Java处理Modbus-RTU协议(另辟蹊径改源码)
开始
看到这篇文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/yangming1996/p/6549800.html
,发现可以用以下类来处理
ByteArrayInputStream bInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytesData);
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bInputStream);
问题
但是当我用
byte[] bytesData = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x03, 0x04, 0x02, (byte)0x92, (byte) 0xFF, (byte)0x9B, 0x5A, 0x3D };
ByteArrayInputStream bInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytesData);
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bInputStream);
// 地址 功能 返回有效字节数 湿度数据 温度数据 校验低位 校验高位
// 01 03 04 02 92 FF 9B 5A 3D
// 计算: 0292 -> 658 湿度 65.8 %RH
// FF9B -> -101 温度 -10.1 ℃
dataInputStream.skipBytes(3);
int value1 = dataInputStream.readShort();//读 0x0292
int value2 = dataInputStream.readShort();//读 0xFF9B
double valuef1 = value1/10.0;
double valuef2 = value2/10.0;
JVM里是这样的
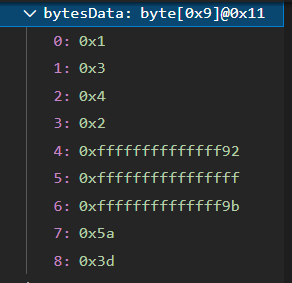
这是正常的,因为Java把0x92认为是有符号的int,超出了byte的范围[-128~127],详见我另一篇文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/yucloud/p/Java_byte.html
发现value1和value2的数值都不对,理论上应该是 658和-101,猜测可能是read()没有取位,果然看了源码发现: DataInputStream的readShort()使用了read(),
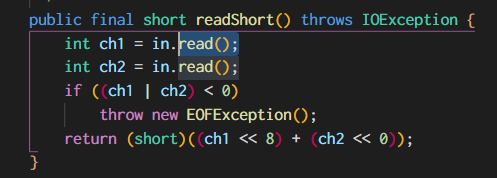
但这里read()只是继承了其父类 FilterInputStream 的 in.read(),
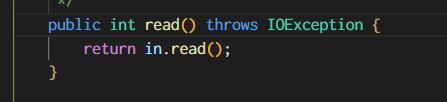
并没有改动,并没有取低位byte&0xFF,因此不适合用于读取 byte 数组。
小解决
因此这里我改为
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class testModBusRtuDataInputStream extends DataInputStream{
public testModBusRtuDataInputStream(InputStream in) {
super(in);
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return super.read()&0xFF;
}
}
然后用 testModBusRtuDataInputStream 代替 DataInputStream 使用即可。
更进一步的改造
当然,我们的需求是把 0x0292 读取为 65.8
0292 -> 658 湿度 65.8 %RH
然后如果想实现这个,甚至更多功能,就得改造源码了
DataInputStream 继承了 FilterInputStream 且实现了 DataInput接口
public class DataInputStream extends FilterInputStream implements DataInput {
...代码略...
}
其方法如下
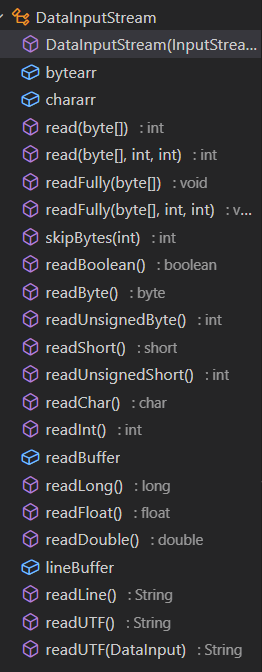
想继承DataInputStream,但发现不能Override DataInputStream里使用到的DataInput的接口
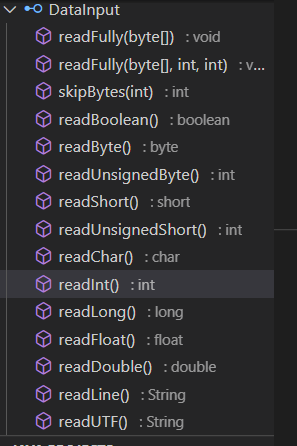
其中的 DataInput 接口,它有如下接口方法
方案:
复制源码并把类改成自定义类,如 RtuDataInputStream.java
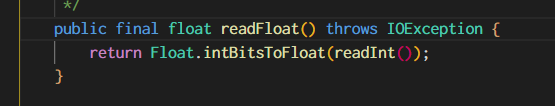
这样就可以根据需求来修改 DataInput 的方法,如修改 readFloat()
DataInputStream.java 里是这样的
修改后的 RtuDataInputStream.java
...其他代码略...
