1。 Off the Trail: Re-examining the CDCL Algorithm
Huang, J.: A Case for Simple SAT Solvers. In: Bessi`ere, C. (ed.) CP 2007. LNCS,
vol. 4741, pp. 839–846. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
|
1 Introduction |
|
|
Combinations of features, however, can sometimes interact in complex ways that can undermine the original motivation of individual features. 译文:然而,特征的组合有时会以复杂的方式相互作用,从而破坏个体特征的原始动机。 For example, phase saving, also called light-weight component caching, was conceived as a progress saving technique, so that backtracking would not retract already discovered solutions of disjoint subproblems [12] and then have to spend time rediscovering these solutions. 译文:阶段保存(也称为轻量级组件缓存)被认为是一种进度保存技术,这样回溯就不会收回已经发现的不相连接的子问题[12]的解决方案,然后就不得不花时间重新发现这些解决方案。 However, when we add phase saving to restarts, we reduce some of the randomization introduced by restarts, potentially limiting the ability of restarts to short-circuit heavy-tailed run-times. 译文:然而,当我们为重启添加阶段保存时,我们减少了由重启引入的一些随机性,潜在地限制了重启的能力,使其成为短路的大尾部运行时。 Nevertheless, even when combined, restarts and phase saving both continue to provide a useful performance boost in practice and are both commonly used in CDCL solvers. 译文:然而,即使将重启和阶段节省结合起来,它们在实践中也会继续提供有用的性能提升,而且它们在CDCL求解器中都是常用的。 |
|
|
When combined with a strong activity-based heuristic, phase saving further 译文:当与强大的基于活动的启发式相结合时,阶段保存将进一步改变重启的行为。 In this context it is no longer obvious that restarts serve to move the solver to a different part of the search space. 译文:在这种情况下,重启不再是将求解器移动到搜索空间的不同部分。 Instead, it can be shown empirically that after a restart a large percentage of the trail is re-created exactly as it was prior to the restart, indicating that the solver typically returns to the same part of the search space. 译文:相反,它可以证明,在重新启动后,很大比例的trail被重新创建,完全与重新启动前一样,这表明求解器通常返回到搜索空间的相同部分。
In fact, there is evidence to support the conclusion that the main effect of restarts in current solvers is simply 译文:事实上,有证据支持这一结论,即当前求解器中重启的主要作用是简单地根据改变的启发式分数更新轨迹。 For example, [14] show that often a large part of the trail can be reused after backtracking. With 译文:例如,[14]表明,在回溯之后,跟踪的很大一部分可以被重用。通过适当的实现技术,重用而不是重建trail可以通过减少重启的计算成本来加快搜索速度。 |
|
|
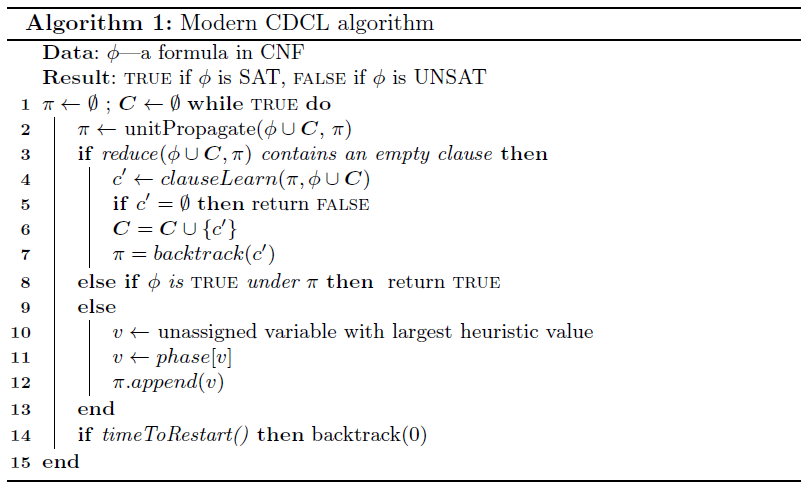
In this paper we examine another feature of modern SAT solvers that ties them with the historical paradigm of DPLL: the trail used to keep track of the current set of variable assignments. 译文:在这篇论文中,我们检查与DPLL的历史范式联系他们的现代SAT求解器的另一个特征:用来保持变量赋值的当前集的跟踪的轨迹。
We show that modern SAT solvers, in which phase savings causes an extensive recreation of the trail after backtracking, can actually be reformulated as local search algorithms. 译文:我们表明,现代的SAT解算器,其中相位节省导致回溯后的广泛重建的轨迹,实际上可以重新制定为局部搜索算法。 |
|
|
Local search solvers work with complete truth assignments [15], and a single step usually consists of picking a variable and flipping its value. Local search algorithms have borrowed techniques from CDCL. For example, unit propagation has been employed [6,8,2], and clause learning as also been used [1]. However, such solvers are usually limited to demonstrating satisfiability, and often cannot be used to reliably prove UNSAT. 译文:然而,这样的求解程序通常被限制于证明可满足性,并且常常不能被可靠地用于证明UNSAT。 Our reformulation of the CDCL algorithm yields a local search algorithm that is able to derive UNSAT since it can perform exactly the same steps as CDCL would. It also gives a different perspective on the role of the trail in CDCL solvers. 译文:我们对CDCL算法的重新表述产生了一个能够导出UNSAT的局部搜索算法,因为它可以执行与CDCL完全相同的步骤。 译文:它也给出了CDCL求解器中trail的角色的不同视角。
In particular, we show that the trail can be viewed as providing an ordering of the literals in the current truth assignment, an ordering that can be used to guide clause learning. 译文:特别地,我们展示了trail可以被视为在当前的真理赋值中提供一个文字的顺序,一个可以用来指导子句学习的顺序。
This view allows more flexible clause learning techniques to be developed, and different types of heuristics to be supported.译文:这个观点允许开发更灵活的子句学习技术,并支持不同类型的启发式。 It also opens the door for potentially reformulating QBF algorithms, which suffer from strong restrictions on the ordering of the variables on the trail. 译文:这也为潜在的重新制定QBF算法打开了大门,这种算法受到路径上变量排序的强烈限制。 |
|
|
2 Examining the CDCL Algorithm 3 Local Search |
|
|
|
|






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
2020-03-28 SLS求解器学习walkSAT2
2020-03-28 定期关注文献——查询关键字
2020-03-28 SLS求解器学习walkSAT1