一、圆角、rgba
设置某一个角的圆角,比如设置左上角的圆角:
border-top-left-radius:30px 60px;
border-top-left-radius: 60px;

同时分别设置四个角:
border-radius:30px 60px 120px 150px;
设置四个圆角相同:
border-radius:50%;
①盒子透明度表示法:
.box { opacity:0.1; /* 兼容IE */ filter:alpha(opacity=10); }
②rgba(0,0,0,0.1) 前三个数值表示颜色,第四个数值表示颜色的透明度
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>透明度</title> <style type="text/css"> body{ background: url(images/banner01.jpg); } .box{ width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: #000; color: #fff; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; font-size: 30px; /*设置透明度*/ opacity: 0.3; /*兼容IE*/ filter: alpha(opacity=30); } .box2{ width: 300px; height: 100px; /*设置盒子透明但文字不会变透明*/ background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.3); color: #fff; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; font-size: 30px; margin-top: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">这是一个div</div> <div class="box2">这是一个div</div> </body> </html>

二、transition动画
1、transition-property 设置过渡的属性,比如:width height background-color
2、transition-duration 设置过渡的时间,比如:1s 500ms
3、transition-timing-function 设置过渡的运动方式,常用有 linear(匀速)|ease(缓冲运动)
4、transition-delay 设置动画的延迟
5、transition: property duration timing-function delay 同时设置四个属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>transition动画</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: gold; transition: width 1s ease,height 1s ease 1s,background-color 1s ease 2s; } .box:hover{ width: 600px; height: 600px; background-color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>
如果是多个属性同时的动画,可以合并成下面语句:
.box{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: gold; /*transition: width 1s ease,height 1s ease,background-color 1s ease;*/ transition: all 1s ease; } .box:hover{ width: 600px; height: 600px; background-color: red; }
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图片说明</title> <style type="text/css"> .pic_con{ width: 200px; height: 300px; margin: 50px auto 0; position: relative; overflow: hidden; } .pic_info{ position: absolute; left: 0; top: 300px; width: 180px; height: 100px; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.3); color: #fff; padding: 10px; transition: all 500ms ease; } .pic_con:hover .pic_info{ top:180px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="pic_con"> <a href=""><img src="images/banner01.jpg" alt=""></a> <div class="pic_info"> <h3>标题</h3> <p>文字说明的内容文字说明的内容</p> </div> </div> </body> </html>

三、transform变换
1、translate(x,y) 设置盒子位移
2、scale(x,y) 设置盒子缩放
3、rotate(deg) 设置盒子旋转
4、skew(x-angle,y-angle) 设置盒子斜切
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>变换</title> <!-- 变换不是动画 --> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; background-color: gold; margin: 50px auto 0; /*translate位移的性能比定位要高*/ transform: translate(0px,0px); transition: all 1s ease; } .box:hover{ transform: translate(30px,30px); } .box2{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; background-color: gold; margin: 50px auto 0; /*放大一倍*/ transform: scale(1,1); transition: all 1s ease; } .box2:hover{ transform: scale(2,2); } .box3{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; background-color: gold; margin: 50px auto 0; /*旋转 默认绕着z轴旋转*/ transform: rotate(0deg); transition: all 1s ease; } .box3:hover{ transform: rotate(45deg); } .box4{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; background-color: gold; margin: 50px auto 0; /*斜切 不好控制一般不用*/ transform: skew(0,0); transition: all 1s ease; } .box4:hover{ transform: skew(45deg,0deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> <div class="box4"></div> </body> </html>
