转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/hadoop-mahout-maven-eclipse/
Hadoop家族系列文章,主要介绍Hadoop家族产品,常用的项目包括Hadoop, Hive, Pig, HBase, Sqoop, Mahout, Zookeeper, Avro, Ambari, Chukwa,新增加的项目包括,YARN, Hcatalog, Oozie, Cassandra, Hama, Whirr, Flume, Bigtop, Crunch, Hue等。
从2011年开始,中国进入大数据风起云涌的时代,以Hadoop为代表的家族软件,占据了大数据处理的广阔地盘。开源界及厂商,所有数据软件,无一不向Hadoop靠拢。Hadoop也从小众的高富帅领域,变成了大数据开发的标准。在Hadoop原有技术基础之上,出现了Hadoop家族产品,通过“大数据”概念不断创新,推出科技进步。
作为IT界的开发人员,我们也要跟上节奏,抓住机遇,跟着Hadoop一起雄起!
关于作者:
- 张丹(Conan), 程序员Java,R,PHP,Javascript
- weibo:@Conan_Z
- blog: http://blog.fens.me
- email: bsspirit@gmail.com
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/hadoop-mahout-maven-eclipse/
前言
基于Hadoop的项目,不管是MapReduce开发,还是Mahout的开发都是在一个复杂的编程环境中开发。Java的环境问题,是困扰着每个程序员的噩梦。Java程序员,不仅要会写Java程序,还要会调linux,会配hadoop,启动hadoop,还要会自己运维。所以,新手想玩起Hadoop真不是件简单的事。
不过,我们可以尽可能的简化环境问题,让程序员只关注于写程序。特别是像算法程序员,把精力投入在算法设计上,要比花时间解决环境问题有价值的多。
目录
- Maven介绍和安装
- Mahout单机开发环境介绍
- 用Maven构建Mahout开发环境
- 用Mahout实现协同过滤userCF
- 用Mahout实现kmeans
- 模板项目上传github
1. Maven介绍和安装
请参考文章:用Maven构建Hadoop项目
开发环境
- Win7 64bit
- Java 1.6.0_45
- Maven 3
- Eclipse Juno Service Release 2
- Mahout 0.6
这里要说明一下mahout的运行版本。
- mahout-0.5, mahout-0.6, mahout-0.7,是基于hadoop-0.20.2x的。
- mahout-0.8, mahout-0.9,是基于hadoop-1.1.x的。
- mahout-0.7,有一次重大升级,去掉了多个算法的单机内存运行,并且了部分API不向前兼容。
注:本文关注于“用Maven构建Mahout的开发环境”,文中的 2个例子都是基于单机的内存实现,因此选择0.6版本。Mahout在Hadoop集群中运行会在下一篇文章介绍。
2. Mahout单机开发环境介绍
如上图所示,我们可以选择在win中开发,也可以在linux中开发,开发过程我们可以在本地环境进行调试,标配的工具都是Maven和Eclipse。
3. 用Maven构建Mahout开发环境
- 1. 用Maven创建一个标准化的Java项目
- 2. 导入项目到eclipse
- 3. 增加mahout依赖,修改pom.xml
- 4. 下载依赖
1). 用Maven创建一个标准化的Java项目
~ D:\workspace\java>mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.apache.maven.archetypes
-DgroupId=org.conan.mymahout -DartifactId=myMahout -DpackageName=org.conan.mymahout -Dversion=1.0-SNAPSHOT -DinteractiveMode=false
进入项目,执行mvn命令
~ D:\workspace\java>cd myMahout
~ D:\workspace\java\myMahout>mvn clean install
2). 导入项目到eclipse
我们创建好了一个基本的maven项目,然后导入到eclipse中。 这里我们最好已安装好了Maven的插件。
3). 增加mahout依赖,修改pom.xml
这里我使用hadoop-0.6版本,同时去掉对junit的依赖,修改文件:pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.conan.mymahout</groupId>
<artifactId>myMahout</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>myMahout</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<mahout.version>0.6</mahout.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mahout</groupId>
<artifactId>mahout-core</artifactId>
<version>${mahout.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.mahout</groupId>
<artifactId>mahout-integration</artifactId>
<version>${mahout.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.cassandra</groupId>
<artifactId>cassandra-all</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>me.prettyprint</groupId>
<artifactId>hector-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
4). 下载依赖
~ mvn clean install在eclipse中刷新项目:
项目的依赖程序,被自动加载的库路径下面。
4. 用Mahout实现协同过滤userCF
Mahout协同过滤UserCF深度算法剖析,请参考文章:用R解析Mahout用户推荐协同过滤算法(UserCF)
实现步骤:
- 1. 准备数据文件: item.csv
- 2. Java程序:UserCF.java
- 3. 运行程序
- 4. 推荐结果解读
1). 新建数据文件: item.csv
~ mkdir datafile
~ vi datafile/item.csv
1,101,5.0
1,102,3.0
1,103,2.5
2,101,2.0
2,102,2.5
2,103,5.0
2,104,2.0
3,101,2.5
3,104,4.0
