Spring事件监听机制源码解析
Spring事件监听器使用
1.Spring事件监听体系包括三个组件:事件、事件监听器,事件广播器。
事件:定义事件类型和事件源,需要继承ApplicationEvent。
package com.ybe.eventLisitener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class OrderEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String name;
public OrderEvent(Object source,String name) {
super(source);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
事件监听器:用来监听某一类的事件,并且执行具体业务逻辑,需要实现ApplicationListener
package com.ybe.eventLisitener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class OrderEventListener implements ApplicationListener<OrderEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(OrderEvent event) {
if(event.getName().equals("下订单")){
System.out.println("下单已完成...");
}
}
}
package com.ybe.eventLisitener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class OrderEventListenerByAnnotation {
@EventListener(OrderEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(OrderEvent event) {
if(event.getName().equals("下订单")){
System.out.println("下单已完成...");
}
}
}
事件多播器:负责广播通知所有监听器,所有的事件监听器都注册在了事件多播器中。好比观察者模式中的被观察者。Spring容器默认生成的是同步事件多播器。可以自定义事件多播器,定义为异步方式。
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Scanner;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.ybe")
public class Config {
@Bean
public ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(){
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster eventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
eventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
return eventMulticaster;
}
}
Spring事件源码分析
1.创建多播器
创建 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的过程中,会执行refresh()中的initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法。该方法先获取bean工厂,然后判断工厂是否包含了beanName 为 applicationEventMulticaster的bean。如果包含了,则获取该bean,赋值给applicationEventMulticaster 属性。如果没有,则创建一个 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 对象,并且赋值给 applicationEventMulticaster 。实现了源码如下:
/**
* Initialize the ApplicationEventMulticaster.
* Uses SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster if none defined in the context.
* @see org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
// 获取当前bean工厂,一般是DefaultListableBeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 判断容器中是否存在bdName为applicationEventMulticaster的bd,
//也就是说自定义的事件监听多路广播器,必须实现 ApplicationEventMulticaster接口
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 如果有,则从bean工厂得到这个bean对象
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
// 如果没有,则默认采用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
2.注册监听器
监听器的注册有两种,通过实现 ApplicationListener接口或者添加@EventListener注解。
一.通过接口方式注册。实现接口 ApplicationListener。
注册的逻辑实现在refresh()中的registerListeners()方法里面。第一步,先获取当前ApplicationContext中已经添加的 applicationListeners(SpringMVC源码中有用到、SpringBoot也有用到),遍历添加到多播器中。第二步,获取实现了ApplicationListener接口的listenerBeanNames集合,添加至多播器中。第三步,判断是否有早期事件,如果有则发起广播。
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
// 遍历应用程序中存在的监听器集合,并将对应的监听器添加到监听器的多路广播器中
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
// 从容器中获取所有实现了ApplicationListener接口的bd的bdName
// 放入ApplicationListenerBeans集合中
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
// 此处先发布早期的监听器集合
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
思考一下,上面的代码中第二步为啥添加的是listenerBeanName?
如果监听器是懒加载的话(即有@Lazy 注解)。那么在这个时候创建监听器显然是不对的,这个时候不能创建监听器。所以将事件监听器添加到applicationContext的监听器集合中的具体逻辑放在初始化具体的Bean对象之后。通过 ApplicationListenerDetector 类来实现 ,这个类是在 refreah()中prepareBeanFactory()方法中添加的。代码如下:
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) {
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 添加 监听器后置处理器,在初始化具体的实现了 ApplicationListener 接口的Bean之后,进行调用。调用的是
// postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME, getApplicationStartup());
}
}
ApplicationListenerDetector 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,所以在Spring容器中Bean对象实例初始完成之后,会调用ApplicationListenerDetector对象的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,其中会判断bean对象是否实现了ApplicationListener接口,如果实现把bean对象实例添加到applicationContext的监听器集合中。方法源码如下,
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
// 把当前Bean对象添加进 applicationContext 的监听器集合对象中
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
二、通过注解的方式注册。@EventListener(T)。
在创建 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的构造方法中,会执行org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry, java.lang.Object) 方法。这个方法中会添加两个 beanDefs, 代码如下:
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor:事件监听器的BeanFactory后置处理器,在前期会创建 DefaultEventListenerFactory ,后期在初始化Bean之后,根据 @EventListener 注解,调用DefaultEventListenerFactory创建具体的 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter 。
