学习AngularJs:Directive指令用法(完整版)
本教程使用AngularJs版本:1.5.3
AngularJs GitHub: https://github.com/angular/angular.js/
AngularJs下载地址:https://angularjs.org/
摘要:Directive(指令)笔者认为是AngularJ非常强大而有有用的功能之一。它就相当于为我们写了公共的自定义DOM元素或CLASS属性或ATTR属性,并且它不只是单单如此,你还可以在它的基础上来操作scope、绑定事件、更改样式等。通过这个Directive,我们可以封装很多公共指令,比如分页指令、自动补全指令等等。然后在HTML页面里只需要简单的写一行代码就可以实现很多强大的功能。一般情况下,需要用Directive有下面的情景:
1. 使你的Html更具语义化,不需要深入研究代码和逻辑即可知道页面的大致逻辑。
2. 抽象一个自定义组件,在其他地方进行重用。
一、Directive的定义及其使用方法
AngularJs的指令定义大致如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
angular.module("app",[]).directive("directiveName",function(){ return{ //通过设置项来定义 }; }) |
Directive可以放置于元素名、属性、class、注释中。下面是引用myDir这个directive的等价方式。(但很多directive都限制为“属性”的使用方式)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<span <span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">directive-name</span><span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">="exp"></span>//属性</span> <span class="<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">directive-name</span>: exp;"></span>//class <<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">directive-name</span>></<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">directive-name</span>>//元素 <!-- directive: <span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">directive-name </span><span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">exp -->//注释</span> |
如下一个实例 :
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
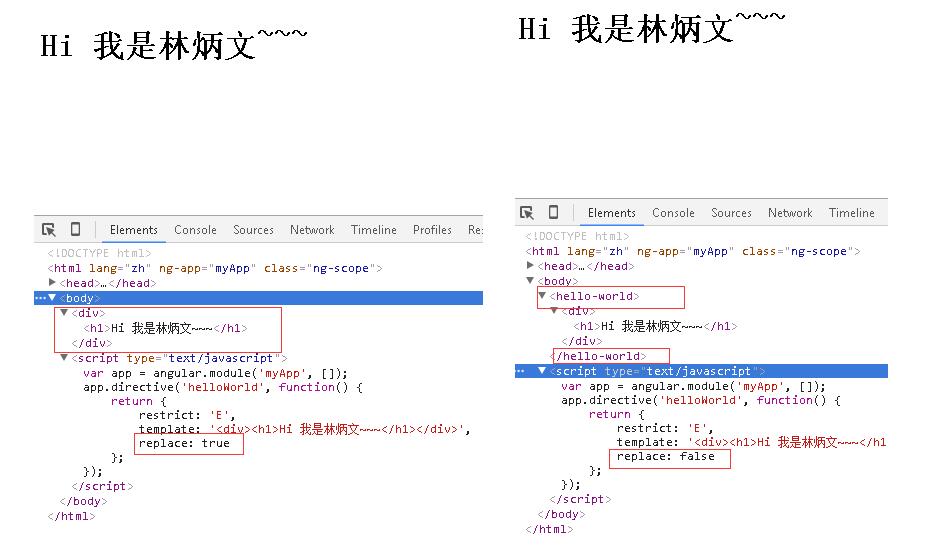
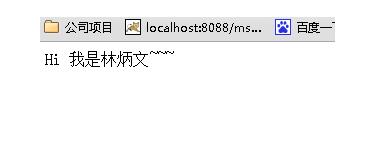
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello-world></hello-world> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('helloWorld', function() { return { restrict: 'E', template: '<div>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</div>', replace: true }; }); </script> </html> |
结果:
下面是一个directive的详细版
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
