Java/C++实现解释器模式---机器人控制程序
某机器人控制程序包含一些简单的英文指令,其文法规则如下:
expression ::= direction action distance | composite
composite ::= expression and expression
direction ::= ‘up’ | ‘down’ | ‘left’ | ‘right’
action ::= ‘move’ | ‘run’
distance ::= an integer //一个整数值
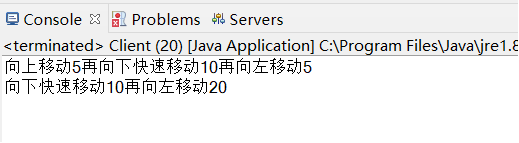
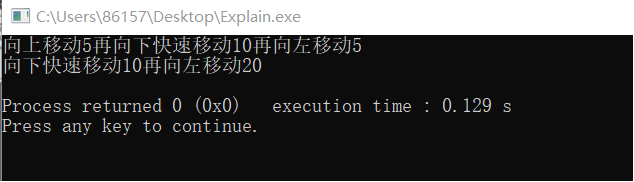
如输入:up move 5,则输出“向上移动5个单位”;输入:down run 10 and left move 20,则输出“向下移动10个单位再向左移动20个单位”。
类图:

Java代码:
import java.util.Stack; public abstract class AbstractNode { public abstract String interpret(); } public class ActionNode extends AbstractNode{ private String action; public ActionNode(String action) { this.action = action; } //动作(移动方式)表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("move")) { return "移动"; } else if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("run")) { return "快速移动"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } } public class AndNode extends AbstractNode{ private AbstractNode left; //And的左表达式 private AbstractNode right; //And的右表达式 public AndNode(AbstractNode left, AbstractNode right) { this.left = left; this.right = right; } //And表达式解释操作 public String interpret() { return left.interpret() + "再" + right.interpret(); } } public class DirectionNode extends AbstractNode{ private String direction; public DirectionNode(String direction) { this.direction = direction; } //方向表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("up")) { return "向上"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("down")) { return "向下"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("left")) { return "向左"; } else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("right")) { return "向右"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } } public class DistanceNode extends AbstractNode{ private String distance; public DistanceNode(String distance) { this.distance = distance; } //距离表达式的解释操作 public String interpret() { return this.distance; } } public class InstructionHandler { private String instruction; private AbstractNode node; public void handle(String instruction) { AbstractNode left = null, right = null; AbstractNode direction = null, action = null, distance = null; Stack stack = new Stack(); //声明一个栈对象用于存储抽象语法树 String[] words = instruction.split(" "); //以空格分隔指令字符串 for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) { //本实例采用栈的方式来处理指令,如果遇到“and”,则将其后的三个单词作为三个终结符表达式连成一个简单句子SentenceNode作为“and”的右表达式,而将从栈顶弹出的表达式作为“and”的左表达式,最后将新的“and”表达式压入栈中。 if (words[i].equalsIgnoreCase("and")) { left = (AbstractNode)stack.pop(); //弹出栈顶表达式作为左表达式 String word1= words[++i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); String word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); String word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); right = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); //右表达式 stack.push(new AndNode(left,right)); //将新表达式压入栈中 } //如果是从头开始进行解释,则将前三个单词组成一个简单句子SentenceNode并将该句子压入栈中 else { String word1 = words[i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); String word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); String word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); left = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); stack.push(left); //将新表达式压入栈中 } } this.node = (AbstractNode)stack.pop(); //将全部表达式从栈中弹出 } public String output() { String result = node.interpret(); //解释表达式 return result; } } public class SentenceNode extends AbstractNode{ private AbstractNode direction; private AbstractNode action; private AbstractNode distance; public SentenceNode(AbstractNode direction,AbstractNode action,AbstractNode distance) { this.direction = direction; this.action = action; this.distance = distance; } //简单句子的解释操作 public String interpret() { return direction.interpret() + action.interpret() + distance.interpret(); } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String instruction1 = "up move 5 and down run 10 and left move 5"; String instruction2="down run 10 and left move 20"; InstructionHandler handler = new InstructionHandler(); handler.handle(instruction1); String outString; outString = handler.output(); System.out.println(outString); handler.handle(instruction2); outString = handler.output(); System.out.println(outString); } }