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.read()&0xFF;
}
...其他代码略...
public final float readFloat() throws IOException {
return (float) (readShort()/10.0);
}
...其他代码略...
然后把main()里用到 DataInputStream 都替换成 RtuDataInputStream 即可,因为这两个类现在有相同的父类和接口,相当于是兄弟类了
这样就可以读取 RTU 的温湿度值了
byte[] bytesData = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x03, 0x04, 0x02, (byte)0x92, (byte) 0xFF, (byte)0x9B, 0x5A, 0x3D };
ByteArrayInputStream bInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytesData);
RtuDataInputStream dataInputStream = new RtuDataInputStream(bInputStream);
//注意这里都换成了 RtuDataInputStream 自定义类
// 地址 功能 返回有效字节数 湿度数据 温度数据 校验低位 校验高位
// 01 03 04 02 92 FF 9B 5A 3D
// 计算: 0292 -> 658 湿度 65.8 %RH
// FF9B -> -101 温度 -10.1 ℃
dataInputStream.skipBytes(3);
float value1 = dataInputStream.readFloat();//读 0x0292 为 65.8
float value2 = dataInputStream.readFloat();//读 0xFF9B 为 -10.1
测试代码和效果
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ModbusRtuParser {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] hexData = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x03, 0x04, 0x02, 0x1F, 0x01, 0x4E, 0x4B, (byte) 0xE9 };
byte[] hexTestData = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x03, 0x04, 0x03, (byte)0xc9, 0x01, 0x26, (byte)0xaa, 0x03};
byte[] hexNagData = new byte[] { 0x01, 0x03, 0x04, 0x02, (byte)0x92, (byte) 0xFF, (byte)0x9B, 0x5A, 0x3D };
byte[] bytesData = new byte[hexNagData.length];
for (int i=0; i<bytesData.length; i++)
bytesData[i] = (byte) (0xFF&hexNagData[i]);
/******************************************** 例子 *******************************************/
// 地址 功能 始地址 数据长度 校验低位 校验高位
// 01 03 00 00 00 02 C4 0B
// 地址 功能 返回有效字节数 湿度数据 温度数据 校验低位 校验高位
// 01 03 04 02 92 FF 9B 5A 3D
// 计算: 0292 -> 658 湿度 65.8 %RH
// FF9B -> -101 温度 -10.1 ℃
// TX: 01 03 00 00 00 02 C4 0B
// RX: 01 03 04 02 1F 01 4E 4B E9
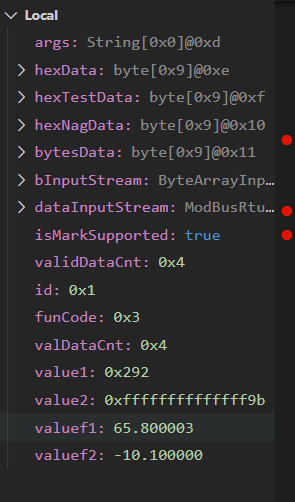
ByteArrayInputStream bInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytesData);
//DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bInputStream);
ModBusRtuDataInputStream dataInputStream = new ModBusRtuDataInputStream(bInputStream);
boolean isMarkSupported = dataInputStream.markSupported();
dataInputStream.skipBytes(2);
int validDataCnt = dataInputStream.readByte();
dataInputStream.reset();
if (dataInputStream.available() != validDataCnt+5)
throw new IOException();
int id = dataInputStream.readByte();
int funCode = dataInputStream.readByte();
int valDataCnt = dataInputStream.readByte();
int value1 = dataInputStream.readShort();
int value2 = dataInputStream.readShort();
dataInputStream.reset();
dataInputStream.skipBytes(3);
double valuef1 = dataInputStream.readFloat();
double valuef2 = value2/10.0;
//ByteArrayOutputStream bOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();//32
//DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(bOutputStream);
}
}
不要问为什么没有打印,因为个人习惯用调试器看结果
改造后的自定义类源码
改动的例子源码太长了,折叠起来:
自定义类 ModBusRtuDataInputStream.java 源码在此
@hasEdited 代表该方法被修改了,没有这个符号就代表和原 DataInputStream 基本一致
**展开查看 ModBusRtuDataInputStream.java 源码**
/* * Copyright (c) 1994, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms. * * @hasEdited * @NOTE: 照着需求修改 java.io.DataInputStream 的.... * 微软 JDK11.0.8 */ import java.io.*; /** * A data input stream lets an application read primitive Java data * types from an underlying input stream in a machine-independent * way. An application uses a data output stream to write data that * can later be read by a data input stream. * <p> * DataInputStream is not necessarily safe for multithreaded access. * Thread safety is optional and is the responsibility of users of * methods in this class. * * @author Arthur van Hoff * @see java.io.DataOutputStream * @since 1.0 */ public class ModBusRtuDataInputStream extends FilterInputStream implements DataInput { /** * Creates a DataInputStream that uses the specified * underlying InputStream. * * @param in the specified input stream */ public ModBusRtuDataInputStream(InputStream in) { super(in); } /** * @author: * @hasEdited * 这里只需要读取byte,因此需要取 &0xFF */ @Override public int read() throws IOException { return super.read()&0xFF; } /** * working arrays initialized on demand by readUTF */ private byte bytearr[] = new byte[80]; private char chararr[] = new char[80]; /** * Reads some number of bytes from the contained input stream and * stores them into the buffer array <code>b</code>. The number of * bytes actually read is returned as an integer. This method blocks * until input data is available, end of file is detected, or an * exception is thrown. * * <p>If <code>b</code> is null, a <code>NullPointerException</code> is * thrown. If the length of <code>b</code> is zero, then no bytes are * read and <code>0</code> is returned; otherwise, there is an attempt * to read at least one byte. If no byte is available because the * stream is at end of file, the value <code>-1</code> is returned; * otherwise, at least one byte is read and stored into <code>b</code>. * * <p>The first byte read is stored into element <code>b[0]</code>, the * next one into <code>b[1]</code>, and