1.2.5 贪婪算法Greedy Algorithms
贪婪算法Greedy Algorithms
1.Dijkstra 的最短路径算法(Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm)
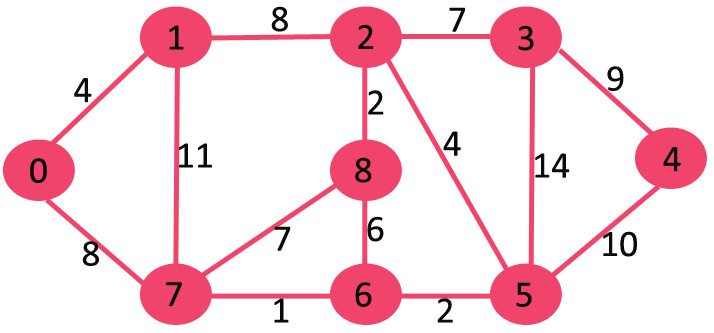
给定一个图和图中的一个源顶点,找出从源到给定图中所有顶点的最短路径。
Dijkstra 的算法与Prim 的最小生成树算法非常相似。与 Prim 的 MST 一样,我们生成一个以给定源为根的SPT(最短路径树)。我们维护两组,一组包含最短路径树中包含的顶点,另一组包含最短路径树中尚未包含的顶点。在算法的每一步,我们都会找到一个顶点,它在另一个集合(尚未包含的集合)中,并且与源的距离最小。
以下是 Dijkstra 算法中使用的详细步骤,用于查找给定图中从单个源顶点到所有其他顶点的最短路径。
算法
1)创建一个集合sptSet(最短路径树集),用于跟踪最短路径树中包含的顶点,即计算并确定其与源的最小距离。最初,这个集合是空的。
2)为输入图中的所有顶点分配一个距离值。将所有距离值初始化为 INFINITE。将源顶点的距离值指定为 0,以便首先拾取它。
3)虽然sptSet不包括所有顶点
...... a)选择一个在sptSet 中不存在并且具有最小距离值的顶点 u 。
…… b)包括 u 到sptSet。
……c)更新 u 的所有相邻顶点的距离值。要更新距离值,请遍历所有相邻顶点。对于每一个相邻的顶点v,如果u(距源)的距离值和边uv的权重之和小于v的距离值,则更新v的距离值。
让我们通过下面的例子来理解:
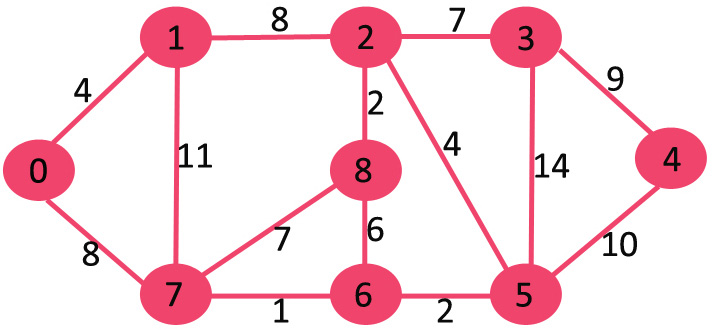
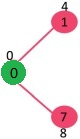
集合sptSet最初是空的,分配给顶点的距离是 {0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},其中 INF 表示无限。现在选择具有最小距离值的顶点。顶点 0 被拾取,将其包含在sptSet 中。所以sptSet变为 {0}。将 0 包含到sptSet 后,更新其相邻顶点的距离值。0 的相邻顶点为 1 和 7。1 和 7 的距离值更新为 4 和 8。以下子图显示了顶点及其距离值,仅显示了具有有限距离值的顶点。SPT 中包含的顶点以绿色显示。
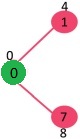
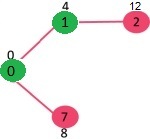
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 1 被拾取并添加到 sptSet。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1}。更新相邻顶点的距离值为1,顶点2的距离值变为12。
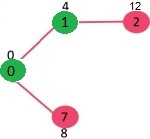
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 7 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7}。更新 7 的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点 6 和 8 的距离值变为有限(分别为 15 和 9)。
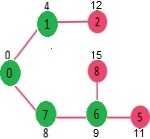
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 6 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7, 6}。更新6的相邻顶点的距离值。更新顶点5和8的距离值。
集合sptSet最初是空的,分配给顶点的距离是 {0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},其中 INF 表示无限。现在选择具有最小距离值的顶点。顶点 0 被拾取,将其包含在sptSet 中。所以sptSet变为 {0}。将 0 包含到sptSet 后,更新其相邻顶点的距离值。0 的相邻顶点为 1 和 7。1 和 7 的距离值更新为 4 和 8。以下子图显示了顶点及其距离值,仅显示了具有有限距离值的顶点。SPT 中包含的顶点以绿色显示。

选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 1 被拾取并添加到 sptSet。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1}。更新相邻顶点的距离值为1,顶点2的距离值变为12。

选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 7 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7}。更新 7 的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点 6 和 8 的距离值变为有限(分别为 15 和 9)。

选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 6 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7, 6}。更新6的相邻顶点的距离值。更新顶点5和8的距离值。

我们使用布尔数组 sptSet[] 来表示 SPT 中包含的顶点集。如果值 sptSet[v] 为真,则顶点 v 包含在 SPT 中,否则不包含。数组 dist[] 用于存储所有顶点的最短距离值。
# Python program for Dijkstra's single
# source shortest path algorithm. The program is
# for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
# Library for INT_MAX
import sys
class Graph():
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(vertices)]
for row in range(vertices)]
def printSolution(self, dist):
print "Vertex \tDistance from Source"
for node in range(self.V):
print node, "\t", dist[node]
# A utility function to find the vertex with
# minimum distance value, from the set of vertices
# not yet included in shortest path tree
def minDistance(self, dist, sptSet):
# Initialize minimum distance for next node
min = sys.maxint
