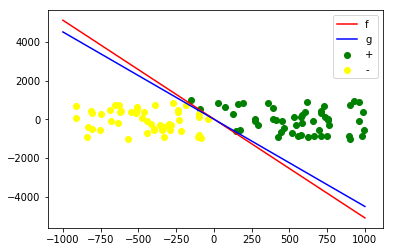
X, y, weights = generate_data(100, 2)
pla = PLA()
w, iternum = pla.train(X, y)
iternum
x_linspace = np.linspace(-1000, 1000, 10000)
y_real = [-weights[1]/weights[2]*x - weights[0]/weights[2] for x in x_linspace]
y_pred = [-w[1]/w[2]*x - w[0]/w[2] for x in x_linspace]
y = y.reshape(-1,)
plt.plot(x_linspace, y_real, 'r', label="f")
plt.plot(x_linspace, y_pred, 'b', label="g")
plt.scatter(X[y==1, 1], X[y==1, 2], color='green', label="+")
plt.scatter(X[y==-1, 1], X[y==-1, 2], color='yellow', label="-")
plt.legend()