七:初探异步编程
同步编程
创建类
using System; using System.Diagnostics; namespace TestAsyncConsole { public class NormalClass { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); public void DoSomething() { const int largeNumber = 600000; sw.Start(); int t1 = CountChar(1,largeNumber); int t2 = CountChar(2,largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); Console.WriteLine("1: {0}",t1); Console.WriteLine("2: {0}",t2); } private int CountChar(int id,int Number) { int Total = 0; Console.WriteLine("开始调用{0} :{1,4} ms",id,sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); for (int i = 0; i < Number;i++ ) { Total += i; } Console.WriteLine("结束调用{0} :{1,4} ms",id,sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); return Total; } private void LongProcess(int largeNumber) { for(int i=0;i<largeNumber;i++) { } Console.WriteLine(" 时长: {0,4} 毫秒",sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); } } }
调用该类
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { NormalClass normal = new NormalClass(); normal.DoSomething(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
得到结果
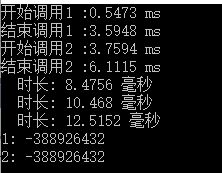
异步编程
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace TestAsyncConsole { public class AsyncClass { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); public void DoSomething() { const int largeNumber = 600000; sw.Start(); var t1 = CountChar(1, largeNumber); var t2 = CountChar(2, largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); LongProcess(largeNumber); Console.WriteLine("1: {0}", t1.Result); Console.WriteLine("2: {0}", t2.Result); } private async Task<int> CountChar(int id, int Number) { int Total = 0; Console.WriteLine("开始调用{0} :{1,4} ms", id, sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); Total = await Task.Run(()=> { for (int i = 0; i < Number; i++) { Total += i; } return Total; } ); Console.WriteLine("结束调用{0} :{1,4} ms", id, sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); return Total; } private void LongProcess(int largeNumber) { for (int i = 0; i < largeNumber; i++) { } Console.WriteLine(" 时长: {0,4} 毫秒", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); } } }
调用该异步类得到的结果如下
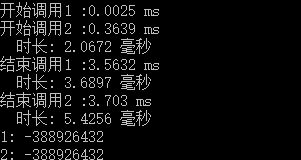
可以看到虽然代码中LongProcess都在调用方法CountChar之后,但是实际执行的结果顺序却不是按照代码中的顺序。
总结异步同步编程的差异
- 关键字只有两个Async和Await
- Async和Await必须成对出现,否则就又会变成同步
- Async用在异步方法的返回值修饰上
- Await比较特殊,这里需要新建一个Task,也就是说必须是有一个新线程来处理异步
- 异步的方法返回值和正常的返回值不同,正常的返回值是类型,而异步的返回值是Task<类型>
- 获取结果的方法不是使用返回值,因为返回值的类型是Task<类型>,而是使用返回值.Result。其中这个Result的类型才是Task<类型>中的类型