5、tranform-origin 设置变形的中心点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>transform</title> <style type="text/css"> div{ width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 3px solid #000; background-color: pink; margin: 30px; float: left; transition: all 500ms ease; } .box2{ transform-origin: left center; } .box3{ transform-origin: left top; } .box4{ transform-origin: 50px 50px; } div:hover{ transform: rotate(45deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> <div class="box3"></div> <div class="box4"></div> </body> </html>
6、rotateX、rotateY、rotateZ 设置三维旋转
7、perspective 设置透视距离
8、transform-style:flat | preserve-3d 设置盒子是否按3d空间显示
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>三维旋转</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: yellowgreen; border: 3px solid #000; margin: 50px auto 0; /*设置盒子按3d显示*/ transform-style: preserve-3d; /*3d旋转需要设置一个透视距离,一般值为800px*/ /*不设置初始值 可能会出现跳变的bug*/ transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(0deg); transition: all 1s ease; } .box:hover{ transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(90deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>
9、scaleX、scaleY、scaleZ 设置三维缩放
10、translateX、translateY、translateZ 设置三维移动
11、backface-visibility 设置盒子背面是否可见
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>图片翻转</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 700px; height: 272px; border: 3px solid #000; margin: 50px auto 0; position: relative; transform-style: preserve-3d; } .box img{ position: absolute; left: 200px; top: 0; transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(0deg); transition: all 1s ease; /*设置盒子背面不可见*/ backface-visibility: hidden; } .box:hover img{ transform:perspective(800px) rotateY(180deg); } .box .back{ width: 300px; height: 272px; background-color: pink; font-size: 20px; text-align: center; line-height: 272px; position: absolute; left: 200px; top: 0; /*背面的初始角度设为-180deg,保证顺时针旋转*/ transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(-180deg); transition: all 1s ease; backface-visibility: hidden; } .box:hover .back{ transform: perspective(800px) rotateY(0deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="images/location_bg.jpg" /> <div class="back">图片的说明文字</div> </div> </body> </html>

四、animation动画
关键帧动画,设置元素自己动,不需要触发。
1、@keyframes 定义关键帧动画
2、animation-name 动画名称
3、animation-duration 动画时间
4、animation-timing-function 动画曲线 linear(匀速)|ease(缓冲)|steps(步数)
5、animation-delay 动画延迟
6、animation-iteration-count 动画播放次数 n|infinite
7、animation-direction 动画结束后是否反向还原 normal|alternate
8、animation-play-state 动画状态 paused(停止)|running(运动)
9、animation-fill-mode 动画前后的状态 none(缺省)|forwards(结束时停留在最后一帧)|backwards(开始时停留在定义的开始帧)|both(前后都应用)
10、animation:name duration timing-function delay iteration-count direction;同时设置多个属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>动画</title> <style type="text/css"> /* 定义动画 */ @keyframes moving{ from{ width: 100px; } to{ width: 500px; } } .box{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: gold; /*名称 时间 动画曲线 动画延迟 播放次数 是否反向还原*/ /*如果设置了反向还原,一去一来算两次播放*/ animation: moving 1s ease 1s 4 alternate; } .box:hover{ /*播放状态变为暂停*/ animation-play-state: paused; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>