# Search not nearest vertex not in the
# shortest path tree
for u in range(self.V):
if dist[u] < min and sptSet[u] == False:
min = dist[u]
min_index = u
return min_index
# Function that implements Dijkstra's single source
# shortest path algorithm for a graph represented
# using adjacency matrix representation
def dijkstra(self, src):
dist = [sys.maxint] * self.V
dist[src] = 0
sptSet = [False] * self.V
for cout in range(self.V):
# Pick the minimum distance vertex from
# the set of vertices not yet processed.
# x is always equal to src in first iteration
x = self.minDistance(dist, sptSet)
# Put the minimum distance vertex in the
# shortest path tree
sptSet[x] = True
# Update dist value of the adjacent vertices
# of the picked vertex only if the current
# distance is greater than new distance and
# the vertex in not in the shortest path tree
for y in range(self.V):
if self.graph[x][y] > 0 and sptSet[y] == False and \
dist[y] > dist[x] + self.graph[x][y]:
dist[y] = dist[x] + self.graph[x][y]
self.printSolution(dist)
# Driver program
g = Graph(9)
g.graph = [[0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0],
[0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6],
[8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0]
];
g.dijkstra(0);
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta
Output:
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14
注:
1)代码计算最短距离,但不计算路径信息。我们可以创建一个父数组,在距离更新时更新父数组(如prim 的实现),并使用它来显示从源到不同顶点的最短路径。
2)代码用于无向图,同样的 Dijkstra 函数也可用于有向图。
3)代码找到从源到所有顶点的最短距离。如果我们只对从源到单个目标的最短距离感兴趣,我们可以在选择的最小距离顶点等于目标时中断 for 循环(算法的步骤 3.a)。
4)实现的时间复杂度为 O(V^2)。如果输入图使用邻接表表示,则可以在二叉堆的帮助下将其简化为 O(E log V)。有关更多详细信息,请参阅
Dijkstra 的邻接表表示算法。
5) Dijkstra 算法不适用于具有负权重循环的图。它可能会为具有负边的图提供正确的结果,但您必须允许一个顶点可以多次访问,并且该版本将失去其快速时间复杂度。对于具有负权重边和环的图,可以使用Bellman-Ford 算法。
2.Dijkstra邻接表表示算法(Dijkstra’s Algorithm for Adjacency List Representation)
我们已经讨论了Dijkstra 算法及其对图的邻接矩阵表示的实现。矩阵表示的时间复杂度为 O(V^2)。在这篇文章中,讨论了用于邻接列表表示的 O(ELogV) 算法。
如上一篇文章所述,在 Dijkstra 的算法中,维护了两个集合,一个集合包含已包含在 SPT(最短路径树)中的顶点列表,另一个集合包含尚未包含的顶点。使用邻接表表示,可以使用 O(V+E) 时间遍历图的所有顶点 BFS。这个想法是使用BFS 遍历图的所有顶点, 并使用最小堆存储尚未包含在 SPT 中的顶点(或尚未确定最短距离的顶点)。最小堆用作优先队列,以从尚未包含的顶点集获取最小距离顶点。对于 Min Heap,extract-min 和 reduce-key value 等操作的时间复杂度为 O(LogV)。
以下是详细步骤。
1) 创建一个大小为 V 的最小堆,其中 V 是给定图中的顶点数。最小堆的每个节点都包含顶点编号和顶点距离值。
2) 以源顶点为根初始化Min Heap(分配给源顶点的距离值为0)。分配给所有其他顶点的距离值为 INF(无限)。
3) 当最小堆不为空时,请执行以下操作
..... a) 从最小堆中提取具有最小距离值节点的顶点。令提取的顶点为 u。
..... b) 对于 u 的每个相邻顶点 v,检查 v 是否在最小堆中。如果v在Min Heap中并且距离值大于uv的权重加上u的距离值,则更新v的距离值。
让我们通过下面的例子来理解。让给定的源顶点为 0
最初,源顶点的距离值为 0,所有其他顶点的距离值为 INF(无限)。因此从最小堆中提取源顶点并更新与 0(1 和 7)相邻的顶点的距离值。Min Heap 包含除顶点 0 之外的所有顶点
。绿色的顶点是最小距离确定的顶点,并且不在 Min Heap 中
由于顶点 1 的距离值在最小堆中的所有节点中最小,因此从最小堆中提取它并更新与 1 相邻顶点的距离值(如果顶点在最小堆中并且通过 1 的距离小于前一个距离)。最小堆包含除顶点 0 和 1 之外的所有顶点。
从最小堆中选取距离值最小的顶点。顶点 7 被选取。所以最小堆现在包含除 0、1 和 7 之外的所有顶点。更新 7 的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点 6 和 8 的距离值变得有限(分别为 15 和 9)。
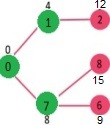
选择与最小堆距离最小的顶点。顶点 6 被选取。所以 min heap 现在包含除 0、1、7 和 6 之外的所有顶点。更新 6 的相邻顶点的距离值。更新顶点 5 和 8 的距离值。
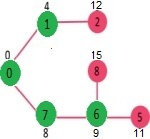
重复上述步骤,直到最小堆不会变空。最后,我们得到如下最短路径树。
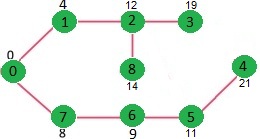
# A Python program for Dijkstra's shortest
# path algorithm for adjacency
# list representation of graph
from collections import defaultdict
