Guiding CDCL SAT Search via Random Exploration amid Conflict Depression
Md Solimul Chowdhury, Martin M¨ uller, Jia-Huai You
Department of Computing Science, University of Alberta
Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
{mdsolimu, mmueller, jyou}@ualberta.ca
Abstract
|
The efficiency of Conflict Driven Clause Learning (CDCL) SAT solving depends crucially on finding conflicts at a We take a closer look at the way in which conflicts are generated over the course of a CDCL SAT search. 译文:我们将仔细研究在CDCL SAT搜索过程中产生冲突的方式。
Our study of the VSIDS branching heuristic shows that conflicts are typically generated in short bursts, followed by what we call a conflict depression phase in which the search fails to generate any conflicts in a span of decisions. 译文:我们对vsid分支启发式的研究表明,冲突通常在短时间内产生,随后是我们所说的冲突抑郁阶段,在这个阶段中,搜索不能在一系列决策中产生任何冲突。 The lack of conflict indicates that the variables that are currently ranked highest by the branching heuristic fail to generate conflicts.译文:缺少冲突表明,目前在分支启发式中排名最高的变量不能产生冲突。 Based on this analysis, we propose an exploration strategy, called expSAT, which randomly samples variable selection sequences in order to learn an updated heuristic from the generated conflicts. 译文:在此基础上,我们提出了一种探索策略,称为expSAT,它随机抽样变量选择序列,以从产生的冲突中学习得到一个更新的启发式。 The goal is to escape from conflict depressions expeditiously. 译文:目标是迅速摆脱冲突带来的萧条。 The branching heuristic deployed in expSAT combines these updates with the standard VSIDS activity scores. 译文:expSAT中部署的分支启发式方法将这些更新与标准vsid活动分数结合起来。 An extensive empirical evaluation with four state-of-the-art CDCL SAT solvers demonstrates good-to-strong performance gains with the expSAT approach. 译文:一个广泛的经验评估与四个最先进的CDCL SAT解决方案,证明了采用expSAT方法能带来良好的性能收益。 |
|
Introduction
|
