视图层
视图函数返回值
视图函数都必须返回一个HttpResponse对象。
首先是之前说的三个返回方法:HttpResponse、render、redirect。
HttpResponse肯定返回的是一个HttpResponse对象,事实上,render()和redirect()方法返回的都是一个HttpResponse对象,我们可以查看这两个方法的源码进行查看。
比如render()方法源码:
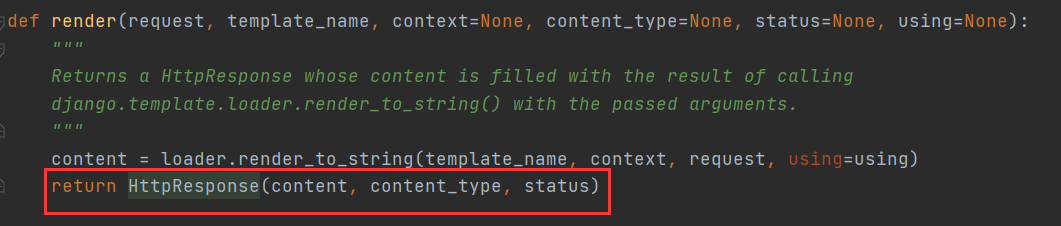
redirect()方法往更深的源码去查看,这里不方便演示。
JsonResponse对象
除了HttpResponse、render、redirect这三个可以给视图函数设置返回值,还有一个JsonResponse也可以,它用于返回一个json格式的数据。
from django.http import JsonResponse
def index(request):
user_dict = {'name':'tom', 'age':18, 'hobby':'读书'}
return JsonResponse(user_dict)

此时的中文是无法正常显示的,我们需要添加参数才能正常显示:
from django.http import JsonResponse
def index(request):
user_dict = {'name':'tom', 'age':18, 'hobby':'读书'}
return JsonResponse(user_dict, json_dumps_params={'ensure_ascii':False})
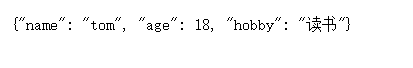
如果想要把其他类型转成json格式发送,需要把JsonResponse方法的safe参数设置为False
from django.http import JsonResponse
def index(request):
l = [11, 22, 33]
return JsonResponse(user_dict, safe=False)
form表单上传文件
form表单上传的数据中如果含有文件,那么需要以下要求:
- 表单属性method必须是post
- 表单属性enctype必须修改为multipart/form-data
- 后端需要使用request.FILES获取
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="">
<input type="file" name="my_file">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
views.py
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.FILES) # 专门获取文件数据
file_obj = request.FILES.get('my_file') # 根据你的input标签的name属性获取
print(file_obj.name) # 查看文件名
with open(file_obj.name,'wb') as f: # 直接通过文件名保存本件
for line in file_obj:
f.write(line)
return render(request, 'index.html')
request方法
| request方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| request.method | 获取请求方法 |
| request.POST | 获取POST请求数据 |
| request.GET | 获取GET请求数据 |
| request.FILES | 获取文件数据 |
| request.body | 获取最原始请求数据(二进制数据) |
| request.path | 获取地址后缀路径,但不会获取路径后面携带的参数 |
| request.path_info | 与request.path一致 |
| request.get_full_path() | 获取地址后缀路径并且还可以获取到路径后面携带的参数 |