var myModule = angular.module(...); myModule.directive('directiveName', function factory(injectables) { var directiveDefinitionObject = { priority: 0, template: '<div></div>', templateUrl: 'directive.html', replace: false, transclude: false, restrict: 'A', scope: false, compile: function compile(tElement, tAttrs, transclude) { return { pre: function preLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... }, post: function postLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... } } }, link: function postLink(scope, iElement, iAttrs) { ... } }; return directiveDefinitionObject; }); |
二、Directive指令内容解读
可 以看到它有8个内容
1.restrict
(字符串)可选参数,指明指令在DOM里面以什么形式被声明;取值有:E(元素),A(属性),C(类),M(注释),其中默认值为A;当然也可以两个一起用,比如EA.表示即可以是元素也可以是属性。
[html] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
E(元素):<directiveName></directiveName>
A(属性):<div directiveName='expression'></div>
C(类): <div class='directiveName'></div>
M(注释):<--directive:directiveName expression-->
一般情况下E/A/C用得比较多。
2.priority
(数字),可选参数,指明指令的优先级,若在单个DOM上有多个指令,则优先级高的先执行;
3.terminal
(布尔型),可选参数,可以被设置为true或false,若设置为true,则优先级低于此指令的其他指令则无效,不会被调用(优先级相同的还是会执行)
4.template(字符串或者函数)可选参数,可以是:
(1)一段HTML文本
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
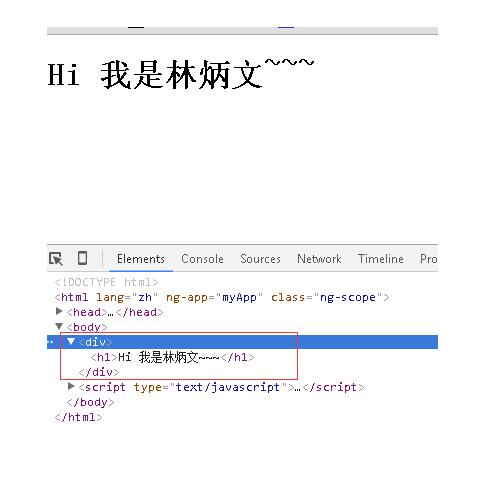
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello-world></hello-world> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('helloWorld', function() { return { restrict: 'E', template: '<div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div>', replace: true }; }); </script> </html> |
(2)一个函数,可接受两个参数tElement和tAttrs
其中tElement是指使用此指令的元素,而tAttrs则实例的属性,它是一个由元素上所有的属性组成的集合(对象)形如:
<hello-world2 title = '我是第二个directive'></hello-world2>
其中title就是tattrs上的属性
下面让我们看看template是一个函数时候的情况
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello-world></hello-world> <hello-world2 title = '我是第二个directive'></hello-world2> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('helloWorld', function() { return { restrict: 'E', template: '<div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div>', replace: true }; }); app.directive("helloWorld2",function(){ return{ restrict:'EAC', template: function(tElement,tAttrs){ var _html = ''; _html += '<div>' +'hello '+tAttrs.title+'</div>'; return _html; } }; }); </script> </html> |
结果:
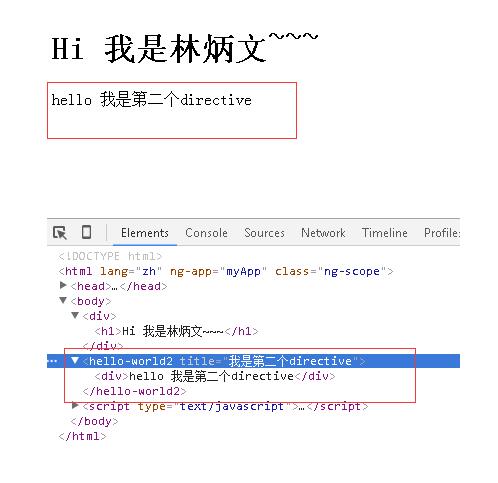
可以看到指令中还用到了hello-world2中的标签中的 title字段
5.templateUrl(字符串或者函数),可选参数,可以是
(1)一个代表HTML文件路径的字符串
(2)一个函数,可接受两个参数tElement和tAttrs(大致同上)