风车动画:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>风车</title> <style type="text/css"> @keyframes fc_rotate{ from{ transform: rotate(0); } to{ transform: rotate(360deg); } } .fc{ display: block; width: 400px; height: 400px; margin: 50px auto 0; /*一次1s 匀速旋转 延迟可以不设 无限次 不设返回*/ animation: fc_rotate 1s linear infinite; animation-play-state: paused; } .fc:hover{ /*鼠标放上去才会转动*/ animation-play-state: running; } </style> </head> <body> <img src="images/fengche.png" alt="风车" class="fc" /> </body> </html>
loading动画:
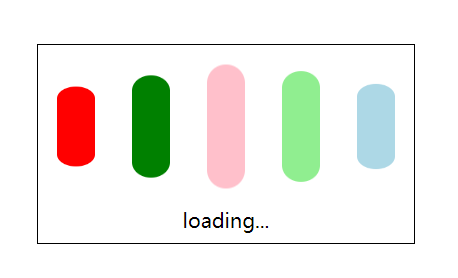
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>loading动画</title> <style type="text/css"> @keyframes loading{ from{ transform: scale(1,1); } to{ transform: scale(1,0.5); } } .con{ width: 300px; height: 158px; border: 1px solid #000; margin: 150px auto 0; } .con div{ width: 30px; height: 100px; float: left; background-color: gold; margin: 15px; border-radius: 15px; animation: loading 500ms ease infinite alternate; } .con div:nth-child(1){ background-color: red; } .con div:nth-child(2){ background-color: green; animation-delay: 100ms; } .con div:nth-child(3){ background-color: pink; animation-delay: 200ms; } .con div:nth-child(4){ background-color: lightgreen; animation-delay: 300ms; } .con div:nth-child(5){ background-color: lightblue; animation-delay: 400ms; } .con p{ text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con"> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> <div></div> <p>loading...</p> </div> </body> </html>
走路动画:
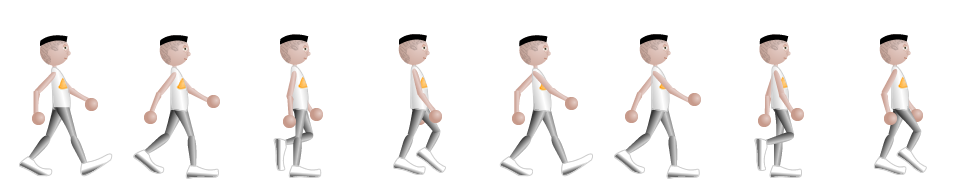
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>走路动画</title> <style type="text/css"> @keyframes walking{ from{ left: 0; } to{ left: -960px; } } .box{ width: 120px; height: 180px; border: 1px solid #000; margin: 50px auto 0; overflow: hidden; position: relative; } .box img{ position: absolute; left: 0; top: 0; /*变换方式为跳变,分八次完成*/ animation: walking 1s steps(8) infinite; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="images/walking.png" alt="走路动画"> </div> </body> </html>
五、CSS3新增选择器
1、E:nth-child(n):匹配元素类型为E且是父元素的第n个子元素
2、E:first-child:匹配元素类型为E且是父元素的第一个子元素
3、E:last-child:匹配元素类型为E且是父元素的最后一个子元素
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .list{ list-style: none; width: 100px; height: 120px; background-color: gold; } .list li:nth-child(2){ color: red; } .list li:nth-child(4){ color: blue; } .list li:last-child{ color: #fff; } </style> </head> <body> <ul class="list"> <li>内容</li> <li>内容</li> <li>内容</li> <li>内容</li> <li>内容</li> </ul> </body> </html>

4、E > F E元素下面第一层子集
5、E ~ F E元素后面的所有兄弟元素
6、E + F 紧挨着的后面的兄弟元素
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style type="text/css"> .box p:nth-child(3)>a{ text-decoration: none; color: pink; } .box~div{ border: 1px solid #000; width: 100px; margin: 10px; } .box+div{ color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> <p><a href="#">链接</a></p> </div> <div> 1234 </div> <div> 0000 </div> </body> </html>

属性选择器:
1、E[attr] 含有attr属性的元素
<style type="text/css"> div[data-attr='ok']{ color:red; } </style> ...... <div data-attr="ok">这是一个div元素</div>
2、E[attr='ok'] 含有attr属性的元素且它的值为“ok”
3、E[attr^='ok'] 含有attr属性的元素且它的值的开头含有“ok”
4、E[attr$='ok'] 含有attr属性的元素且它的值的结尾含有“ok”
5、E[attr*='ok'] 含有attr属性的元素且它的值中含有“ok”
六、CSS权重
CSS权重指的是样式的优先级,有两条或多条样式作用于一个元素,权重高的那条样式对元素起作用,权重相同的,后写的样式会覆盖前面写的样式。
把样式的应用方式分为几个等级,按照等级来计算权重
1、!important,加在样式属性值后,权重值为 10000
2、内联样式,如:style=””,权重值为1000
3、ID选择器,如:#content,权重值为100
4、类,伪类和属性选择器,如: content、:hover 权重值为10
5、标签选择器和伪元素选择器,如:div、p、:before 权重值为1
6、通用选择器(*)、子选择器(>)、相邻选择器(+)、同胞选择器(~)、权重值为0