import sys
class Heap():
def __init__(self):
self.array = []
self.size = 0
self.pos = []
def newMinHeapNode(self, v, dist):
minHeapNode = [v, dist]
return minHeapNode
# A utility function to swap two nodes
# of min heap. Needed for min heapify
def swapMinHeapNode(self,a, b):
t = self.array[a]
self.array[a] = self.array[b]
self.array[b] = t
# A standard function to heapify at given idx
# This function also updates position of nodes
# when they are swapped.Position is needed
# for decreaseKey()
def minHeapify(self, idx):
smallest = idx
left = 2*idx + 1
right = 2*idx + 2
if left < self.size and
self.array[left][1] \
< self.array[smallest][1]:
smallest = left
if right < self.size and
self.array[right][1]\
< self.array[smallest][1]:
smallest = right
# The nodes to be swapped in min
# heap if idx is not smallest
if smallest != idx:
# Swap positions
self.pos[ self.array[smallest][0]]
= idx
self.pos[ self.array[idx][0]] =
smallest
# Swap nodes
self.swapMinHeapNode(smallest, idx)
self.minHeapify(smallest)
# Standard function to extract minimum
# node from heap
def extractMin(self):
# Return NULL wif heap is empty
if self.isEmpty() == True:
return
# Store the root node
root = self.array[0]
# Replace root node with last node
lastNode = self.array[self.size - 1]
self.array[0] = lastNode
# Update position of last node
self.pos[lastNode[0]] = 0
self.pos[root[0]] = self.size - 1
# Reduce heap size and heapify root
self.size -= 1
self.minHeapify(0)
return root
def isEmpty(self):
return True if self.size == 0 else False
def decreaseKey(self, v, dist):
# Get the index of v in heap array
i = self.pos[v]
# Get the node and update its dist value
self.array[i][1] = dist
# Travel up while the complete tree is
# not hepified. This is a O(Logn) loop
while i > 0 and self.array[i][1] <
self.array[(i - 1) / 2][1]:
# Swap this node with its parent
self.pos[ self.array[i][0] ] = (i-1)/2
self.pos[ self.array[(i-1)/2][0] ] = i
self.swapMinHeapNode(i, (i - 1)/2 )
# move to parent index
i = (i - 1) / 2;
# A utility function to check if a given
# vertex 'v' is in min heap or not
def isInMinHeap(self, v):
if self.pos[v] < self.size:
return True
return False
def printArr(dist, n):
print "Vertex\tDistance from source"
for i in range(n):
print "%d\t\t%d" % (i,dist[i])
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Adds an edge to an undirected graph
def addEdge(self, src, dest, weight):
# Add an edge from src to dest. A new node
# is added to the adjacency list of src. The
# node is added at the beginning. The first
# element of the node has the destination
# and the second elements has the weight
newNode = [dest, weight]
self.graph[src].insert(0, newNode)
# Since graph is undirected, add an edge
# from dest to src also
newNode = [src, weight]
self.graph[dest].insert(0, newNode)
# The main function that calculates distances
# of shortest paths from src to all vertices.
# It is a O(ELogV) function
def dijkstra(self, src):
V = self.V # Get the number of vertices in graph
dist = [] # dist values used to pick minimum
# weight edge in cut
# minHeap represents set E
minHeap = Heap()
# Initialize min heap with all vertices.
# dist value of all vertices
for v in range(V):
dist.append(sys.maxint)
minHeap.array.append( minHeap.
