LeetCode 初级算法
删除排序数组中的重复项

class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int size=nums.size();//获取数组的长度
int left=0;//定义左指针
int right=1;//定义右指针
for(int i=right;i<size;i++){
if(nums[left]==nums[i]){
//如果左指针和右指针指向的值相等,则左指针不动,右指针向前移动
continue;
}
if(nums[left]!=nums[i]){
//如果左指针和右指针指向的值不相等,则左指针向前移动,然后将右指针的值赋给左指针,右指针向前移动
left++;
nums[left]=nums[i];
continue;
}
}
//左指针所处的下标即数组的长度-1
return left+1;
}
};

买卖股票的最佳时机 ΙΙ
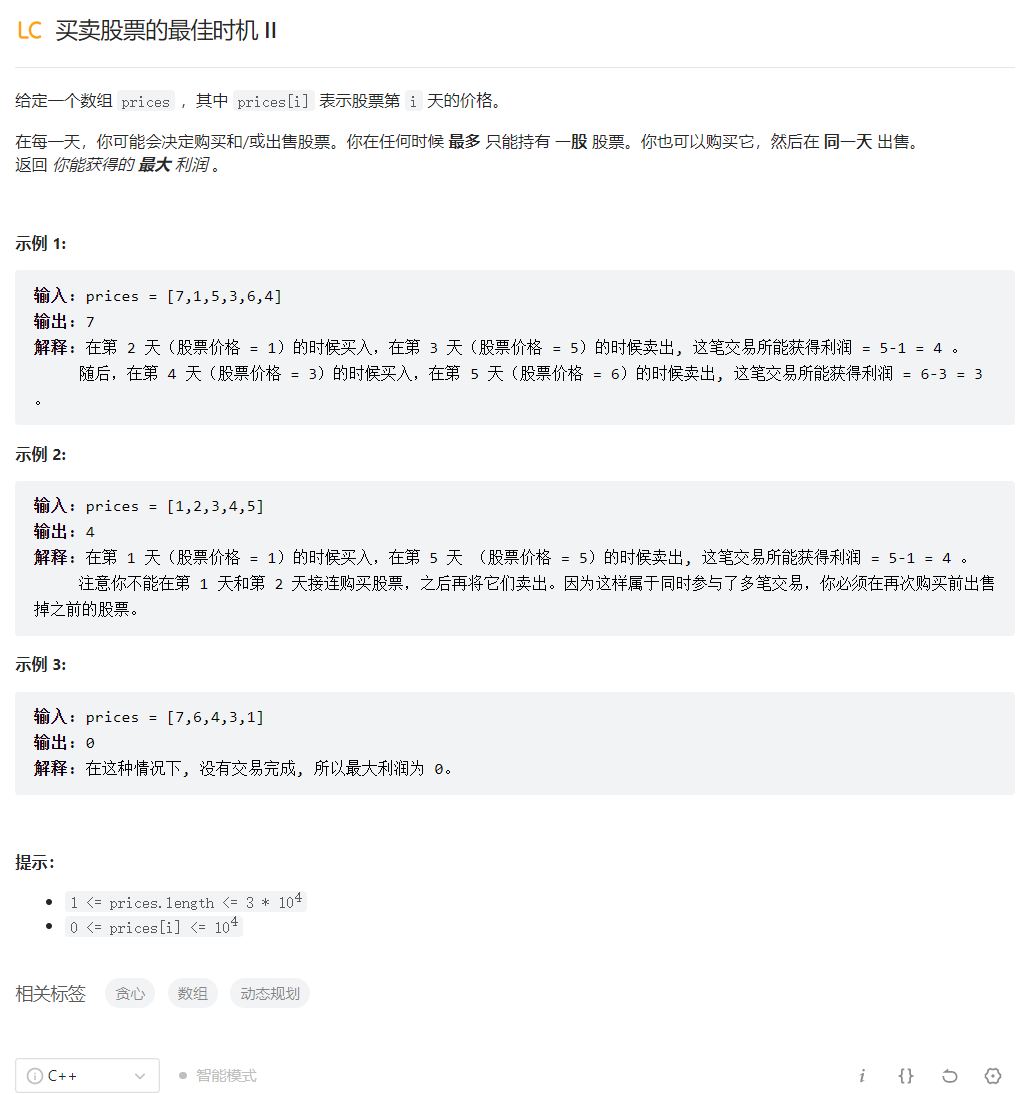
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
//本题相当于求所有上升区间的总和,最简单的方法是贪心法
int max=0;//收益最大值
for(int i=1;i<prices.size();i++){
int price=prices[i]-prices[i-1];//当天价格和前一天价格的差值
if(price>0){
//如果差值大于0,则卖出
max+=price;
}
}
return max;
}
};

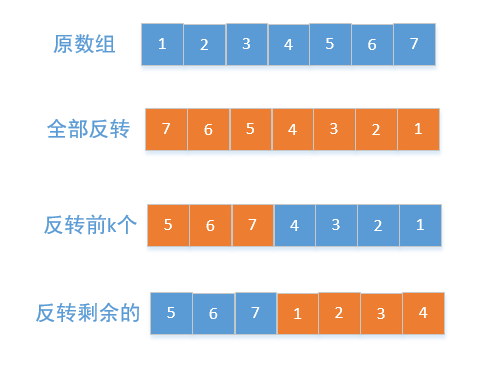
旋转数组
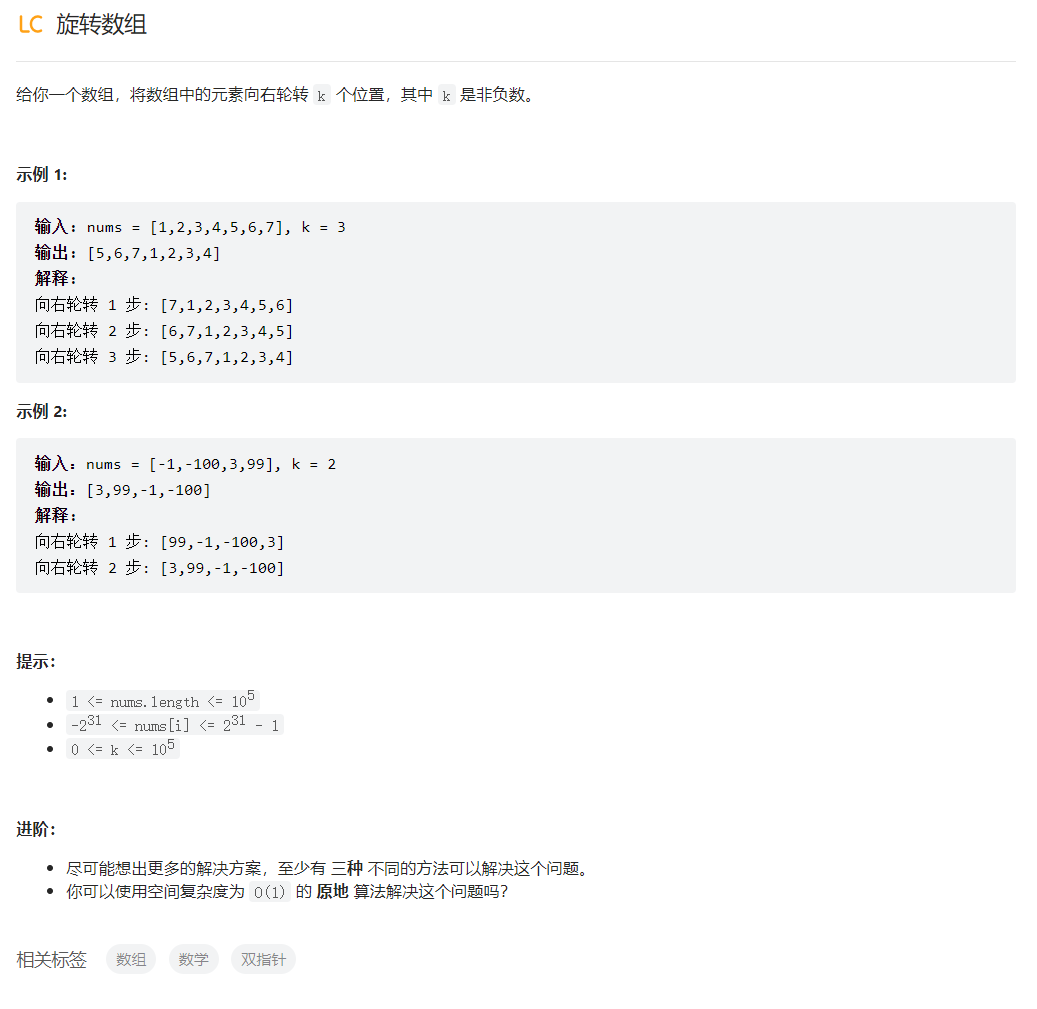
class Solution {
public:
void reverse(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){
while(start<end){
int temp=nums[start];
nums[start++]=nums[end];
nums[end--]=temp;
}
}
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int size=nums.size();
k%=size;
reverse(nums,0,size-1);
reverse(nums,0,k-1);
reverse(nums,k,size-1);
}
};
解题思路

存在重复元素
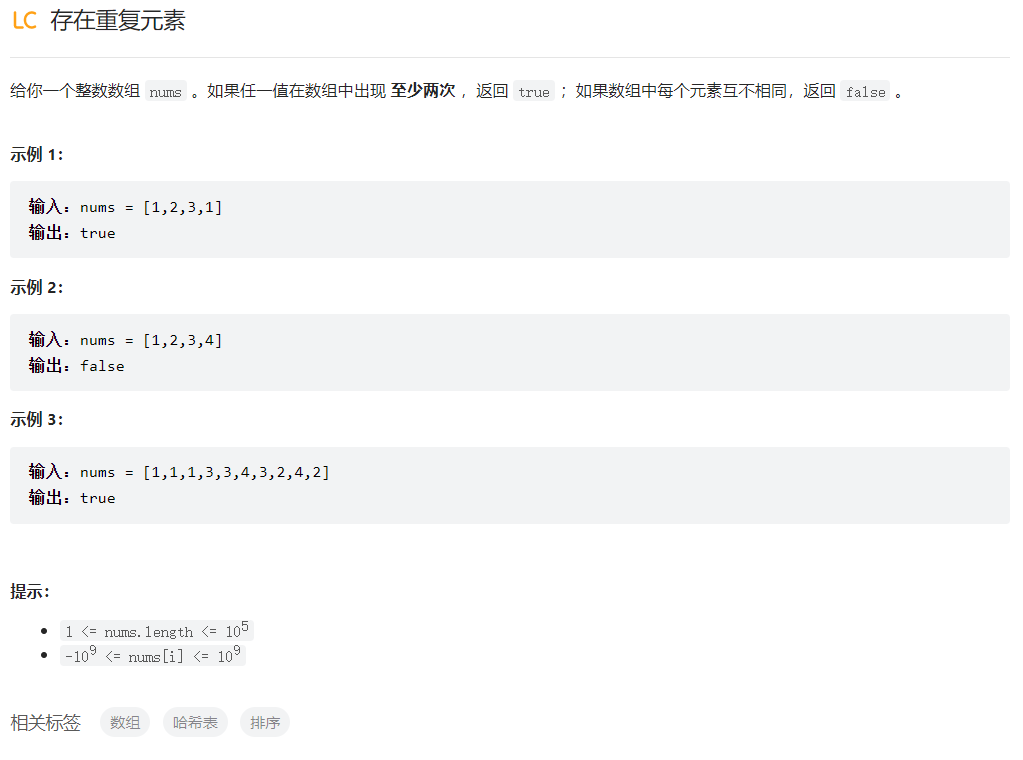
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
//先排序再比较
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
if(nums[i]==nums[i-1]){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};

只出现一次的数字
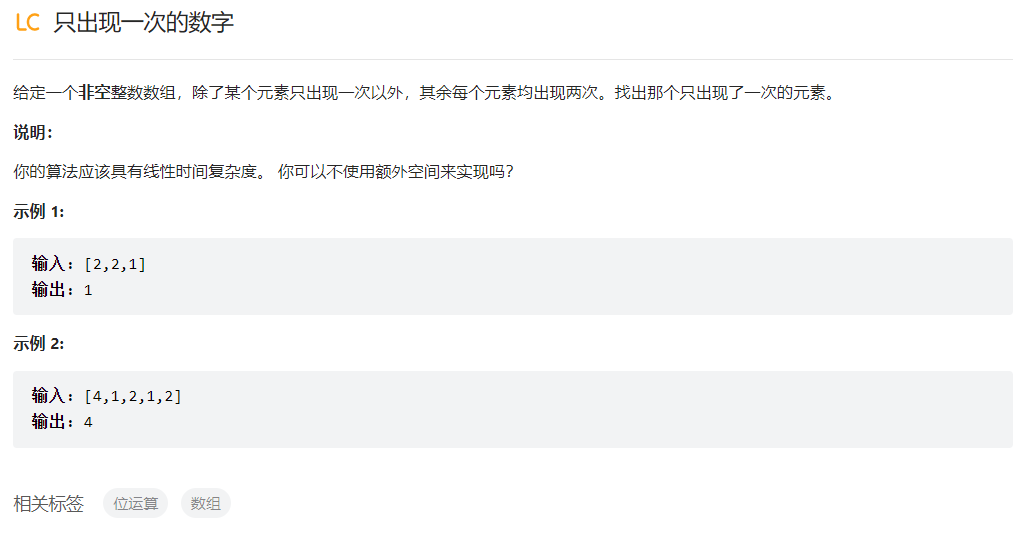
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int result=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
result^=nums[i];
}
return result;
}
};