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>权重</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ color: red!important; } #content div.main_content h2{ color: gold; } #content .main_content h2{ color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box" style="color: blue;"> 这是一个div元素 </div> <div id="content"> <div class="main_content"> <h2>这是一个h2标题</h2> </div> </div> <!-- 第一条样式的权重计算: 100+1+10+1,结果为112; 第二条样式的权重计算: 100+10+1,结果为111; h2标题的最终颜色为red --> </body> </html>

七、移动端与PC端布局区别
视口
视口是移动设备上用来显示网页的区域,一般会比移动设备可视区域大,宽度可能是980px或者1024px,目的是为了显示下整个为PC端设计的网页,这样带来的后果是移动端会出现横向滚动条,为了避免这种情况,移动端会将视口缩放到移动端窗口的大小。这样会让网页不容易观看。
可以用 meta 标签,name=“viewport ” 来设置视口的大小,将视口的大小设置为和移动设备可视区一样的大小。
设置方法如下( 快捷方式:meta:vp + tab ):
<head> ...... <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> ...... </head>
pc端与移动端渲染网页过程
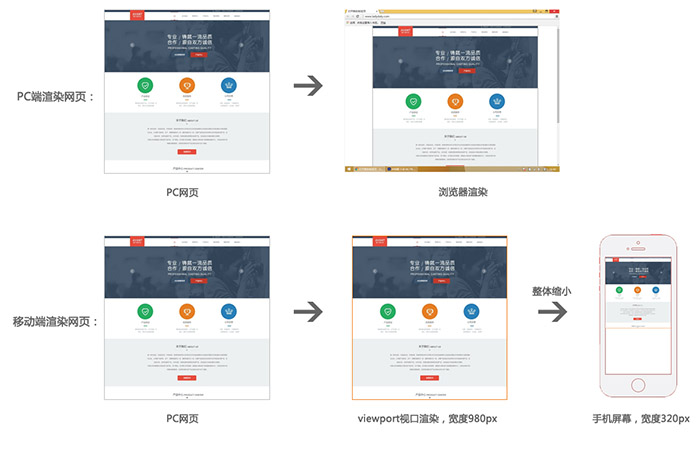
视口默认按980px渲染网页,然后直接缩放,这样虽然不会出现滚动条,但会导致页面内容过小。
设置视口大小,可以使视口渲染时就按照手机屏幕大小来渲染
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>视口</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: gold; } </style> <!-- 快捷键 meta:vp + tab --> <!-- width=device-width 视口宽度 --> <!-- user-scalable=no 不允许用户自己缩放 --> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>
视网膜屏幕(retina屏幕)清晰度解决方案
视网膜屏幕指的是屏幕的物理像素密度更高的屏幕,物理像素可以理解为屏幕上的一个发光点,无数发光的点组成的屏幕,视网膜屏幕比一般屏幕的物理像素点更小,常见有2倍的视网膜屏幕和3倍的视网膜屏幕,2倍的视网膜屏幕,它的物理像素点大小是一般屏幕的1/4,3倍的视网膜屏幕,它的物理像素点大小是一般屏幕的1/9。
图像在视网膜屏幕上显示的大小和在一般屏幕上显示的大小一样,但是由于视网膜屏幕的物理像素点比一般的屏幕小,图像在上面好像是被放大了,图像会变得模糊,为了解决这个问题,可以使用比原来大一倍的图像,然后用css样式强制把图像的尺寸设为原来图像尺寸的大小,就可以解决模糊的问题。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>retina</title> <style type="text/css"> <!-- 通过样式将尺寸设为原来的一半 --> .shipei{ width: 300px; height: 215px; } </style> </head> <body> <img src="images/pic1x.jpg" alt="1倍图"> <img src="images/pic2x.jpg" alt="2倍图" class="shipei"> </body> </html>
背景图为了适配retina,也要用两倍图片来缩放。
背景图强制改变大小,可以使用background新属性:
background-size:
length:用长度值指定背景图像大小。不允许负值。
percentage:用百分比指定背景图像大小。不允许负值。
auto:背景图像的真实大小。
cover:将背景图像等比缩放到完全覆盖容器,背景图像有可能超出容器。
contain:将背景图像等比缩放到宽度或高度与容器的宽度或高度相等,背景图像始终被包含在容器内。
八、适配布局类型
适配方法
设备屏幕有多种不同的分辨率,页面适配方案有如下几种:
1、全适配:响应式布局+流体布局
2、移动端适配:
流体布局+少量响应式
基于rem的布局
流体布局
流体布局,就是使用百分比来设置元素的宽度,元素的高度按实际高度写固定值,流体布局中,元素的边线无法用百分比,可以使用样式中的计算函数 calc() 来设置宽度,或者使用 box-sizing 属性将盒子设置为从边线计算盒子尺寸。
calc()
可以通过计算的方式给元素加尺寸,比如: width:calc(25% - 4px);
box-sizing
1、content-box 默认的盒子尺寸计算方式
2、border-box 设置盒子的尺寸计算方式为从边框开始,盒子的尺寸,边框和内填充算在盒子尺寸内
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>流体布局</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <style type="text/css"> body{ margin: 0; } .con a{ display: block; /*css3新属性 解决边框问题 要写空格*/ width: calc(25% - 4px); height: 100px; background-color: gold; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; font-size: 18px; float: left; border: 2px solid #000; } .con2 a{ display: block; width: 25%; height: 100px; background-color: gold; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; font-size: 18px; float: left; border: 2px solid #000; /*设置宽度从边框开始计算*/ box-sizing: border-box; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con"> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> </div> <div class="con2"> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> <a href="#">链接</a> </div> </body> </html>
响应式布局
响应式布局就是使用媒体查询的方式,通过查询浏览器宽度,不同的宽度应用不同的样式块,每个样式块对应的是该宽度下的布局方式,从而实现响应式布局。响应式布局的页面可以适配多种终端屏幕(pc、平板、手机)
@media (max-width:960px){
.left_con{width:58%;}
.right_con{width:38%;}
}
@media (max-width:768px){
.left_con{width:100%;}
.right_con{width:100%;}