newMinHeapNode(v, dist[v]))
minHeap.pos.append(v)
# Make dist value of src vertex as 0 so
# that it is extracted first
minHeap.pos[src] = src
dist[src] = 0
minHeap.decreaseKey(src, dist[src])
# Initially size of min heap is equal to V
minHeap.size = V;
# In the following loop,
# min heap contains all nodes
# whose shortest distance is not yet finalized.
while minHeap.isEmpty() == False:
# Extract the vertex
# with minimum distance value
newHeapNode = minHeap.extractMin()
u = newHeapNode[0]
# Traverse through all adjacent vertices of
# u (the extracted vertex) and update their
# distance values
for pCrawl in self.graph[u]:
v = pCrawl[0]
# If shortest distance to v is not finalized
# yet, and distance to v through u is less
# than its previously calculated distance
if minHeap.isInMinHeap(v) and
dist[u] != sys.maxint and \
pCrawl[1] + dist[u] < dist[v]:
dist[v] = pCrawl[1] + dist[u]
# update distance value
# in min heap also
minHeap.decreaseKey(v, dist[v])
printArr(dist,V)
# Driver program to test the above functions
graph = Graph(9)
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 4)
graph.addEdge(0, 7, 8)
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 8)
graph.addEdge(1, 7, 11)
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 7)
graph.addEdge(2, 8, 2)
graph.addEdge(2, 5, 4)
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 9)
graph.addEdge(3, 5, 14)
graph.addEdge(4, 5, 10)
graph.addEdge(5, 6, 2)
graph.addEdge(6, 7, 1)
graph.addEdge(6, 8, 6)
graph.addEdge(7, 8, 7)
graph.dijkstra(0)
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta
Output:
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14
时间复杂度: 上述代码/算法的时间复杂度看起来是 O(V^2),因为有两个嵌套的 while 循环。如果我们仔细观察,我们可以观察到内循环中的语句执行了 O(V+E) 次(类似于 BFS)。内循环有 reduceKey() 操作,需要 O(LogV) 时间。所以整体时间复杂度是 O(E+V)O(LogV) 即 O((E+V)LogV) = O(ELogV)
注意上面的代码使用二叉堆来实现优先队列。使用斐波那契堆可以将时间复杂度降低到 O(E + VLogV)。原因是,Fibonacci Heap 进行减键操作的时间为 O(1),而 Binary Heap 的时间为 O(Logn)。
注:
- 该代码计算最短距离,但不计算路径信息。我们可以创建一个父数组,在距离更新时更新父数组(如 prim 的实现),并使用它显示从源到不同顶点的最短路径。
- 该代码用于无向图,同样的 dijekstra 函数也可用于有向图。
- 该代码查找从源到所有顶点的最短距离。如果我们只对从源到单个目标的最短距离感兴趣,我们可以在选择的最小距离顶点等于目标时中断 for 循环(算法的步骤 3.a)。
- Dijkstra 算法不适用于具有负权重边的图。对于具有负权重边的图, 可以使用Bellman-Ford 算法
3.Prim 的最小生成树(Prim’s Minimum Spanning Tree (MST))
我们已经讨论了 Kruskal 的最小生成树算法。和 Kruskal 算法一样,Prim 算法也是一种 贪心算法。它从一棵空的生成树开始。这个想法是维护两组顶点。第一组包含已包含在 MST 中的顶点,另一组包含尚未包含的顶点。在每一步,它都会考虑连接这两个集合的所有边,并从这些边中挑选出权重最小的边。拾取边后,它将边的另一个端点移动到包含 MST 的集合中。
连接图中两组顶点的一组边在图论中称为 割。 因此,在 Prim 算法的每一步,我们都会找到一个切割(两个集合,一个包含已经包含在 MST 中的顶点,另一个包含其余的顶点),从切割中选择权重最小的边并将这个顶点包含到 MST 集合中(包含已包含顶点的集合)。
Prim 的算法如何工作?Prim 算法背后的思想很简单,生成树意味着必须连接所有顶点。因此必须连接两个不相交的顶点子集(上面讨论过)以形成 生成树 。并且它们必须与最小权重边相连以使其成为 最小 生成树。