These heuristics reward variables involved in recent conflicts. The intuition is that assignments of these variables are likely to generate further conflicts, leading to useful learned clauses and thus pruning the search space. 译文:这些启发策略奖励最近冲突中涉及的变量。直觉是,这些变量的赋值很可能产生进一步的冲突,导致有用的学习子句,从而修剪搜索空间。 |
|
Preliminaries
|
We assume familiarity with SAT solving (Biere et al. 2009). |
|
|
Software, Hardware and Test Environment In this varying the range parameter, which determines the difficulty |
|
Conflict Depression and Conflict Bursts
 |
|
|
Let us represent the conflict history of the search by the sequence of ci and define a conflict depression (CD) phase as a sequence of one or more consecutive decisions with no conflict. 译文:让我们用ci的序列来表示搜索的冲突历史,并将冲突压抑(CD)阶段定义为一个或多个没有冲突的连续决策的序列。 |
|
| Let us define a conflict burst (CB) phase as a sequence of one or more consecutive decisions with at least one conflict.译文:让我们将冲突爆发(CB)阶段定义为一个或多个具有至少一个冲突的连续决策的序列。 | |
 |
|
|
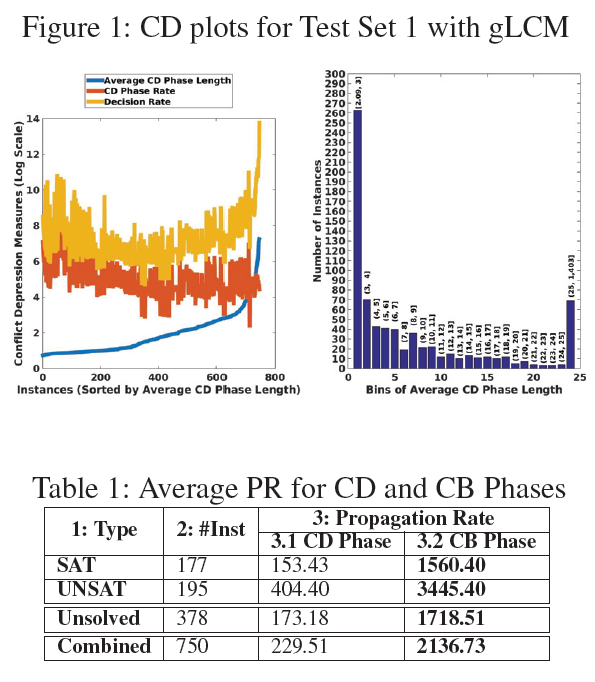
译文:我们注意到,大多数情况下,CD的平均阶段长度都很短,但仍然包含多个决策(蓝色)。 译文:不管它们的平均CD阶段长度如何,在给定决策率(黄色)的情况下,几乎所有的CD阶段(橙色)都以很高的速率出现. |
|
|
译文:图1右侧的直方图显示了CD相平均长度的分布。 译文:这个平均值从2.09到1402.30。263个实例的长度很短(最多3个)。分布是重尾的,有69个平均长度大于25(最右边的bin)。 |
|
|
Overall, the data indicates that for gLCM on Test Set 1, conflict depressions occur frequently and often last over |
|
|
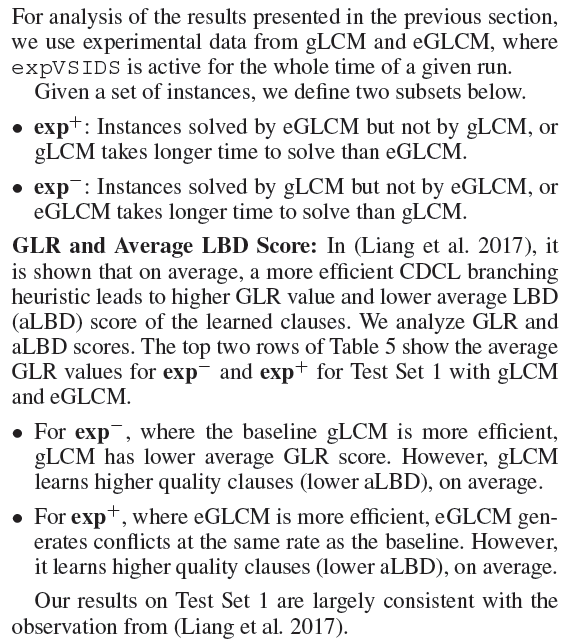
Propagation Depression Amid a CD Phase During a CD phase, VSIDS scores are not a good predictor of a variable’s future performance, since branching decisions fail to produce any conflict and perform only truth value propagations.译文:在CD阶段,vsid分数并不是变量未来性能的良好预测器,因为分支决策不会产生任何冲突,只执行真值传播。
