201521123019 《Java程序设计》第7周学习总结
1. 本章学习总结
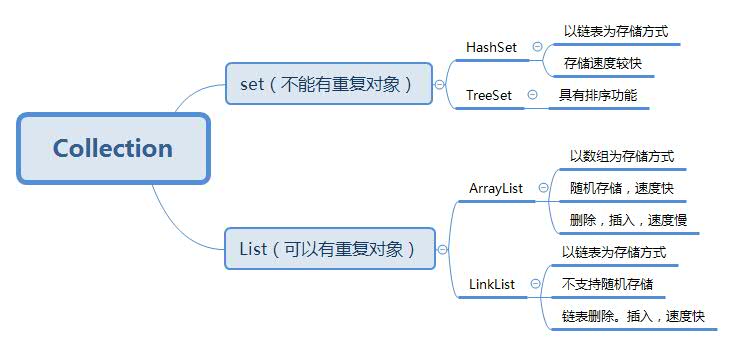
2. 书面作业
一、ArrayList代码分析
1.1 解释ArrayList的contains源代码
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
答:boolean类型函数,遍历元素,如存在查找的元素,返回true,否则返回false;
1.2 解释E remove(int index)源代码
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
答:查找此ArrayList中是否包含要找的元素,若有,返回true,否则返回false;在源代码注释中,Removes the element at the specified position in this list.删除此列表中指定位置的元素。
1.3 结合1.1与1.2,回答ArrayList存储数据时需要考虑元素的类型吗?
答:不用考虑,因为其参数为Objcet类型的对象,Object类又是所有类的父类。
1.4 分析add源代码,回答当内部数组容量不够时,怎么办?
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
继续看ensureCapacityInternal方法描述
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是一个空数组,用于判断此时ArrayList是否为空。此时,数组的默认长度DEFAULT_CAPACITY值为10。
继续看ensureExplicitCapacity方法描述
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
这里出现数组是否到头的判断,继续看grow方法描述
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
将原有的数组扩容为1.5倍长度的数组(使用移位运算<<),将原有的数组元素赋值到新数组中。
1.5 分析private void rangeCheck(int index)源代码,为什么该方法应该声明为private而不声明为public?
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
答:rangeCheck的作用是检查数组是否越界,它不需要外部的进行修改或者访问。也就是说对与用户而言只需要知道remove的结果而不需要知道如何实现。所以没必要用public声明。
二、HashSet原理
2.1 将元素加入HashSet(散列集)中,其存储位置如何确定?需要调用那些方法?
-
HashSet的存储实现方式采用数组+链表。
-
"implements Set
, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable"HsashSet实现Set接口但HashSet实质上使用HashMap来实现的。因为Set不保存重复元素,所以存入Set的每个元素都必须是唯一的。必须要定义equals()方法来确保对象的唯一性,存入HashSet当中的元素还要定义hashCode()方法。所以当我们向HashSet中添加一个元素时,hashset会先调用该对象的hashCode()方法得到其hashCode值,根据该值决定该对象在列表中存储位置。然后如果列表中已有其他元素,则调用加入对象的equals()方法与已有元素进行比较。如果比较结果为假,则将对象插入列表中。如果比较结果为真,则用新的值替换旧的值。 -
如果有两个元素通过equals()方法比较返回true,而它们的hashCode()方法返回值不等,HashSet也会将它们存储在不同的位置。因为是先调用hashCode()方法,一旦返回值不等,就直接将它们存储在不同的位置,并不会调用equals()方法,也就是说,hashCode()方法不关心比较对象的内容是否相同。
2.2 选做:尝试分析HashSet源代码后,重新解释1.1
三、ArrayListIntegerStack,题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-1 ArrayListIntegerStack
3.1 比较自己写的ArrayListIntegerStack与自己在题集jmu-Java-04-面向对象2-进阶-多态、接口与内部类中的题目5-3自定义接口ArrayIntegerStack,有什么不同?(不要出现大段代码)
- ArrayListIntegerStack是用ArrayList来实现栈,ArrayIntegerStack是用Integer数组来实现栈。
- 当数组的空间全部被用完的情况下ArrayIntegerStack是会存在栈满的情况,而ArrayListIntegerStack不存在,因为ArrayList在数组空间被用完之后会自动扩容。
- ArrayIntegerStack在出栈的时候需要移动top指针,ArrayListIntegerStack不需要,调用remove()方法就可以。
3.2 简单描述接口的好处.