算法
1)创建一个集合mstSet来跟踪已经包含在 MST 中的顶点。
2)为输入图中的所有顶点分配一个键值。将所有键值初始化为 INFINITE。将第一个顶点的键值指定为 0,以便它首先被拾取。
3)虽然 mstSet 不包括所有顶点
...... a)选择mstSet 中不存在的顶点u并且具有最小键值。 …… b) 将u包含到 mstSet。 …… c)更新u的所有相邻顶点的键值
. 要更新键值,请遍历所有相邻顶点。对于每个相邻的顶点v,如果边uv 的权重小于v的前一个键值,则将键值更新为uv
的权重。使用键值的想法是从cut 中选取权重最小的边。键值仅用于尚未包含在 MST 中的顶点,这些顶点的键值指示将它们连接到包含在 MST 中的顶点集的最小权重边。
让我们通过下面的例子来理解:

集合mstSet最初是空的,分配给顶点的键是 {0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},其中 INF 表示无限。现在选择具有最小键值的顶点。顶点 0 被拾取,将其包含在mstSet 中。因此mstSet变为 {0}。包含到mstSet 后,更新相邻顶点的键值。0 的相邻顶点是 1 和 7。1 和 7 的键值更新为 4 和 8。下面的子图显示了顶点及其键值,只显示了具有有限键值的顶点。MST 中包含的顶点以绿色显示。

选择具有最小键值且尚未包含在 MST 中(不在 mstSET 中)的顶点。顶点 1 被拾取并添加到 mstSet。所以 mstSet 现在变成了 {0, 1}。更新1的相邻顶点的键值,顶点2的键值变为8。
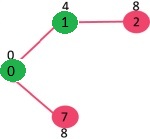
选择具有最小键值且尚未包含在 MST 中(不在 mstSET 中)的顶点。我们可以选择顶点 7 或顶点 2,让顶点 7 被拾取。所以 mstSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7}。更新 7 的相邻顶点的键值。顶点 6 和 8 的键值变为有限(分别为 1 和 7)。
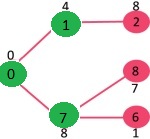
选择具有最小键值且尚未包含在 MST 中(不在 mstSET 中)的顶点。顶点 6 被选取。所以 mstSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7, 6}。更新6的相邻顶点的键值,更新顶点5和8的键值。
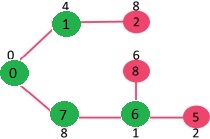
我们重复上述步骤,直到mstSet包含给定图的所有顶点。最后,我们得到下图。
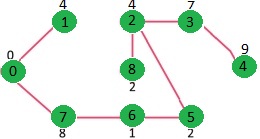
如何实现上述算法?
我们使用布尔数组 mstSet[] 来表示 MST 中包含的顶点集。如果值 mstSet[v] 为真,则顶点 v 包含在 MST 中,否则不包含。数组 key[] 用于存储所有顶点的键值。另一个数组 parent[] 用于在 MST 中存储父节点的索引。父数组是输出数组,用于显示构造的 MST。
# A Python program for Prim's Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) algorithm.
# The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
import sys # Library for INT_MAX
class Graph():
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(vertices)]
for row in range(vertices)]
# A utility function to print the constructed MST stored in parent[]
def printMST(self, parent):
print "Edge \tWeight"
for i in range(1, self.V):
print parent[i], "-", i, "\t", self.graph[i][ parent[i] ]
# A utility function to find the vertex with
# minimum distance value, from the set of vertices
# not yet included in shortest path tree
def minKey(self, key, mstSet):
# Initialize min value
min = sys.maxsize
for v in range(self.V):
if key[v] < min and mstSet[v] == False:
min = key[v]
min_index = v
return min_index
# Function to construct and print MST for a graph
# represented using adjacency matrix representation
def primMST(self):
# Key values used to pick minimum weight edge in cut
key = [sys.maxsize] * self.V
parent = [None] * self.V # Array to store constructed MST
# Make key 0 so that this vertex is picked as first vertex
key[0] = 0
mstSet = [False] * self.V
parent[0] = -1 # First node is always the root of
for cout in range(self.V):
