RNN pytorch 源码之头发掉光版解析
本萌新本来想好好学习下PYTORCH 版LSTM使用,学着学着还是一知半解 就准备去看看LSTM源码实现,发现是继承自RNN 类,结果就来弄清楚RNN 源码,真实学海无涯 头发有限。。。。
咱先从最简单的RNN模型下手,先不管几层layer叠加、方向问题,小萌新突然发现 从源码学习真的进步大,胜过看好多别人整理的博客。
那我就从源码注释处
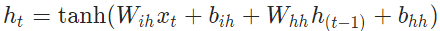
Inputs: input, h_0 - **input** of shape `(seq_len, batch, input_size)`: tensor containing the features of the input sequence. The input can also be a packed variable length sequence. See :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence` or :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_sequence` for details. - **h_0** of shape `(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)`: tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch. Defaults to zero if not provided. If the RNN is bidirectional, num_directions should be 2, else it should be 1. Outputs: output, h_n - **output** of shape `(seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size)`: tensor containing the output features (`h_t`) from the last layer of the RNN, for each `t`. If a :class:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence` has been given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence. For the unpacked case, the directions can be separated using ``output.view(seq_len, batch, num_directions, hidden_size)``, with forward and backward being direction `0` and `1` respectively. Similarly, the directions can be separated in the packed case. - **h_n** of shape `(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)`: tensor containing the hidden state for `t = seq_len`. Like *output*, the layers can be separated using ``h_n.view(num_layers, num_directions, batch, hidden_size)``. Shape: - Input1: :math:`(L, N, H_{in})` tensor containing input features where :math:`H_{in}=\text{input\_size}` and `L` represents a sequence length. - Input2: :math:`(S, N, H_{out})` tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch. :math:`H_{out}=\text{hidden\_size}` Defaults to zero if not provided. where :math:`S=\text{num\_layers} * \text{num\_directions}` If the RNN is bidirectional, num_directions should be 2, else it should be 1. - Output1: :math:`(L, N, H_{all})` where :math:`H_{all}=\text{num\_directions} * \text{hidden\_size}` - Output2: :math:`(S, N, H_{out})` tensor containing the next hidden state for each element in the batch Attributes: weight_ih_l[k]: the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape `(hidden_size, input_size)` for `k = 0`. Otherwise, the shape is `(hidden_size, num_directions * hidden_size)` weight_hh_l[k]: the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape `(hidden_size, hidden_size)` bias_ih_l[k]: the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer, of shape `(hidden_size)` bias_hh_l[k]: the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer, of shape `(hidden_size)` .. note:: All the weights and biases are initialized from :math:`\mathcal{U}(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k})` where :math:`k = \frac{1}{\text{hidden\_size}}` .. include:: ../cudnn_rnn_determinism.rst .. include:: ../cudnn_persistent_rnn.rst Examples:: >>> rnn = nn.RNN(10, 20, 2) >>> input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10) >>> h0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20) >>> output, hn = rnn(input, h0)
输入
输入句子shape= `(seq_len, batch, input_size),我们一下子往模型输入5个句子,每个句子长度不一致,以最长长度10作为MAX_LENGTH,每个token 用300个数字来表示,那shape=(5,10,300)
h_0 shape=(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size),如果没有提供的话,就设为0
输出