3,105,4.5
3,107,5.0
4,101,5.0
4,103,3.0
4,104,4.5
4,106,4.0
5,101,4.0
5,102,3.0
5,103,2.0
5,104,4.0
5,105,3.5
5,106,4.0
数据解释:每一行有三列,第一列是用户ID,第二列是物品ID,第三列是用户对物品的打分。
2). Java程序:UserCF.java
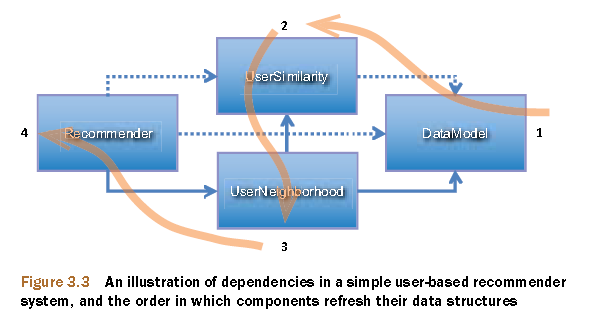
Mahout协同过滤的数据流,调用过程。
上图摘自:Mahout in Action
新建JAVA类:org.conan.mymahout.recommendation.UserCF.java
package org.conan.mymahout.recommendation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.common.TasteException;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.impl.common.LongPrimitiveIterator;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.impl.model.file.FileDataModel;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.impl.neighborhood.NearestNUserNeighborhood;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.impl.recommender.GenericUserBasedRecommender;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.impl.similarity.EuclideanDistanceSimilarity;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.model.DataModel;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.recommender.RecommendedItem;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.recommender.Recommender;
import org.apache.mahout.cf.taste.similarity.UserSimilarity;
public class UserCF {
final static int NEIGHBORHOOD_NUM = 2;
final static int RECOMMENDER_NUM = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TasteException {
String file = "datafile/item.csv";
DataModel model = new FileDataModel(new File(file));
UserSimilarity user = new EuclideanDistanceSimilarity(model);
NearestNUserNeighborhood neighbor = new NearestNUserNeighborhood(NEIGHBORHOOD_NUM, user, model);
Recommender r = new GenericUserBasedRecommender(model, neighbor, user);
LongPrimitiveIterator iter = model.getUserIDs();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
long uid = iter.nextLong();
List list = r.recommend(uid, RECOMMENDER_NUM);
System.out.printf("uid:%s", uid);
for (RecommendedItem ritem : list) {
System.out.printf("(%s,%f)", ritem.getItemID(), ritem.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
3). 运行程序
控制台输出:
SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
uid:1(104,4.274336)(106,4.000000)
uid:2(105,4.055916)
uid:3(103,3.360987)(102,2.773169)
uid:4(102,3.000000)
uid:5
4). 推荐结果解读
- 向用户ID1,推荐前二个最相关的物品, 104和106
- 向用户ID2,推荐前二个最相关的物品, 但只有一个105
- 向用户ID3,推荐前二个最相关的物品, 103和102
- 向用户ID4,推荐前二个最相关的物品, 但只有一个102
- 向用户ID5,推荐前二个最相关的物品, 没有符合的
5. 用Mahout实现kmeans
- 1. 准备数据文件: randomData.csv
- 2. Java程序:Kmeans.java
- 3. 运行Java程序
- 4. mahout结果解读
- 5. 用R语言实现Kmeans算法
- 6. 比较Mahout和R的结果
1). 准备数据文件: randomData.csv
~ vi datafile/randomData.csv
-0.883033363823402,-3.31967192630249
-2.39312626419456,3.34726861118871
2.66976353341256,1.85144276077058
-1.09922906899594,-6.06261735207489
-4.36361936997216,1.90509905380532
-0.00351835125495037,-0.610105996559153
-2.9962958796338,-3.60959839525735
-3.27529418132066,0.0230099799641799
2.17665594420569,6.77290756817957
-2.47862038335637,2.53431833167278
5.53654901906814,2.65089785582474
5.66257474538338,6.86783609641077
-0.558946883114376,1.22332819416237
5.11728525486132,3.74663871584768
1.91240516693351,2.95874731384062
-2.49747101306535,2.05006504756875
3.98781883213459,1.00780938946366
这里只截取了一部分,更多的数据请查看源代码。