We define the Propagation Rate (PR) as the number of propagations per decision. Table 1 compares the average PR values for Test Set 1 over the decisions in CD and CB phases.译文:我们将传播速率(PR)定义为每个决策的传播次数。表1比较了测试集1在CD和CB阶段的平均PR值。 On average, PR values during a CD phase are almost 10 times lower than CB phases. Clearly, this result demonstrates that during a CD phase, VSIDS branching decisions go through propagation depression as well.译文:平均而言,CD阶段的PR值几乎比CB阶段低10倍。显然,这一结果表明,在CD阶段,vsid分支决策也经历了传播抑制。 |
|
|
Conflict Bursts in gLCM Thus, on average, shorter CB phases are followed by much longer CD phases.译文:因此,平均而言,较短的转CB阶段之后是较长的CD阶段。 |
|
|
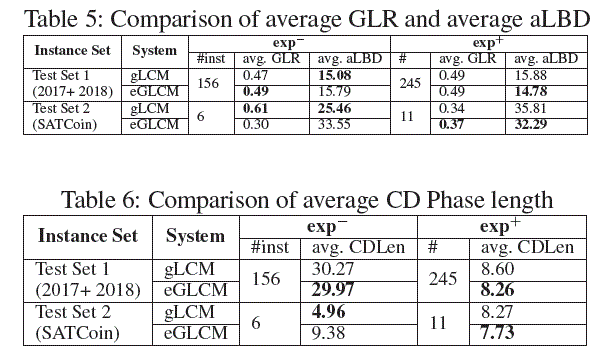
Bursts of Conflict Generation 冲突的爆发 Table 2 shows the average values of GLR, FDC, FDOC and FDMC for Test Set 1. Column 3 shows the average GLR values for all three types of problems to be close to 0.5.译文:三种问题的平均GLR值均接近0.5。 In contrast, the average FDC values in column 4 are much lower, averaging 0.2507 over all instances.译文:相比之下,第4列中的平均FDC值要低得多,所有实例的平均FDC值为0.2507。
Therefore, on average, about 75% of all than 1 conflict. This is evident in the average FDMC value
译文:典型的搜索行为包括较短的CB阶段,随后是较长的CD阶段,在这些阶段中搜索不会发现任何冲突。
|
|
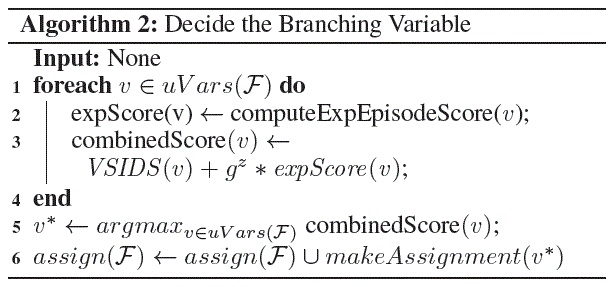
Exploration Guided VSIDS 探索vsid的引导作用
|
Is it possible to correct the course of the search in a CD phase by identifying promising variables that are currently underranked by VSIDS? 译文:是否有可能通过识别目前vsid低估的有希望的变量来纠正CD阶段的搜索过程? In this work, we address this question by formulating a solver framework, called expSAT, which performs The goal is to discover branching variables that are likely to lead to conflicts from which clauses are learned.译文:其目标是发现可能导致冲突的分支变量。
1. Before each branching decision, if a substantial CD phase is detected, then with probability pexp, expSAT performs an exploration episode, consisting of a fixed number nW of random walks. 译文:在每个分支决策之前,如果检测到一个重要的CD阶段,那么expSAT将以概率pexp执行一个由固定数量的nW随机漫步组成探索阶段。
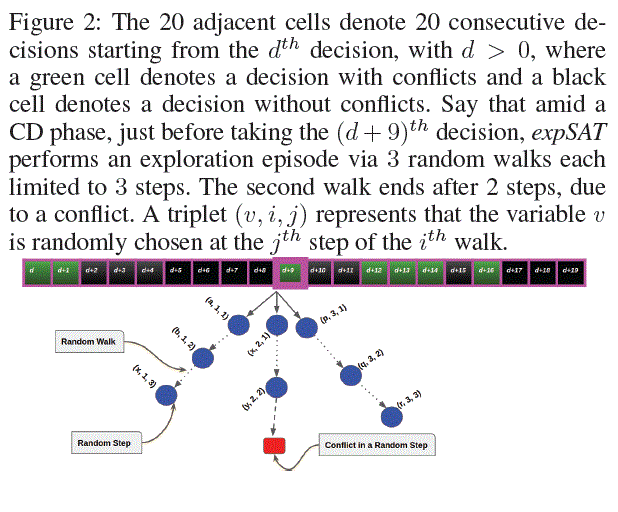
