Url通配符映射
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/liukemng/p/3726897.ht
1.URL路径映射
1.1.对一个action配置多个URL映射:
我们把上一篇中的HelloWorldController的index() action方法的@RequestMapping更改为@RequestMapping(value={"/index", "/hello"}, method = {RequestMethod.GET}),这表示对该action配置了/index和/hello两个映射。运行测试,如下:
可以看到/helloworld/hello请求也成功匹配。
1.2.URL请求参数映射:
这在查询的时候经常用到,比如我们根据id或编号来获取某一条记录。
在HelloWorldController添加一个getDetail的action,代码如下:
@RequestMapping(value="/detail/{id}", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public ModelAndView getDetail(@PathVariable(value="id") Integer id){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("id", id);
modelAndView.setViewName("detail");
return modelAndView;
}
其中value="/detail/{id}",中的{id}为占位符表示可以映射请求为/detail/xxxx 的URL如:/detail/123等。
方法的参数@PathVariable(value="id") Integer id 用于将URL中占位符所对应变量映射到参数id上,@PathVariable(value="id") 中value的值要和占位符/{id}大括号中的值一致。
在views中添加detail.jsp视图,用于将获取到的id值展示出来。视图内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
${id}
</body>
</html>
运行测试,请求URL地址 http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCLesson/helloworld/detail/123 ,结果如下:
可以看到已经正确的显示了我们请求的id。
1.3.URL通配符映射:
我们还可以通过通配符对URL映射进行配置,通配符有“?”和“*”两个字符。其中“?”表示1个字符,“*”表示匹配多个字符,“**”表示匹配0个或多个路径。
例如:
“/helloworld/index?”可以匹配“/helloworld/indexA”、“/helloworld/indexB”,但不能匹配“/helloworld/index”也不能匹配“/helloworld/indexAA”;
“/helloworld/index*”可以匹配“/helloworld/index”、“/helloworld/indexA”、“/helloworld/indexAA”但不能匹配“/helloworld/index/A”;
“/helloworld/index/*”可以匹配“/helloworld/index/”、“/helloworld/index/A”、“/helloworld/index/AA”、“/helloworld/index/AB”但不能匹配 “/helloworld/index”、“/helloworld/index/A/B”;
“/helloworld/index/**”可以匹配“/helloworld/index/”下的多有子路径,比如:“/helloworld/index/A/B/C/D”;
如果现在有“/helloworld/index”和“/helloworld/*”,如果请求地址为“/helloworld/index”那么将如何匹配?Spring MVC会按照最长匹配优先原则(即和映射配置中哪个匹配的最多)来匹配,所以会匹配“/helloworld/index”,下面来做测试:
在HelloWorldController添加一个urlTest的action,内容如下:
@RequestMapping(value="/*", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public ModelAndView urlTest(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("urltest");
return modelAndView;
}
在views文件夹中新加一个视图urltest.jsp,为了和index.jsp做区别urltest.jsp的内容如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
urlTest!
</body>
</html>
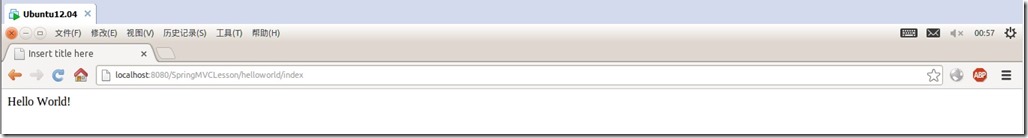
请求http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCLesson/helloworld/index查看结果:
可以看出映射的是index对应的action。
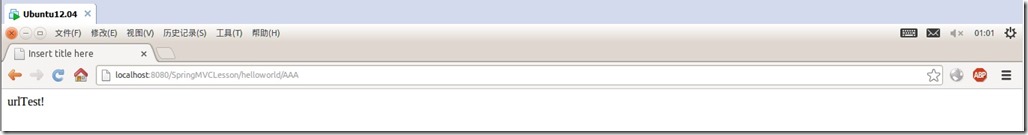
请求http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCLesson/helloworld/AAA查看结果:
可以看出映射的是urlTest对应的action。
本人亲测代码:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/helloworld") public class HelloWorldContrloller { //一个action匹配多个URL路径 @RequestMapping(value={"/index","/hello"},method=RequestMethod.GET) public String hello(String username,Model model){ System.out.println("//////////"+username); model.addAttribute("hello111", "Hello:"+username);//username匹配jsp页input文本框的name值 return "success"; } //通配符 @RequestMapping(value="/detail/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET) public String getDetail(@PathVariable(value="id") Integer id,Model model){ model.addAttribute("id", id); return "detail"; } }