# Pick the minimum distance vertex from
# the set of vertices not yet processed.
# u is always equal to src in first iteration
u = self.minKey(key, mstSet)
# Put the minimum distance vertex in
# the shortest path tree
mstSet[u] = True
# Update dist value of the adjacent vertices
# of the picked vertex only if the current
# distance is greater than new distance and
# the vertex in not in the shortest path tree
for v in range(self.V):
# graph[u][v] is non zero only for adjacent vertices of m
# mstSet[v] is false for vertices not yet included in MST
# Update the key only if graph[u][v] is smaller than key[v]
if self.graph[u][v] > 0 and mstSet[v] == False and key[v] > self.graph[u][v]:
key[v] = self.graph[u][v]
parent[v] = u
self.printMST(parent)
g = Graph(5)
g.graph = [ [0, 2, 0, 6, 0],
[2, 0, 3, 8, 5],
[0, 3, 0, 0, 7],
[6, 8, 0, 0, 9],
[0, 5, 7, 9, 0]]
g.primMST();
# Contributed by Divyanshu Mehta
Output:
Edge Weight
0 - 1 2
1 - 2 3
0 - 3 6
1 - 4 5
上述程序的时间复杂度为 O(V^2)。如果输入图使用邻接表表示,那么借助二叉堆,Prim 算法的时间复杂度可以降低到 O(E log V)。
4.Prim 用于邻接列表5.(Prim’s MST for Adjacency List Representation)
我们已经讨论了Prim 的算法及其在图的邻接矩阵表示中的实现。矩阵表示的时间复杂度为 O(V^2)。在这篇文章中,讨论了用于邻接列表表示的 O(ELogV) 算法。
正如在前一篇文章中所讨论的,在 Prim 的算法中,维护了两个集合,一个集合包含已包含在 MST 中的顶点列表,另一个集合包含尚未包含的顶点。使用邻接表表示,可以使用BFS在 O(V+E) 时间内遍历图的所有顶点. 这个想法是使用BFS遍历图的所有顶点,并使用最小堆来存储尚未包含在 MST 中的顶点。Min Heap 用作优先队列以从cut 中获取最小权重边。Min Heap 用作操作的时间复杂度,例如在 Min Heap 中提取最小元素和减少键值是 O(LogV)。
以下是详细步骤。
1)创建一个大小为 V 的最小堆,其中 V 是给定图中的顶点数。最小堆的每个节点都包含顶点号和顶点的键值。
2)以第一个顶点为根初始化Min Heap(分配给第一个顶点的键值为0)。分配给所有其他顶点的键值是 INF(无限)。
3)当最小堆不为空时,请执行以下操作
..... a)从最小堆中提取最小值节点。令提取的顶点为 u。
..... b)对于 u 的每个相邻顶点 v,检查 v 是否在最小堆中(尚未包含在 MST 中)。如果 v 在 Min Heap 中,并且其 key 值大于 uv 的权重,则将 v 的 key 值更新为 uv 的权重。
# A Python program for Prims's MST for
# adjacency list representation of graph
from collections import defaultdict
import sys
class Heap():
def __init__(self):
self.array = []
self.size = 0
self.pos = []
def newMinHeapNode(self, v, dist):
minHeapNode = [v, dist]
return minHeapNode
# A utility function to swap two nodes of
# min heap. Needed for min heapify
def swapMinHeapNode(self, a, b):
t = self.array[a]
self.array[a] = self.array[b]
self.array[b] = t
# A standard function to heapify at given idx
# This function also updates position of nodes
# when they are swapped. Position is needed
# for decreaseKey()
def minHeapify(self, idx):
smallest = idx
left = 2 * idx + 1
right = 2 * idx + 2
if left < self.size and self.array[left][1] < \
self.array[smallest][1]:
smallest = left
if right < self.size and self.array[right][1] < \
self.array[smallest][1]:
smallest = right
# The nodes to be swapped in min heap
# if idx is not smallest
if smallest != idx:
# Swap positions
self.pos[ self.array[smallest][0] ] = idx
self.pos[ self.array[idx][0] ] = smallest
# Swap nodes
self.swapMinHeapNode(smallest, idx)
self.minHeapify(smallest)
# Standard function to extract minimum node from heap
def extractMin(self):
# Return NULL wif heap is empty
if self.isEmpty() == True:
return
# Store the root node
root = self.array[0]
# Replace root node with last node
lastNode = self.array[self.size - 1]
self.array[0] = lastNode
# Update position of last node
self.pos[lastNode[0]] = 0
self.pos[root[0]] = self.size - 1
# Reduce heap size and heapify root
self.size -= 1
self.minHeapify(0)
return root
def isEmpty(self):
return True if self.size == 0 else False
def decreaseKey(self, v, dist):
# Get the index of v in heap array
i = self.pos[v]
# Get the node and update its dist value
self.array[i][1] = dist
# Travel up while the complete tree is not
# hepified. This is a O(Logn) loop
while i > 0 and self.array[i][1] < \
self.array[(i - 1) / 2][1]:
# Swap this node with its parent
self.pos[ self.array[i][0] ] = (i-1)/2
self.pos[ self.array[(i-1)/2][0] ] = i
self.swapMinHeapNode(i, (i - 1)/2 )
# move to parent index
i = (i - 1) / 2;
# A utility function to check if a given vertex
# 'v' is in min heap or not
def isInMinHeap(self, v):
if self.pos[v] < self.size:
return True
return False
def printArr(parent, n):
for i in range(1, n):
print("% d - % d" % (parent[i], i))
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# Adds an edge to an undirected graph
def addEdge(self, src, dest, weight):
# Add an edge from src to dest. A new node is
# added to the adjacency list of src. The node
# is added at the beginning. The first element of
# the node has the destination and the second
# elements has the weight
newNode = [dest, weight]
self.graph[src].insert(0, newNode)
# Since graph is undirected, add an edge from
# dest to src also
newNode = [src, weight]
self.graph[dest].insert(0, newNode)