注意:在本地开发时候,需要运行一个服务器,不然使用templateUrl会报错 Cross Origin Request Script(CORS)错误。由于加载html模板是通过异步加载的,若加载大量的模板会拖慢网站的速度,这里有个技巧,就是先缓存模板
你可以再你的index页面加载好的,将下列代码作为你页面的一部分包含在里面。
|
1
2
3
|
<script type='text/ng-template' id='hello.html'> <div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div> </script> |
这里的id属性就是被设置在templateUrl上用的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello-world></hello-world> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('helloWorld', function() { return { restrict: 'E', templateUrl: 'hello.html', replace: true }; }); </script> <script type='text/ng-template' id='hello.html'> <div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div> </script> </html> |
输出结果:
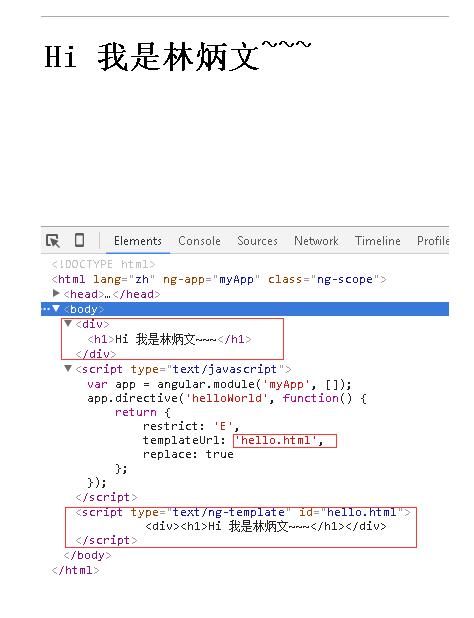
另一种办法缓存是:
|
1
2
3
4
|
app.run(["$templateCache", function($templateCache) { $templateCache.put("hello.html", "<div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div>"); }]); |
使用实例如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <hello-world></hello-world> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('helloWorld', function() { return { restrict: 'E', templateUrl: 'hello.html', replace: true }; }); app.run(["$templateCache", function($templateCache) { $templateCache.put("hello.html", "<div><h1>Hi 我是林炳文~~~</h1></div>"); }]); </script> </html> |
结果:
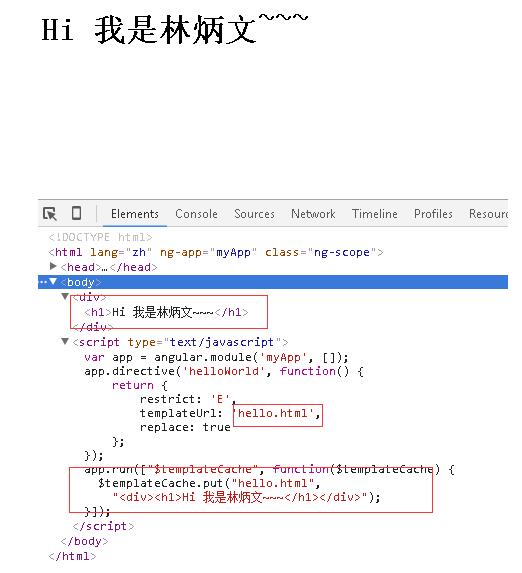
其实第一种方法还好一些,写起来会比较快,笔者就得最多的也是第一种写法,直接包在scprit当中
6.replace
(布尔值),默认值为false,设置为true时候,我们再来看看下面的例子(对比下在template时候举的例子)
replace为true时,hello-world这个标签不在了,反之,则存在。
7.scope
(1)默认值false。表示继承父作用域;
(2)true。表示继承父作用域,并创建自己的作用域(子作用域);
(3){}。表示创建一个全新的隔离作用域;
7.1首先我们先来了解下scope的继承机制。我们用ng-controller这个指令举例,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller='MainController'> 父亲:{{name}}<input ng-model="name" /> <div my-directive></div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller('MainController', function ($scope) { $scope.name = '林炳文'; }); app.directive('myDirective', function () { return { restrict: 'EA', scope:false, template: '<div>儿子:{{ name }}<input ng-model="name"/></div>' }; }); </script> </html> |
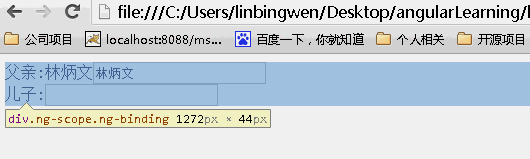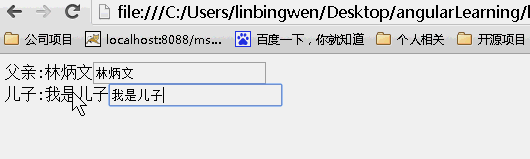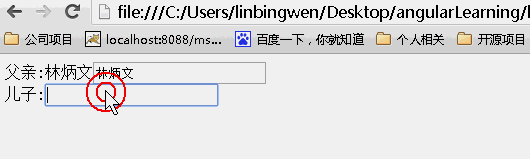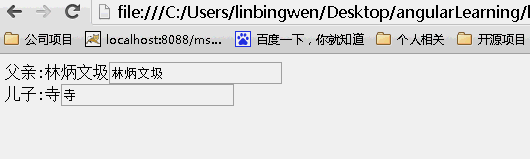
