i2c驱动理解
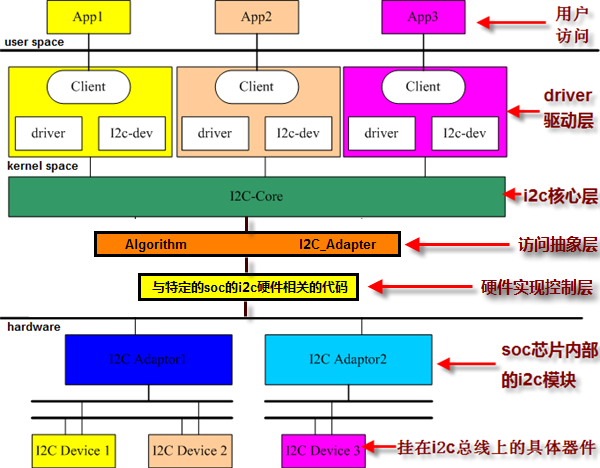
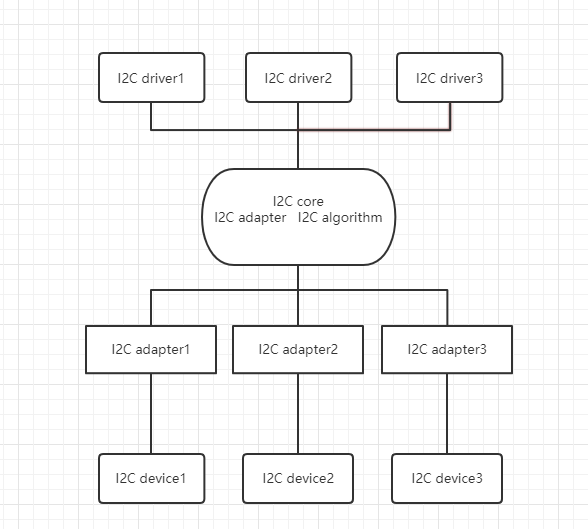
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/166124369
i2cdev_ioctl函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){ struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; unsigned long funcs; dev_dbg(&client->adapter->dev, "ioctl, cmd=0x%02x, arg=0x%02lx\n", cmd, arg); switch (cmd) { case I2C_SLAVE: case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE: // if ((arg > 0x3ff) || (((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f)) return -EINVAL; if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg)) //地址检查 return -EBUSY; /* REVISIT: address could become busy later */ client->addr = arg; //传从机地址给驱动 return 0; case I2C_TENBIT: //十位还是七位地址flag if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_M_TEN; else client->flags &= ~I2C_M_TEN; return 0; case I2C_PEC: // //设置传输后增加校验标志 /* * Setting the PEC flag here won't affect kernel drivers, * which will be using the i2c_client node registered with * the driver model core. Likewise, when that client has * the PEC flag already set, the i2c-dev driver won't see * (or use) this setting. */ if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_CLIENT_PEC; else client->flags &= ~I2C_CLIENT_PEC; return 0; case I2C_FUNCS: funcs = i2c_get_functionality(client->adapter); //获取适配器支持的功能 :获取访问总线的协议,i2c协议还是smbus协议 return put_user(funcs, (unsigned long __user *)arg); case I2C_RDWR: //i2c数据传输 return i2cdev_ioctl_rdwr(client, arg); case I2C_SMBUS: //smbus数据传输 return i2cdev_ioctl_smbus(client, arg); case I2C_RETRIES: //设置重试次数 client->adapter->retries = arg; break; case I2C_TIMEOUT: //设置超时时间 /* For historical reasons, user-space sets the timeout * value in units of 10 ms. */ client->adapter->timeout = msecs_to_jiffies(arg * 10); break; default: /* NOTE: returning a fault code here could cause trouble * in buggy userspace code. Some old kernel bugs returned * zero in this case, and userspace code might accidentally * have depended on that bug. */ return -ENOTTY; } return 0;} |
memdup_user()函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | 用户态到内核态的拷贝,都会涉及到两个必要的步骤: * void *memdup_user(const void __user *src, size_t len) * { * void *p; * * p = kmalloc_track_caller(len, GFP_KERNEL); //内核态分配个空间 * if (!p) * return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); * * if (copy_from_user(p, src, len)) { //从用户态拷过来 * kfree(p); * return ERR_PTR(-EFAULT); * } * * return p; * } |
i2cdev_read:在主机模式,接收从机发过来的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | static ssize_t i2cdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset){ char *tmp; int ret; struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; if (count > 8192) count = 8192; tmp = kmalloc(count, GFP_KERNEL); //内核分配空间 if (tmp == NULL) return -ENOMEM; pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d reading %zu bytes.\n", iminor(file_inode(file)), count); ret = i2c_master_recv(client, tmp, count); //主机接收数据 if (ret >= 0) ret = copy_to_user(buf, tmp, count) ? -EFAULT : ret; //将数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间 kfree(tmp); return ret;} |
i2cdev_write:主机模式下,发送数据到从机。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | static ssize_t i2cdev_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset){ int ret; char *tmp; struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; if (count > 8192) count = 8192; tmp = memdup_user(buf, count); //从用户空间拷贝数据到内核空间(内核空间分配+拷贝) if (IS_ERR(tmp)) return PTR_ERR(tmp); pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d writing %zu bytes.\n", iminor(file_inode(file)), count); ret = i2c_master_send(client, tmp, count); //发数据 kfree(tmp); return ret;} |
https://www.cnblogs.com/embInn/p/13289367.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)