C++代码:
#include<iostream> #include<stack> #include <sstream> #include<string> using namespace std; class AbstractNode { public: virtual string interpret()=0; }; class ActionNode:public AbstractNode{ private: string action; public: ActionNode(string action) { this->action = action; } string interpret() { if (action=="move") { return "移动"; } else if (action=="run") { return "快速移动"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } }; class AndNode:public AbstractNode{ private: AbstractNode *left; //And的左表达式 AbstractNode *right; //And的右表达式 public: AndNode(AbstractNode *left, AbstractNode *right) { this->left = left; this->right = right; } //And表达式解释操作 string interpret() { return left->interpret() + "再" + right->interpret(); } }; class DirectionNode :public AbstractNode{ private: string direction; public: DirectionNode(string direction) { this->direction = direction; } //方向表达式的解释操作 string interpret() { if (direction=="up") { return "向上"; } else if (direction=="down") { return "向下"; } else if (direction=="left") { return "向左"; } else if (direction=="right") { return "向右"; } else { return "无效指令"; } } }; class DistanceNode:public AbstractNode{ private: string distance; public: DistanceNode(string distance) { this->distance = distance; } //距离表达式的解释操作 string interpret() { return this->distance; } }; class SentenceNode:public AbstractNode{ private: AbstractNode *direction; AbstractNode *action; AbstractNode *distance; public: SentenceNode(AbstractNode *direction,AbstractNode *action,AbstractNode *distance) { this->direction = direction; this->action = action; this->distance = distance; } //简单句子的解释操作 string interpret() { return direction->interpret() + action->interpret() + distance->interpret(); } }; class InstructionHandler { private: string instruction; AbstractNode *node; public: void handle(string instruction) { AbstractNode *left = NULL, *right = NULL; AbstractNode *direction = NULL, *action = NULL, *distance = NULL; stack<AbstractNode*> stack; //声明一个栈对象用于存储抽象语法树 istringstream str1(instruction); istringstream str2(instruction); string out; int j=0,k=0; int n; //以空格分隔指令字符串 while (str1 >> out) { j++; } n=j; string words[n]; string out2; while (str2 >> out2) { words[k]=out2; k++; } for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) { //本实例采用栈的方式来处理指令,如果遇到“and”,则将其后的三个单词作为三个终结符表达式连成一个简单句子SentenceNode作为“and”的右表达式,而将从栈顶弹出的表达式作为“and”的左表达式,最后将新的“and”表达式压入栈中。 if (words[i]=="and") { left = stack.top(); //弹出栈顶表达式作为左表达式 stack.pop(); string word1= words[++i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); string word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); string word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); right = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); //右表达式 stack.push(new AndNode(left,right)); //将新表达式压入栈中 } //如果是从头开始进行解释,则将前三个单词组成一个简单句子SentenceNode并将该句子压入栈中 else { string word1 = words[i]; direction = new DirectionNode(word1); string word2 = words[++i]; action = new ActionNode(word2); string word3 = words[++i]; distance = new DistanceNode(word3); left = new SentenceNode(direction,action,distance); stack.push(left); //将新表达式压入栈中 } } this->node = stack.top(); //将全部表达式从栈中弹出 stack.pop(); } string output() { string result = node->interpret(); //解释表达式 return result; } }; int main(){ string instruction1 = "up move 5 and down run 10 and left move 5"; string instruction2="down run 10 and left move 20"; InstructionHandler *handler = new InstructionHandler(); handler->handle(instruction1); string outString; outString = handler->output(); cout<<outString<<endl; handler->handle(instruction2); outString = handler->output(); cout<<outString<<endl; }
运行结果:





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!