[数据结构]之栈
1. 概述
-
- 栈对应的操作是数组的子集
- 只能从一端添加元素,也只能从一端获取元素;这一端称之为栈顶
- 栈是一种后进先出的数据结构(LIFO:Last In First Out)
2. 栈的应用
-
- 撤销操作
- 程序调用的系统栈
3. 栈的实现
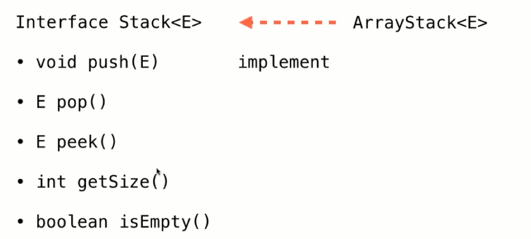
定义栈的接口,根据栈的数据结构特性,它有以下基本的方法:

栈接口定义代码:
package com.ytuan.stack; public interface Stack<E> { public void push(E e); public E pop(); public E peek(); public int getSize(); public boolean isEmpty(); }
对于栈的实现,在底层有很多的实现方式,在这里我么使用的是数组的实现方式,也会重用之前实现的动态数组。参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ytuan996/p/10692548.html
栈的实现代码:

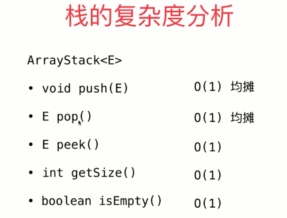
package com.ytuan.stack; import com.ytuan.array.Array; public class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private Array<E> array; public ArrayStack(int capacity) { array = new Array<>(capacity); } public ArrayStack() { this(10); } @Override public void push(E e) { array.addLast(e); } @Override public E pop() { return array.removeLast(); } @Override public E peek() { return array.getLast(); } @Override public int getSize() { return array.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return array.isEmpty(); } public int getCapacity() { return array.getCapacity(); } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); res.append(String.format("Stack: size = %d, capacity= %d. \n", array.getSize(),array.getCapacity())); res.append('['); for (int i = 0; i < array.getSize(); i++) { res.append(array.get(i)); if (i != array.getSize() - 1) res.append(','); } res.append("] top"); return res.toString(); } }
4. 栈的实际应用
括号匹配:leetcode的20问题:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/
使用JDK标准库中的栈解答:
import java.util.Stack; class Solution { public boolean isValid(String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') stack.push(c); else { if (stack.isEmpty()) return false; Character pop = stack.pop(); if (c == ')' && pop != '(') return false; if (c == ']' && pop != '[') return false; if (c == '}' && pop != '{') return false; } } return stack.isEmpty() ? true : false; } }
使用我们自定义的栈解答:

package com.ytuan.stack; class Solution { public boolean isValid(String s) { Stack<Character> stack = new ArrayStack<Character>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') stack.push(c); else { if (stack.isEmpty()) return false; Character pop = stack.pop(); if (c == ')' && pop != '(') return false; if (c == ']' && pop != '[') return false; if (c == '}' && pop != '{') return false; } } return stack.isEmpty() ? true : false; } public static void main(String[] args) { boolean valid = new Solution().isValid("[(({})}]"); System.out.println(valid); } private interface Stack<E> { public void push(E e); public E pop(); public E peek(); public int getSize(); public boolean isEmpty(); } private class Array<E> { private E[] data; // 数组中元素的个数 private int size; /** * 根据传入的容量初始化一个数组 * * @param capacity 容量 */ public Array(int capacity) { data = (E[]) new Object[capacity]; this.size = 0; } /** * 根据传入的数组构建动态数组 * * @param arr 构建动态数组的原始数组 */ public Array(E arr[]) { int n = arr.length; data = (E[]) new Object[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) data[i] = arr[i]; // 当前数组的元素个数等于传入数组的元素个数 this.size = n; } /** * 数组默认的构造函数,默认初始化数组的容量为10 */ public Array() { this(10); } /** * 得到当前数组的元素个数 * * @return 数组的元素个数 */ public int getSize() { return this.size; } /** * 判断数组当前是否还有元素 * * @return 没有元素返回true,否则放回false */ public boolean isEmpty() { return this.size == 0; } /** * * @return 当前数组的容量大小 */ public int getCapacity() { return this.data.length; } /** * 在数组的最后添加一个元素 * <p> * 其实就是在数组的size位置之前添加一个元素 * </p> * * @param e 添加的元素 */ public void addLast(E e) { this.addBefore(this.size, e); } public void addFirst(E e) { this.addBefore(0, e); } /** * 在指定的索引元素之前插入新元素。 * <P> * 在这个方法的实现中,我们需要把数组中指定索引元素之后的元素全部往后移动一个位置,然后将新的元素插入到指定的索引位置 * </p> * * @param pos 指定元素的索引 * @param e 新插入的元素 */ public void addBefore(int pos, E e) { if (pos < 0 || pos > this.size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("add faild! index is Illegalment"); if (this.size == this.getCapacity()) // 判断容量是否足够 resize(this.getCapacity() * 2); for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= pos; i--) { this.data[i + 1] = this.data[i]; } data[pos] = e; size++; } /** * 重写Object类的toString方法,按照一定的格式打印数组 */ @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d." + "\n", this.size, this.getCapacity())); res.append('['); for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) { res.append(this.data[i]); if (i != this.size - 1) res.append(','); } res.append(']'); return new String(res); } /** * 根据索引放回对应的元素 * * @param index * @return */ public E get(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("get faild! index is Illegalment"); return this.data[index]; } public E getLast() { return this.get(size - 1); } public E getFirst() { return get(0); } /** * * @param index * @param e */ public void set(int index, E e) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("set faild! index is Illegalment"); this.data[index] = e; } /** * * @param e * @return */ public boolean contains(E e) { for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) { if (this.data[i].equals(e)) return true; } return false; } /** * * @param e * @return */ public int find(E e) { for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) { if (this.data[i].equals(e)) return i + 1; } return -1; } /** * * @param index */ public E remove(int index) { if (index < 0 || index == this.size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("the index is Ilegalment"); E res = this.data[index]; for (int i = index; i < this.size - 1; i++) { this.data[i] = this.data[i + 1]; } size--; data[this.size] = null; if (this.size == this.getCapacity() / 4 && this.getCapacity() / 2 > 0) this.resize(this.getCapacity() / 2); return res; } public E removeFirst() { return this.remove(0); } public E removeLast() { return this.remove(this.size - 1); } /** * */ public void removeAll() { for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= 0; i--) this.remove(i); } /** * * @param e */ public void removeElement(E e) { int index = this.find(e); if (index != -1) { this.remove(index); } } /** * 增加数组的容量 * * @param capacity */ private void resize(int newCapacity) { E newData[] = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity]; for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) newData[i] = this.data[i]; this.data = newData; } } private class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E> { private Array<E> array; public ArrayStack(int capacity) { array = new Array<>(capacity); } public ArrayStack() { this(10); } @Override public void push(E e) { array.addLast(e); } @Override public E pop() { return array.removeLast(); } @Override public E peek() { return array.getLast(); } @Override public int getSize() { return array.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return array.isEmpty(); } public int getCapacity() { return array.getCapacity(); } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); res.append(String.format("Stack: size = %d, capacity= %d. \n", array.getSize(), array.getCapacity())); res.append('['); for (int i = 0; i < array.getSize(); i++) { res.append(array.get(i)); if (i != array.getSize() - 1) res.append(','); } res.append("] top"); return res.toString(); } } }





