Design based on biology
通过比较基因组学的方法,将脊椎动物基因组的数据,解决生物学各方面问题。新的调控注释(在脊椎动物的进化过程中的出现的)可以丰富物种树(比如不同功能蛋白质进化速度上的差异(因为编码蛋白质基因和早期进化基因的发现))。
Sequencing 需要以下两种策略叠加:
1.Pooled genome sequence strategies :测同一物种的不同个体,不同个体叠加。
2.representative genome assembly approaches :因为有质量好的序列片段(reasonable N50 contig),所以可适用于缺乏长序列的情况。如果assembly质量好可以作为参考序列
Domestication:因为自然改变使得人改变,使得人为选择改变,人为改变部分导致的变化。
Project design:
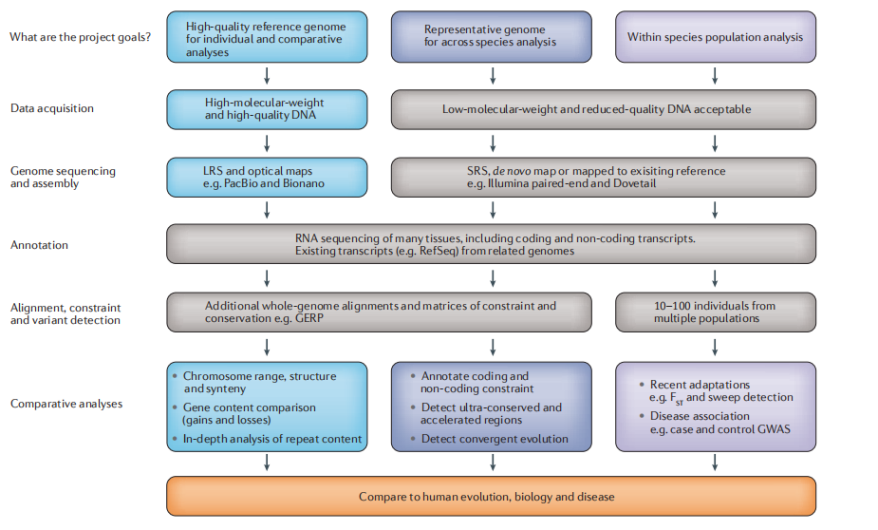

因为生物学分析依赖于assembly数据,所以assembly需要关注细节缩小误差(confounding effects)。
Data acquisition
Flowchart:1.什么样的测序方式对应什么样的研究2.除资源导向外,比较基因组学可以帮助找到内在机制3.
statistics:fixation index
GERP:genome evolutionary rate profiling:"GERP identifies constrained elements in multiple alignments by quantifying substitution deficits. These deficits represent substitutions that would have occurred if the element were neutral DNA, but did not occur because the element has been under functional constraint. We refer to these deficits as "Rejected Substitutions". Rejected substitutions are a natural measure of constraint that reflects the strength of past purifying selection on the element."
GWAS:genome-wide association studies
The effect of genome content:如果测序质量好,则可以扩大改数据的适用范围。测序质量的好坏与测序技术(以前的技术:radiation hybrids and BAC maps, BACs and fosmids,现在PacBio, Dovetail and Bionano)有关。
因为可以assembly大部分基因,所以邻近物种共线保守性可以用来研究基因组结构,新技术的综合使用使得assembly质量更好(N50变长),从而解决以前因技术不足造成的问题。由于脊椎动物基因组的复杂性(因为脊柱动物基因组有自己独特的特征:1.高重复2.高CG含量3.微染色体(质量较小的染色体)),更需要这种新技术(因为新技术对于重复区域可以单独span)。
Standing variation, imputation and mapping:
variation:发现突变重点在于选择样本:可以选择因为选择样本和探测差异同等重要,所以综合多个个体的低覆盖率序列(具体方式是综合使用软件探测差异)是合算的。
Imputation:确认发生突变的原因:可以通过1.计算遗传距离,2.滑动窗口model确认sweep或杂交或回交。
selective sweep:选择转移:因为对某位点的选择导致该位点周围的多样性下降。
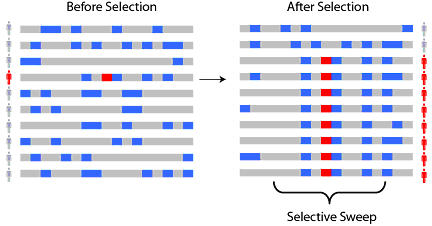
A selective sweep
Under natural selection, a new beneficial mutation will rise in frequency (prevalence) in a population. A schematic of polymorphisms along a chromosome, including the selected allele, before and after selection. Ancestral alleles are shown in gray and derived (non-ancestral) alleles are shown in blue. As a new positively selected allele (red) rises to high frequency, nearby linked alleles on the chromosome 'hitchhike' along with it to high frequency, creating a 'selective sweep.'