DefaultEventListenerFactory:事件监听器的创建工厂,用来创建 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter(实现了GenericApplicationListener接口)事件监听器对象。
EventListenerMethodProcessor 的类继承图如下:
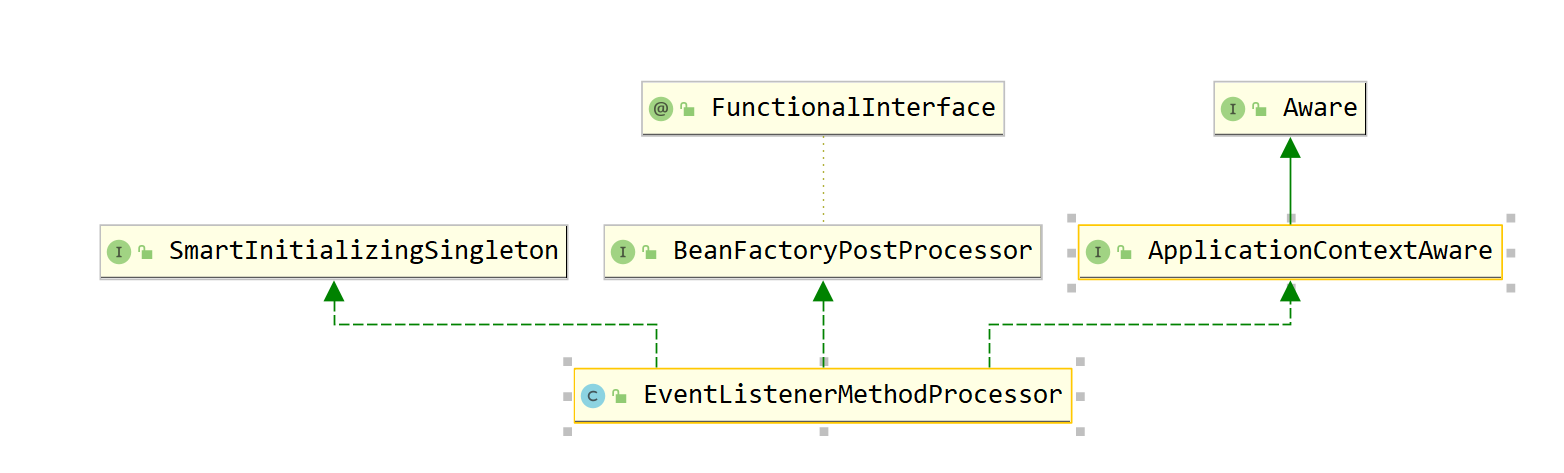
在refreash的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()中会调用 EventListenerMethodProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory方法,获取EventListenerFactory 类型的 Bean。代码如下:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
// 获取或创建 EventListenerFactory 类型的 Bean
Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false);
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories);
this.eventListenerFactories = factories;
}
在 DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons 方法中,创建完所有的单例 Bean 之后,会遍历所有BeanName查找Bean对象是否实现了 SmartInitializingSingleton 接口,最终找到EventListenerMethodProcessor对象实例,并调用该实例对象的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法。代码如下:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 将所有BeanDefinition的名字创建一个集合
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 触发所有非延迟加载单例bean的初始化,遍历集合的对象
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 合并父类BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 条件判断,抽象,单例,非懒加载
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判断是否实现了FactoryBean接口
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 根据&+beanName来获取具体的对象
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
// 进行类型转换
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
// 判断这个FactoryBean是否希望立即初始化
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
// 如果希望急切的初始化,则通过beanName获取bean实例
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 如果beanName对应的bean不是FactoryBean,只是普通的bean,通过beanName获取bean实例
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 遍历beanNames,触发所有SmartInitializingSingleton的后初始化回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 获取beanName对应的bean实例
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 判断singletonInstance是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
// 类型转换
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
// 触发SmartInitializingSingleton实现类的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
afterSingletonsInstantiated 中会调用 主要逻辑为:先从容器中获取Object.class对象的beanNames,然后循环遍历 beanName和 beanType , 调用 processBean()方法 ,进行 ApplicationEventAdatper 对象的创建并将创建的ApplicationListener添加到context容器中监听器集合中。代码如下:
/**
* 该方法拿到某个bean的名称和它的目标类,再这个范围上检测@EventListener注解方法,生成和注册 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter 实例
* @param beanName
* @param targetType
*/
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
try {
// 检测当前类targetType上使用了注解@EventListener的方法
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
// 如果当前类targetType中没有任何使用了注解@EventListener的方法,则将该类保存到缓存nonAnnotatedClasses,从而
// 避免当前处理方法重入该类,避免二次处理
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
// 如果当前类targetType中有些方法使用了注解@EventListener,那么根据方法上的信息对应的创建和注册ApplicationListener实例
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
// 此处使用了this.eventListenerFactories,这些EventListenerFactory是在该类postProcessBeanFactory方法调用时被记录的
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
// 如果当前EventListenerFactory支持处理该@EventListener注解的方法,则使用它创建 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
// 将创建的ApplicationListener加入到容器中
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}
3.多播器广播事件
可以通过调用 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent(java.lang.Object, org.springframework.core.ResolvableType) 方法进行事件的调用,其中的关键代码在getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType)中,主要逻辑:获取多播器,调用多播器的发布事件方法 ,其中会找到符合要求的事件监听器进行调用。代码如下:
/**
* 将给定事件发布到所有监听器
*/
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
// 如果event为null,抛出异常
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
// 装饰事件作为一个应用事件,如果有必要
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
// 如果event是ApplicationEvent的实例
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
// 将event强转为ApplicationEvent对象
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
// PayloadApplicationEvent:携带任意有效负载的ApplicationEvent。
// 创建一个新的PayloadApplicationEvent
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
// 如果eventType为 null
if (eventType == null) {
// 将applicationEvent转换为PayloadApplicationEvent 象,引用其ResolvableType对象
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
// 如果可能的话,现在就进行组播——或者在组播初始化后延迟
// earlyApplicationEvents:在多播程序设置之前发布的ApplicationEvent
// 如果earlyApplicationEvents不为 null,这种情况只在上下文的多播器还没有初始化的情况下才会成立,会将applicationEvent
// 添加到earlyApplicationEvents保存起来,待多博器初始化后才继续进行多播到适当的监听器
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
//将applicationEvent添加到 earlyApplicationEvents