接下来我们通过一个简单明了的例子来说明scope取值不同的差别:
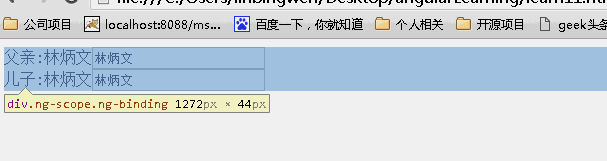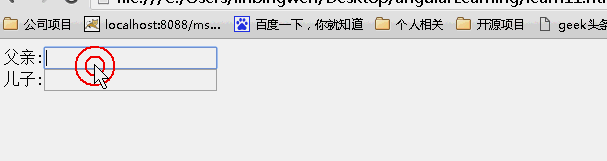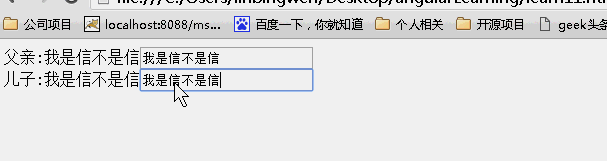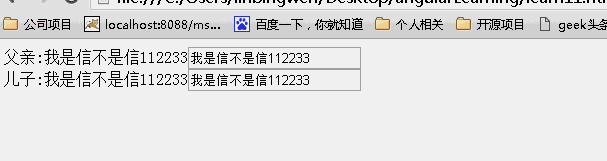
scope:false
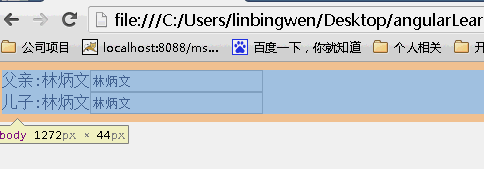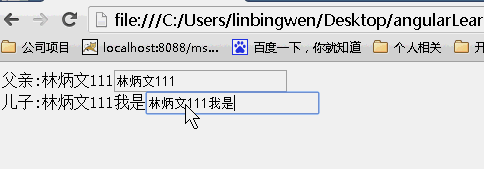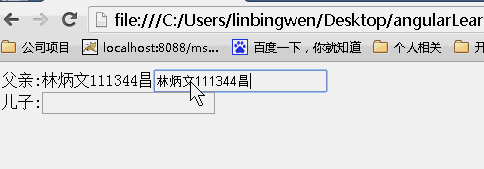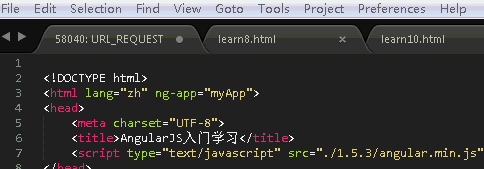
scope:true
scope:{}
当为false时候,儿子继承父亲的值,改变父亲的值,儿子的值也随之变化,反之亦如此。(继承不隔离)
当为true时候,儿子继承父亲的值,改变父亲的值,儿子的值随之变化,但是改变儿子的值,父亲的值不变。(继承隔离)
当为{}时候,没有继承父亲的值,所以儿子的值为空,改变任何一方的值均不能影响另一方的值。(不继承隔离)
tip:当你想要创建一个可重用的组件时隔离作用域是一个很好的选择,通过隔离作用域我们确保指令是‘独立'的,并可以轻松地插入到任何HTML app中,并且这种做法防止了父作用域被污染;
7.2隔离作用域可以通过绑定策略来访问父作用域的属性。
directive 在使用隔离 scope 的时候,提供了三种方法同隔离之外的地方交互。这三种分别是
@ 绑定一个局部 scope 属性到当前 dom 节点的属性值。结果总是一个字符串,因为 dom 属性是字符串。
& 提供一种方式执行一个表达式在父 scope 的上下文中。如果没有指定 attr 名称,则属性名称为相同的本地名称。
= 通过 directive 的 attr 属性的值在局部 scope 的属性和父 scope 属性名之间建立双向绑定。
@ 局部 scope 属性
@ 方式局部属性用来访问 directive 外部环境定义的字符串值,主要是通过 directive 所在的标签属性绑定外部字符串值。这种绑定是单向的,即父 scope 的绑定变化,directive 中的 scope 的属性会同步变化,而隔离 scope 中的绑定变化,父 scope 是不知道的。
如下示例:directive 声明未隔离 scope 类型,并且使用@绑定 name 属性,在 directive 中使用 name 属性绑定父 scope 中的属性。当改变父 scope 中属性的值的时候,directive 会同步更新值,当改变 directive 的 scope 的属性值时,父 scope 无法同步更新值。
js 代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
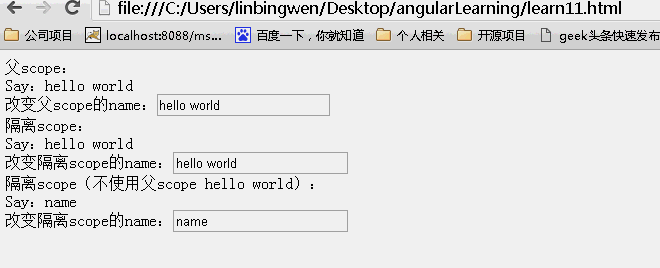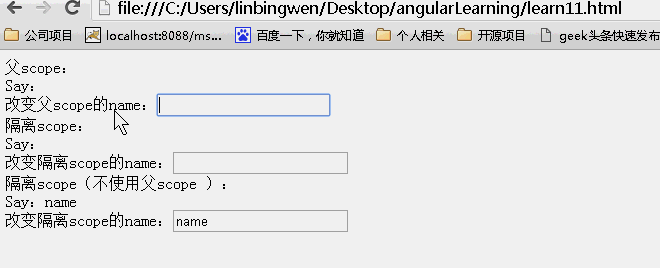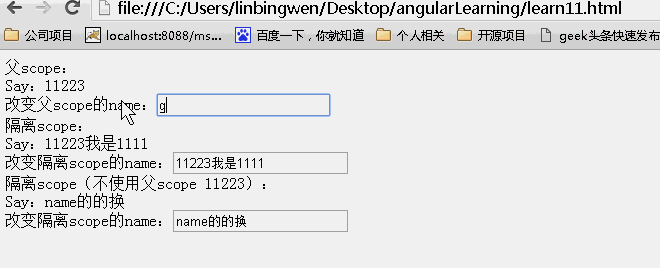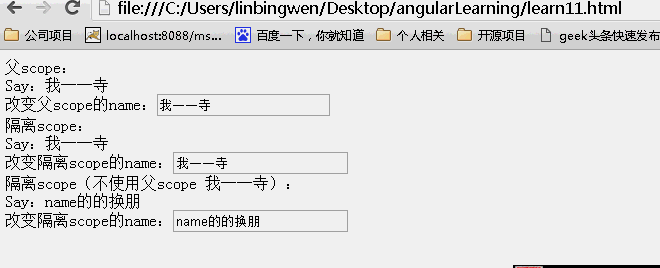
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myController"> <div class="result"> <div>父scope: <div>Say:{{name}}<br>改变父scope的name:<input type="text" value="" ng-model="name"/></div> </div> <div>隔离scope: <div isolated-directive name="{{name}}"></div> </div> <div>隔离scope(不使用父scope {{name}}): <div isolated-directive name="name"></div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller("myController", function ($scope) { $scope.name = "hello world"; }).directive("isolatedDirective", function () { return { scope: { name: "@" }, template: 'Say:{{name}} <br>改变隔离scope的name:<input type="buttom" value="" ng-model="name" class="ng-pristine ng-valid">' }; }); </script> </html> |
结果:页面初始效果

动画效果:
可以看到父scope上的内容发生改变,子scope同时发生改变。而子scope上的内容发生改变。不影响父scope上的内容!