Each walk consists of a limited number of random steps. Each such step consists of the uniform random selection of an unassigned step variable, followed by unit propagation (UP).译文:每次行走都包含有限的随机步数。每个这样的步骤由一个未分配的步骤变量的均匀随机选择,然后是单位传播(UP)。 A walk terminates either when a conflict occurs during UP, or after a fixed number lW of random steps have been taken.译文:当UP期间发生冲突时,或者在执行了固定数量的lW随机步骤后,游走终止 After each walk, the search state is restored and the next walk begins.译文:每次行走之后,将恢复搜索状态,并开始下一次行走。 Fig. 2 illustrates an exploration episode with 3 walks and a maximum of 3 random steps per walk.译文:图2显示了3次行走和每次最多3次随机行走的探索阶段。
• An exploration score is computed for each step variable.译文:为每个步骤变量计算一个探索分数。
|
||
|
Algorithm Details
Input and Parameters
All these parameters are explained above, except ω, which we explain below. 译文:所有这些参数都在上面解释了,除了ω,我们在下面解释。
In expSAT, we assign the most credit to the most recently assigned variable, and exponentially decay the credit for the variables assigned earlier in the walk, by a factor of ω per decision step. This approach is patterned on reward decay in reinforcement learning (Sutton and Barto 1998).译文:在expSAT中,我们为最近分配的变量分配了最多的积分,并以指数形式衰减在行走中较早分配的变量的积分,每个决策步骤的系数为ω。这种方法是以强化学习中的奖励衰减为模式的(Sutton and Barto 1998)。 |
||
|
|

|
|
 |
||
 |
||
Experiments
|
We implemented expSAT in four systems gLCM, MplCOMSPS, |
|
|
We compare the performance of these systems on Test |
|
 |
|
|
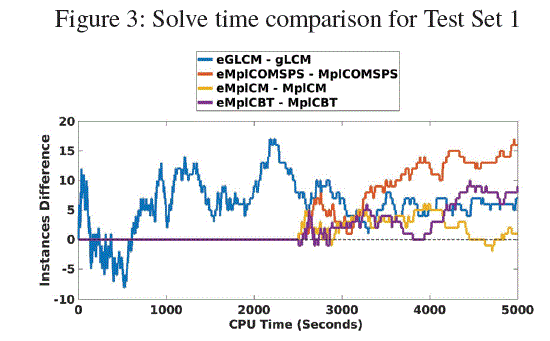
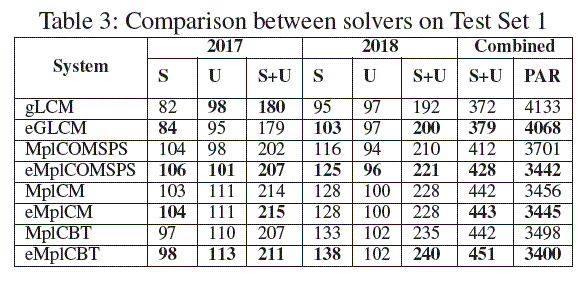
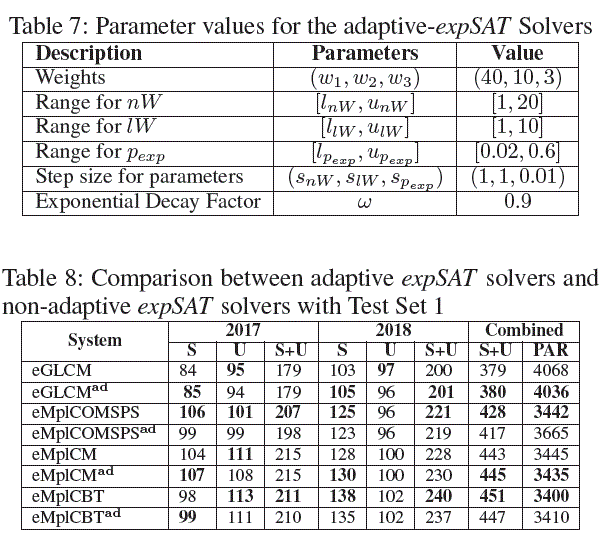
Comparison on Test Set 1 Table 3 (S: SAT, U: UNSAT) |
|
|
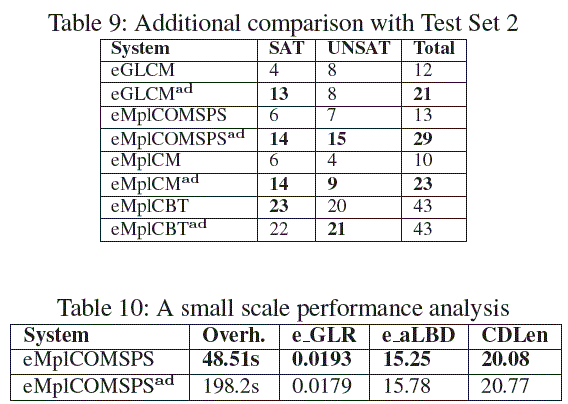
Comparison on Test Set 2 For SAT-2018, 17 SATCoin iment into perspective, we ran experiment with CryptoMiniSAT57, |
|
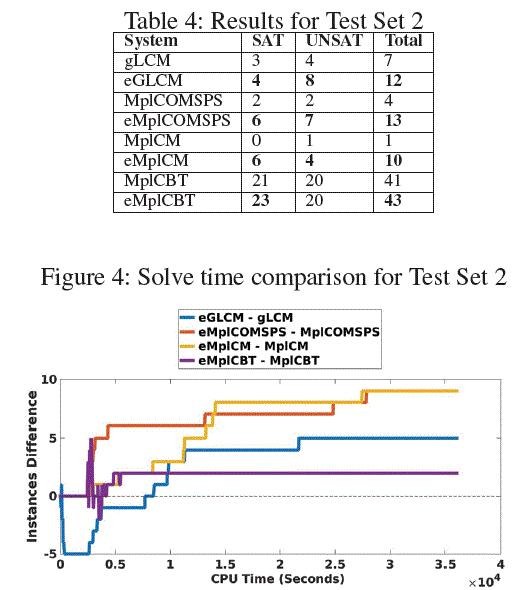
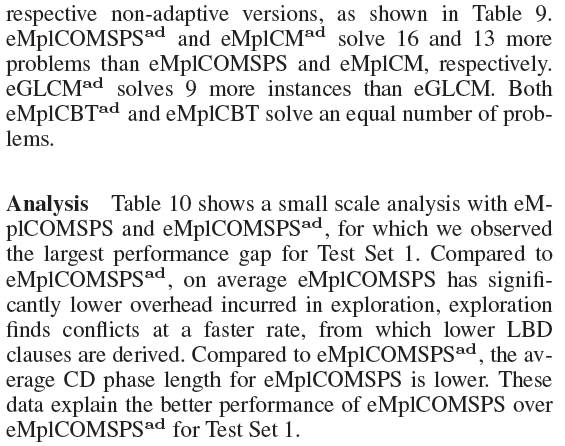
Analysis of the Experimental Results