FBV与CBV
FBV即基于函数的视图,CBV即基于类的视图。我们之前一直都是使用FBV。
CBV使用
视图层(views.py)
from django import views
class MyView(views.View):
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse("from CBV get view")
def post(self, request):
return HttpResponse("from CBV post view")
路由层(urls.py)
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^index/', views.MyView.as_view()),
]
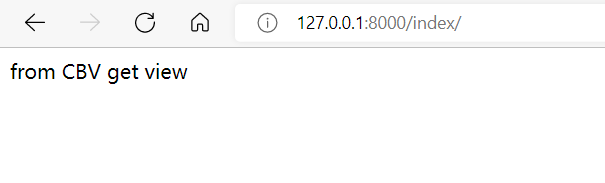
如果请求方式是GET,则会自动执行类里面的get方法;如果请求方式是POST,则会自动执行类里面的post方法;
CBV源码剖析
想详细了解CBV源码我们可以从路由层出发。
1.首先views.MyView.as_view()很明显是调用了类里面的as_view方法,在pycharm中按住ctrl点击as_view()查看详情。
2.因为我们在类中并没有定义as_view方法,所以这是父类Views中的方法。
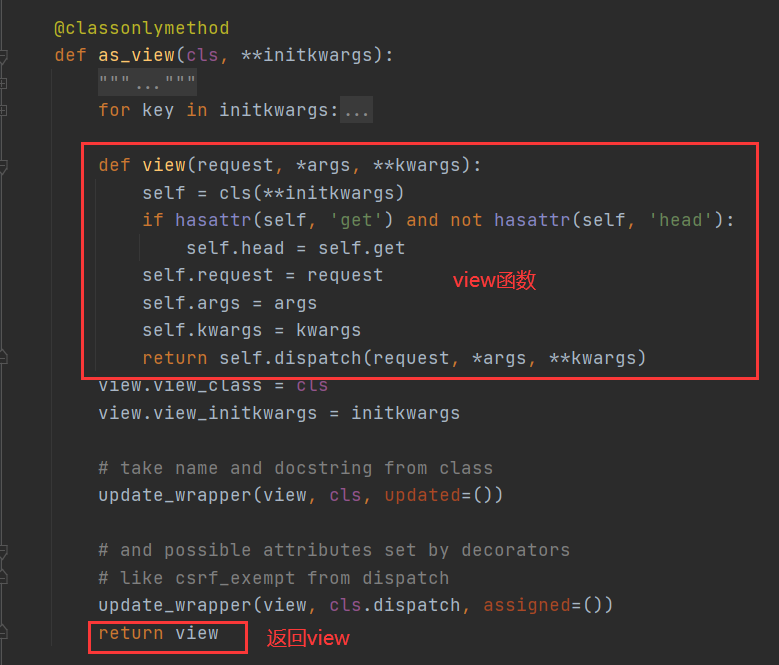
3.as_view()返回的是一个view函数,说明路由匹配成功执行了view函数,然后我们在细看view函数。
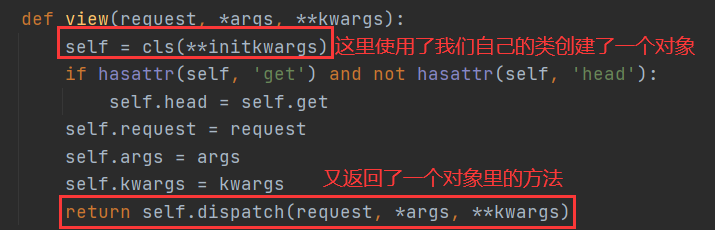
4.view函数返回了一个dispatch()方法,并且是用我们自己的类实例化得到的对象调用的,我们的类中没有dispatch()这个方法,所以这个明显又是父类Views中的方法。
5.查看dispatch()详情
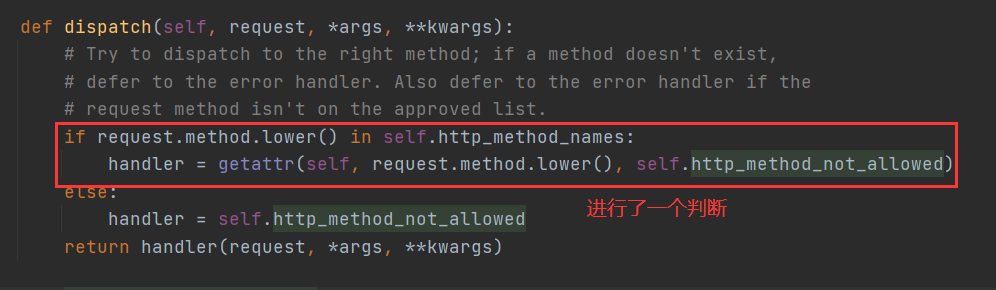
6.request.method这个方法我们都知道,用于返回请求方法的,这里进行了一个判断:判断请求方法是否在http_method_names中。
7.我们再来看看http_method_names有哪些内容。

8.再回到dispatch()方法if判断中,说如果request.method在http_method_names中,就使用getattr()获取对象中的方法,最后在return那里调用并返回。
总结:也就是说,如果请求的方法(request.method)在http_method_names中,就会调用我们类中的对应的方法。
CBV添加装饰器
如果想要给CBV添加装饰器需要借助一个专门的装饰器模块:method_decorator
导入:
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
方式一:直接在类中的某个方法上添加
class MyCBV(views.View):
@method_decorator(装饰器名称)
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse("from CBV get view")
方式二:直接在类上添加,并指定内部方法
@method_decorator(装饰器名称,name='get')
@method_decorator(装饰器名称,name='post')
class MyCBV(views.View):
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse("from CBV get view")
def post(self, request):
return HttpResponse("from CBV post view")
方式三:重写dispatch方法并添加装饰器,这会作用于类中所有的方法
class MyCBV(views.View):
@method_decorator(装饰器名称)
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号