注:我是通过R语言生成的randomData.csv
x1<-cbind(x=rnorm(400,1,3),y=rnorm(400,1,3))
x2<-cbind(x=rnorm(300,1,0.5),y=rnorm(300,0,0.5))
x3<-cbind(x=rnorm(300,0,0.1),y=rnorm(300,2,0.2))
x<-rbind(x1,x2,x3)
write.table(x,file="randomData.csv",sep=",",row.names=FALSE,col.names=FALSE)
2). Java程序:Kmeans.java
Mahout中kmeans方法的算法实现过程。
上图摘自:Mahout in Action
新建JAVA类:org.conan.mymahout.cluster06.Kmeans.java
package org.conan.mymahout.cluster06;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.mahout.clustering.kmeans.Cluster;
import org.apache.mahout.clustering.kmeans.KMeansClusterer;
import org.apache.mahout.common.distance.EuclideanDistanceMeasure;
import org.apache.mahout.math.Vector;
public class Kmeans {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List sampleData = MathUtil.readFileToVector("datafile/randomData.csv");
int k = 3;
double threshold = 0.01;
List<Vector> randomPoints = MathUtil.chooseRandomPoints(sampleData, k);
for (Vector vector : randomPoints) {
System.out.println("Init Point center: " + vector);
}
List clusters = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
clusters.add(new Cluster(randomPoints.get(i), i, new EuclideanDistanceMeasure()));
}
List<List<Cluster >> finalClusters = KMeansClusterer.clusterPoints(sampleData, clusters, new EuclideanDistanceMeasure(), k, threshold); for (Cluster cluster : finalClusters.get(finalClusters.size() - 1)) { System.out.println("Cluster id: " + cluster.getId() + " center: " + cluster.getCenter().asFormatString()); } } } 3). 运行Java程序
控制台输出:
Init Point center: {0:-0.162693685149196,1:2.19951550286862}
Init Point center: {0:-0.0409782183083317,1:2.09376666042057}
Init Point center: {0:0.158401778474687,1:2.37208412905273}
SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
Cluster id: 0 center: {0:-2.686856800552941,1:1.8939462954763795}
Cluster id: 1 center: {0:0.6334255423230666,1:0.49472852972602105}
Cluster id: 2 center: {0:3.334520309711998,1:3.2758355898247653}
4). mahout结果解读
- 1. Init Point center表示,kmeans算法初始时的设置的3个中心点
- 2. Cluster center表示,聚类后找到3个中心点
5). 用R语言实现Kmeans算法
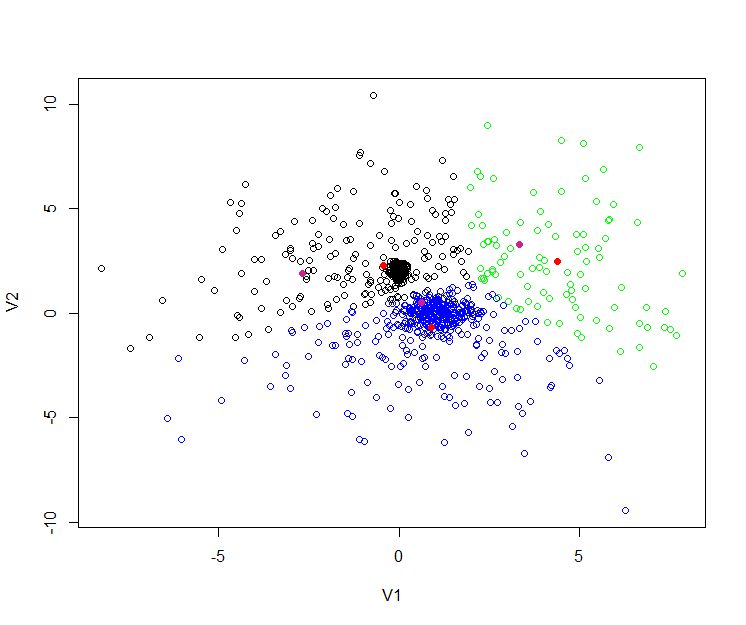
接下来为了让结果更直观,我们再用R语言,进行kmeans实验,操作相同的数据。
R语言代码:
> y<-read.csv(file="randomData.csv",sep=",",header=FALSE)
> cl<-kmeans(y,3,iter.max = 10, nstart = 25)
> cl$centers
V1 V2
1 -0.4323971 2.2852949
2 0.9023786 -0.7011153
3 4.3725463 2.4622609
# 生成聚类中心的图形
> plot(y, col=c("black","blue","green")[cl$cluster])
> points(cl$centers, col="red", pch = 19)
# 画出Mahout聚类的中心
> mahout<-matrix(c(-2.686856800552941,1.8939462954763795,0.6334255423230666,0.49472852972602105,3.334520309711998,3.2758355898247653),ncol=2,byrow=TRUE)
> points(mahout, col="violetred", pch = 19)
6). 比较Mahout和R的结果
从上图中,我们看到有 黑,蓝,绿,三种颜色的空心点,这些点就是原始的数据。
3个红色实点,是R语言kmeans后生成的3个中心。
3个紫色实点,是Mahout的kmeans后生成的3个中心。
R语言和Mahout生成的点,并不是重合的,原因有几点:
- 1. 距离算法不一样:
Mahout中,我们用的 “欧氏距离(EuclideanDistanceMeasure)”
R语言中,默认是”Hartigan and Wong” - 2. 初始化的中心是不一样的。
- 3. 最大迭代次数是不一样的。
- 4. 点合并时,判断的”阈值(threshold)”是不一样的。
6. 模板项目上传github
https://github.com/bsspirit/maven_mahout_template/tree/mahout-0.6
大家可以下载这个项目,做为开发的起点。
~ git clone https://github.com/bsspirit/maven_mahout_template
~ git checkout mahout-0.6
我们完成了第一步,下面就将正式进入mahout算法的开发实践,并且应用到hadoop集群的环境中。