实验18:迭代器模式
本次实验属于模仿型实验,通过本次实验学生将掌握以下内容:
1、理解迭代器模式的动机,掌握该模式的结构;
2、能够利用迭代器模式解决实际问题。
[实验任务一]:JAVA和C++常见数据结构迭代器的使用
信1305班共44名同学,每名同学都有姓名,学号和年龄等属性,分别使用JAVA内置迭代器和C++中标准模板库(STL)实现对同学信息的遍历,要求按照学号从小到大和从大到小两种次序输出学生信息。
实验要求:
1. 搜集并掌握JAVA和C++中常见的数据结构和迭代器的使用方法,例如,vector, list, map和set等;
2. 提交源代码;
3. 注意编程规范。
1、使用方法
JAVA
(1)List 是一个有序集合,允许重复的元素。在 Java 中常用的 List 实现包括 ArrayList 和 LinkedList。
ArrayList:底层使用动态数组实现,支持快速随机访问。
LinkedList:底层使用双向链表实现,适合频繁插入和删除元素。
实现方法:import java.util.*;
public class ListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用 ArrayList 实现 List
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Java");
list.add("C++");
list.add("Python");
// 迭代器遍历
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 使用 LinkedList
List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (Integer number : linkedList) {
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}
(2)Set 是一个无序集合,不允许重复元素。在 Java 中常用的 Set 实现包括 HashSet 和 TreeSet。
HashSet:底层使用哈希表实现,元素是无序的。
TreeSet:底层使用红黑树实现,元素会自动按升序排序。
实现方法:import java.util.*;
public class SetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用 HashSet 实现 Set
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("Java");
set.add("C++");
set.add("Python");
// 迭代器遍历
Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 使用 TreeSet
Set<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add(3);
treeSet.add(1);
treeSet.add(2);
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (Integer number : treeSet) {
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}
(3)Map 是一个键值对集合,不允许重复的键。在 Java 中常用的 Map 实现包括 HashMap 和 TreeMap。
HashMap:底层使用哈希表实现,键值对无序。
TreeMap:底层使用红黑树实现,键按升序排序。
实现方法:import java.util.*;
public class MapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用 HashMap 实现 Map
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "C++");
map.put(3, "Python");
// 通过键遍历
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
// 使用 TreeMap
Map<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put(3, "Java");
treeMap.put(1, "C++");
treeMap.put(2, "Python");
// 遍历
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
C++
(1)vector 是一个动态数组,支持快速随机访问,元素按插入顺序排列。
实现方法:#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<string> vec = {"Java", "C++", "Python"};
// 迭代器遍历
for (vector<string>::iterator it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (const auto& str : vec) {
cout << str << endl;
}
return 0;
}
(2)list 是双向链表实现的容器,适用于频繁的插入和删除操作。
实现方法:#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
list<int> myList = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 迭代器遍历
for (list<int>::iterator it = myList.begin(); it != myList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (const auto& num : myList) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
(3)set 是一个不允许重复元素的集合,元素按升序排列。
实现方法:#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
set<string> mySet = {"Java", "C++", "Python"};
// 迭代器遍历
for (set<string>::iterator it = mySet.begin(); it != mySet.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (const auto& str : mySet) {
cout << str << endl;
}
return 0;
}
(4)map 是一个有序的键值对集合,键不重复。
实现方法:#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<int, string> myMap = {{1, "Java"}, {2, "C++"}, {3, "Python"}};
// 迭代器遍历
for (map<int, string>::iterator it = myMap.begin(); it != myMap.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}
// 增强 for 循环遍历
for (const auto& entry : myMap) {
cout << entry.first << ": " << entry.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、源代码
C++
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Student{
public:
long studentid;
string name;
int age;
string major;
public:
Student(long studentid, string name, int age, string major) {
this->studentid = studentid;
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->major = major;
}
void show(){
cout<<"姓名: "<<this->name<<"\t学号: "<<this->studentid <<"\t年龄: "<< this->age<< "\t专业: " << this->major<<endl;
}
};
bool compMax(Student *a,Student *b){
if (a->studentid> b->studentid)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool compMin(Student *a,Student *b){
if (a->studentid< b->studentid)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main(){
Student *s1 = new Student(20223794, "袁", 20, "软工");
Student *s2 = new Student(20224056, "高", 21, "软工");
Student *s3 = new Student(20223782, "艾", 21, "软工");
Student *s4 = new Student(20223695, "万", 20, "软工");
vector<Student*> vec;
vec.push_back(s1);
vec.push_back(s2);
vec.push_back(s3);
vec.push_back(s4);
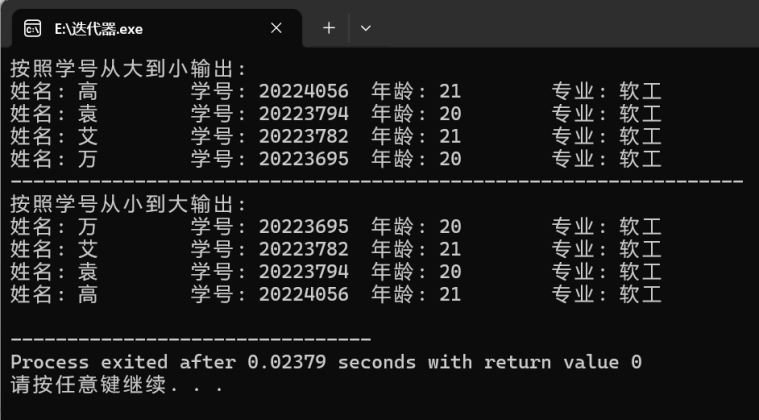
cout<<"按照学号从大到小输出: "<<endl;
vector<Student*>::iterator it;
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(),compMax);
for(it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it++){
(*it)->show();
}
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl;
cout<<"按照学号从小到大输出: "<<endl;
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(),compMin);
for(it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it++){
(*it)->show();
}
}
JAVA
package org.example;
class Student {
String name;
int studentId;
int age;
String major; // 添加专业属性
public Student(String name, int studentId, int age, String major) {
this.name = name;
this.studentId = studentId;
this.age = age;
this.major = major; // 初始化专业
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名: " + name + ", 学号: " + studentId + ", 年龄: " + age + ", 专业: " + major;
}
}
package org.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建学生对象时添加专业
students.add(new Student("袁", 20223794, 20, "软工"));
students.add(new Student("高", 20224056, 21, "软工"));
students.add(new Student("艾", 20223782, 21, "软工"));
students.add(new Student("万", 20223695, 20, "软工"));
// 按学号从小到大排序
students.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(s -> s.studentId));
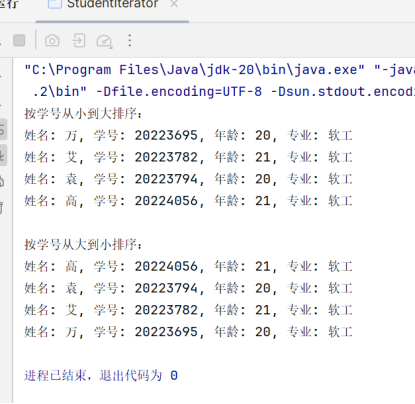
System.out.println("按学号从小到大排序:");
Iterator<Student> iterator = students.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
// 按学号从大到小排序
students.sort((s1, s2) -> Integer.compare(s2.studentId, s1.studentId));
System.out.println("\n按学号从大到小排序:");
iterator = students.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
3、运行截图
C++
JAVA




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?