两个数组的交集 ΙΙ
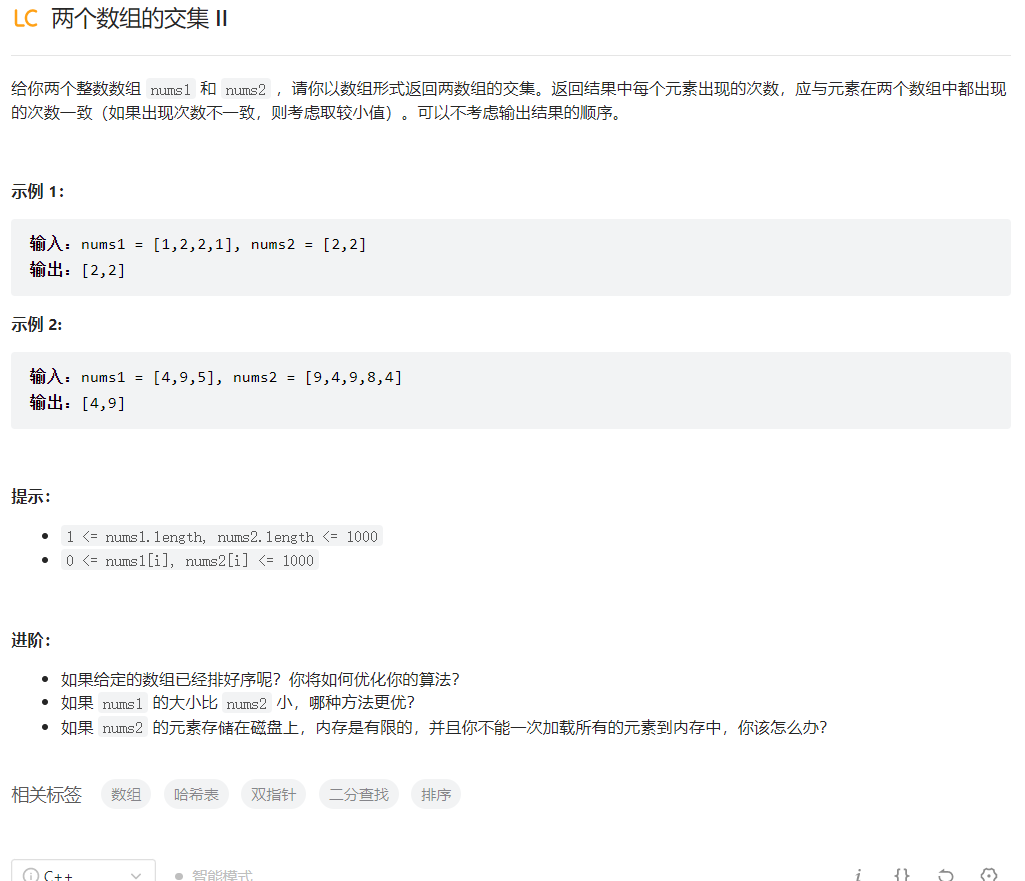
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
//先对nums1和nums2进行排序
sort(nums1.begin(),nums1.end());
sort(nums2.begin(),nums2.end());
vector<int> result;
int p1=0,p2=0;//定义双指针,初始化为指向数组的第一个元素
while(p1<nums1.size() && p2<nums2.size()){
if(nums1[p1]<nums2[p2]){
//如果p1指向的值小于p2指向的值,则指针p1向前移动
p1++;
} else if(nums1[p1]>nums2[p2]) {
//如果p2指向的值小于p1指向的值,则指针p2向前移动
p2++;
} else {
//如果p1指向的值和p2指向的值相等,则将该值添加到返回数组中,p1和p2同时向前移动
result.push_back(nums1[p1]);
p1++;
p2++;
}
}
return result;
}
};

加一
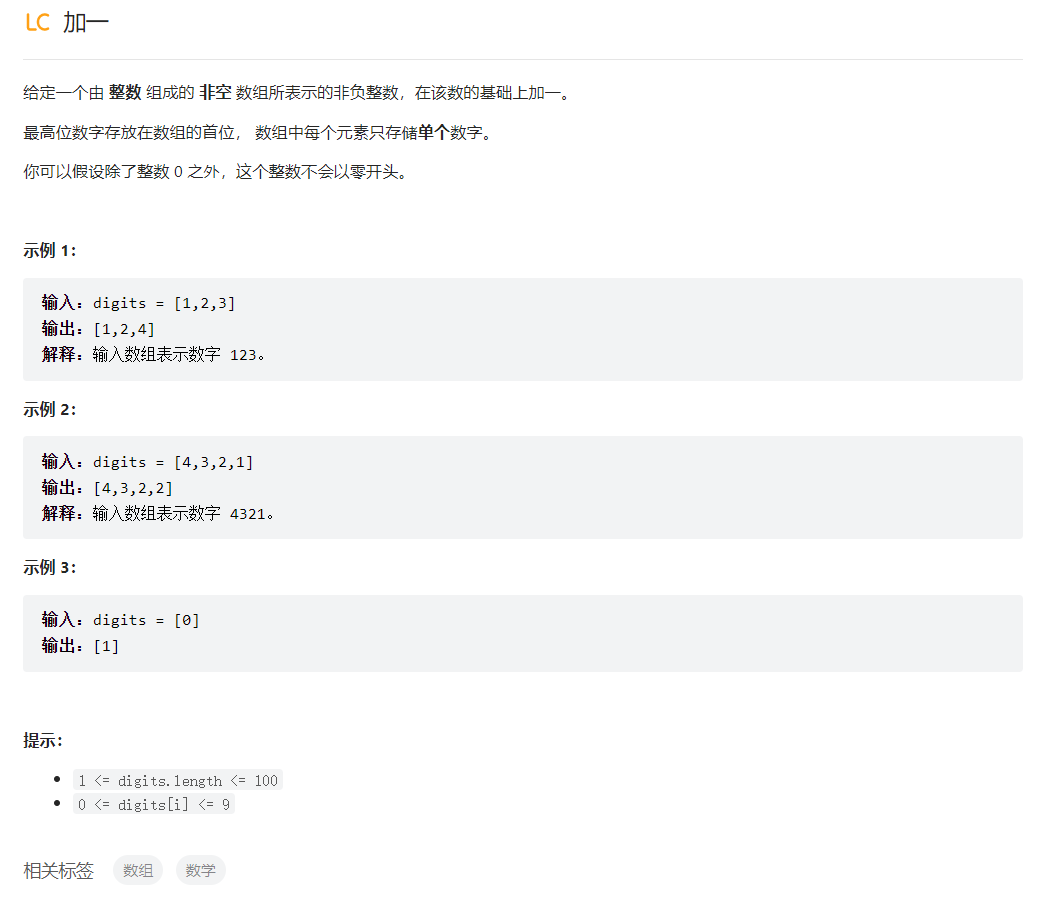
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {
int size=digits.size();
for(int i=size-1;i>=0;i--){
//如果i执行的的值为9则将该值置为0,否则将该值+1直接返回结果
if(digits[i]!=9){
digits[i]+=1;
return digits;
} else {
digits[i]=0;
}
}
//如果最后一位不是9则执行不到这里
vector<int> result;
//将第1位置为1
result.push_back(1);
//将其余size位置为0
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
result.push_back(0);
}
return result;
}
};

移动零
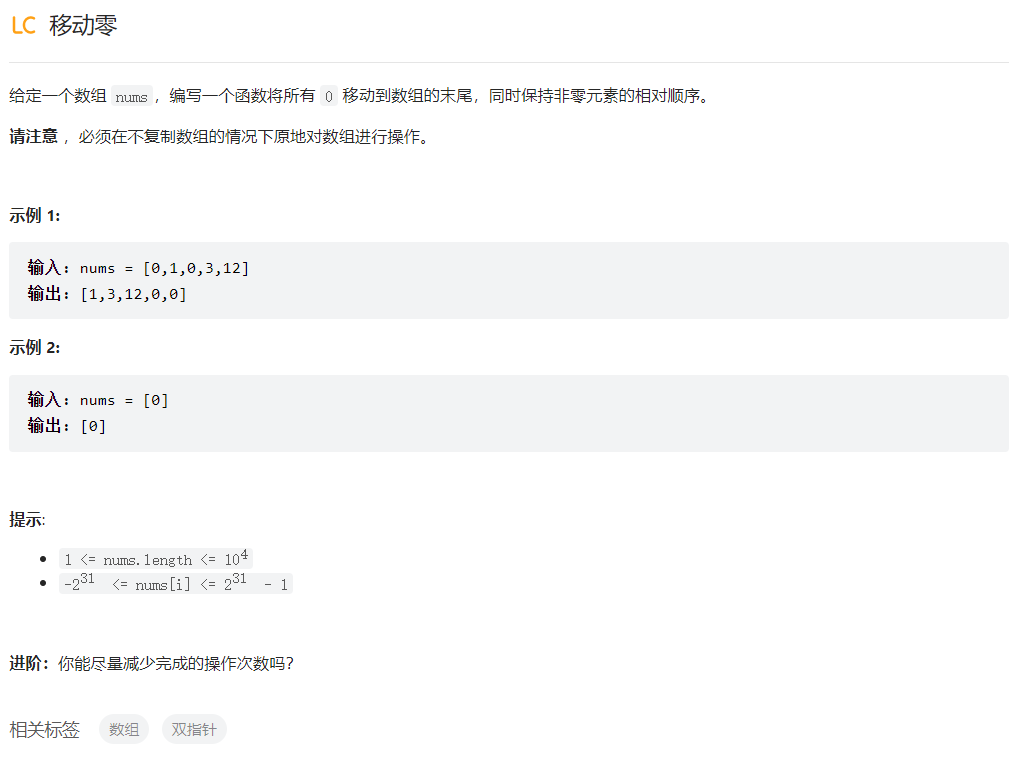
class Solution {
public:
//交换两个数的值
void swap(int &num1,int &num2){
int temp=num1;
num1=num2;
num2=temp;
}
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
//如果数组长度为1则直接结束
if(nums.size()==1){
return;
}
int p1=0,p2=0;//定义双指针并初始化为0
while(p2<nums.size()){
if(nums[p2]!=0){
//当p2指向的值不为0,并且p1不等于p2时,则交换两个数的值
if(p1!=p2){
swap(nums[p1],nums[p2]);
}
//p1向前移动
p1++;
}
//p2向前移动
p2++;
}
}
};

两数之和
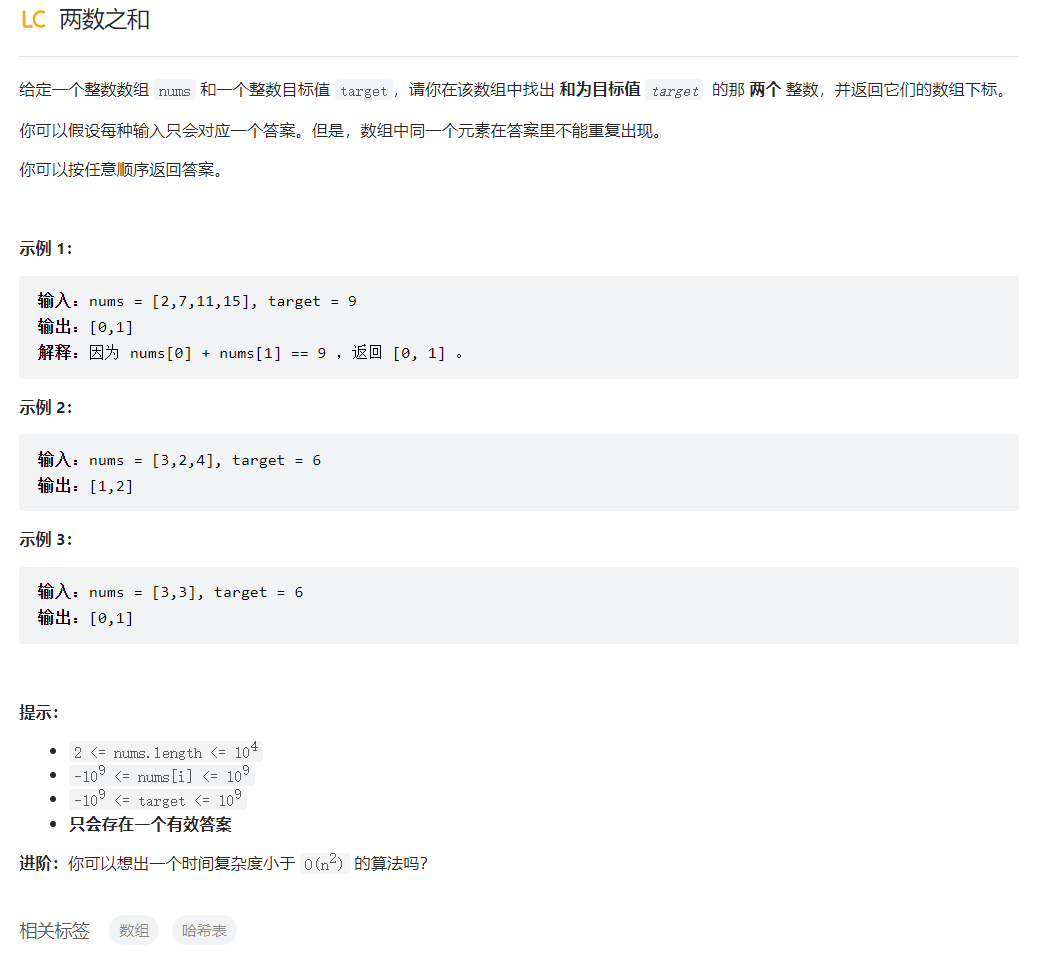
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int,int> temp;//定义一个map
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
//如果map中存在target-nums[i]的键值对,则返回结果;否则将{nums[i],i}添加到map中
unordered_map<int,int>::iterator iter=temp.find(target-nums[i]);
if(iter!=temp.end()){
return {iter->second,i};
}
pair<int,int> pair(nums[i],i);
temp.insert(pair);
}
return {0,0};
}
};