 |
|
 |
|
|
|

|
|
 |
|
 |
|
Exploration Parameter Adaptation
|
A parameter setting that is effective for one instance may not |
|
|
paramAdapt The three exploration parameters nW, lW, |
|

|
|
|
|
Related Work (前期有随机探索工作文献 和 CDCL与SLS结合文献)
|
Randomized exploration in SAT is used in local search methods such as GSAT (Selman, Levesque, and Mitchell 译文:SAT中的随机探索被用于局部搜索方法,如GSAT(Selman, Levesque,和Mitchell)和walksat (Selman, Kautz和Cohen 1993)。
The Satz algorithm (Li and Anbulagan 1997) heuristically selects a variable x, then performs two separate unit propagations with x and (¬x) respectively, in order to evaluate the potential of x. 译文:Satz算法(Li和Anbulagan 1997)启发式地选择一个变量x,然后分别用x和(¬)执行两个单独的单元传播,以评估x的潜力。
Modern CDCL SAT solvers include exploration components such as a small amount of random variable
UCTSAT (Previti et al. 2011) employs Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to build a SAT search tree. 译文:UCTSAT (Previti et al. 2011)采用蒙特卡洛树搜索(Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS)构建SAT搜索树。
Exploration can make a search process more robust by allowing an escape from early mistakes caused by inaccurate heuristics (Xie et al. 2014). 译文:探索可以通过避免不准确的启发式导致的早期错误而使搜索过程更加健壮(Xie et al. 2014)。
Examples of recently popular exploration methods in search are MCTS (Browne et al. 2012) and the random walk techniques used in classical planning (Nakhost andM¨uller 2009). 译文:最近在搜索中流行的探索方法的例子是MCTS (Browne et al. 2012)和经典规划中使用的随机游走技术(Nakhost and m¨uller 2009)。 These techniques motivated our work on random exploration in CDCL SAT. 译文:这些技术激发了我们在CDCL SAT中进行随机探索的工作。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CDCL与SLS的结合文献 SATHYS (Audemard et al. 2010) employs both a CDCL SAT solver and a local search SAT solver. The latter helps the CDCL solver by identifying the most promising literal assignment to branch on, and the CDCL search process guides the local search process to flee from local minima. 译文:SATHYS (Audemard等人2010)同时使用CDCL SAT求解器和本地搜索SAT求解器。后者帮助CDCL求解器识别最有希望的文字分配到分支上,CDCL搜索过程指导局部搜索过程逃离局部最小值。