= 局部 scope 属性
= 通过 directive 的 attr 属性的值在局部 scope 的属性和父 scope 属性名之间建立双向绑定。
意思是,当你想要一个双向绑定的属性的时候,你可以使用=来引入外部属性。无论是改变父 scope 还是隔离 scope 里的属性,父 scope 和隔离 scope 都会同时更新属性值,因为它们是双向绑定的关系。
示例代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myController"> <div>父scope: <div>Say:{{user.name}}<br>改变父scope的name:<input type="text" value="" ng-model="userBase.name"/></div> </div> <div>隔离scope: <div isolated-directive user="userBase"></div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller("myController", function ($scope) { $scope.userBase = { name: 'hello', id: 1 }; }).directive("isolatedDirective", function () { return { scope: { user: "=" }, template: 'Say:{{user.name}} <br>改变隔离scope的name:<input type="buttom" value="" ng-model="user.name"/>' } }) </script> </html> |
效果:
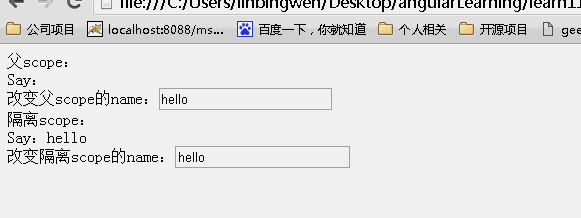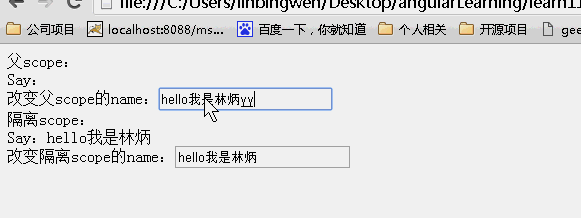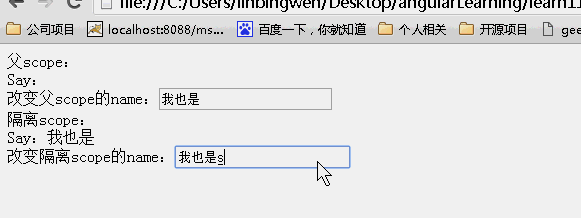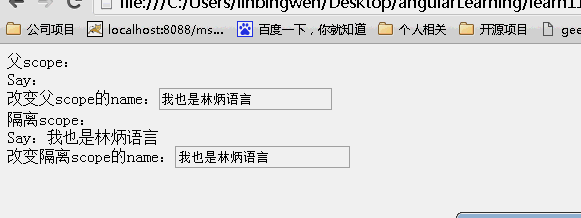
可以看到父scope和子scope上的内容一直都是一样的!
& 局部 scope 属性
& 方式提供一种途经是 directive 能在父 scope 的上下文中执行一个表达式。此表达式可以是一个 function。
比如当你写了一个 directive,当用户点击按钮时,directive 想要通知 controller,controller 无法知道 directive 中发生了什么,也许你可以通过使用 angular 中的 event 广播来做到,但是必须要在 controller 中增加一个事件监听方法。
最好的方法就是让 directive 可以通过一个父 scope 中的 function,当 directive 中有什么动作需要更新到父 scope 中的时候,可以在父 scope 上下文中执行一段代码或者一个函数。
如下示例在 directive 中执行父 scope 的 function。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="myController"> <div>父scope: <div>Say:{{value}}</div> </div> <div>隔离scope: <div isolated-directive action="click()"></div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.controller("myController", function ($scope) { $scope.value = "hello world"; $scope.click = function () { $scope.value = Math.random(); }; }).directive("isolatedDirective", function () { return { scope: { action: "&" }, template: '<input type="button" value="在directive中执行父scope定义的方法" ng-click="action()"/>' } }) </script> </html> |
效果:
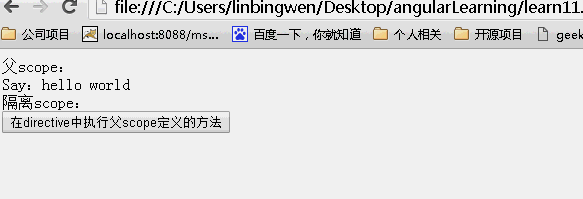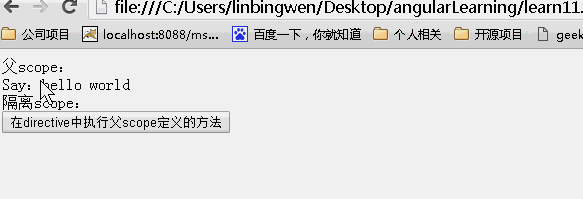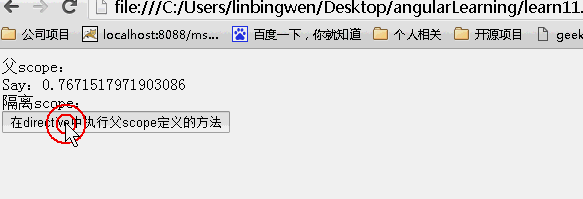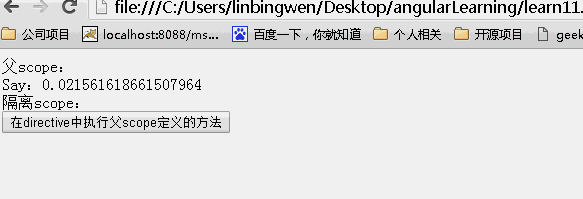
指令的内容比较多,下面再来讲讲transclude、compline、link、contrller
8.transclude
如果不想让指令内部的内容被模板替换,可以设置这个值为true。一般情况下需要和ngTransclude指令一起使用。 比如:template:"<div>hello every <div ng-transclude></div></div>",这时,指令内部的内容会嵌入到ng-transclude这个div中。也就是变成了<div>hello every <div>这是指令内部的内容</div></div>。默认值为false;这个配置选项可以让我们提取包含在指令那个元素里面的内容,再将它放置在指令模板的特定位置。当你开启transclude后,你就可以使用ng-transclude来指明了应该在什么地方放置transcluded内容