有效的数独

class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int row[9]={0},col[9]={0},cell[9]={0};//分别代表行、列、单元格
int shift;//用于记录位运算后的结果
for(int i=0;i<board.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<board[i].size();j++){
if(board[i][j]=='.'){
//如果当前字符为 . 则直接跳过
continue;
}
shift=1<<(board[i][j]-'0');
//k表示当前位于第几个单元格内
int k=(i/3)*3+j/3;
//当row[i]&shift>0或者col[j]&shift>0或者cell[k]&shift>0时,表示该值在行内或者列内或者单元格内冲突,直接返回false
if((row[i]&shift)>0 || (col[j]&shift)>0 || (cell[k]&shift)>0){
return false;
}
//将row[i]、col[j]、cell[k]与shift相与
row[i]|=shift;
col[j]|=shift;
cell[k]|=shift;
}
}
return true;
}
};

旋转图像
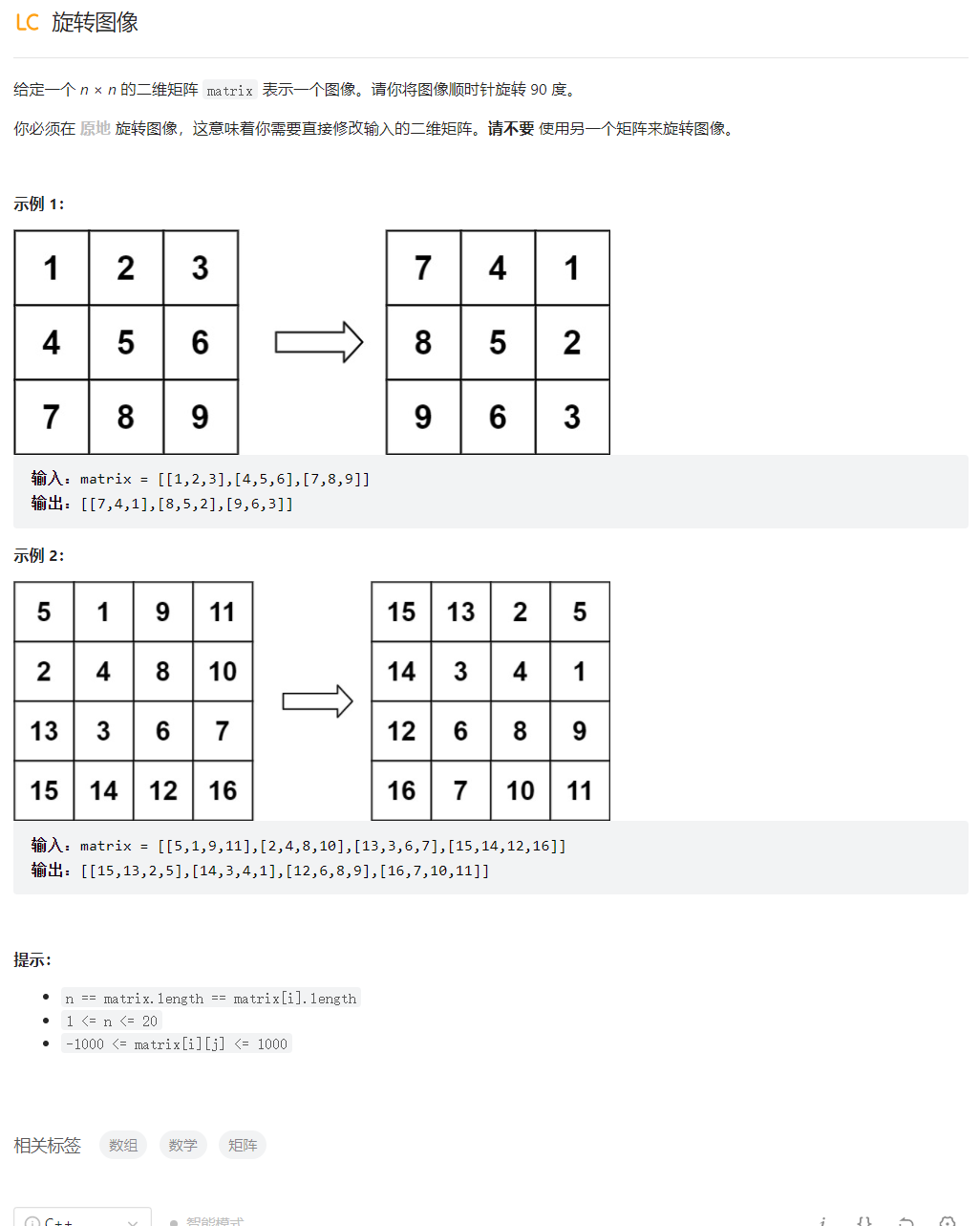
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int size=matrix.size();
//上下交换
for(int i=0;i<size/2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<matrix[i].size();j++){
swap(matrix[i][j],matrix[size-i-1][j]);
}
}
//对角线交换
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<size;j++){
swap(matrix[i][j],matrix[j][i]);
}
}
}
};


反转字符串
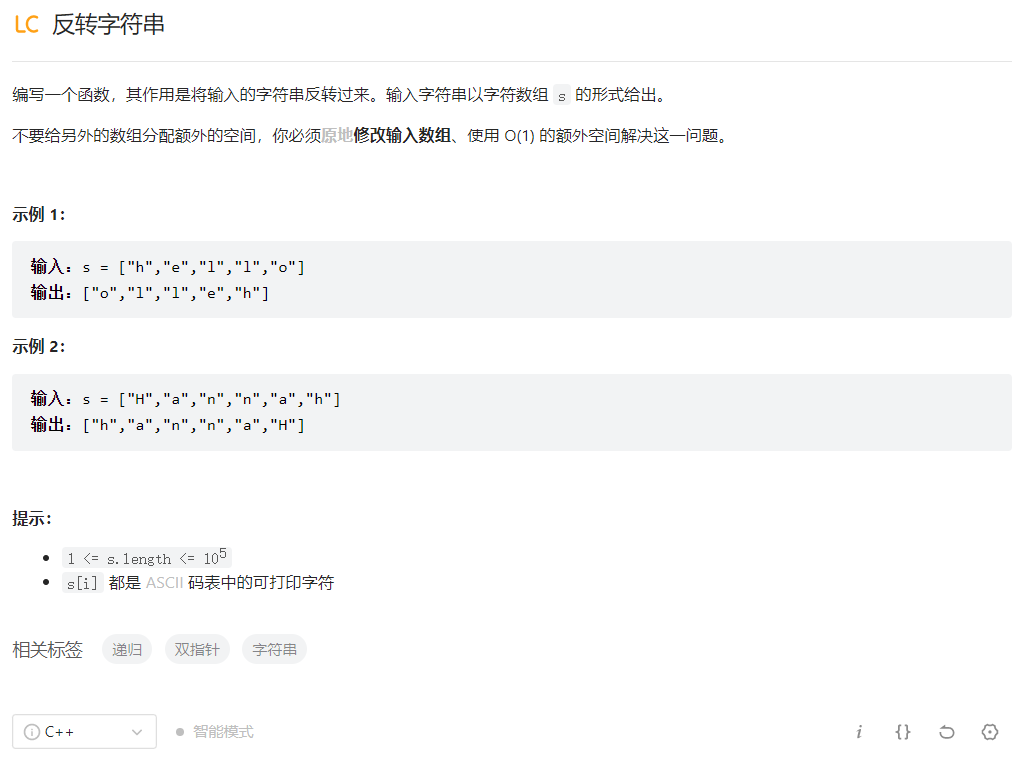
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
int left=0,right=s.size()-1;//定义双指针
while(left<right){
//交换首尾指针指向的值
swap(s[left],s[right]);
left++;//左指针向前移动
right--;//右指针向后移动
}
}
};

整数反转
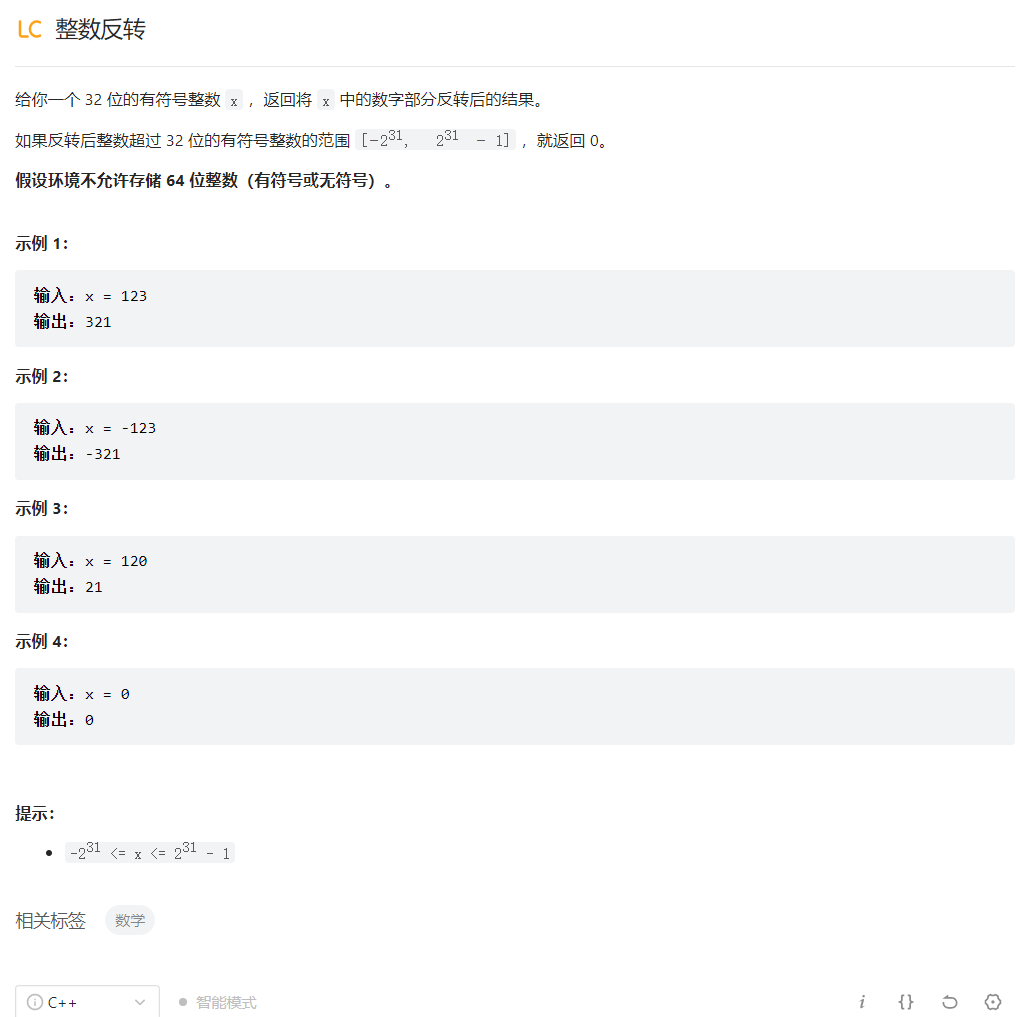
class Solution {
public:
int reverse(int x) {
long res=0;//定义返回的结果
while(x!=0){
int one=x%10;//取当前数的个位数字
res=res*10+one;//将结果*10+个位
x/=10;//当前数除以10
}
return (int)res==res?(int)res:0;//如果超出范围则强转后与返回结果不等,返回0;否则返回原结果
}
};