The Conflict History Based (CHB) (Liang et al. 2016a) and Learning Rate Based (LRB) (Liang et al. 2016b) heuristics model variable selection as a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) problem, which is solved using the Exponential Recency Weighted Average (ERWA) algorithm. 译文:基于冲突历史(CHB) (Liang et al. 2016a)和基于学习率(LRB) (Liang et al. 2016b)启发式模型变量选择作为一个多武装强盗(MAB)问题,该问题使用指数近期加权平均(ERWA)算法解决。
Both of these heuristics compute rewards from the conflict history of unassigned variables, in order to rank them. 译文:这两种启发法都从未分配变量的冲突历史中计算奖励,以便对它们进行排序。
In contrast, we modify the VSIDS rank of variables based on the quality of conflicts generated by random exploration of the future states. 译文:相比之下,我们根据对未来状态的随机探索所产生的冲突的质量来修改变量的VSIDS排名。
Compared to the look-ahead based heuristic that maximize the GLR score (Liang et al. 2017), we perform nondeterministic exploration of the search space with a small subset of unassigned variables per random walk, and prioritize variables that generate high-quality conflicts. 译文:与最大化GLR分数的基于前瞻的启发式方法(Liang et al. 2017)相比,我们在每次随机游走中使用一小部分未分配变量对搜索空间进行不确定性探索,并对产生高质量冲突的变量进行优先排序。
As overhead is disregarded in their work, there is no direct basis for comparison. 译文:由于在他们的工作中忽略了间接费用,因此没有直接的比较基础。 |
|
Future Work
|
Future Work The ineffectiveness of VSIDS in conflict depressions can be addressed by performing exploration. Interesting research avenues to explore further include: 译文:将expSAT与基于LRB和CHB的系统集成
译文:研究探索,如expSAT指导极性选择。,通过扩展节省相位的启发式。
译文:开发机器学习方法来预测长CD期的开始。
译文:更好地理解CD相的性质(如长度)与求解器性能之间的关系。
译文:确定影响勘探效果的SAT领域的特征。 |
|