答:接口可以做到相同方法,不同实现。拿3.1来举例,ArrayListIntegerStack和ArrayIntegerStack两个类都继承了一个IntegerStack接口。这样可以使用一个接口来操作不同的类。ArrayListIntegerStack和ArrayIntegerStack两个类都有pop()方法,但是实现pop()方法不同。这样我们修改ArrayListIntegerStack的pop()方法而不影响ArrayIntegerStack的pop方法。
四、Stack and Queue
4.1 编写函数判断一个给定字符串是否是回文,一定要使用栈,但不能使用java的Stack类(具体原因自己搜索)。请粘贴你的代码,类名为Main你的学号。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
interface StringStack{
public String push(String item);
public String pop();
}
class ArrayListStringStack implements StringStack{
private List<String> list;
public ArrayListStringStack() {
list=new ArrayList<String>();
}
@Override
public String push(String item) {
if(item==null)
return null;
list.add(item);
return item;
}
@Override
public String pop() {
if(list.isEmpty())
return null;
return list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
public class Main201521123018 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
StringStack stack=new ArrayListStringStack();
String m=sc.next();
int f=1;
for(int i=0;i<m.length();i++)
{
stack.push(String.valueOf(m.charAt(i)));
}
for(int i=0;i<m.length();i++)
{
if(String.valueOf(m.charAt(i)).equals(stack.pop()))f=1;
else
{
f=0;
break;
}
}
if(f==1)System.out.println("true");
else System.out.println("flase");
}
}
4.2 题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-6 银行业务队列简单模拟。(不要出现大段代码)
while(!link1.isEmpty()||!link2.isEmpty())
{
Integer a1=link1.poll();
if(a1!=null)
{
if(link1.isEmpty()&&link2.isEmpty())
System.out.println(a1);
else
System.out.print(a1+" ");
}
Integer a2=link1.poll();
if(a2!=null)
{
if(link1.isEmpty()&&link2.isEmpty())
System.out.println(a2);
else
System.out.print(a2+" ");
}
Integer b=link2.poll();
if(b!=null)
{
if(link1.isEmpty()&&link2.isEmpty())
System.out.println(b);
else
System.out.print(b+" ");
}
}

五、统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出
题集jmu-Java-05-集合之5-2 统计文字中的单词数量并按单词的字母顺序排序后输出 (不要出现大段代码)
TreeSet<String> strSet=new TreeSet<String>();
for(String e:strSet)
{
if(i==10)
{
break;
}
System.out.println(e);
i++;
}
5.1 实验总结
答:用TreeSet的add方法将指定的元素添加到此 set(如果该元素尚未存在于 set 中)。更确切地讲,如果该 set 不包含满足 (enull ? e2null : e.equals(e2)) 的元素 e2,则将指定元素 e 添加到此 set 中。如果此 set 已经包含这样的元素,则该调用不改变此 set 并返回 false。且就会默认帮我们排好序,最后按要求输出一下即可。
3. PTA实验总结及码云上代码提交记录
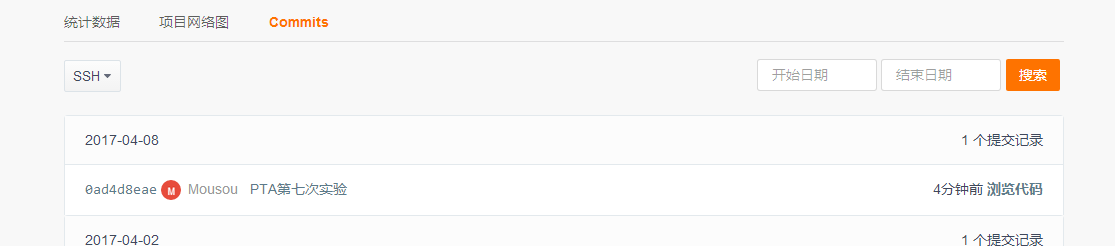
3.1本周Commit历史截图
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”,然后搜索并截图,如下图所示
3.2 PTA实验总结
- 编程(5-1, 5-2, 5-3(选做), 5-6)
- 实验总结已经在作业中体现,不用写。



