[论文笔记] Direct Answers for Search Queries in the Long Tail (CHI, 2012)
Time: 2.5 hours
Timespan: July 17 – July 19, 2012
Michael S. Bernstein, Jaime Teevan, Susan Dumais, Daniel Liebling, and Eric Horvitz. 2012. Direct answers for search queries in the long tail. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM annual conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '12). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 237-246.
作者Michael Bernstein今年才刚从EECS@MIT毕业,师从David Karger and Rob Miller,将去斯坦福的计算机系做assistant professor。他的研究方向是"combine computation with crowds to create systems that are powered by collective intelligence",博士毕业论文题目是"Crowd-Powered Systems"。
这篇论文获得了CHI12的"best paper nomination ",主要讨论了在搜索引擎中,如何为不太常见的问题设计嵌入下拉式的"长尾答案"。以下是论文笔记:
1. 本文中的一个重要概念: Tail Answers (长尾答案,以下简称TA)
"a large collection of direct answers that are unpopular individually, but together address a large proportion of search traffic."
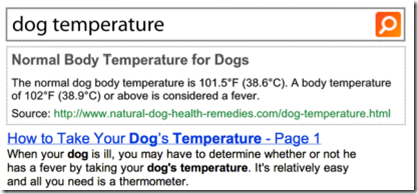
比如以下问题的答案就属于TA: 狗的平均体温是多少?糖浆的替代品是什么?
从形式上来看,TA是嵌入下拉式的(如下图),以减少用户操作步骤。
2. 研究问题:现有搜索引擎对一些很常用的信息(比如温度)提供嵌入下拉式的答案(无须用户进一步点击),使用传统方法制作这种嵌入下拉式的答案成本较高(需要指派编码人员、设计人员、测试人员等创建和维护);对于众多的"长尾问题"(一年可能会出现几千次,在互联网上算比较小的数量),从成本上来说无法使用传统方法制作嵌入下拉式答案。
本文正是提出了一种基于日志分析及众包技术,来创建长尾答案的解决方案。主要分为以下三个步骤(技术细节见论文S3):
- identify answer candidates – using aggregate search and browsing patterns
- filter answer candidates – using search logs and paid crowdsourcing
- extracting the tail anserver – using paid crowdsourcing