制作 Linux 根文件系统
使用 Ubuntu Server 镜像
通过下面方式将 Ubuntu Server 系统安装到镜像文件中:
qemu-img create -q -f qcow2 ubuntu.img 10G
下面命令安装的时候,注意文件系统应该去掉 LVM 勾选。
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -m 2048 -cdrom ubuntu-22.04.2-live-server-amd64.iso --enable-kvm ubuntu.img
尝试简单启动该镜像:
sudo qemu-system-x86_64 -m 2048 --enable-kvm ubuntu.img
启动参数大概如下:
qemu-system-x86_64 -smp 2 -m 2048 \
-kernel linux/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage \
-hda ubuntu.img \
-append "root=/dev/sda2 rw console=ttyS0" \
-enable-kvm \
-nographic \
-serial mon:stdio \
NOTICE - 调试的时候应该去掉
-enable-kvm选项,才能正常打断点。
参考:
使用Busybox制作
包括的组件有:Init程序和基本的shell工具(Busybox)、SSH工具(Dropbbear)
敬请期待,可参考如下:
- https://wiki.beyondlogic.org/index.php?title=Cross_Compiling_BusyBox_for_ARM
- https://www.centennialsoftwaresolutions.com/post/build-the-linux-kernel-busybox-glibc-and-dropbear-for-arm-and-run-them-on-qemu
使用buildroot制作
buildroot简介
Buildroot是Linux平台上一个构建嵌入式Linux系统的框架。整个Buildroot是由Makefile(*.mk)脚本和Kconfig(Config.in)配置文件构成的,因此可以像配置Linux内核一样执行make menuconfig进行配置,编译出一个完整的、可以直接烧写到机器上运行的Linux系统文件(包含bootloader、kernel、rootfs以及rootfs中的各种库和应用程序)。
使用方式
到https://buildroot.uclibc.org/下载源码。
配置
在configs目录下有一些默认的配置,比如qemu_aarch64_virt_defconfig,将其拷贝到 buildroot 的目录下,重命名为.config,然后执行如下:
make menuconfig
设置好大小端:一般在Target options里面选择Arm小端。
可选配置:
(1)默认的配置中编译了Linux内核源码,如果不需要就在make menuconfig中将其关掉。
Kernel -->
(2)可以生成对应的文件系统格式,比如ext2,默认是一个tar包。
Filesystem images -->

编译
make -j $(nproc)
选项配置
Target options:机器类型和二进制文件格式
Target options --->
Target Architecture (ARM (little endian)) ---> //目标处理器的架构和大小端模式 [ARM (little endian)]
Target Binary Format (ELF) ---> //目标二进制格式 [ELF]
Target Architecture Variant (cortex-A7) ---> //目标处理器核心类型 [cortex-A7]
Target ABI (EABIhf) ---> //目标应用程序二进制接口(Application Binary Interface) [EABIhf] ①
Floating point strategy (NEON/VFPv4) ---> //浮点运算策略 [NEON/VFPv4] ②
ARM instruction set (ARM) --->
构建选项
Build options --->
Commands ---> //指定下载、解压命令参数选项
(wget --passive-ftp -nd -t 3) Wget command //用于常规FTP/HTTP下载压缩包 [被动传输模式;不创建目录;超时重试次数为3]
(svn --non-interactive) Subversion (svn) command //通过SSH下载压缩包 [禁用所有交互式提示]
(bzr) Bazaar (bzr) command //版本控制工具Bazaa
(git) Git command //版本控制工具Git
(cvs) CVS command //版本控制工具CVS
(cp) Local files retrieval command //本地文件拷贝命令
(scp) Secure copy (scp) command //基于ssh的安全的远程文件拷贝命令
(hg) Mercurial (hg) command //版本控制工具hg
(gzip -d -c) zcat command //zip包解压缩查看 [解压zip文件 解压到指定路径,源文件不消失]
(bzcat) bzcat command //bz2包解压缩查看
(xzcat) xzcat command //xz包解压缩查看
(lzip -d -c) lzcat command //lz包解压缩查看
() Tar options //bz2包解压缩查看
(/home/hceng/imx6ul_buildroot/configs/imx6ulevk_defconfig) Location to save buildroot config //指定配置文件保存路径
($(TOPDIR)/dl) Download dir //指定文件下载保存路径 [./dl/]
($(BASE_DIR)/host) Host dir //指定主机编译所需工具安装目录 [./output/host]
Mirrors and Download locations ---> //镜像和下载位置
() Primary download site
(http://sources.buildroot.net) Backup download site