}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>响应式布局</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <style type="text/css"> body{ margin: 0; } .con div{ width: 23%; height:200px; border: 2px solid #000; background-color: gold; margin: 1%; float: left; /*边框算到23%里*/ box-sizing: border-box; } /*屏幕宽度小于800时下面的样式起作用*/ @media (max-width: 800px) { .con div{ width: 46%; margin: 2%; } } @media (max-width: 400px) { .con div{ width: 94%; margin: 3%; } } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con"> <div>1</div> <div>2</div> <div>3</div> <div>4</div> </div> </body> </html>
基于rem的布局
首先了解em单位,em单位是参照元素自身的文字大小来设置尺寸。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>em</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ font-size: 15px; width: 20em;/*300px*/ height: 10em;/*150px*/ background-color: gold; } .box2{ font-size: 20px; width: 20em;/*400px*/ height: 10em;/*200px*/ text-indent: 2em;/*缩进两个字大小*/ background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">这是一个盒子</div> <div class="box2">这是一个盒子</div> </body> </html>
rem指的是参照根节点的文字大小,根节点指的是html标签,设置html标签的文字大小,其他的元素相关尺寸设置用rem,这样,所有元素都有了统一的参照标准,改变html文字的大小,就会改变所有元素用rem设置的尺寸大小。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" style="font-size: 20px;"> <!-- rem参照HTML的文字大小标准 --> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>rem</title> <style type="text/css"> .box{ font-size: 15px; width: 20rem; height: 10rem; background-color: gold; } .box2{ font-size: 20px; width: 20rem; height: 10rem; text-indent: 2rem; background-color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box">这是一个盒子</div> <div class="box2">这是一个盒子</div> </body> </html>
cssrem安装
cssrem插件可以动态地将px尺寸换算成rem尺寸
下载本项目,比如:git clone https://github.com/flashlizi/cssrem 进入packages目录:Sublime Text -> Preferences -> Browse Packages,复制下载的cssrem目录到刚才的packges目录里。 重启Sublime Text。
配置参数 参数配置文件:Sublime Text -> Preferences -> Package Settings -> cssrem px_to_rem - px转rem的单位比例,默认为40。 max_rem_fraction_length - px转rem的小数部分的最大长度。默认为6。 available_file_types - 启用此插件的文件类型。默认为:[".css", ".less", ".sass"]。
九、浏览器前缀
为了让CSS3样式兼容,需要将某些样式加上浏览器前缀:
-ms- 兼容IE浏览器
-moz- 兼容firefox
-o- 兼容opera
-webkit- 兼容chrome 和 safari(一般加这一句就可以了)
div { -ms-transform: rotate(30deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(30deg); -o-transform: rotate(30deg); -moz-transform: rotate(30deg); transform: rotate(30deg); }
自动添加浏览器前缀:
目前的状况是,有些CSS3属性需要加前缀,有些不需要加,有些只需要加一部分,这些加前缀的工作可以交给插件来完成,比如安装: autoprefixer
可以在Sublime text中通过package control 安装 autoprefixer
Autoprefixer在Sublime text中的设置:
1、preferences/key Bindings-User
{ "keys": ["ctrl+alt+x"], "command": "autoprefixer" }
2、Preferences>package setting>AutoPrefixer>Setting-User
{
"browsers": ["last 7 versions"],
"cascade": true,
"remove": true
}
last 7 versions:最新的浏览器的7个版本
cascade:缩进美化属性值
remove:是否去掉不必要的前缀
十、HTML5新增标签
新增语义标签
1、<header> 页面头部、页眉
2、<nav> 页面导航
3、<article> 一篇文章
4、<section> 文章中的章节
5、<aside> 侧边栏
6、<footer> 页面底部、页脚
音频视频
1、<audio>
2、<video>
以上标签实际使用不多。
PC端兼容h5的新标签的方法,在页面中引入以下js文件
<script type="text/javascript" src="//cdn.bootcss.com/html5shiv/r29/html5.js"></script>
HTML5新增表单控件
新增类型:网址 邮箱 日期 时间 星期 数量 范围 电话 颜色 搜索
<label>网址:</label><input type="url" name="" required><br><br> <label>邮箱:</label><input type="email" name="" required><br><br> <label>日期:</label><input type="date" name=""><br><br> <label>时间:</label><input type="time" name=""><br><br> <label>星期:</label><input type="week" name=""><br><br> <label>数量:</label><input type="number" name=""> <br><br> <label>范围:</label><input type="range" name=""><br><br> <label>电话:</label><input type="tel" name=""><br><br> <label>颜色:</label><input type="color" name=""><br><br> <label>搜索:</label><input type="search" name=""><br><br>
新增常用表单控件属性:
1、placeholder 设置文本框默认提示文字
2、autofocus 自动获得焦点(不用设置值)
3、autocomplete 联想关键词