字符串中的第一个唯一字符
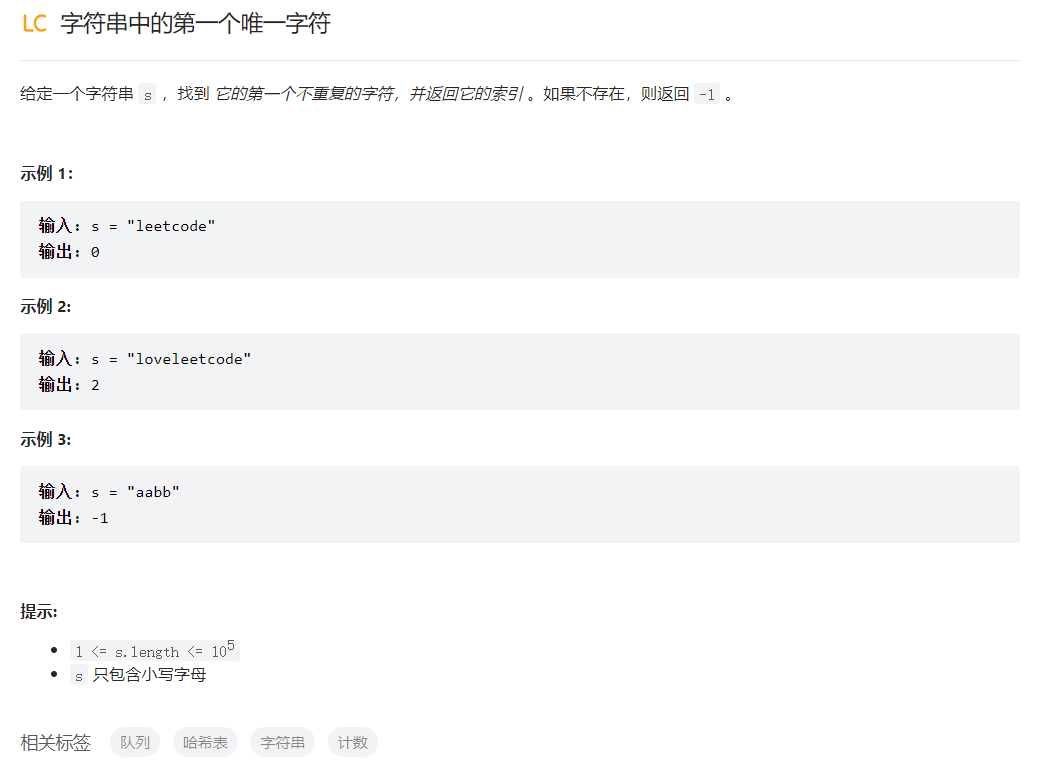
class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s) {
int count[26]={0};
for(auto c:s){
count[c-'a']++;
}
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(count[s[i]-'a']==1){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};

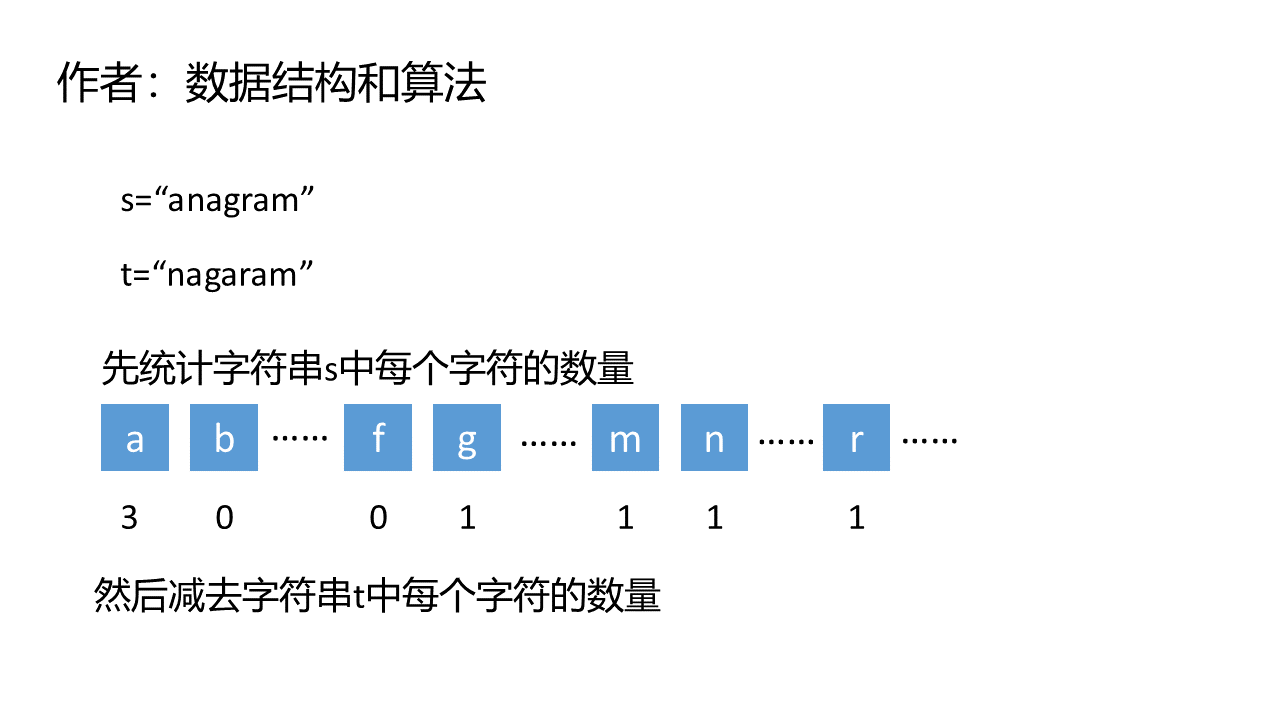
有效的字母异位词
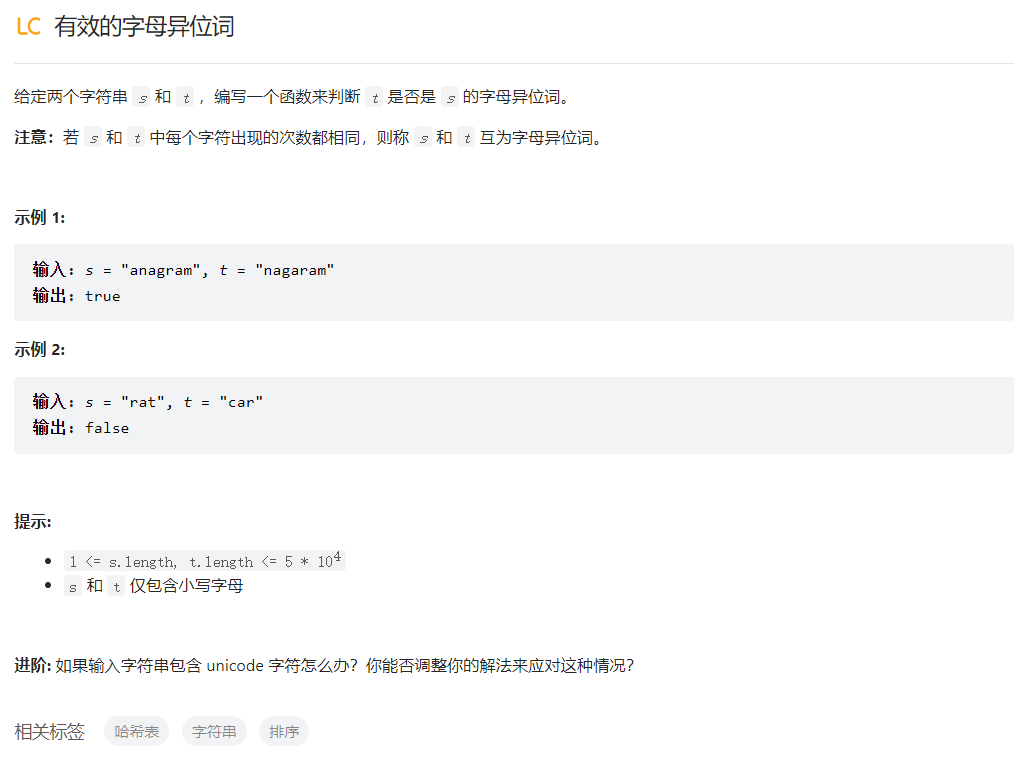
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
if(s.length()!=t.length()){
return false;
}
int letterCount[26]={0};
for(auto c:s){
letterCount[c-'a']++;
}
for(auto c:t){
letterCount[c-'a']--;
}
for(auto count:letterCount){
if(count!=0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};

验证回文串
class Solution {
public:
//判断该字符是否是字母或者是数字
bool isLetterOrDigit(char c){
if((c>=48&&c<=57)||(c>=65&&c<=90)||(c>=97&&c<=122)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//将字符转换为小写并返回
char toLower(char c){
if(c>=65 && c<=90){
return c+32;
}
return c;
}
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int left=0,right=s.length()-1;//定义双指针,分别指向第一个字符和最后一个字符
while(left<right){
if(!isLetterOrDigit(s[left])){
//如果左指针指向的字符不是字母或数字则左指针向右移动一位
left++;
continue;
}
if(!isLetterOrDigit(s[right])){
//如果有指针指向的字符不是字母或数字则右指针向左移动一位
right--;
continue;
}
//如果左指针和有指针指向的字符不相等则直接返回false
if(toLower(s[left]) != toLower(s[right])){
return false;
}
//如果左指针和有指针指向的字符相等则左指针向右移动一位,右指针向左移动一位
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
};

字符串转换整数

class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
const int MAX=2147483647;//定义最大值。即2^31-1
const int MIN=-2147483648;//定义最小值。即-2^31
bool flag = true;//是否已识别到有效字符。即是否已经识别到数字或正负号。true表示没有识别到,false表示识别到
int op=1;//数字的符号,判断结果是正数还是负数
long result=0;//返回的结果
for(auto c:s){
if(flag && c==' ')
continue;
if(c>='0' && c<='9'){
flag=false;
}
if(flag && c=='-'){
op=-1;
flag=false;
continue;
}
if(flag && c=='+'){
flag=false;
continue;
}
if(c<'0' || c>'9')
break;
result=result*10+(c-'0');
if(result>MAX){
return op==1?MAX:MIN;
}
}
return (int)result*op;
}
};

实现 strStr()

class Solution {
public:
/**
* 本题是一道经典的KMP算法题,能力有限,示例代码使用的是较容易理解的滑动窗口解决的
*/
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
if(needle.length()==0){
return 0;
}
int l1=haystack.length(),l2=needle.length();
bool match;
for(int i=0;i<l1-l2+1;i++){
match=true;
for(int j=0;j<l2;j++){
if(haystack[j+i]!=needle[j]){
match=false;
break;
}
}
if(match){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};

外观数列

class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
if(n==1){
return "1";
}
string temp=countAndSay(n-1);
string result="";
int count=0;
char c=temp[0];
for(int i=0;i<temp.length();i++){
if(temp[i]==c){
count++;
}
else{
result+=to_string(count)+c;
count=1;
c=temp[i];
}
}
result+=to_string(count)+c;
return result;
}
};
解题思路
- 先确立递归出口 n = 1时 为1
- 对上一个结果进行遍历获取值
- 设定计数器,计算同一个数字出现的次数
- 如果数字相同,计数器加一
- 若当前不满足,则将上次的值记录下,并重置计数器,重置需要判断是否重复的字符
- 将最后的结果也追加到字符串上

最长公共前缀
class Solution {
public:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
int minLength=200;//strs中最短字符串的长度
for(auto s:strs){
minLength=minLength<s.length()?minLength:s.length();
}
string prefix="";
//最长公共前缀最长为minLength,所以只需要遍历每个字符串前minLength个字符是否相等
for(int i=0;i<minLength;i++){
for(int j=0;j<strs.size()-1;j++){
if(strs[j][i]!=strs[j+1][i])
return prefix;
}
prefix+=strs[0][i];
}
return prefix;
}
};

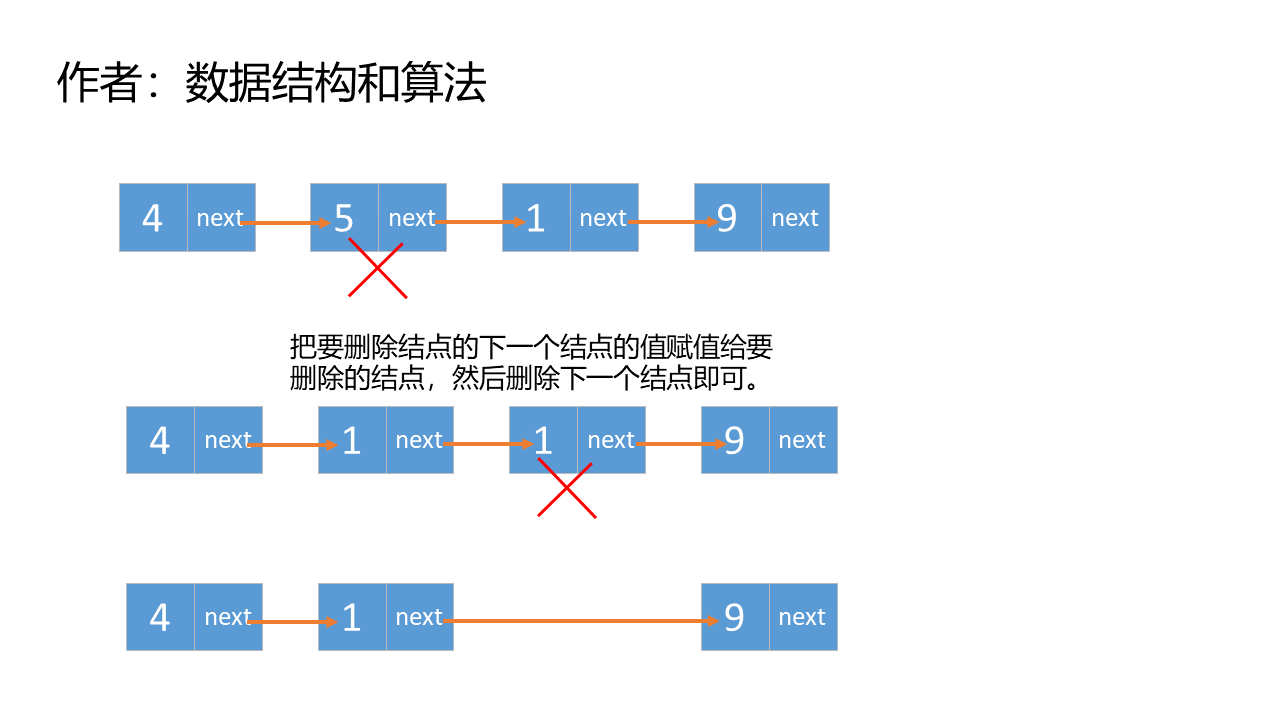
删除链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val=node->next->val;
node->next=node->next->next;
}
};
解题思路