(https://cdn.kernel.org/pub) Kernel.org mirror
(http://ftpmirror.gnu.org) GNU Software mirror
(http://rocks.moonscript.org) LuaRocks mirror
(http://cpan.metacpan.org) CPAN mirror (Perl packages)
(0) Number of jobs to run simultaneously (0 for auto) //指定编译时运行的CPU核心数 [0自动]
[ ] Enable compiler cache //使能编译器缓存
[ ] build packages with debugging symbols //启用带调试编译软件包
[*] strip target binaries //binaries和libraries在打包到target目录的时候会被strip命令裁减掉调试信息
() executables that should not be stripped //剥离时跳过可执行文件
() directories that should be skipped when stripping //剥离时跳过的目录
gcc optimization level (optimize for size) ---> //GCC优化等级 [优化大小]
[ ] Enable google-breakpad support //启动崩溃日志收集
libraries (shared only) ---> //库类型 [只共享库]
($(CONFIG_DIR)/local.mk) location of a package override file //包覆盖文件的位置
() global patch directories //全局补丁目录
Advanced --->
[*] paranoid check of library/header paths //检查库/头文件路径
[ ] Force the building of host dependencies //强制构建主机依赖
[ ] Make the build reproducible (experimental) //构建可重复(实验)
*** Security Hardening Options *** //安全加固选项
Stack Smashing Protection (None) ---> //堆栈粉碎保护 [无]
RELRO Protection (None) ---> //RELRO只读重定位(Relocation Read Only)保护 [无]
Buffer-overflow Detection (FORTIFY_SOURCE) (None) ---> //缓冲区溢出检测(强制源) [无]
工具链
Toolchain --->
Toolchain type (External toolchain) ---> //工具链类型 [外部工具链]
*** Toolchain External Options *** //外部工具链选项
Toolchain (Custom toolchain) ---> //工具链 [自定义工具链]
Toolchain origin (Toolchain to be downloaded and installed) ---> //工具链来源 [工具链将被下载安装]
(https://releases.linaro.org/……) Toolchain URL //工具链下载链接 ①
(bin) Toolchain relative binary path //工具链二进制文件相对路径 [bin目录]
($(ARCH)-linux-gnueabihf) Toolchain prefix //工具链前缀 [arm-linux-gnueabihf]
External toolchain gcc version (6.x) ---> //外部工具链GCC版本 [6.x]
External toolchain kernel headers series (4.6.x) ---> //外部工具链内核头文件系列 [4.6.x]
External toolchain C library (glibc/eglibc) ---> //外部工具链C库 [glibc/eglibc] ②
[*] Toolchain has SSP support? //工具链是否支持SSP? ③
[*] Toolchain has RPC support? //工具链是否支持RPC? ④
[*] Toolchain has C++ support? //工具链是否支持C++?
[*] Toolchain has Fortran support? //工具链是否支持Fortran? (一种编程语言)
() Extra toolchain libraries to be copied to target //复制额外工具链库到目标
[ ] Copy gdb server to the Target //复制GDB服务到目标
*** Host GDB Options *** //主机GDB选项
[ ] Build cross gdb for the host //为主机交叉编译GDB
*** Toolchain Generic Options *** //工具链通用选项
[ ] Copy gconv libraries //复制gconv库 (gconv库用于在不同的字符集之间进行转换)
[ ] Enable WCHAR support // python等语言需要开启此项
[*] Enable MMU support //使能MMU支持
() Target Optimizations //目标优化 (需设置前面的GCC优化等级)
() Target linker options //目标链接器选项 (构建目标时传递给链接器的额外选项)
[ ] Register toolchain within Eclipse Buildroot plug-in //在Eclipse Buildroot插件中注册工具链
系统配置选项
System configuration ---> 系统配置
Root FS skeleton (default target skeleton) ---> //根文件系统框架 [典型目标框架]
(ebf6ull) System hostname //系统主机名字(自取任意) [ebf6ull]
(Welcome to ixm6ull Buildroot!) System banner //系统开机提示 [Welcome to ixm6ull Buildroot!]
