C++ string 内存管理
String 是STL里面的类似一个字符串容器。
String对象调用append(),不能之家已有的字符串加大,因为相邻的内存可能被占用,因此需要分配一个新的内存块,将原来的内存赋值到新的内存块中。这样会降低效率。
所以c++实现分配了一个比实际字符串大的内存块,如果字符串不断增大,超过了内存块大小,程序将分配一个大小为原理两倍的新内存卡,以提高足够的空间。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string empty;
string small = "bit";
string large = "Elephants are a girl's best friend";
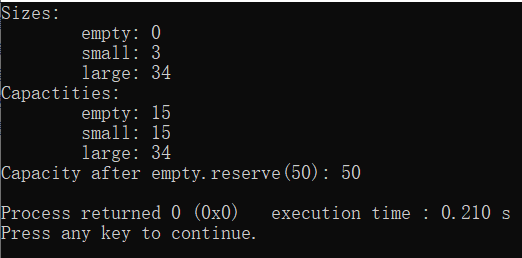
cout << "Sizes:"<<endl;
cout << "\tempty: "<< empty.size()<<endl;
cout << "\tsmall: "<< small.size()<<endl;
cout << "\tlarge: "<< large.size()<<endl;
//重新分配内存大小
cout << "Capactities: \n";
cout << "\tempty: "<< empty.capacity()<<endl;
cout << "\tsmall: "<< small.capacity()<<endl;
cout << "\tlarge: "<< large.capacity()<<endl;
//reserve方法能够请求内存块的最小长度
empty.reserve(50);
cout << "Capacity after empty.reserve(50): "
<< empty.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号