# The main function that prints the Minimum
# Spanning Tree(MST) using the Prim's Algorithm.
# It is a O(ELogV) function
def PrimMST(self):
# Get the number of vertices in graph
V = self.V
# key values used to pick minimum weight edge in cut
key = []
# List to store contructed MST
parent = []
# minHeap represents set E
minHeap = Heap()
# Initialize min heap with all vertices. Key values of all
# vertices (except the 0th vertex) is is initially infinite
for v in range(V):
parent.append(-1)
key.append(sys.maxint)
minHeap.array.append( minHeap.newMinHeapNode(v, key[v]) )
minHeap.pos.append(v)
# Make key value of 0th vertex as 0 so
# that it is extracted first
minHeap.pos[0] = 0
key[0] = 0
minHeap.decreaseKey(0, key[0])
# Initially size of min heap is equal to V
minHeap.size = V;
# In the following loop, min heap contains all nodes
# not yet added in the MST.
while minHeap.isEmpty() == False:
# Extract the vertex with minimum distance value
newHeapNode = minHeap.extractMin()
u = newHeapNode[0]
# Traverse through all adjacent vertices of u
# (the extracted vertex) and update their
# distance values
for pCrawl in self.graph[u]:
v = pCrawl[0]
# If shortest distance to v is not finalized
# yet, and distance to v through u is less than
# its previously calculated distance
if minHeap.isInMinHeap(v) and pCrawl[1] < key[v]:
key[v] = pCrawl[1]
parent[v] = u
# update distance value in min heap also
minHeap.decreaseKey(v, key[v])
printArr(parent, V)
# Driver program to test the above functions
graph = Graph(9)
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 4)
graph.addEdge(0, 7, 8)
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 8)
graph.addEdge(1, 7, 11)
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 7)
graph.addEdge(2, 8, 2)
graph.addEdge(2, 5, 4)
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 9)
graph.addEdge(3, 5, 14)
graph.addEdge(4, 5, 10)
graph.addEdge(5, 6, 2)
graph.addEdge(6, 7, 1)
graph.addEdge(6, 8, 6)
graph.addEdge(7, 8, 7)
graph.PrimMST()
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta
Output:
0 - 1
5 - 2
2 - 3
3 - 4
6 - 5
7 - 6
0 - 7
2 - 8
时间复杂度:上述代码/算法的时间复杂度看起来是 O(V^2),因为有两个嵌套的 while 循环。如果我们仔细观察,我们可以观察到内循环中的语句执行了 O(V+E) 次(类似于 BFS)。内循环有 reduceKey() 操作,需要 O(LogV) 时间。所以整体时间复杂度是 O(E+V)O(LogV) 也就是 O((E+V)LogV) = O(ELogV) (对于连通图,V = O(E))
5.Kruskal 的最小生成树(Kruskal’s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm)
什么是最小生成树?
给定一个连通图和无向图,该图的生成树是一个子图,它是一棵树并将所有顶点连接在一起。单个图可以有许多不同的生成树。加权、连通、无向图的最小生成树 (MST)或最小权重生成树是权重小于或等于其他所有生成树权重的生成树。生成树的权重是赋予生成树每条边的权重之和。
最小生成树有多少条边?
最小生成树有 (V – 1) 条边,其中 V 是给定图中的顶点数。
以下是使用 Kruskal 算法查找 MST 的步骤
1. Sort all the edges in non-decreasing order of their weight.
2. Pick the smallest edge. Check if it forms a cycle with the spanning tree formed so far. If cycle is not formed, include this edge. Else, discard it.
3. Repeat step#2 until there are (V-1) edges in the spanning tree.
第 2 步使用Union-Find 算法来检测循环。
该算法是一种贪心算法。贪婪的选择是选择在迄今为止构建的 MST 中不会导致循环的最小权重边。让我们通过一个例子来理解它:考虑下面的输入图。
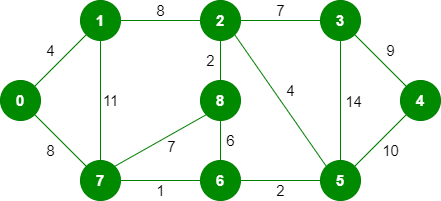
该图包含 9 个顶点和 14 条边。因此,形成的最小生成树将具有 (9 – 1) = 8 条边。
After sorting:
Weight Src Dest
1 7 6
2 8 2
2 6 5
4 0 1
4 2 5
6 8 6
7 2 3
7 7 8
8 0 7
8 1 2
9 3 4
10 5 4
11 1 7
14 3 5
现在从边
1 的排序列表中一一选取所有边 。选取边 7-6:未形成环,将其包括在内。

2. 选取边 8-2:不形成环,包括它。
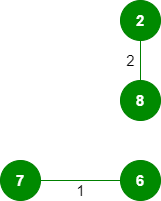