删除链表的倒数第N个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *rHead=new ListNode(0,head);//定义一个假的头结点指向头结点
ListNode *fast=rHead,*slow=rHead;//定义快慢指针
while(n>0){
//将块指针向右移动n
fast=fast->next;
n--;
}
if(n==1){
//如果n=1,则表示删除的是最后一个,直接将慢指针的next置为nullptr即可,返回假的头结点的next
slow->next= nullptr;
return rHead->next;
}
while(fast->next!= nullptr){
//将快慢指针同时向右移动,直至快指针移到最后一个节点
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
//将slow的next指针指向slow的next->next节点
slow->next=slow->next->next;
//返回假的头结点的next即可
return rHead->next;
}
};

反转链表
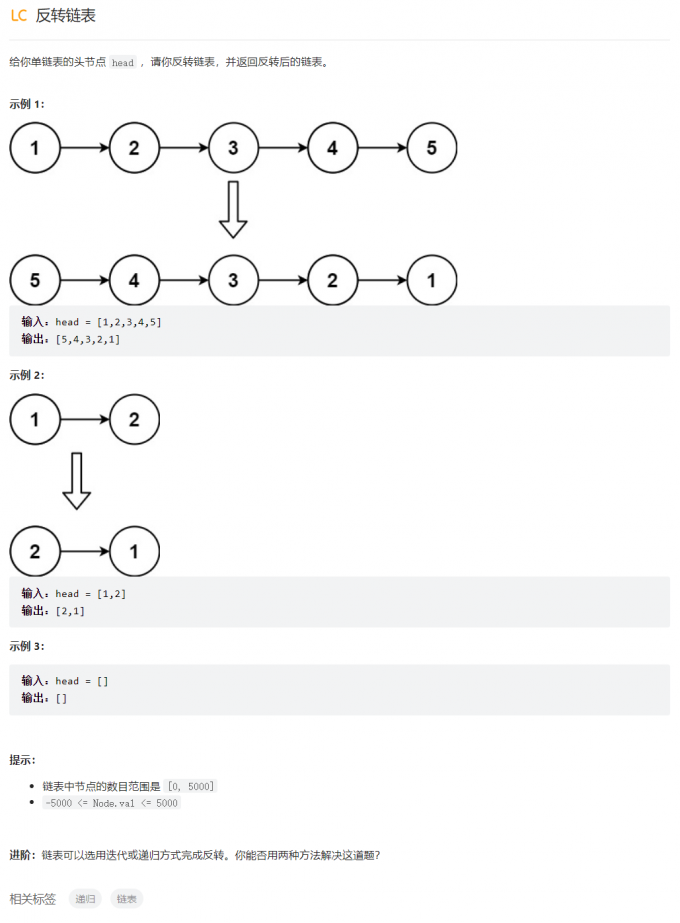
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 使用递归解决
*/
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
//如果是空链表或者节点的next为nullptr则直接返回head
if(head==NULL || head->next== nullptr){
return head;
}
//递归调用
ListNode *reverse=reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next=head;
head->next= nullptr;
return reverse;
}
};

合并两个有序链表
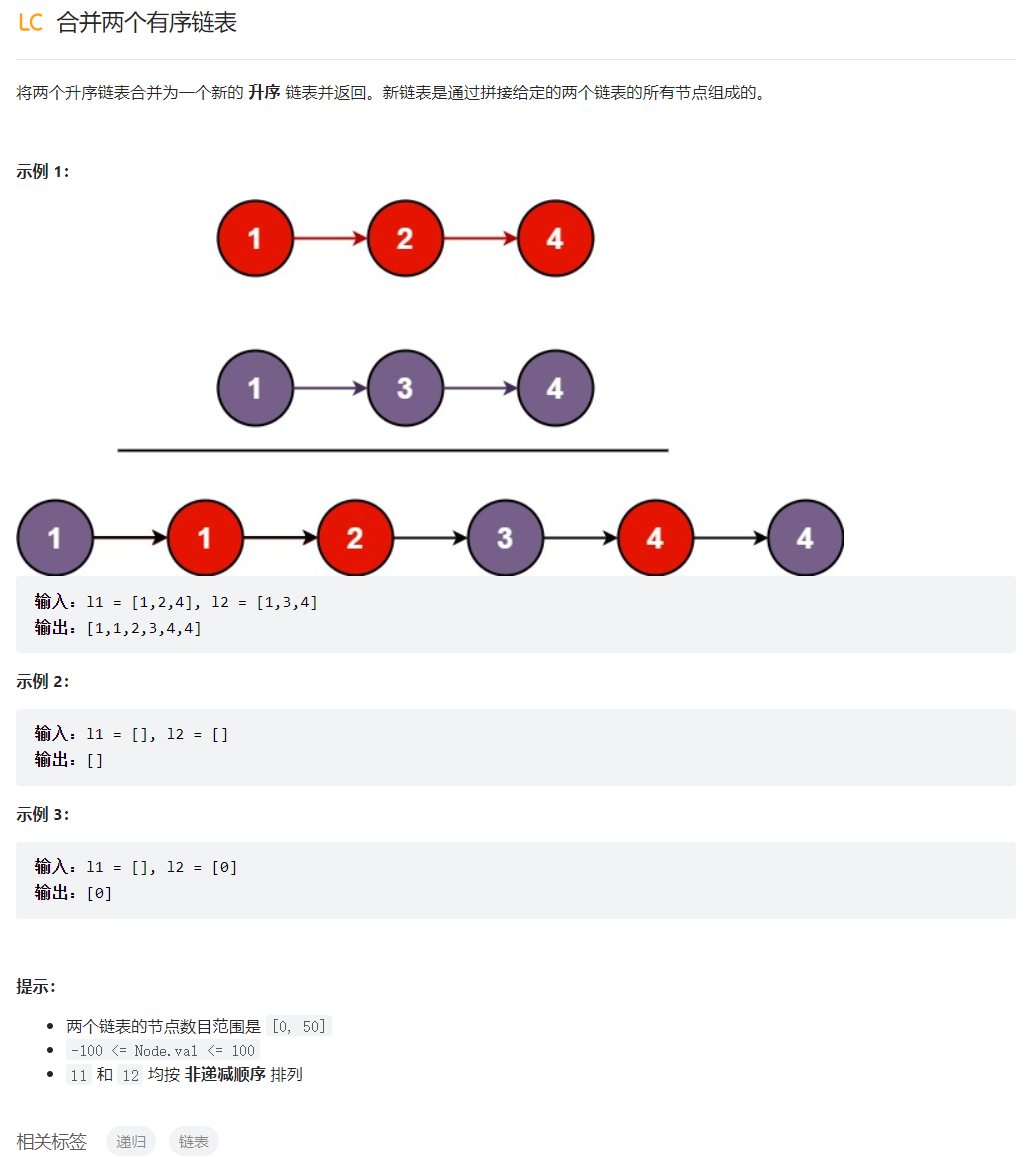
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 本题使用递归解决
*/
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
//如果list1是空链表则返回list2;如果list2是空链表则返回list1
if(list1==NULL || list2==NULL){
return list1==NULL?list2:list1;
}
ListNode *head=(list1->val <= list2->val)?list1:list2;
head->next=mergeTwoLists(head->next,head==list1?list2:list1);
return head;
}
};

回文链表

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
//与上面的反转链表算法一样
ListNode * reverseList(ListNode *head){
if(head == NULL || head->next == nullptr){
return head;
}
ListNode *reverse=reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next=head;
head->next= nullptr;
return reverse;
}
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head;
if(head->next == nullptr){
return head;
}
while(fast->next!=nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
slow=reverseList(slow->next);
fast=head;
while(slow!= nullptr){
if(slow->val!=fast->val)
return false;
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return true;
}
};
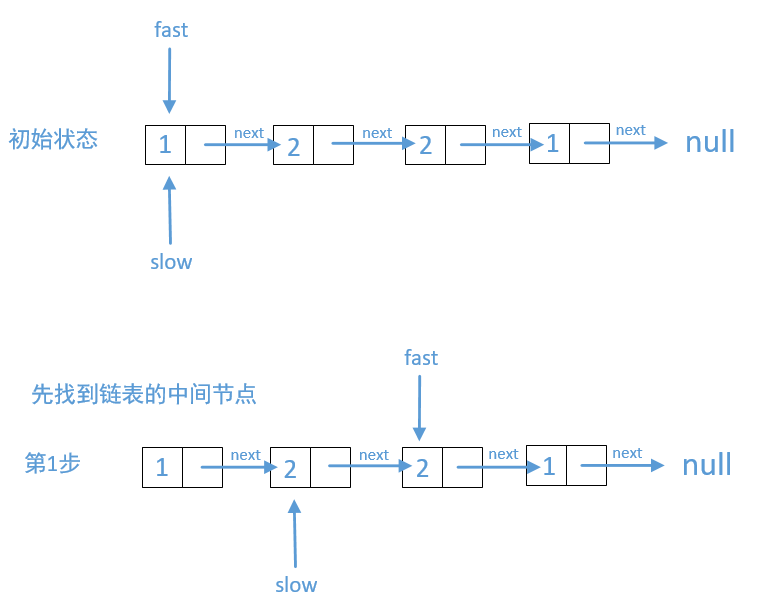
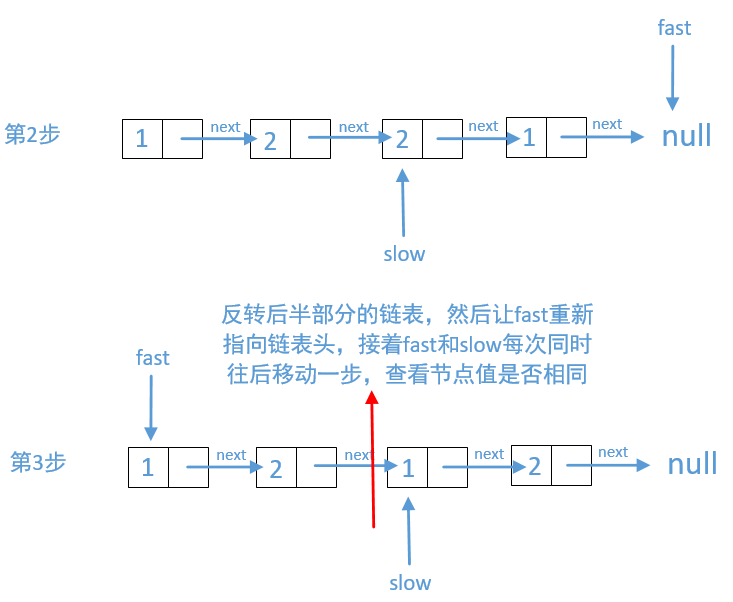

环形链表
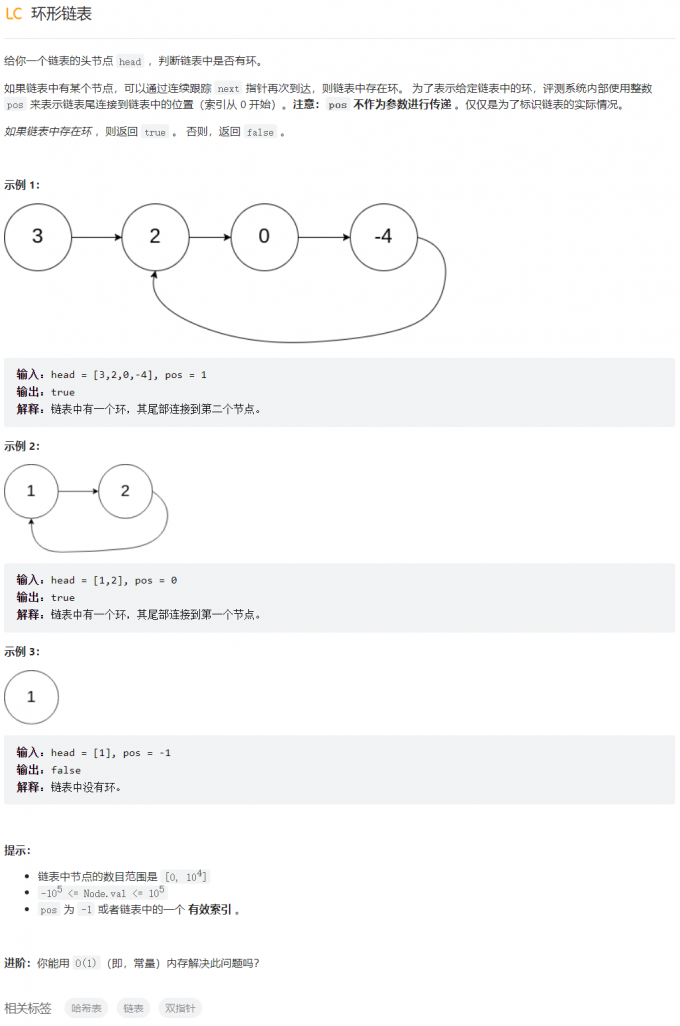
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head==NULL || head->next== nullptr){
return false;
}
ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head;
while(fast->next!= nullptr && fast->next->next!= nullptr){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};