第一个返回值(output)是最后一层 所有时刻的隐藏状态,因为每个time step 都有输出,所以第一维大小等于 seq_length,第三维的话,如果是双向的话,是需要在每个time step上将前向的隐状态和后向的隐状态进行拼接,因而大小是 方向数*hidden_size,维度是 (seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size)第二个返回值(hn)是每一层最后一个时刻的隐藏状态,如果是最简单的一层lstm,单向的话,hn 就等于output[-1],维度是(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size),我们解释下第一维度,该维度表示每一层最后一个time step的输出,假设我们现在是双向的,共有两层,h_n[0]表示第一层前向传播最后一个time
step的输出,h_n[1]表示第一层后向传播最后一个time step的输出,h_n[2]表示第二层前向传播最后一个time step的输出,h_n[3]表示第二层后向传播最后一个time step的输出
import torch import torch.nn as nn rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=150, hidden_size=300, num_layers=2, bidirectional=True,batch_first=False) input = torch.randn(10, 5, 150) h0 = torch.randn(4, 5, 300) c0 = torch.randn(4, 5, 300) output,hn = rnn(input, h0) print('output shape: ', output.shape) print('hn shape: ', hn.shape) 运行结果如下: output shape: torch.Size([10, 5, 600]) hn shape: torch.Size([4, 5, 300])
接下来加深下我们对参数output,hn的理解
1.前向传播时,output中最后一个time step的前300个 应该与hn最后一层前向传播的输出应该一致。
output[-1, 0, :20] == hn[2, 0,:]
output中第一个句子 最后一个time step的前300个 应该写成 output[-1, 0, :300](或者 output[9, 0, :300])hn第一个句子最后一层前向传播的输出hn[2, 0,:],0表示 第一层前向传播最后一个time step,1表示第一层后向传播最后一个time step,2表示第二次前向传播最后一个time step
print(output[-1,0,:300]) print(output[-1,0,:300]==hn[2,0,:])
跑出来结果是对的哦,只怪我不该取那么高的hidden size,打印出来太多了
需要训练的参数
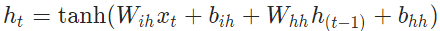
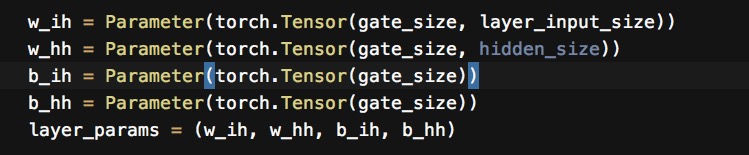
在forward()函数之前,有很多准备函数,检查input,hidden,我们一个一个来瞅瞅
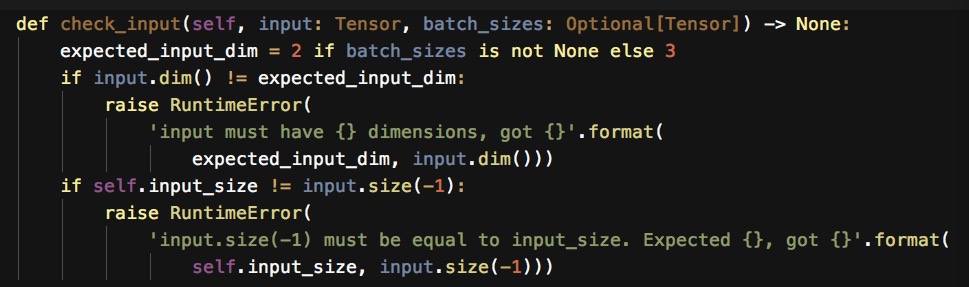
这个函数检查了要前向传输的自变量,当batch_size不为空时,这意味着我们的sequence已经是pack之后的了,当这个sequence是pad之后的,我们输入的期待维度便是2维了
1 def forward(self, input: Tensor, hx: Optional[Tensor] = None) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]: 2 is_packed = isinstance(input, PackedSequence) 3 if is_packed: 4 input, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, unsorted_indices = input 5 max_batch_size = batch_sizes[0] 6 max_batch_size = int(max_batch_size) 7 else: 8 batch_sizes = None 9 max_batch_size = input.size(0) if self.batch_first else input.size(1) 10 sorted_indices = None 11 unsorted_indices = None 12 if hx is None: 13 num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1 14 hx = torch.zeros(self.num_layers * num_directions, 15 max_batch_size, self.hidden_size, 16 dtype=input.dtype, device=input.device) 17 else: 18 # Each batch of the hidden state should match the input sequence that 19 # the user believes he/she is passing in. 20 hx = self.permute_hidden(hx, sorted_indices) 21 self.check_forward_args(input, hx, batch_sizes) 22 _impl = _rnn_impls[self.mode] 23 if batch_sizes is None: 24 result = _impl(input, hx, self._flat_weights, self.bias, self.num_layers, 25 self.dropout, self.training, self.bidirectional, self.batch_first) 26 else: 27 result = _impl(input, batch_sizes, hx, self._flat_weights, self.bias, 28 self.num_layers, self.dropout, self.training, self.bidirectional) 29 output = result[0] 30 hidden = result[1] 31 if is_packed: 32 output = PackedSequence(output, batch_sizes, sorted_indices, unsorted_indices) 33 return output, self.permute_hidden(hidden, unsorted_indices)
上来先判断输入是否已经packed 了,再采取不同后续处理,
那我们先来了解下 PackedSequence,PackedSequence目的是将 将一批长度不同的句子 封装成一个batch,可以直接作为RNN/LSTM的输入.Pytorch提供了pack_padded_sequence()方法。
如果是已经pack过的,则batch_sizes 是从大到小降序的,因此max_batch_size 等于batch_sizes里的第一个元素。
相反没经过pack处理的话,如果输入第一维是batch,那max_batch_size 等于输入第一维度,如果输入第二维是batch, max_batch_size=input.size(1)
接下来判断我们的隐向量输入hx了,同时默认hx为空,此处是如果我们没有默认的隐向量输入时,hx会初始化为0
_impl = _rnn_impls[self.mode]
_rnn_impls = { 'RNN_TANH': _VF.rnn_tanh, 'RNN_RELU': _VF.rnn_relu, }
小萌新读到这 头有点大了,去网上找找资料才发现,查询_rnn_impls来知道我们要启用的前向函数。pytorch上找到了相关源码,贴c++代码 https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/1a93b96815b5c87c92e060a6dca51be93d712d09/aten/src/ATen/native/RNN.cpp