Passwords encoding (sha-256) ---> //密码编码 [sha-256]
Init system (systemV) ---> //初始化系统方案 [systemV] ①
/dev management (Dynamic using devtmpfs + eudev) ---> //dev管理方案 [Dynamic using devtmpfs + eudev] ②
(system/device_table.txt) Path to the permission tables //权限表路径
[ ] support extended attributes in device tables //支持设备表中的扩展属性
[ ] Use symlinks to /usr for /bin, /sbin and /lib //是否将/bin,/sbin,/lib链接到/usr
[*] Enable root login with password //使能root登陆密码
() Root password //设置root密码
/bin/sh (bash) ---> //选择shell类型 [bash] ③
[*] Run a getty (login prompt) after boot ---> //启动后运行getty(登录提示)--->
(ttymxc0) TTY port //设置TTY硬件端口
Baudrate (keep kernel default) ---> //比特率 [与内核保持一致]
(vt100) TERM environment variable //TERM环境变量 (终端类型xterm、vt100)
() other options to pass to getty //传递给getty的其他选项
[*] remount root filesystem read-write during boot //在引导期间安装根文件系统支持读和写
(eth0) Network interface to configure through DHCP //设置DHCP配置的网络接口 [eth0]
(/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin) Set the system's default PATH //设置系统的默认路径
[*] Purge unwanted locales //清除不需要的区域设置
(C en_US) Locales to keep //要保留的语言环境
() Generate locale data //生成区域设置数据
[ ] Enable Native Language Support (NLS) //启用本地语言支持(NLS)
-*- Install timezone info //安装时区信息
(default) timezone list //时区清单 [典型]
(Etc/UTC) default local time //用户表的路径
() Path to the users tables
(board/hceng/nxp-imx6ull/rootfs-overlay) Root filesystem overlay directories //根文件系统覆盖目录
() Custom scripts to run before creating filesystem images //在创建文件系统映像之前运行的自定义脚本
() Custom scripts to run inside the fakeroot environment //自定义脚本在fakeroot(模拟root权限)环境中运行
(board/……) Custom scripts to run after creating filesystem images //创建文件系统映像后运行的自定义脚本 ④
() Extra arguments passed to custom scripts //传递给自定义脚本的额外参数
①:可选选项有BusyBox、systemV、systemd、None:
BusyBox init:
- 不支持运行等级,设置的运行等级将被忽略,要使用运行等级,请使用sysvinit;
- 语法格式:
: : :
<id>:process执行所在的tty设备,内容为/dev目录中tty设备的文件名;
<runlevels>:此字段完全被忽略;
<action>:支持sysinit、respawn、askfirst、wait、once、restart、ctrlaltdel、shutdown;
<process>:指定要执行的进程及其命令行;
- BusyBox init程序将在启动时读取/etc/inittab文件,以了解该做什么,默认inittab存储在./package/busybox/inittab;
- inittab除了安装几个重要的文件系统之外,还要启动/etc/init.d/rcS中的shell脚本,并启动一个getty程序(提供一个登录提示);
systemV:
- 使用传统sysvinit程序,之前大多数台式机Linux发行版都使用该方案,现在有些变为了Upstart或Systemd;
- 在/ect目录下会生成init.d、rc0.d、rc1.d、rc2.d、rc3.d、rc4.d、rc5.d、rc6.d、rc.loacl;
init.d里面包含的是真正的服务脚本;
rcN.d里面是链接向init.d里脚本的软链接,N表示运行级别,进入哪个运行级别,就会执行对应rcN.d文件夹的脚本;
当所有的当前运行级别的脚本都运行完了之后,会运行rc.local;
- 脚本的命名规则:以[S|K]+NN+其它,以S开头的是启动脚本,以K开头的是停止脚本,init进程会按照S或者K后面的数字的顺序来启动或停止服务;
- sysvinit还使用/etc/inittab文件(与BusyBox的语法略有不同),默认inittab存储在./package/sysvinit/inittab;