二叉树的最大深度
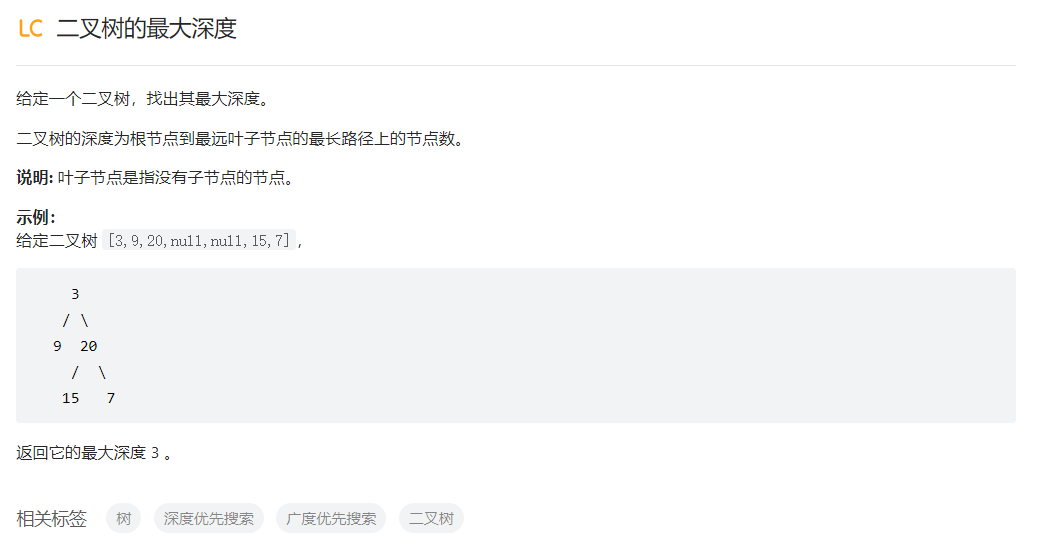
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL){
return 0;
}
return max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}
};

验证二叉搜索树
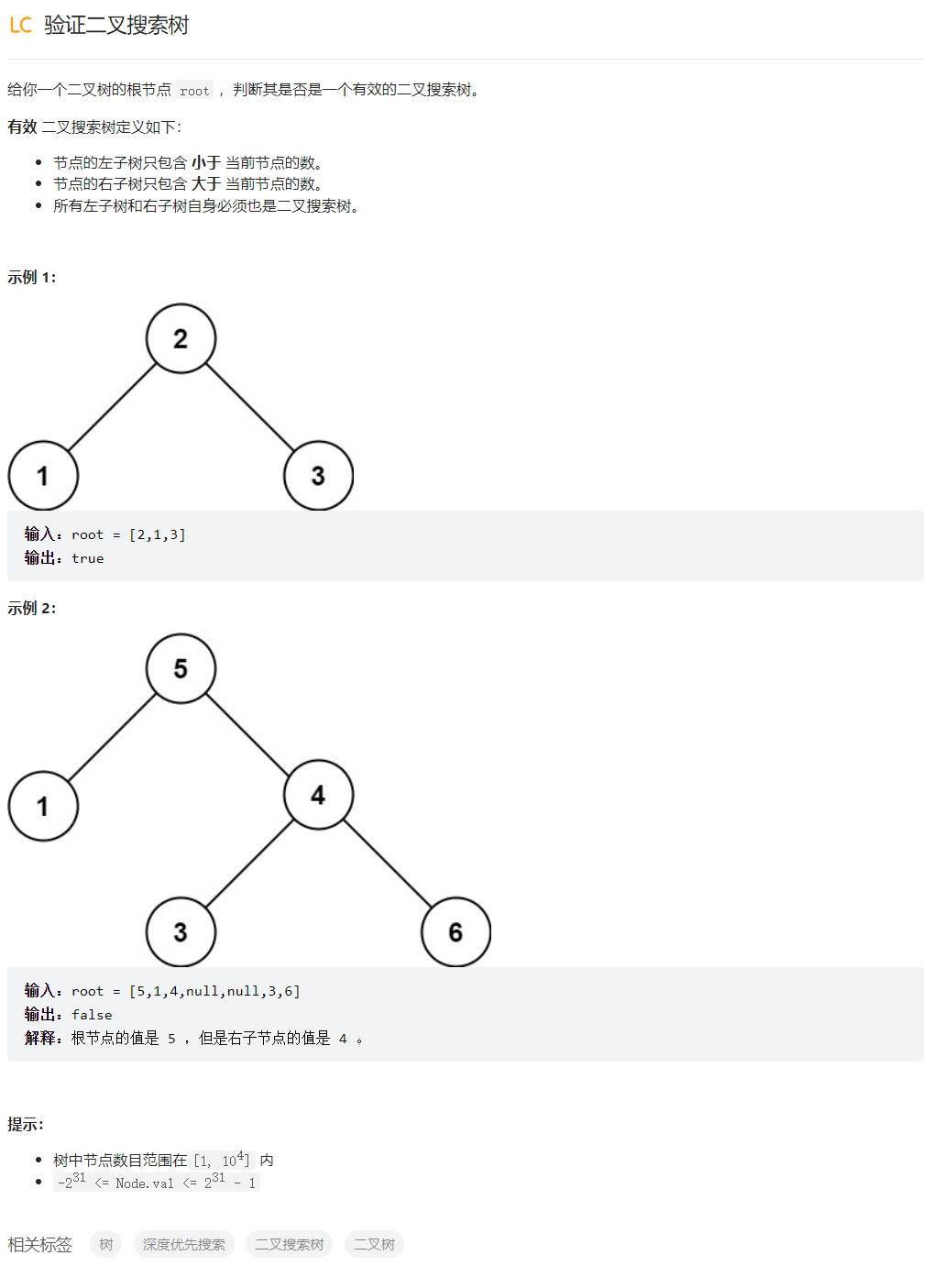
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode *root,long minVal,long maxVal){
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->val<=minVal || root->val>=maxVal)
return false;
return isValidBST(root->left,minVal,root->val) && isValidBST(root->right,root->val,maxVal);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return isValidBST(root,LONG_MIN,LONG_MAX);
}
};
解题思路
做这题之前我们首先要明白什么是二叉搜索树,就是每个节点左子树的值都比当前节点小,右子树的值都比当前节点大。所以看到这里我们最先想到的就是递归,我最先想到的是下面这种写法(注意是错误的)
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return true;
if (root.left != null && root.val <= root.left.val || root.right != null && root.val >= root.right.val)
return false;
return isValidBST(root.left) && isValidBST(root.right);
}
如果一个结点是空的,我们默认他是有效的二叉搜索树。
否则如果左节点不为空,我们要判断是否大于左节点的值。
如果右节点不为空,我们还要判断小于右节点的值。
然后我们再以左右两个子节点用相同的方式判断。看起来好像没什么问题,但我们好像忽略了一个每个节点的上限和下限,比如下面这棵树
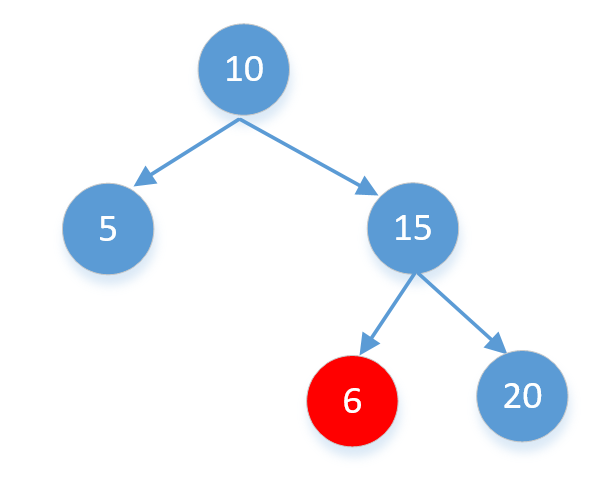
注意6这个节点不光要小于15而且还要大于10,所以这里的每一个节点都是有一个范围的,上面的代码我只判断了6比15小,但没有和10进行比较,所以代码是错误的。这里我们来给每个节点添加一个范围,如果不在这个范围之内直接返回false,比如6的范围是(10,15),很明显他不在这个范围内,所以他不是二叉搜索树。根节点的范围我们从Long.MIN_VALUE到Long.MAX_VALUE。

对称二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetricHelper(TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right){
//如果left和right都是NULL则直接返回true
if(left==NULL && right==NULL)
return true;
//如果left或right其中一个为NULL或者left的值与right的值不等则直接返回false
if(left==NULL || right==NULL || left->val!=right->val)
return false;
return isSymmetricHelper(left->left,right->right) && isSymmetricHelper(left->right,right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return isSymmetricHelper(root->left,root->right);
}
};

二叉树的层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root==NULL){
return result;
}
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while (!queue.empty()){
vector<int> row;
int num=queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
TreeNode *node=queue.front();
row.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left!= nullptr){
queue.push(node->left);
}
if(node->right!= nullptr){
queue.push(node->right);
}
queue.pop();
}
result.push_back(row);
}
return result;
}
};

将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){
if(start>end){
return nullptr;
}
int mid=(start+end)>>1;
TreeNode *root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left=sortedArrayToBST(nums,start,mid-1);
root->right=sortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1,end);
return root;
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
return sortedArrayToBST(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
}
};
解题思路
题中说了要转换为一棵高度平衡的二叉搜索树,并且数组又是排过序的,这就好办了,我们可以使用递归的方式,每次取数组中间的值比如m作为当前节点,m前面的值作为他左子树的结点值,m后面的值作为他右子树的节点值,示例中一个可能的结果是
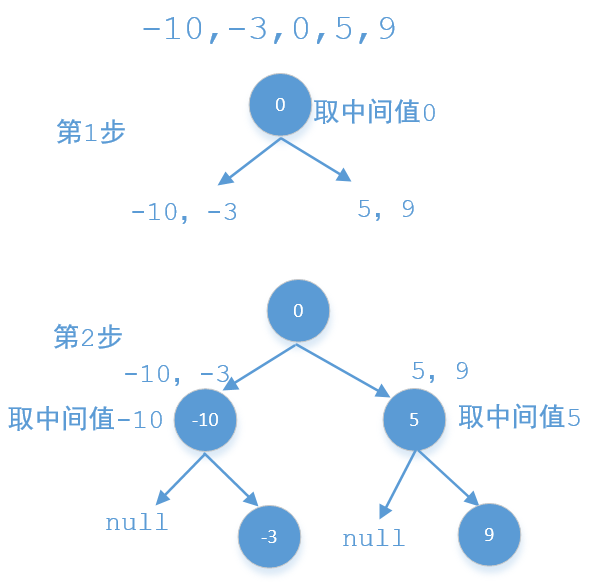

合并两个有序数组

class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {
int p1=0,p2=0;//定义双指针
while(p1<m && p2<n){
if(nums2[p2]<nums1[p1]){
//如果p2指针指向的值小于p1指向的值,则p1后面的值全部向右移动一位
for(int i=m-1;i>=p1;i--){
nums1[i+1]=nums1[i];
}
//将p2指向的值插入到p1指向的位置
nums1[p1]=nums2[p2];
//m表示当前nums1数组的长度
m++;
//p2指针向右移动一位
p2++;
}
//p1指针向右移动一位
p1++;
}
//如果p2指针没有指向nums2的末尾,则将其剩余的值添加到p1指针的后面
if(p2<n){
for(int i=p1;i<nums1.size();i++){
nums1[i]=nums2[p2];
p2++;
}
}
}
};