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <div sidebox title="Links"> <ul> <li>First link</li> <li>Second link</li> </ul> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('sidebox', function() { return { restrict: 'EA', scope: { title: '@' }, transclude: true, template: '<div class="sidebox">\ <div class="content">\ <h2 class="header">{{ title }}</h2>\ <span class="content" ng-transclude>\ </span>\ </div>\ </div>' }; }); </script> </html> |
结果:
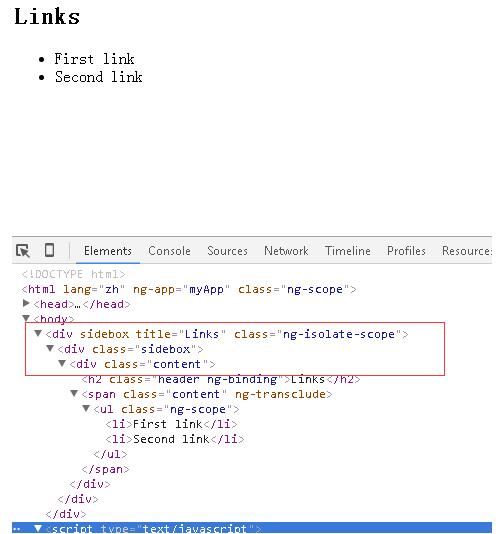
当 transclude: false,时
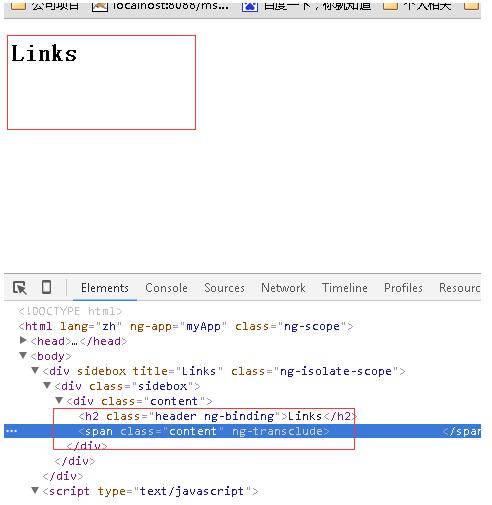
如果指令使用了transclude参数,那么在控制器无法正常监听数据模型的变化了。建议在链接函数里使用$watch服务。
9.controller
可以是一个字符串或者函数。
若是为字符串,则将字符串当做是控制器的名字,来查找注册在应用中的控制器的构造函数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
angular.module('myApp', []) .directive('myDirective', function() { restrict: 'A', // 始终需要 controller: 'SomeController' }) // 应用中其他的地方,可以是同一个文件或被index.html包含的另一个文件 angular.module('myApp') .controller('SomeController', function($scope, $element, $attrs, $transclude) { // 控制器逻辑放在这里 }); 也可以直接在指令内部的定义为匿名函数,同样我们可以再这里注入任何服务($log,$timeout等等)[html] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片angular.module('myApp',[]) .directive('myDirective', function() { restrict: 'A', controller: function($scope, $element, $attrs, $transclude) { // 控制器逻辑放在这里 } }); |
另外还有一些特殊的服务(参数)可以注入
(1)$scope,与指令元素相关联的作用域
(2)$element,当前指令对应的 元素
(3)$attrs,由当前元素的属性组成的对象
(4)$transclude,嵌入链接函数,实际被执行用来克隆元素和操作DOM的函数
注意: 除非是用来定义一些可复用的行为,一般不推荐在这使用。
指令的控制器和link函数(后面会讲)可以进行互换。区别在于,控制器主要是用来提供可在指令间复用的行为但link链接函数只能在当前内部指令中定义行为,且无法再指令间复用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh" ng-app="myApp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>AngularJS入门学习</title> <script type="text/javascript" src="./1.5.3/angular.min.js"></script> </head> <hello mycolor ="red">我是林炳文~~~</hello> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('hello', function() { return { restrict: 'EA', transclude: true, //注意此处必须设置为true controller: function ($scope, $element,$attrs,$transclude,$log) { //在这里你可以注入你想注入的服务 $transclude(function (clone) { var a = angular.element('<p>'); a.css('color', $attrs.mycolor); a.text(clone.text()); $element.append(a); }); $log.info("hello everyone"); } }; }); </script> </html> |
输出结果:
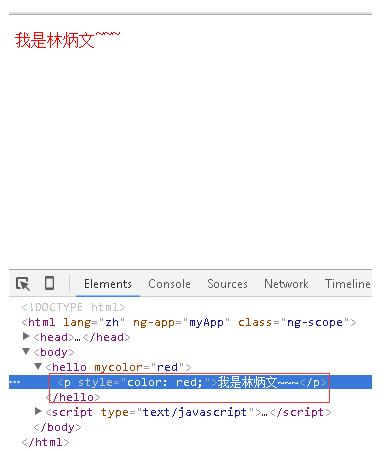
并且在控制台下输出hello everyone
让我们看看$transclude();在这里,它可以接收两个参数,第一个是$scope,作用域,第二个是带有参数clone的回调函数。而这个clone实际上就是嵌入的内容(经过jquery包装),可以在它上做很多DOM操作。
它还有最简单的用法就是
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<script> angular.module('myApp',[]).directive('mySite', function () { return { restrict: 'EA', transclude: true, controller: function ($scope, $element,$attrs,$transclude,$log) { var a = $transclude(); //$transclude()就是嵌入的内容 $element.append(a); } }; }); </script> |