so on. The number of bytes read * is, at most, equal to the length of <code>b</code>. Let <code>k</code> * be the number of bytes actually read; these bytes will be stored in * elements <code>b[0]</code> through <code>b[k-1]</code>, leaving * elements <code>b[k]</code> through <code>b[b.length-1]</code> * unaffected. * * <p>The <code>read(b)</code> method has the same effect as: * <blockquote><pre> * read(b, 0, b.length) * </pre></blockquote> * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read. * @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or * <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end * of the stream has been reached. * @exception IOException if the first byte cannot be read for any reason * other than end of file, the stream has been closed and the underlying * input stream does not support reading after close, or another I/O * error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in * @see java.io.InputStream#read(byte[], int, int) */ public final int read(byte b[]) throws IOException { return in.read(b, 0, b.length); } /** * Reads up to <code>len</code> bytes of data from the contained * input stream into an array of bytes. An attempt is made to read * as many as <code>len</code> bytes, but a smaller number may be read, * possibly zero. The number of bytes actually read is returned as an * integer. * * <p> This method blocks until input data is available, end of file is * detected, or an exception is thrown. * * <p> If <code>len</code> is zero, then no bytes are read and * <code>0</code> is returned; otherwise, there is an attempt to read at * least one byte. If no byte is available because the stream is at end of * file, the value <code>-1</code> is returned; otherwise, at least one * byte is read and stored into <code>b</code>. * * <p> The first byte read is stored into element <code>b[off]</code>, the * next one into <code>b[off+1]</code>, and so on. The number of bytes read * is, at most, equal to <code>len</code>. Let <i>k</i> be the number of * bytes actually read; these bytes will be stored in elements * <code>b[off]</code> through <code>b[off+</code><i>k</i><code>-1]</code>, * leaving elements <code>b[off+</code><i>k</i><code>]</code> through * <code>b[off+len-1]</code> unaffected. * * <p> In every case, elements <code>b[0]</code> through * <code>b[off]</code> and elements <code>b[off+len]</code> through * <code>b[b.length-1]</code> are unaffected. * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read. * @param off the start offset in the destination array <code>b</code> * @param len the maximum number of bytes read. * @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or * <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end * of the stream has been reached. * @exception NullPointerException If <code>b</code> is <code>null</code>. * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If <code>off</code> is negative, * <code>len</code> is negative, or <code>len</code> is greater than * <code>b.length - off</code> * @exception IOException if the first byte cannot be read for any reason * other than end of file, the stream has been closed and the underlying * input stream does not support reading after close, or another I/O * error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in * @see java.io.InputStream#read(byte[], int, int) */ public final int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException { return in.read(b, off, len); } /** * See the general contract of the {@code readFully} * method of {@code DataInput}. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code b} is {@code null}. * @throws EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading all the bytes. * @throws IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException { readFully(b, 0, b.length); } /** * See the general contract of the {@code readFully} * method of {@code DataInput}. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read. * @param off the start offset in the data array {@code b}. * @param len the number of bytes to read. * @exception NullPointerException if {@code b} is {@code null}. * @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code off} is negative, * {@code len} is negative, or {@code len} is greater than * {@code b.length - off}. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading all the bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final void readFully(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException { if (len < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); int n = 0; while (n < len) { int count = in.read(b, off + n, len - n); if (count < 0) throw new EOFException(); n += count; } } /** * See the general contract of the <code>skipBytes</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @param n the number of bytes to be skipped. * @return the actual number of bytes skipped. * @exception IOException if the contained input stream does not support * seek, or the stream has been closed and * the contained input stream does not support * reading after close, or another I/O error occurs. */ public final int skipBytes(int n) throws IOException { int total = 0; int cur = 0; while ((total<n) && ((cur = (int) in.skip(n-total)) > 0)) { total += cur; } return total; } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readBoolean</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the <code>boolean</code> value read. * @exception EOFException if this input stream has reached the end. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException { int ch = in.read(); if (ch < 0) throw new EOFException(); return (ch != 0); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readByte</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next byte of this input stream as a signed 8-bit * <code>byte</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream has reached the end. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final byte readByte() throws IOException { int ch = in.read(); if (ch < 0) throw new EOFException(); return (byte)(ch); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readUnsignedByte</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next byte of this input stream, interpreted as an * unsigned 8-bit number. * @exception EOFException if this input stream has reached the end. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException { int ch = in.read(); if (ch < 0) throw new EOFException(); return ch; } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readShort</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next two bytes of this input stream, interpreted as a * signed 16-bit number. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading two bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final short readShort() throws IOException { int ch1 = in.read(); int ch2 = in.read(); if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0) throw new EOFException(); return (short)((ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0)); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readUnsignedShort</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next two bytes of this input stream, interpreted as an * unsigned 16-bit integer. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading two bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException { int ch1 = in.read(); int ch2 = in.read(); if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0) throw new EOFException(); return (ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readChar</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next two bytes of this input stream, interpreted as a * <code>char</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading two bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final char readChar() throws IOException { int ch1 = in.read(); int ch2 = in.read(); if ((ch1 | ch2) < 0) throw new EOFException(); return (char)((ch1 << 8) + (ch2 << 0)); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readInt</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next four bytes of this input stream, interpreted as an * <code>int</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading four bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final int readInt() throws IOException { int ch1 = in.read(); int ch2 = in.read(); int ch3 = in.read(); int ch4 = in.read(); if ((ch1 | ch2 | ch3 | ch4) < 0) throw new EOFException(); return ((ch1 << 24) + (ch2 << 16) + (ch3 << 8) + (ch4 << 0)); } private byte readBuffer[] = new byte[8]; /** * See the general contract of the <code>readLong</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next eight bytes of this input stream, interpreted as a * <code>long</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading eight bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ public final long readLong() throws IOException { readFully(readBuffer, 0, 8); return (((long)readBuffer[0] << 56) + ((long)(readBuffer[1] & 255) << 48) + ((long)(readBuffer[2] & 255) << 40) + ((long)(readBuffer[3] & 255) << 32) + ((long)(readBuffer[4] & 255) << 24) + ((readBuffer[5] & 255) << 16) + ((readBuffer[6] & 255) << 8) + ((readBuffer[7] & 255) << 0)); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readFloat</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @hasEdited * * @return the next four bytes of this input stream, interpreted as a * <code>float</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading four bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.DataInputStream#readInt() * @see java.lang.Float#intBitsToFloat(int) */ public final float readFloat() throws IOException { return (float) (readShort()/10.0); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readDouble</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return the next eight bytes of this input stream, interpreted as a * <code>double</code>. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading eight bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.DataInputStream#readLong() * @see java.lang.Double#longBitsToDouble(long) */ public final double readDouble() throws IOException { return Double.longBitsToDouble(readLong()); } private char lineBuffer[]; /** * See the general contract of the <code>readLine</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes to characters. * As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to read lines of text is via the * <code>BufferedReader.readLine()</code> method. Programs that use the * <code>DataInputStream</code> class to read lines can be converted to use * the <code>BufferedReader</code> class by replacing code of the form: * <blockquote><pre> * DataInputStream d = new DataInputStream(in); * </pre></blockquote> * with: * <blockquote><pre> * BufferedReader d * = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); * </pre></blockquote> * * @return the next line of text from this input stream. * @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs. * @see java.io.BufferedReader#readLine() * @see java.io.FilterInputStream#in */ @Deprecated public final String readLine() throws IOException { char buf[] = lineBuffer; if (buf == null) { buf = lineBuffer = new char[128]; } int room = buf.length; int offset = 0; int c; loop: while (true) { switch (c = in.read()) { case -1: case '\n': break loop; case '\r': int c2 = in.read(); if ((c2 != '\n') && (c2 != -1)) { if (!(in instanceof PushbackInputStream)) { this.in = new PushbackInputStream(in); } ((PushbackInputStream)in).unread(c2); } break loop; default: if (--room < 0) { buf = new char[offset + 128]; room = buf.length - offset - 1; System.arraycopy(lineBuffer, 0, buf, 0, offset); lineBuffer = buf; } buf[offset++] = (char) c; break; } } if ((c == -1) && (offset == 0)) { return null; } return String.copyValueOf(buf, 0, offset); } /** * See the general contract of the <code>readUTF</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * <p> * Bytes * for this operation are read from the contained * input stream. * * @return a Unicode string. * @exception EOFException if this input stream reaches the end before * reading all the bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @exception UTFDataFormatException if the bytes do not represent a valid * modified UTF-8 encoding of a string. * @see java.io.DataInputStream#readUTF(java.io.DataInput) */ public final String readUTF() throws IOException { return readUTF(this); } /** * Reads from the * stream <code>in</code> a representation * of a Unicode character string encoded in * <a href="DataInput.html#modified-utf-8">modified UTF-8</a> format; * this string of characters is then returned as a <code>String</code>. * The details of the modified UTF-8 representation * are exactly the same as for the <code>readUTF</code> * method of <code>DataInput</code>. * * @param in a data input stream. * @return a Unicode string. * @exception EOFException if the input stream reaches the end * before all the bytes. * @exception IOException the stream has been closed and the contained * input stream does not support reading after close, or * another I/O error occurs. * @exception UTFDataFormatException if the bytes do not represent a * valid modified UTF-8 encoding of a Unicode string. * @see java.io.DataInputStream#readUnsignedShort() */ public static final String readUTF(DataInput in) throws IOException { int utflen = in.readUnsignedShort(); byte[] bytearr = null; char[] chararr = null; if (in instanceof ModBusRtuDataInputStream) { ModBusRtuDataInputStream dis = (ModBusRtuDataInputStream)in; if (dis.bytearr.length < utflen){ dis.bytearr = new byte[utflen*2]; dis.chararr = new char[utflen*2]; } chararr = dis.chararr; bytearr = dis.bytearr; } else { bytearr = new byte[utflen]; chararr = new char[utflen]; } int c, char2, char3; int count = 0; int chararr_count=0; in.readFully(bytearr, 0, utflen); while (count < utflen) { c = (int) bytearr[count] & 0xff; if (c > 127) break; count++; chararr[chararr_count++]=(char)c; } while (count < utflen) { c = (int) bytearr[count] & 0xff; switch (c >> 4) { case 0: case 1: case 2: case 3: case 4: case 5: case 6: case 7: /* 0xxxxxxx*/ count++; chararr[chararr_count++]=(char)c; break; case 12: case 13: /* 110x xxxx 10xx xxxx*/ count += 2; if (count > utflen) throw new UTFDataFormatException( "malformed input: partial character at end"); char2 = (int) bytearr[count-1]; if ((char2 & 0xC0) != 0x80) throw new UTFDataFormatException( "malformed input around byte " + count); chararr[chararr_count++]=(char)(((c & 0x1F) << 6) | (char2 & 0x3F)); break; case 14: /* 1110 xxxx 10xx xxxx 10xx xxxx */ count += 3; if (count > utflen) throw new UTFDataFormatException( "malformed input: partial character at end"); char2 = (int) bytearr[count-2]; char3 = (int) bytearr[count-1]; if (((char2 & 0xC0) != 0x80) || ((char3 & 0xC0) != 0x80)) throw new UTFDataFormatException( "malformed input around byte " + (count-1)); chararr[chararr_count++]=(char)(((c & 0x0F) << 12) | ((char2 & 0x3F) << 6) | ((char3 & 0x3F) << 0)); break; default: /* 10xx xxxx, 1111 xxxx */ throw new UTFDataFormatException( "malformed input around byte " + count); } } // The number of chars produced may be less than utflen return new String(chararr, 0, chararr_count); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号