第一个错误的版本
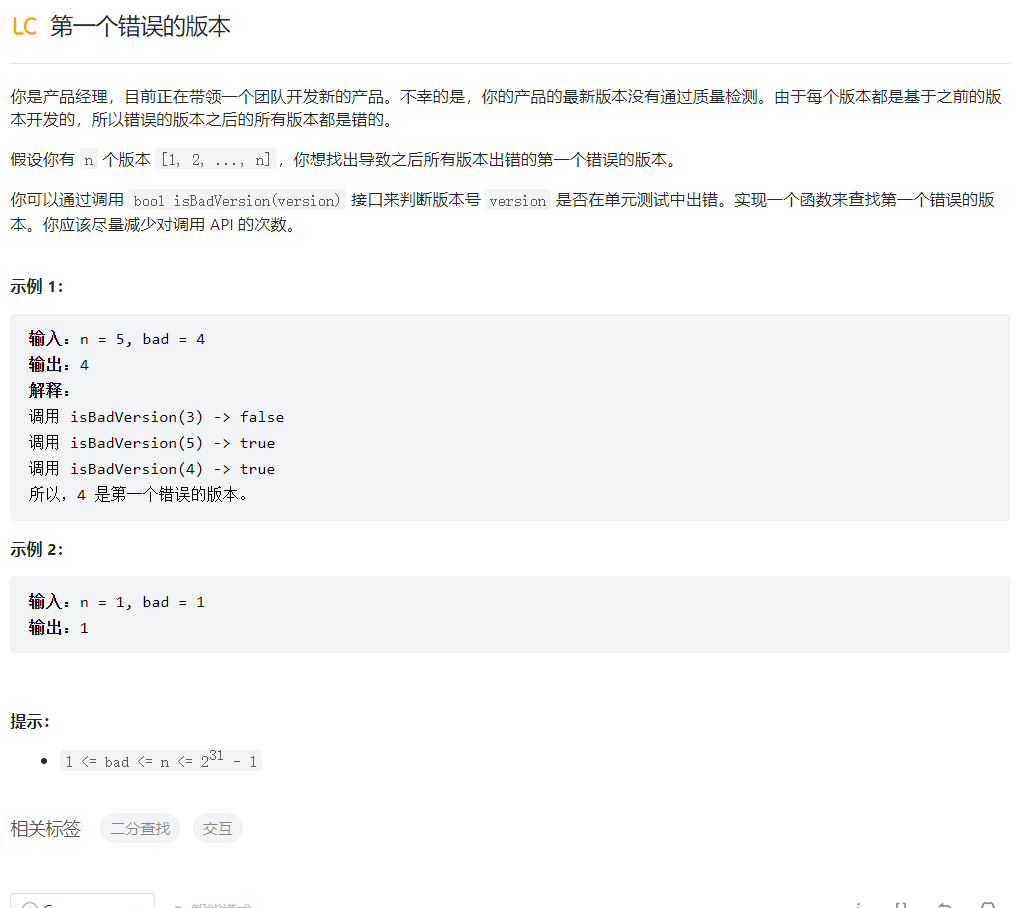
// The API isBadVersion is defined for you.
// bool isBadVersion(int version);
class Solution {
public:
int firstBadVersion(int n) {
int start=1,end=n;
int minBad=n;
while(start<=end){
//使用 mid=(start+end)/2 会超出int范围,所以使用这种去中间值的方法
int mid=start+(end-start)/2;
bool isBad=isBadVersion(mid);
if(isBad){
minBad=min(minBad,mid);
end=mid-1;
}
else {
start=mid+1;
}
}
return minBad;
}
};

爬楼梯

class Solution {
public:
//n阶楼梯的方法数与斐波那契数列相对应,所以本题只需要构建一个斐波那契数列即可
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<4){
return n;
}
int *arr=new int[n+1]{0};
arr[1]=1;
arr[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<n+1;i++){
arr[i]=arr[i-1]+arr[i-2];
}
return arr[n];
}
};

买卖股票的最佳时机

class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int p1=0,p2=1;
int maxProfit=0;
while(p2<prices.size()){
if(prices[p2]<prices[p1]){
p1=p2;
}
if(prices[p2]-prices[p1]>maxProfit){
maxProfit=prices[p2]-prices[p1];
}
p2++;
}
return maxProfit;
}
};
解题思路
我们还可以使用两个指针,一个指针记录访问过的最小值(注意这里是访问过的最小值),一个指针一直往后走,然后计算他们的差值,保存最大的即可,这里就以示例1为例来画个图看下
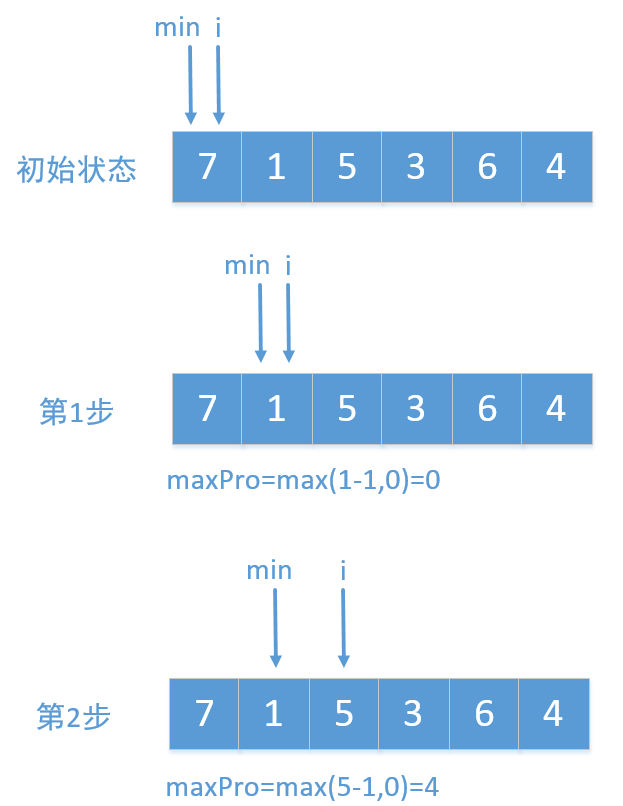
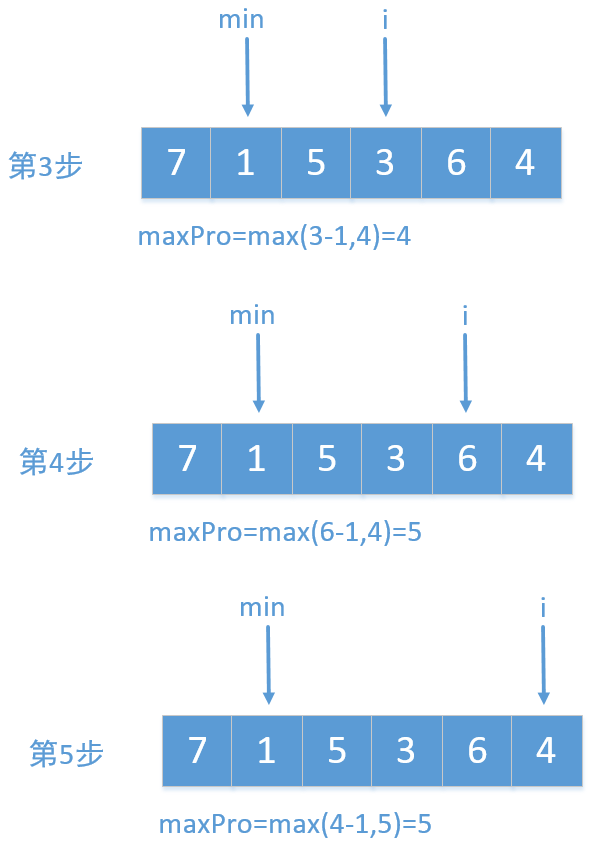

最大子序和
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int cur=nums[0];
int max=cur;
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
cur=std::max(cur,0)+nums[i];
max=std::max(max,cur);
}
return max;
}
};
解题思路
1,动态规划解决
这题是让求最大的连续子序和,如果不是连续的非常简单,只需要把所有的正数相加即可。但这里说的是连续的,中间可能掺杂负数,如果求出一个最大子序和在加上负数肯定要比原来小了。解这题最简单的一种方式就是使用动态规划。
我们先来了解一下动态规划的几个步骤
1,确定状态
2,找到转移公式
3,确定初始条件以及边界条件
4,计算结果。
最后一个不用看,只看前3个就行,因为前3个一旦确定,最后一个结果也就出来了。我们试着找一下
1,定义dp[i]表示数组中前i+1(注意这里的i是从0开始的)个元素构成的连续子数组的最大和。
2,如果要计算前i+1个元素构成的连续子数组的最大和,也就是计算dp[i],只需要判断dp[i-1]是大于0还是小于0。如果dp[i-1]大于0,就继续累加,dp[i]=dp[i-1]+num[i]。如果dp[i-1]小于0,我们直接把前面的舍弃,也就是说重新开始计算,否则会越加越小的,直接让dp[i]=num[i]。所以转移公式如下
dp[i]=num[i]+max(dp[i-1],0);
3,边界条件判断,当i等于0的时候,也就是前1个元素,他能构成的最大和也就是他自己,所以
dp[0]=num[0];

打家劫舍

class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int noSteal=0;//没偷第一家
int steal=nums[0];//偷了第一家
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
int temp=std::max(noSteal,steal);
//将上一家没偷和偷了的值进行比较,取较大值
//max(noSteal,steal)表示当前这一家没有偷,则上一家偷没偷都可以,取较大值
//noSteal+nums[i]表示当前这一家被偷了,则上一家必定没有被偷
steal=noSteal+nums[i];
noSteal=temp;
}
return max(noSteal,steal);
}
};
1,动态规划解决
数组中的值表示的是存放的金额,小偷可以选择偷和不偷,如果前一个偷了,那么下一个肯定是不能偷的,因为相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。如果上一个没偷,那么下一个可以选择偷也可以选择不偷,视情况而定。
这里可以定义一个二维数组dp[length][2],其中dp[i][0]表示第i+1(因为数组下标是从0开始的,所以这里是i+1)家偷了的最大总金额,dp[i][1]表示的是第i+1家没偷的最大总金额。那么我们找出递推公式
1,dp[i][0]=max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1])
他表示如果第i+1家没偷,那么第i家有没有偷都是可以的,我们取最大值即可。
2,dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][0]+nums[i]
他表示的是如果第i+1家偷了,那么第i家必须没偷,这里nums[i]表示的是第i+1家偷的金额。
递推公式找出来之后我们再来看下边界条件,第一家可以选择偷,也可以选择不偷,所以
dp[0][0]=0,第一家没偷
dp[0][1]=nums[0],第一家偷了

打乱数组
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> v;
public:
Solution(vector<int>& nums) {
v=nums;
}
vector<int> reset() {
return v;
}
vector<int> shuffle() {
int size=v.size();
vector<int> arr(v);
for(int i=1;i<size;i++){
swap(arr[i],arr[rand()%(i+1)]);
}
return arr;
}
};
/**
* Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Solution* obj = new Solution(nums);
* vector<int> param_1 = obj->reset();
* vector<int> param_2 = obj->shuffle();
*/

最小栈
class MinStack {
private:
stack<long> stack;
vector<long> minValue;
int index;
public:
MinStack() {
index=0;
}
void push(long val) {
if(index==0){
minValue.push_back(val);
}
else{
minValue.push_back(min(val,minValue[index-1]));
}
index++;
stack.push(val);
}
void pop() {
index--;
minValue.pop_back();
stack.pop();
}
int top() {
return stack.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minValue[index-1];
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(val);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/
Fizz Buzz
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> fizzBuzz(int n) {
vector<string> res;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i%15==0){
res.push_back("FizzBuzz");
}
else if(i%3==0){
res.push_back("Fizz");
}
else if(i%5==0){
res.push_back("Buzz");
}
else {
res.push_back(to_string(i));
}
}
return res;
}
};

计数质数
class Solution {
public:
int countPrimes(int n) {
int count=0;
vector<bool> isPrime(n,true);
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
if(isPrime[i-1]){
count++;
for(int j=i*2;j<n;j+=i){
isPrime[j-1]=false;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
解题思路
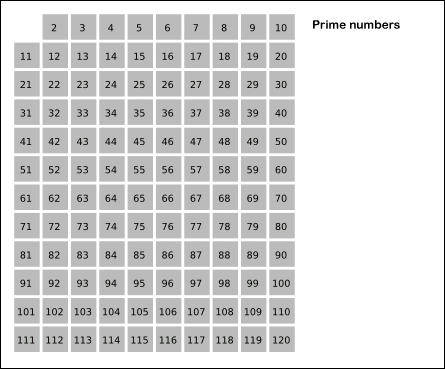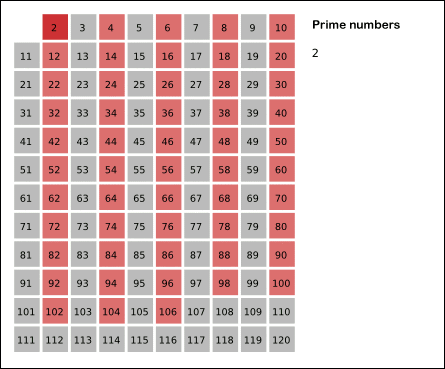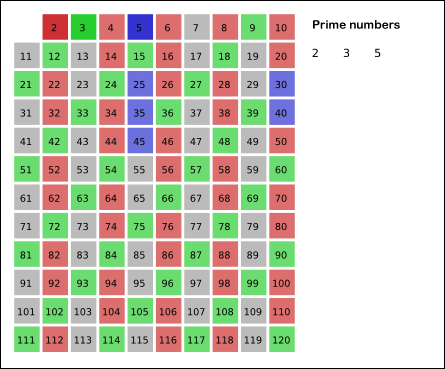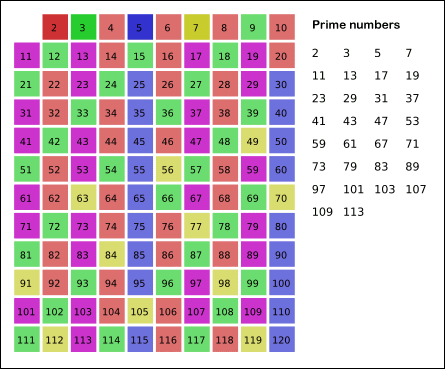
首先,将2到n范围内的所有整数写下来。其中最小的数字2是素数。将表中所有2的倍数都划去。表中剩余的最小数字是3,它不能被更小的数整除,所以是素数。再将表中所有3的倍数全都划去。依次类推,如果表中剩余的最小数字是m时,m就是素数。然后将表中所有m的倍数全部划去。像这样反复操作,就能依次枚举n以内的素数。

3的幂
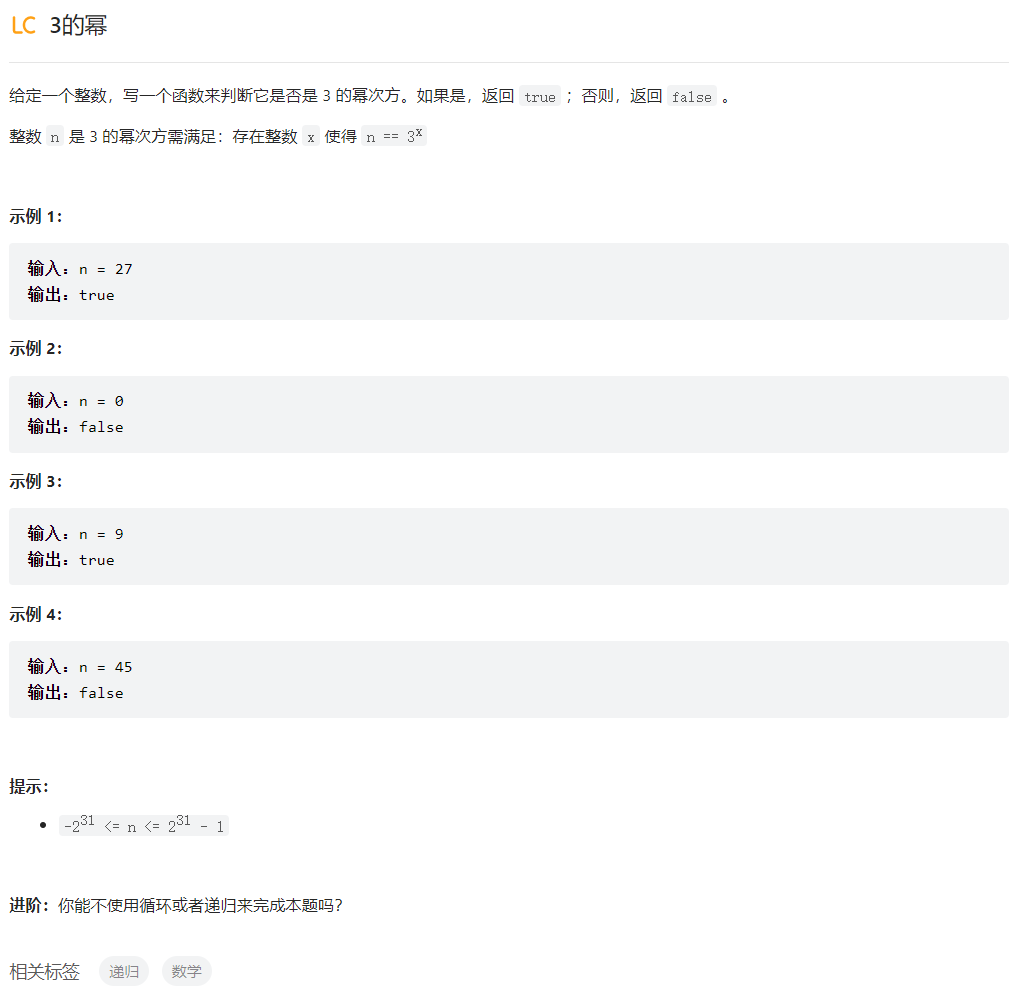
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfThree(int n) {
return n>0 && (n==1 || (n%3==0 && isPowerOfThree(n/3)));
/*题中n的范围是-2^31 <= n <= 2^31 - 1,而在这个范围内3的最大幂是1162261467,在比他大就超过int表示的范围了,我们直接用它对n求余即可,过求余的结果是0,说明n是3的幂次方*/
//return n>0 && 1162261467%n==0;
}
};

罗马数字转整数

class Solution {
public:
int getValue(char c){
switch (c) {
case 'I':
return 1;
case 'V':
return 5;
case 'X':
return 10;
case 'L':
return 50;
case 'C':
return 100;
case 'D':
return 500;
case 'M':
return 1000;
default:
return 0;
}
}
int romanToInt(string s) {
int preVal=getValue(s[0]);
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){
int val=getValue(s[i]);
if(preVal<val){
res-=preVal;
}
else {
res+=preVal;
}
preVal=val;
}
res+=preVal;
return res;
}
};
通常情况下,罗马数字中小的数字在大的数字的右边。也就是说如果小写的在大写的右边,每个字符都是一个有效的数字,他表示的数字就是所有字符相加,比如VI就是5+1=6。
如果小写的在大写的左边,就是无效的,只有一种情况,就是这个小写的和大写的组成一个数字,比如IV表示的是5-1=4。

位1的个数

class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int count=0;
while(n!=0){
if(n%2!=0){
count++;
}
n=n>>1;
}
return count;
}
};

汉明距离
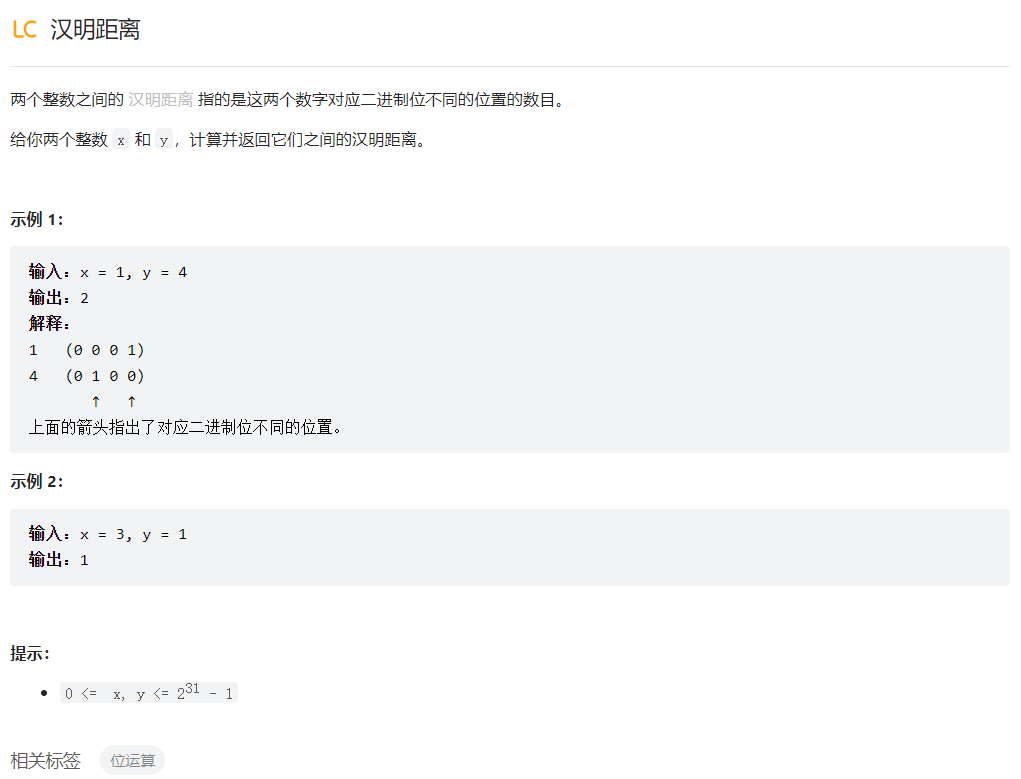
class Solution {
public:
int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int temp=x^y;
int distance=0;
while(temp!=0){
if(temp%2!=0){
distance++;
}
temp>>=1;
}
return distance;
}
};

颠倒二进制位
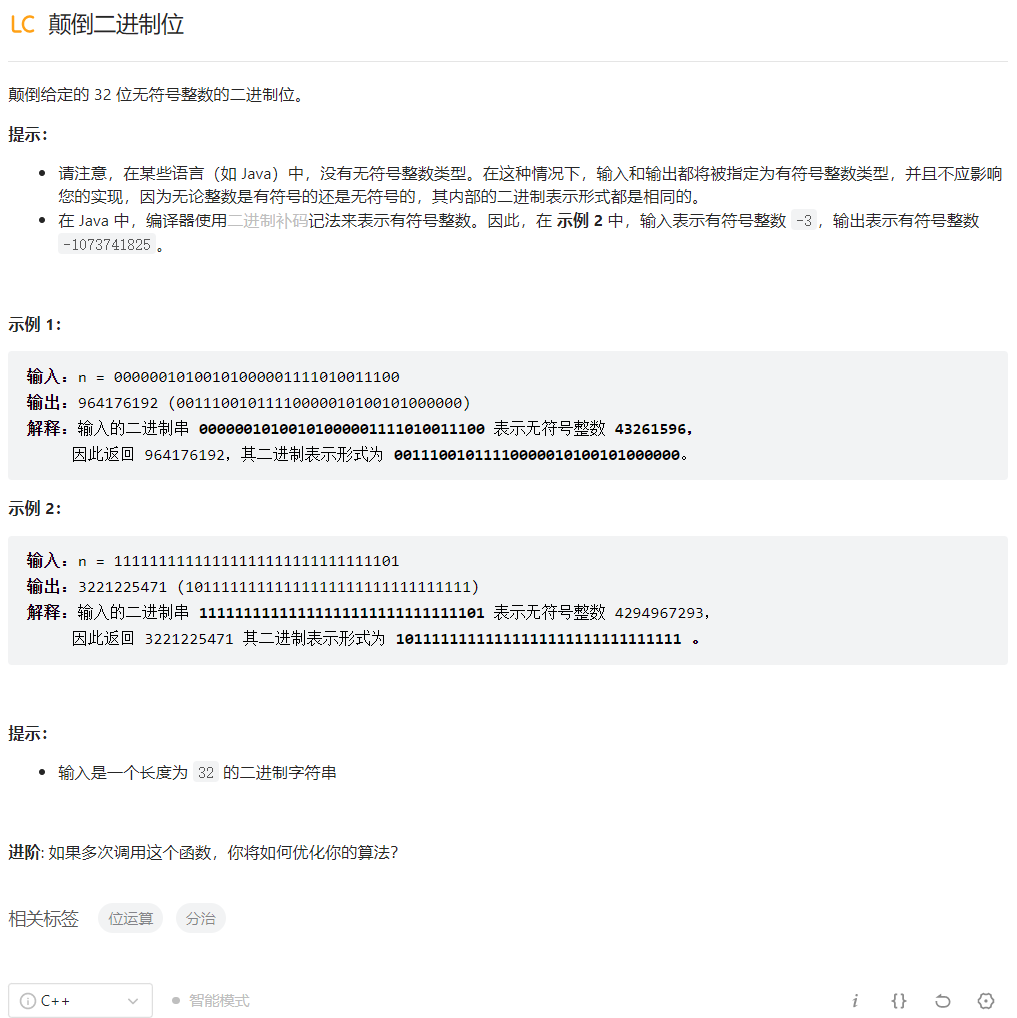
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
int end=n%2;
res<<=1;
res|=end;
n/=2;
}
return res;
}
};

杨辉三角
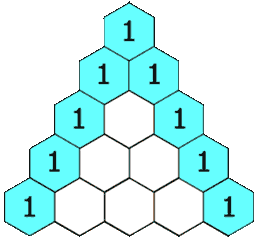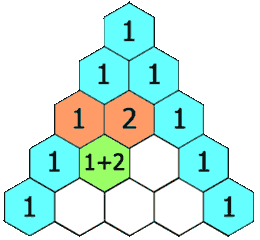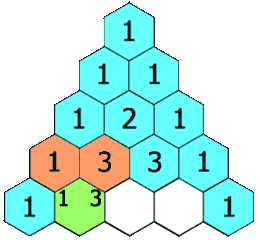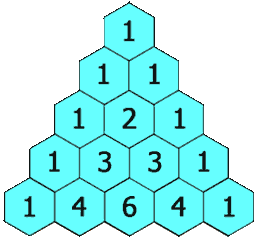
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
for(int i=0;i<numRows;i++){
vector<int> row;
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
if(j==0 || i==j){
row.push_back(1);
}
else{
row.push_back(res[i-1][j-1]+res[i-1][j]);
}
}
res.push_back(row);
}
return res;
}
};

有效的括号

class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> stack;
for(char c:s){
if(c=='(' || c=='[' || c=='{'){
stack.push(c);
}
else {
if(stack.empty()){
return false;
}
char temp=stack.top();
if(!((c==')' && (c-1)==temp) || ((c-2)==temp))){
return false;
}
stack.pop();
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
};

缺失数字

class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
res^=nums[i]^i;
}
return res^nums.size();
}
};
解题思路
将这题转换思路,改成仅仅出现一次的数字是谁
比如原先数字是0,1,3 那么我为他补上0,1,2,3那么2就是仅出现一次的数字
使用异或运算,将所有值进行异或
异或运算,相异为真,相同为假,所以 a^a = 0 ;0^a = a
因为异或运算 满足交换律 a^b^a = a^a^b = b 所以数组经过异或运算,单独的值就剩下了
请参考下面的例题:只出现一次的数字

-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
万水千山总是情,打赏一分行不行,所以如果你心情还比较高兴,也是可以扫码打赏博主,哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!