systemd:
- systemd是Linux的新一代init系统,以前的运行级别(runlevel)的概念被新的运行目标(target)所取代;
- 支持并行化任务;采用socket式与D-Bus总线式激活服务;按需启动守护进程(daemon);支持快照和系统恢复;
- 功能强大的同时,也带来了相当大数量的大型依赖:dbus,udev等;
②:/dev设备文件的管理方式,可选选项有四个:
- Static using device table:使用静态的设备表,/dev将根据system/device_table _dev.txt的内容创建设备,进入系统添加或删除设备时,无法自动更新;
- Dynamic using devtmpfs only:在系统启动过程中,会动态生成/dev文件,进入系统添加或删除设备时,无法自动更新;
- Dynamic using devtmpfs + mdev:在前面devtmpfs的基础上加入mdev用户空间实用程序,进入系统添加或删除设备时,可以自动更新,自动创建规则在/etc/mdev.conf;
- Dynamic using devtmpfs + eudev:在前面devtmpfs的基础上加入eudev用户空间守护程序,eudev是udev的独立版本,是Systemd的一部分,提供更多的功能也更占用资源;
③:在Linux下编写shell脚本文件时,经常会看到在第一行中标注#!/bin/bash,这句话的意思是告诉系统强制用bash,避免出现一些不兼容的问题。因此,除了bash外,还有很多shell工具,比如这里可选busybox自带的shell、小巧但功能很少的dash、高效紧凑的mksh、功能强大体积也稍大的zsh。此外,可以通过ls -l /bin/sh查看当前使用的是何种shell工具。
④:受限每行字数,该处完整路径为board/freescale/common/imx/post-image.sh。
这里是如何产生sdcard.img,用于sd卡启动的原理部分。
针对我现在imx6ull的情况,board/freescale/common/imx目录下有两个文件值得关注:genimage.cfg.template和post-image.sh。
先来看genimage.cfg.template:
# Minimal SD card image for the Freescale boards Template
#
# We mimic the .sdcard Freescale's image format:
# * the SD card must have 1 kB free space at the beginning,
# * U-Boot is dumped as is,
# * a FAT partition at offset 8 MB is containing zImage/uImage and DTB files
# * a single root filesystem partition is required (ext2, ext3 or ext4)
#
image boot.vfat {
vfat {
files = {
%FILES%
}
}
size = 16M
}
image sdcard.img {
hdimage {
}
partition u-boot {
in-partition-table = "no"
image = "%UBOOTBIN%"
offset = 1024
}
partition boot {
partition-type = 0xC
bootable = "true"
image = "boot.vfat"
offset = 8M
}
partition rootfs {
partition-type = 0x83
image = "rootfs.ext2"
}
}
该配置文件显示会生成两个文件,一个boot.vfat,一个sdcard.img;
boot.vfat由"%FILES%"所表示内容组成(后面会得知是kernel+dtb);
sdcard.img有四个分区,第一个是空,第二个是偏移1024字节(1k)后,内容为"%UBOOTBIN%"(u-boot),第三个为偏移8M后,存放前面生成的boot.vfat(kernel+dtb),最后存放rootfs.ext2。
此时分区情况如下:
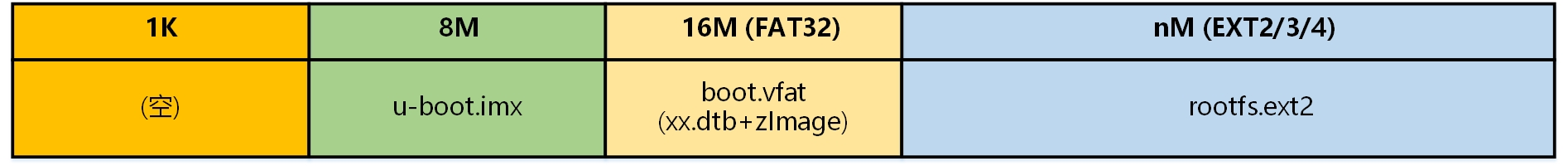
分区类型和数值的对应关系可通过该文章查询:List of partition identifiers for PCs or Listing of MBR/EBR Partition Types
此时将sd卡插入Windows电脑,可以发现只能识别存放boot.vfat(kernel+dtb)的分区,因为该分区为FAT32格式,Windows可以识别,而存放rootfs.ext2的分区为ext2/3/4,Windows是无法识别的,与生活常识是吻合的。
另外,如果想在SD卡创建其它自定义分区,可以再加一个partition:
partition user {
partition-type = 0xC
size = 10M
}
再来看看post-image.sh是如何解析genimage.cfg.template:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#
# dtb_list extracts the list of DTB files from BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_INTREE_DTS_NAME
# in ${BR_CONFIG}, then prints the corresponding list of file names for the
# genimage configuration file
#
dtb_list()