注意:使用$transclude会生成一个新的作用域。
默认情况下,如果我们简单实用$transclude(),那么默认的其作用域就是$transclude生成的作用域
但是如果我们实用$transclude($scope,function(clone){}),那么作用域就是directive的作用域了
那么问题又来了。如果我们想实用父作用域呢
可以使用$scope.$parent
同理想要一个新的作用域也可以使用$scope.$parent.new();
10.controllerAs
这个选项的作用是可以设置你的控制器的别名
一般以前我们经常用这样方式来写代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
angular.module("app",[]) .controller("demoController",["$scope",function($scope){ $scope.title = "angualr"; }]) <div ng-app="app" ng-controller="demoController"> {{title}} </div> |
后来angularjs1.2给我们带来新语法糖,所以我们可以这样写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
angular.module("app",[]) .controller("demoController",[function(){ this.title = "angualr"; }]) <div ng-app="app" ng-controller="demoController as demo"> {{demo.title}} </div> |
同样的我们也可以再指令里面也这样写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<script> angular.module('myApp',[]).directive('mySite', function () { return { restrict: 'EA', transclude: true, controller:'someController', controllerAs:'mainController' //..其他配置 }; }); </script> |
11.require(字符串或者数组)
字符串代表另一个指令的名字,它将会作为link函数的第四个参数。具体用法我们可以举个例子说明。假设现在我们要编写两个指令,两个指令中的link链接函数中(link函数后面会讲)存在有很多重合的方法,这时候我们就可以将这些重复的方法写在第三个指令的controller中(上面也讲到controller经常用来提供指令间的复用行为)然后在这两个指令中,require这个拥有controller字段的的指令(第三个指令),
最后通过link链接函数的第四个参数就可以引用这些重合的方法了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
<!doctype html> <html ng-app="myApp"> <head> </head> <body> <outer-directive> <inner-directive></inner-directive> <inner-directive2></inner-directive2> </outer-directive> <script> var app = angular.module('myApp', []); app.directive('outerDirective', function() { return { scope: {}, restrict: 'AE', controller: function($scope) { this.say = function(someDirective) { console.log('Got:' + someDirective.message); }; } }; }); app.directive('innerDirective', function() { return { scope: {}, restrict: 'AE', require: '^outerDirective', link: function(scope, elem, attrs, controllerInstance) { scope.message = "Hi,leifeng"; controllerInstance.say(scope); } }; }); app.directive('innerDirective2', function() { return { scope: {}, restrict: 'AE', require: '^outerDirective', link: function(scope, elem, attrs, controllerInstance) { scope.message = "Hi,shushu"; controllerInstance.say(scope); } }; }); </script> </body> </html> |
上面例子中的指令innerDirective和指令innerDirective2复用了定义在指令outerDirective的controller中的方法
也进一步说明了,指令中的controller是用来让不同指令间通信用的。
