7.3 P-Value Approach to Hypothesis Testing†
前面步骤同one mean 值,后面计算出H0所对应的概率即为p值,再用p值与significant level相比。
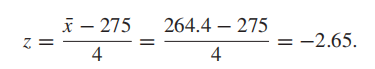
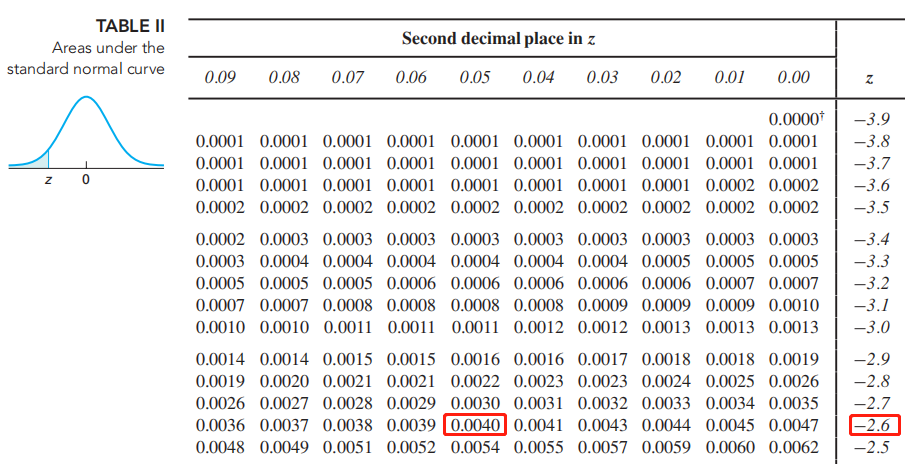
-(2.6+0.05)=-2.65
p值是假如H0假设正确的情况下,得到该值的概率,如果非常小,即在扩大容忍程度的前提下,依然得到偶然值,则说明ho 不被选择,同时满足h1假设(即该值小于H0中的值)
The sample data provide very strong evidence against the null hypothesis (Jack’s claim) and in favor of the alternative hypothesis (Jean’s suspicion)

p是指在该sample情况下,可以容忍的假阴性个数(即The P-value of a hypothesis test is also referred to as the observed significance level.),如果significant level指该h0情况下,可以容忍的假阴性个数,
如果sample情况的假阴性个数小于h0情况下的假阴性个数,则真实情况更严格,则证明h0的情况并非真实情况(以sample作为真实情况的抽样),所以reject H0
如果sample情况的假阴性个数大于h0情况下的假阴性个数,则真实情况更宽松,则证明h0的情况是真实情况(以sample作为真实情况的抽样) ,所以not to reject H0
本质在于:小概率事件不可能发生
不同类型的p-value:
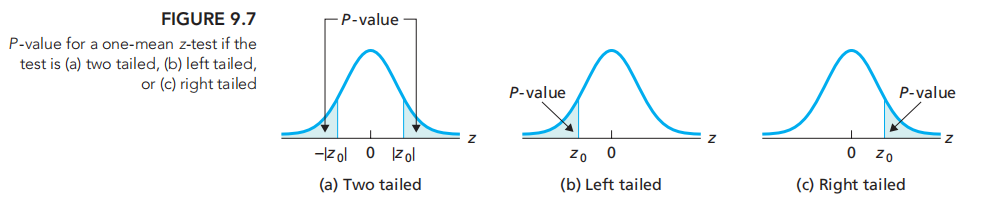
如果是双尾值:

所以:

Using the P-Value to Assess the Evidence Against the Null Hypothesis

we can use the P-value to evaluate the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis without reference to significance levels.Hypothesis Tests Without Significance Levels: Many researchers do not explicitly refer to significance levels. Instead, they simply obtain the P-value and use it (or let the reader use it) to assess the strength of the evidence against the null hypothesis



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步