[数据结构]之链表
1. 链表与数组的比较:

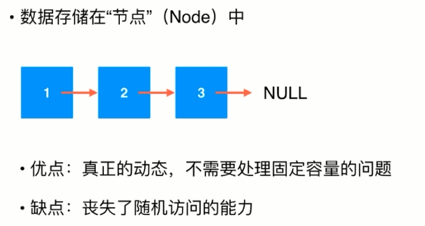

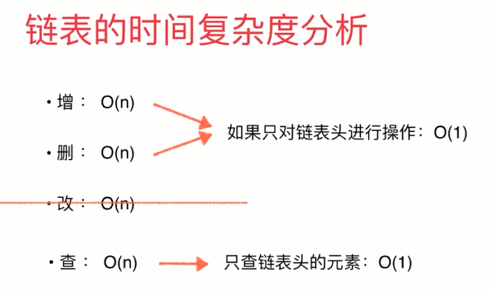
2. 链表的实现:
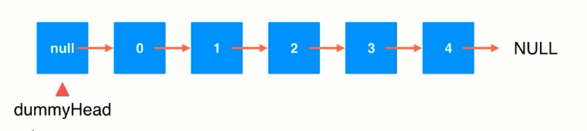

package com.ytuan.linkedList; public class LinkedList<E> { // private Node head; private Node dummyHead; private int size; public LinkedList() { // head = new Node(); dummyHead = new Node(); size = 0; } public int getSize() { return size; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** * 找到需要插入索引的前一个节点是关键 * * @param index * @param e */ public void add(int index, E e) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("add faild! index illegalment"); Node pre = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { pre = pre.next; } // Node newNode = new Node(e); // newNode.next = pre.next; // pre.next = newNode; pre.next = new Node(e, pre.next); size++; } public void addFirst(E e) { add(0, e); } public void addLast(E e) { add(size, e); } public E get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("add faild! index illegalment"); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { // 共需要next index- 1 次 cur = cur.next; } return cur.e; } public E getFirst() { return get(0); } public E getLast() { return get(size - 1); } public void set(int index, E e) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("add faild! index illegalment"); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) cur = cur.next; cur.e = e; } public boolean contains(E e) { Node cur = dummyHead.next; while (cur!= null) { if (cur.e.equals(e)) return true; cur = cur.next; } return false; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); // res.append(String.format("LinkedList size = %d \n", size)); Node pre = dummyHead; while (pre.next != null) { res.append(pre.next.e + " ->"); pre = pre.next; } res.append("null"); return res.toString(); } public E remove(int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("add faild! index illegalment"); Node pre = dummyHead; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) pre = pre.next; Node delNode = pre.next; E res = delNode.e; pre.next = delNode.next; delNode.next = null; size--; return res; } public E removeFirst() { return remove(0); } public E removeLast() { return remove(size - 1); } private class Node { E e; Node next; public Node(E e, Node node) { this.e = e; this.next = node; } public Node(E e) { this(e, null); } public Node() { this(null, null); } @Override public String toString() { return e.toString(); } } }

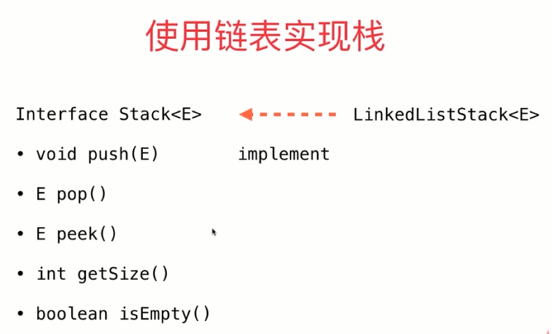
3. 使用链表实现的栈:

package com.ytuan.stack; import com.ytuan.linkedList.LinkedList; public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private LinkedList<E> list; public LinkedListStack() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub list = new LinkedList<>(); } @Override public void push(E e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub list.addLast(e); } @Override public E pop() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return list.removeFirst(); } @Override public E peek() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return list.getFirst(); } @Override public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return list.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return list.isEmpty(); } @Override public String toString() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); res.append("Stack : top "); res.append(list); return res.toString(); } }
4. 使用链表实现队列
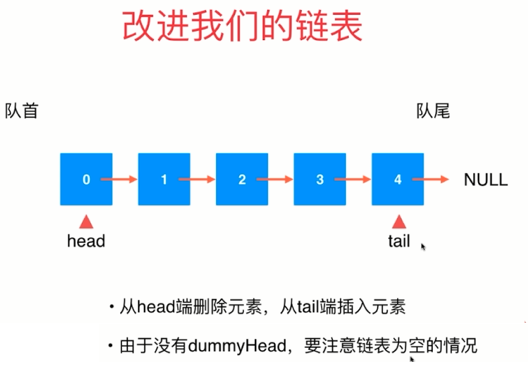
代码实现:

package com.ytuan.queue; public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> { private Node head; private Node tail; private int size; public LinkedListQueue() { this.head = null; this.tail = null; this.size = 0; } @Override public void enqueue(E e) { if (tail == null) { // 此时链表为空 tail = new Node(e); head = tail; } else { tail.next = new Node(e); tail = tail.next; } size++; } @Override public E dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("no element to dequeue"); Node delNode = head; head = head.next; if (head == null) tail = null; delNode.next = null; size--; return delNode.e; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } @Override public int getSize() { return size; } @Override public E getFront() { if (isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("queue is empty"); return head.e; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); res.append("Queue front ->"); Node cur = head; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (cur != null) res.append(cur.e + "->"); if (cur.next != null) cur = cur.next; } res.append("tail"); return res.toString(); } private class Node { private E e; private Node next; public Node(E e) { this.e = e; this.next = null; } public Node(E e, Node next) { this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node() { this.e = null; this.next = null; } public String toString() { return e.toString(); } } }
5. 链表实战
leetcode 230 号问题 :https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
无头节点解答:

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { // head 就是目标元素 while (head != null && head.val == val) { head = head.next; } // 没有元素了 if (head == null) return head; ListNode pre = head; while (pre.next != null) { if (pre.next.val == val) { pre.next = pre.next.next; } else { pre = pre.next; } } return head; } }
带头节点解答:

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0); public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if (head == null) return head; dummyNode.next = head; ListNode pre = dummyNode; while (pre.next != null) { if (pre.next.val == val) pre.next = pre.next.next; else pre = pre.next; } return dummyNode.next; } }