{
local DTB_LIST="$(sed -n 's/^BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_INTREE_DTS_NAME="\([\/a-z0-9 \-]*\)"$/\1/p' ${BR2_CONFIG})"
for dt in $DTB_LIST; do
echo -n "\"`basename $dt`.dtb\", "
done
}
#
# linux_image extracts the Linux image format from BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_UIMAGE in
# ${BR_CONFIG}, then prints the corresponding file name for the genimage
# configuration file
#
linux_image()
{
if grep -Eq "^BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_UIMAGE=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "\"uImage\""
elif grep -Eq "^BR2_LINUX_KERNEL_IMAGE=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "\"Image\""
else
echo "\"zImage\""
fi
}
genimage_type()
{
if grep -Eq "^BR2_PACKAGE_FREESCALE_IMX_PLATFORM_IMX8M=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "genimage.cfg.template_imx8"
elif grep -Eq "^BR2_TARGET_UBOOT_SPL=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "genimage.cfg.template_spl"
else
echo "genimage.cfg.template"
fi
}
uboot_image()
{
if grep -Eq "^BR2_TARGET_UBOOT_FORMAT_DTB_IMX=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "u-boot-dtb.imx"
elif grep -Eq "^BR2_TARGET_UBOOT_FORMAT_IMX=y$" ${BR2_CONFIG}; then
echo "u-boot.imx"
fi
}
main()
{
local FILES="$(dtb_list) $(linux_image)"
local UBOOTBIN="$(uboot_image)"
local GENIMAGE_CFG="$(mktemp --suffix genimage.cfg)"
local GENIMAGE_TMP="${BUILD_DIR}/genimage.tmp"
sed -e "s/%FILES%/${FILES}/" \
-e "s/%UBOOTBIN%/${UBOOTBIN}/" \
board/freescale/common/imx/$(genimage_type) > ${GENIMAGE_CFG}
rm -rf "${GENIMAGE_TMP}"
genimage \
--rootpath "${TARGET_DIR}" \
--tmppath "${GENIMAGE_TMP}" \
--inputpath "${BINARIES_DIR}" \
--outputpath "${BINARIES_DIR}" \
--config "${GENIMAGE_CFG}"
rm -f ${GENIMAGE_CFG}
exit $?
}
main $@
可以在main看到,FILES为dtb和kernel,UBOOTBIN为u-boot,再传入配置文件。
最后使用genimage生成,genimage在后面2.9Host utilities(主机工具)部分需要勾选上,它的作用是给定根文件系统树,生成多个文件系统和闪存镜像的工具。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42553314/article/details/118696618
使用 Ubuntu-Base 包
注意:由于这个包不全面,适合作为 chroot 的目录,不适合做根文件系统,所以不推荐。
前往 Ubuntu仓库,挑一个版本,下载例如 ubuntu-base-22.04.2-base-arm64.tar.gz 这样一个成品在某个空目录下,然后解压,如下:
wget http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-base/releases/20.04/release/ubuntu-base-20.04.5-base-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xvf ubuntu-base-20.04.5-base-amd64.tar.gz
这个目录大概 105M,建一个大于 200 M 的空文件。
dd if=/dev/zero of=ubuntu.img bs=1M count=200
sudo mkfs.ext4 ubuntu.img
然后 mount ubuntu.img 到某个目录下,将解压的内容拷贝进去。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)