Hybridization:杂交:不同亲本之间杂交。
Introgression:回交:亲本和子代杂交。
Integrated haplotype homozygosity score:iHS (Integrated Haplotype Score) is a statistic that has been developed to detect evidence of recent positive selection at a locus. It is based on the differential levels of linkage disequilibrium(LD) surrounding a positively selected allele compared to the background allele at the same position.
Mapping:基因型与性状相对应:随着(1.SNP微阵列技术2.高通量测序价格下降),单倍体模型(通过足够的SNP密度数据)用于研究种群历史和基因型与性状的对应。
SNP genotyping arrays:SNP阵列是一种DNA微阵列,用于检测群体内的多态性。单核苷酸多态性是DNA中单个位点的变异,是基因组中最常见的变异类型。在人类基因组中已经鉴定了大约3.35亿个SNP,其中1500万个在全世界不同人群中以1%或更高的频率存在。
单倍型(haplotype:若干个决定同一性状的紧密连锁的基因构成的基因型
Complex mutation types: the good with the bad:
the bad:因为技术水平所限(SRS),所以许多高区域性突变(高区域性杂合和基因组断裂)无法找到,仅有少部分例子通过精确比对,可以解剖重排。
The good:现在出现了PacBio SMRT技术可以解开结构多样性
Layering complexity: gene and transcript annotation:
1.DNA Annotation>transcription annotation(方式1:比照相似物种的基因组;方式2:mapping RefSeq上的转录组)后可得到RNA序列(转录组,物种特异性的)
2.调节原件信息进行注释:调节原件导致突变(因为GWAS利用非编码区识别突变(GWAS可以map outside gene,以此达到检测疾病的目的。))
3.非编码区:GWAS基因组关联分析(genome-wide association studies, GWAS)已经被广泛用于复杂疾病的遗传位点的分析。 然而,GWAS 发现的复杂疾病相关的遗传变异,即单核苷酸多态性(SNP)位点大多位于基因的非编码区,并且同一区域中连锁的遗传变异(SNP)位点可以多达成百上千个。
4.特殊(特殊分类标准的)生物数据平台上的特殊data set进行注释
5.通过识别保守原件(来自不同物种的)进行注释
Vertebrate comparative genomics:Natural disease models: domestic animals:
物种分为模式生物和自然生物,自然生物正是研究稳态和健康特征的优选,所以在多目标的前体下驯化动物和自然动物都可以作为模型对象。
驯化的结果是表型的一致和疾病的富集。最近发现驯养动物有类人疾病(虽然没有实验室环境,但也是人类选择的结果)。用该动物不仅可以研究人类疾病,也可以造福该物种。
物种基因组比较,有助于annotation 2.通过GWAS找到SNP3.有助于找到sweep
Intraspecies comparison: a tool to study recent phenotypic adaptations:种内多个体比较可得到selective sweeps(特点是聚集多基因和基因多态)eg(不同季节的)鱼的单倍体基因长序列(coding区和非coding区,共同控制)控制一类及相关性状;eg不同海拔的sheep(由同一物种得到的性状different,采用不同物种作为验证。)
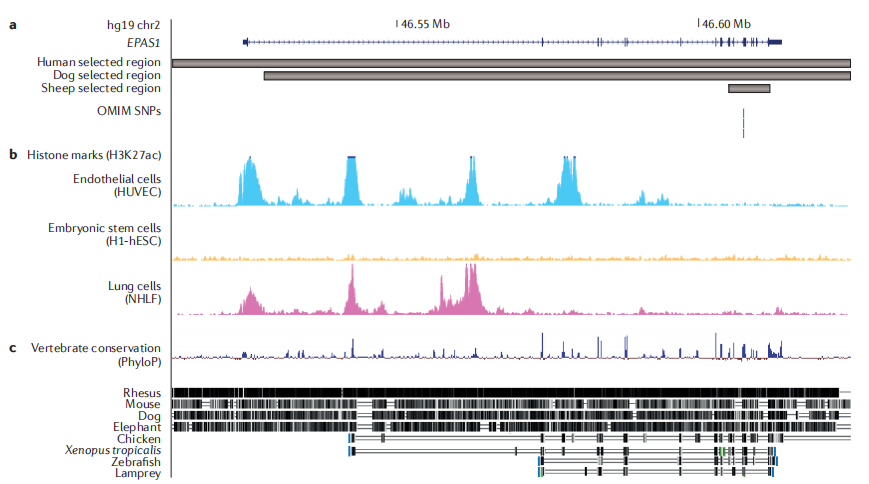


adaptations (microevolution)