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
// 获取多播器,调用多播器的发布事件方法 ,其中会找符合要求的事件监听器进行调用。
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
// 通过父上下文发布事件
// 如果parent不为null
if (this.parent != null) {
// 如果parent是AbstractApplicationContext的实例
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
// 将event多播到所有适合的监听器。如果event不是ApplicationEvent实例,会将其封装成PayloadApplicationEvent对象再进行多播
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
// 通知与event事件应用程序注册的所有匹配的监听器
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
getApplicationEventMulticaster()默认会拿到SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 对象,multicasEvent方法用来发布具体的事件,主要逻辑:根据事件类型对象和事件类型在Spring容器中找出符合要求的事件监听器列表方法并进行处理。代码如下:
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 获取符合要求的事件监听器,进行遍历
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
getApplicationListeners中会根据事件监听器对象和事件类型在多播器的监听器对象中查找满足条件的事件监听器对象,并进行缓存。
invokeListener 先判断是否有设置错误处理程序,如果有则需要用错误处理程序来处理事件监听器中发生的异常。代码如下:
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
// 获取此多播器的当前错误处理程序
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
// 如果errorHandler不为null
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
// 回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入event
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// 交给errorHandler接收处理err
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
// 回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入event
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
doInvokeListener具体调用listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入event。
/**
* 回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入 event
* @param listener
* @param event
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入 event:contextrefreshListener:onapplicaitonEvent:FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent()
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
//获取异常信息
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
//抛出异常
throw ex;
}
}
}
SpringMVC中事件使用
SpringMVC中就是通过Spring的事件机制进行九大组件的初始化。
1.ContextRefreshListener监听器的初始化
事件监听器定义在FrameworkServlet类中,作为内部类。代码如下:
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
监听器的添加逻辑在org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext 中。通过添加 SourceFilteringListener 进行包装。代码如下:
// 添加监听器sourceFilteringListener到wac中,实际监听的是ContextRefreshListener所监听的事件,监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件,
// 当接收到消息之后会调用onApplicationEvent方法,调用onRefresh方法,并将refreshEventReceived标志设置为true,表示已经refresh过
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
2.ContextRefreshListener事件监听器注入多播器中
在多播器中添加事件监听器的具体逻辑在wac.refresh方法中的registerListeners方法中,代码如下:
// Register statically specified listeners first.
// 遍历应用程序中存在的监听器集合,并将对应的监听器添加到监听器的多路广播器中
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
3.多播器触发ContextRefreshListener事件监听器
在refresh中的finishRefresh()方法中,会调用publishEvnet(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)) 发布事件。进行多播器广播,代码如下
// 多播applicationEvent到适当的监听器
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
最终会调到FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event)。
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
// 标记 refreshEventReceived 为true
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 处理事件中的 ApplicationContext 对象,空实现,子类DispatcherServlet会实现
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
onRefresh代码如下:
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
initStrategies具体代码如下:
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 初始化 MultipartResolver:主要用来处理文件上传.如果定义过当前类型的bean对象,那么直接获取,如果没有的话,可以为null
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 初始化 LocaleResolver:主要用来处理国际化配置,基于URL参数的配置(AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver),基于session的配置(SessionLocaleResolver),基于cookie的配置(CookieLocaleResolver)
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 初始化 ThemeResolver:主要用来设置主题Theme
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化 HandlerMapping:映射器,用来将对应的request跟controller进行对应
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化 HandlerAdapter:处理适配器,主要包含Http请求处理器适配器,简单控制器处理器适配器,注解方法处理器适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化 HandlerExceptionResolver:基于HandlerExceptionResolver接口的异常处理
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化 RequestToViewNameTranslator:当controller处理器方法没有返回一个View对象或逻辑视图名称,并且在该方法中没有直接往response的输出流里面写数据的时候,spring将会采用约定好的方式提供一个逻辑视图名称
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化 ViewResolver: 将ModelAndView选择合适的视图进行渲染的处理器
initViewResolvers(context);
// 初始化 FlashMapManager: 提供请求存储属性,可供其他请求使用
initFlashMapManager(context);
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix