ioctl命令字解释
1、命令字字段说明
每个 ioctl 命令实际上都是一个 32 位整型数,各字段和含义如表 2.1 所示。
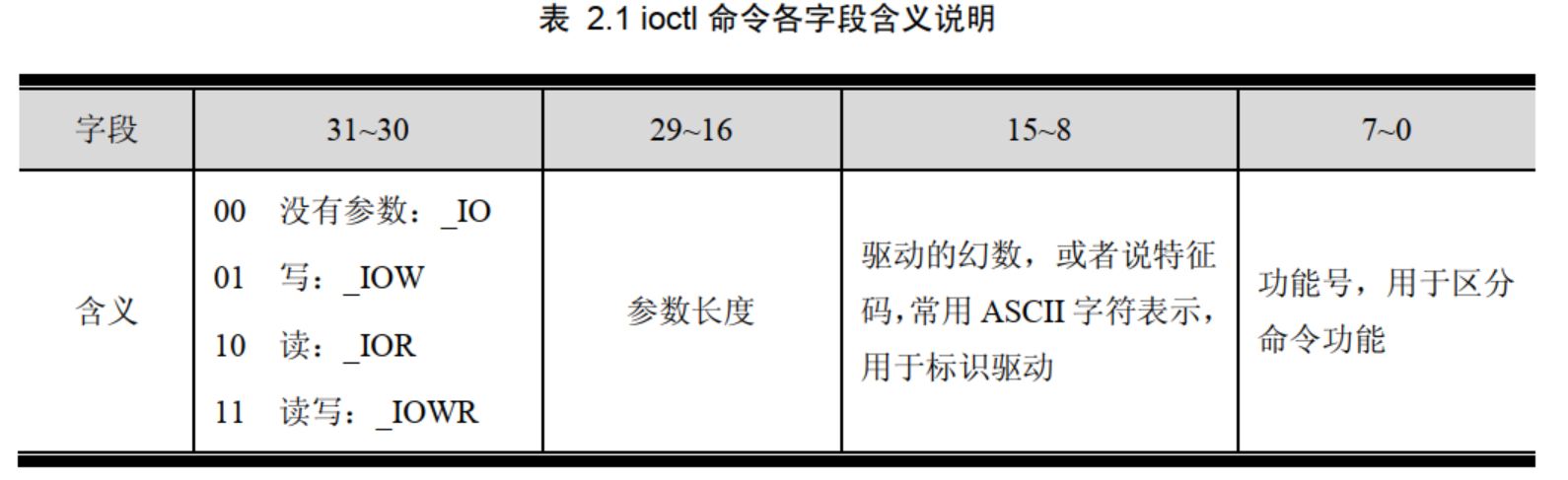
例如, 0x82187201 是带长度为 0x218 的参数读命令,功能号为 1,幻数用 ASCII 表示是“r”,实际上这个命令是<linux/msdos_fs.h>中的 VFAT_IOCTL_READDIR_BOTH 命令:
1 | #define VFAT_IOCTL_READDIR_BOTH _IOR('r', 1, struct __fat_dirent[2]) |
2. 构造 ioctl 命令
为驱动构造 ioctl 命令,首先要为驱动选择一个可用的幻数作为驱动的特征码,以区分不同驱动的命令。内核已经使用了很多幻数,为了防止冲突,最好不要再使用这些系统已经占用的幻数来作为驱动的特征码。已经被使用的幻数列表详见<Documentation/ioctl/ioctl-number.txt>文件。在不同平台上,幻数所使用情况都不同,为防止冲突,可以选择其它平台使用的幻数来用。
选定幻数后,可以这样来进行定义:
1 | #define LED_IOC_MAGIC 'Z' |
ioctl 命令字段的 bit[31:30]表示命令的方向,分别表示使用_IO、 _IOW、 _IOR 和_IOWR这几个宏定义,分别用于构造不同的命令:
| _IO(type, nr) _IOW(type, nr, size) _IOR(type, nr, size) _IOWR(type, nr, size) |
构造无参数的命令编号 构造往驱动写入数据的命令编号 构造从驱动中读取数据的命令编号 构造双向传输的命令编号 |
这些宏定义中, type 是幻数, nr 是功能号, size 是数据大小。
例如,为 LED 驱动构造 ioctl 命令,由于控制 LED 无需数据传输,可以这样定义:
1 2 | #define SET_LED_ON _IO(LED_IOC_MAGIC, 0)#define SET_LED_OFF _IO(LED_IOC_MAGIC, 1) |
如果想在 ioctl 中往驱动写入一个 int 型的数据,可以这样定义:
1 | #define CHAR_WRITE_DATA _IOW(CHAR_IOC_MAGIC, 2, int) |
类似的,要从驱动中读取 int 型的数据,则定义为:
1 | #define CHAR_READ_DATA _IOR(CHAR_IOC_MAGIC, 3, int) |
注意:同一份驱动的 ioctl 命令定义,无论有无数据传输以及数据传输方向是否相同,各命令的序号都不能相同。定义完所需的全部命令后,还需定义一个命令的最大的编号,防止传入参数超过编号范围。
3. 解析 ioctl 命令驱动程序必须对传入的命令进行解析,包括传输方向、命令类型、命令编号以及参数大
小,分别可以通过下面的宏定义完成:
| _IOC_DIR(nr) _IOC_TYPE(nr) _IOC_NR(nr) _IOC_SIZE(nr) |
解析命令的传输方向 解析命令类型 解析命令序号 解析参数大小 |
如果解析发现命令出错,可以返回-ENOTTY,如:
1 2 3 | if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != LED_IOC_MAGIC) { return -ENOTTY;}if (_IOC_NR(cmd) >= LED_IOC_MAXNR) { return -ENOTTY;} |
3、实例
led灯驱动
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 | #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/version.h> #include <asm/mach/arch.h> #include <mach/hardware.h> #include <mach/gpio.h> #include <asm/gpio.h> #include "led_drv.h" static int major; static int minor;struct cdev *led; /* cdev 数据结构 */static dev_t devno; /* 设备编号 */static struct class *led_class; #define DEVICE_NAME "led" #define GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM 55 /* gpio 1_23 */ static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file ){ try_module_get(THIS_MODULE); gpio_direction_output(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM, 1); return 0;} static int led_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file ){ module_put(THIS_MODULE); gpio_direction_output(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM, 1); return 0; } #if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(2,6,36) int led_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) #else static int led_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) #endif{ if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != LED_IOC_MAGIC) { return -ENOTTY; } if (_IOC_NR(cmd) > LED_IOCTL_MAXNR) { return -ENOTTY; } switch(cmd) { case LED_ON: gpio_set_value(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM, 0); break; case LED_OFF: gpio_set_value(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM, 1); break; default: gpio_set_value(27, 0); break; } return 0;} struct file_operations led_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = led_open, .release = led_release, #if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(2,6,36) .unlocked_ioctl = led_ioctl #else .ioctl = led_ioctl #endif };static int __init led_init(void){ int ret; gpio_free(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM); if (gpio_request(GPIO_LED_PIN_NUM, "led_run")) { printk("request %s gpio faile \n", "led_run"); return -1; } ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, minor, 1, "led"); /* 从系统获取主设备号 */ major = MAJOR(devno); if (ret < 0) { printk(KERN_ERR "cannot get major %d \n", major); return -1; } led = cdev_alloc(); /* 分配 led 结构 */ if (led != NULL) { cdev_init(led, &led_fops); /* 初始化 led 结构 */ led->owner = THIS_MODULE; if (cdev_add(led, devno, 1) != 0) { /* 增加 led 到系统中 */ printk(KERN_ERR "add cdev error!\n"); goto error; } } else { printk(KERN_ERR "cdev_alloc error!\n"); return -1;}led_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "led_class"); if (IS_ERR(led_class)) { printk(KERN_INFO "create class error\n"); return -1;} device_create(led_class, NULL, devno, NULL, "led"); return 0; error: unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1); /* 释放已经获得的设备号 */ return ret; } static void __exit led_exit(void) { cdev_del(led); /* 移除字符设备 */ unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1); /* 释放设备号 */ device_destroy(led_class, devno); class_destroy(led_class); }module_init(led_init);module_exit(led_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");MODULE_AUTHOR("Chenxibing, linux@zlgmcu.com"); |
main.c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/ioctl.h>#include <errno.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include "../led_drv.h"#define DEV_NAME "/dev/led"int main(int argc, char *argv[]){int i;int fd = 0;fd = open (DEV_NAME, O_RDONLY);if (fd < 0) { perror("Open "DEV_NAME" Failed!\n"); exit(1);} for (i=0; i<3; i++) { ioctl(fd, LED_ON); sleep(1); ioctl(fd, LED_OFF); sleep(1); } close(fd); return 0;} |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
2019-12-27 DVB-C\DVB-S\DVB-T知识介绍
2019-12-27 广播与电视波段频率划分表