另外我们可以在require的参数值加上下面的某个前缀,这会改变查找控制器的行为:
(1)没有前缀,指令会在自身提供的控制器中进行查找,如果找不到任何控制器,则会抛出一个error
(2)?如果在当前的指令没有找到所需的控制器,则会将null传给link连接函数的第四个参数
(3)^如果在当前的指令没有找到所需的控制器,则会查找父元素的控制器
(4)?^组合
12.Anguar的指令编译过程
首先加载angularjs库,查找到ng-app指令,从而找到应用的边界,
根据ng-app划定的作用域来调用$compile服务进行编译,angularjs会遍历整个HTML文档,并根据js中指令的定义来处理在页面上声明的各个指令按照指令的优先级(priority)排列,根据指令中的配置参数(template,place,transclude等)转换DOM然后就开始按顺序执行各指令的compile函数(如果指令上有定义compile函数)对模板自身进行转换
注意:此处的compile函数是我们指令中配置的,跟上面说的$compile服务不一样。每个compile函数执行完后都会返回一个link函数,所有的link函数会合成一个大的link函数
然后这个大的link函数就会被执行,主要做数据绑定,通过在DOM上注册监听器来动态修改scope中的数据,或者是使用$watchs监听 scope中的变量来修改DOM,从而建立双向绑定等等。若我们的指令中没有配置compile函数,那我们配置的link函数就会运行,她做的事情大致跟上面complie返回之后所有的link函数合成的的大的link函数差不多。
所以:在指令中compile与link选项是互斥的,如果同时设置了这两个选项,那么就会把compile所返回的函数当做是链接函数,而link选项本身就会被忽略掉
13、编译函数 Compile function
function compile(tElement, tAttrs, transclude) { ... }
编译函数是用来处理需要修改模板DOM的情况的。因为大部分指令都不需要修改模板,所以这个函数也不常用。需要用到的例子有ngTrepeat,这个是需要修改模板的,还有ngView这个是需要异步载入内容的。编译函数接受以下参数。
tElement - template element - 指令所在的元素。对这个元素及其子元素进行变形之类的操作是安全的。
tAttrs - template attributes - 这个元素上所有指令声明的属性,这些属性都是在编译函数里共享的。
transclude - 一个嵌入的链接函数function(scope, cloneLinkingFn)。
注意:在编译函数里面不要进行任何DOM变形之外的操作。 更重要的,DOM监听事件的注册应该在链接函数中做,而不是编译函数中。
编译函数可以返回一个对象或者函数。
返回函数 - 等效于在编译函数不存在时,使用配置对象的link属性注册的链接函数。
返回对象 - 返回一个通过pre或post属性注册了函数的对象。参考下面pre-linking和post-liking函数的解释。
14、链接函数 Linking function
function link(scope, iElement, iAttrs, controller) { ... }
链接函数负责注册DOM事件和更新DOM。它是在模板被克隆之后执行的,它也是大部分指令逻辑代码编写的地方。
scope - 指令需要监听的作用域。
iElement - instance element - 指令所在的元素。只有在postLink函数中对元素的子元素进行操作才是安全的,因为那时它们才已经全部链接好。
iAttrs - instance attributes - 实例属性,一个标准化的、所有声明在当前元素上的属性列表,这些属性在所有链接函数间是共享的。
controller - 控制器实例,也就是当前指令通过require请求的指令direct2内部的controller。比如:direct2指令中的controller:function(){this.addStrength = function(){}},那么,在当前指令的link函数中,你就可以通过controller.addStrength进行调用了。
Pre-linking function 在子元素被链接前执行。不能用来进行DOM的变形,以防链接函数找不到正确的元素来链接。
Post-linking function 所有元素都被链接后执行。
说明:
compile选项本身并不会被频繁使用,但是link函数则会被经常使用。本质上,当我们设置了link选项,实际上是创建了一个postLink() 链接函数,以便compile() 函数可以定义链接函数。通常情况下,如果设置了compile函数,说明我们希望在指令和实时数据被放到DOM中之前进行DOM操作,在这个函数中进行诸如添加和删除节点等DOM操作是安全的。compile和link选项是互斥的。如果同时设置了这两个选项,那么会把compile所返回的函数当作链接函数,而link选项本身则会被忽略。译函数负责对模板DOM进行转换。链接函数负责将作用域和DOM进行链接。 在作用域同DOM链接之前可以手动操作DOM。在实践中,编写自定义指令时这种操作是非常罕见的,但有几个内置指令提供了这样的功能。 链接函数是可选的。如果定义了编译函数,它会返回链接函数,因此当两个函数都定义时,编译函数会重载链接函数。如果我们的指令很简单,并且不需要额外的设置,可以从工厂函数(回调函数)返回一个函数来代替对象。如果这样做了,这个函数就是链接函数。
本文转载http://blog.csdn.net/evankaka
以上就是AngularJs:Directive指令用法的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。