3. 选取边 6-5:不形成环,包括它。
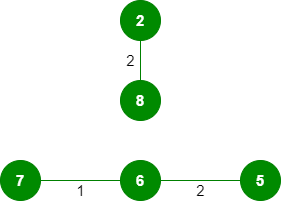
4. 选取边 0-1:不形成环,包括它。
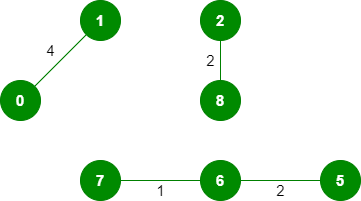
5. 选取边 2-5:不形成循环,包括它。
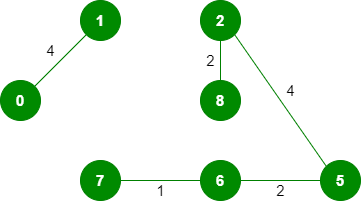
6.选取边 8-6:由于将这条边包含在循环中,因此将其丢弃。
7. 选取边2-3:不形成环,包括它。
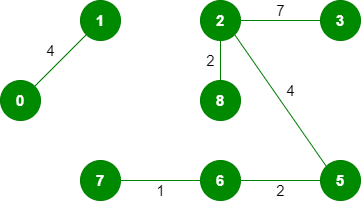
8. 选取边 7-8:由于在循环中包含此边,因此将其丢弃。
9. 拾取边 0-7:不形成循环,包括它。
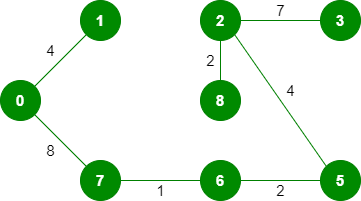
10. 选取边 1-2:由于将这条边包含在循环中,因此将其丢弃。
11. 拾取边3-4:不形成循环,包括它。
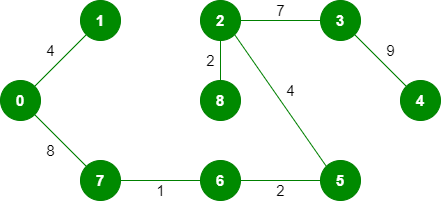
由于包含的边数等于 (V – 1),算法到此停止。
# Python program for Kruskal's algorithm to find
# Minimum Spanning Tree of a given connected,
# undirected and weighted graph
from collections import defaultdict
# Class to represent a graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices # No. of vertices
self.graph = [] # default dictionary
# to store graph
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, u, v, w):
self.graph.append([u, v, w])
# A utility function to find set of an element i
# (uses path compression technique)
def find(self, parent, i):
if parent[i] == i:
return i
return self.find(parent, parent[i])
# A function that does union of two sets of x and y
# (uses union by rank)
def union(self, parent, rank, x, y):
xroot = self.find(parent, x)
yroot = self.find(parent, y)
# Attach smaller rank tree under root of
# high rank tree (Union by Rank)
if rank[xroot] < rank[yroot]:
parent[xroot] = yroot
elif rank[xroot] > rank[yroot]:
parent[yroot] = xroot
# If ranks are same, then make one as root
# and increment its rank by one
else:
parent[yroot] = xroot
rank[xroot] += 1
# The main function to construct MST using Kruskal's
# algorithm
def KruskalMST(self):
result = [] # This will store the resultant MST
# An index variable, used for sorted edges
i = 0
# An index variable, used for result[]
e = 0
# Step 1: Sort all the edges in
# non-decreasing order of their
# weight. If we are not allowed to change the
# given graph, we can create a copy of graph
self.graph = sorted(self.graph,
key=lambda item: item[2])
parent = []
rank = []
# Create V subsets with single elements
for node in range(self.V):
parent.append(node)
rank.append(0)
# Number of edges to be taken is equal to V-1
while e < self.V - 1:
# Step 2: Pick the smallest edge and increment
# the index for next iteration
u, v, w = self.graph[i]
i = i + 1
x = self.find(parent, u)
y = self.find(parent, v)
# If including this edge does't
# cause cycle, include it in result
# and increment the indexof result
# for next edge
if x != y:
e = e + 1
result.append([u, v, w])
self.union(parent, rank, x, y)
# Else discard the edge
minimumCost = 0
print ("Edges in the constructed MST")
for u, v, weight in result:
minimumCost += weight
print("%d -- %d == %d" % (u, v, weight))
print("Minimum Spanning Tree" , minimumCost)
# Driver code
g = Graph(4)
g.addEdge(0, 1, 10)
g.addEdge(0, 2, 6)
g.addEdge(0, 3, 5)
g.addEdge(1, 3, 15)
g.addEdge(2, 3, 4)
# Function call
g.KruskalMST()
# This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav
Output
Following are the edges in the constructed MST
2 -- 3 == 4
0 -- 3 == 5
0 -- 1 == 10
Minimum Cost Spanning Tree: 19
时间复杂度: O(ElogE) 或 O(ElogV)。边的排序需要 O(ELogE) 时间。排序后,我们遍历所有边并应用 find-union 算法。find 和 union 操作最多需要 O(LogV) 时间。所以整体复杂度是 O(ELogE + ELogV) 时间。E 的值最多可以是 O(V 2 ),所以 O(LogV) 与 O(LogE) 相同。因此,整体时间复杂度为 O(ElogE) 或 O(ElogV)



