React.js Component组件,生命周期
首先声明因为公司需要用到react.js自己就学习了下,最基础得教程可以直接百度快速链接地址(https://www.runoob.com/react/react-install.html),以下是react各个组件得生命周期
一、概述
React可以将组件定义为类或函数。定义为类的组件当前提供了更多的功能。要定义React组件类,您需要扩展React.Component:
class Welcome extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>;
}
}
必须在React.Component子类中定义的唯一方法称为render()。描述的所有其他方法都是可选的。
强烈建议不要创建您自己的基础组件类。在React组件中,代码重用主要是通过组合而不是继承来实现的。
二、组件的生命周期
每个组件都有几个“生命周期方法”,您可以重写以在该进程中的特定时间运行代码。您可以使用此生命周期图作为备忘单。在下面的列表中,常用的生命周期方法标记为粗体。其余的存在于相对罕见的用例中。

2.1、创建【Mount】
2.2、更新
static getDerivedStateFromProps()shouldComponentUpdate()render()getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()componentDidUpdate()
2.3、卸载【Unmounting】
三、其他API
Each component also provides some other APIs:
Class Properties
Instance Properties
四、详细介绍
4.1、render【渲染】
render()方法是类组件中唯一需要的方法。调用时,它应该检查this.props和this.state并返回以下类型之一:React elements.Arrays and fragments. Portals. String and numbers. Booleans or null.
注意:如果shouldComponentUpdate()返回false,则不会调用render()。
4.2、constructor【构造方法】
如果您没有初始化状态并且没有绑定方法,则不需要为您的React组件实现构造函数。
通常,React构造函数只用于两个目的:通过将对象分配给this.state来初始化本地状态。 将事件处理程序方法绑定到实例。
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// Don't call this.setState() here!
this.state = { counter: 0 };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
构造函数是你应该直接分配this.state的唯一地方。在所有其他方法中,您需要使用this.setState()。
避免在构造函数中引入任何副作用或订阅。对于这些用例,请改用componentDidMount()
以下是错误的
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// Don't do this!
this.state = { color: props.color };
}
4.3、componentDidMount
componentDidMount()在装载组件(插入树中)后立即调用。需要DOM节点的初始化应该放在这里。如果您需要从远程端点加载数据,则这是一个实例化网络请求的好地方。
此方法是设置任何订阅的好地方。如果你这样做,不要忘记在componentWillUnmount()中取消订阅。
您可以立即在componentDidMount()中调用setState()。它会触发一个额外的渲染,但它会在浏览器更新屏幕之前发生。这保证即使render()在这种情况下被调用两次,用户也不会看到中间状态。请谨慎使用此模式,因为它经常会导致性能问题。在大多数情况下,您应该能够在构造函数()中分配初始状态。然而,当你需要在渲染依赖于它的大小或位置的东西之前测量DOM节点时,它可能需要类似于模态和工具提示的情况。
4.4、componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
在更新发生后立即调用componentDidUpdate()。此方法不用于初始渲染。
在更新组件时,将此用作在DOM上操作的机会。只要您将当前的道具与以前的道具进行比较(例如,如果道具没有改变,则可能不需要网络请求),这也是做网络请求的好地方。
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
// Typical usage (don't forget to compare props):
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
}
您可以在componentDidUpdate()中立即调用setState(),但请注意它必须像上例那样包装,否则会导致无限循环。它也会导致额外的重新渲染,虽然用户不可见,但会影响组件的性能。
如果您的组件实现getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()生命周期(很少见),则它返回的值将作为第三个“快照”参数传递给componentDidUpdate()。否则这个参数将是未定义的。
注意:如果shouldComponentUpdate()返回false,则不会调用componentDidUpdate()。
4.5、componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount()在组件被卸载并销毁之前立即被调用。在此方法中执行任何必要的清理,例如使定时器无效,取消网络请求或清理在componentDidMount()中创建的任何预订。
您不应该在componentWillUnmount()中调用setState(),因为组件不会被重新渲染。一旦组件实例被卸载,它将永远不会再被挂载。
4.6、很少使用的生命周期方法
https://reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html#rarely-used-lifecycle-methods
4.7、整个生命周期简介
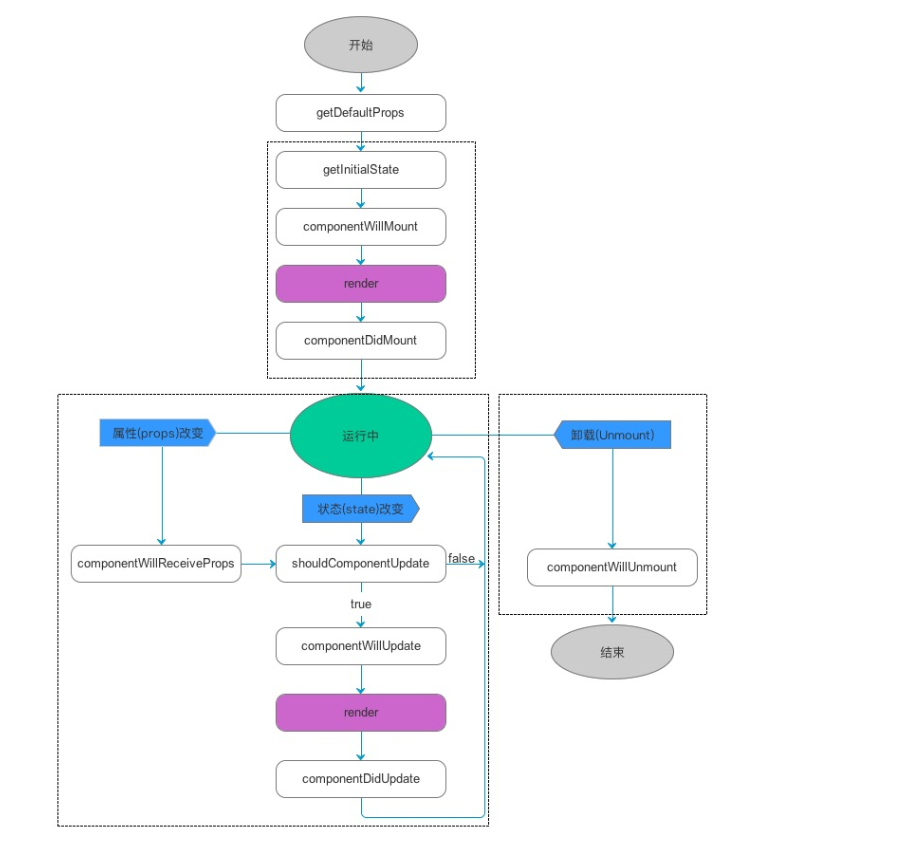
getDefaultProps
object getDefaultProps()
执行过一次后,被创建的类会有缓存,映射的值会存在this.props,前提是这个prop不是父组件指定的
这个方法在对象被创建之前执行,因此不能在方法内调用this.props ,另外,注意任何getDefaultProps()返回的对象在实例中共享,不是复制
getInitialState
object getInitialState()
控件加载之前执行,返回值会被用于state的初始化值
componentWillMount
void componentWillMount()
执行一次,在初始化render之前执行,如果在这个方法内调用setState,render()知道state发生变化,并且只执行一次
render
ReactElement render()
render的时候会调用render()会被调用
调用render()方法时,首先检查this.props和this.state返回一个子元素,子元素可以是DOM组件或者其他自定义复合控件的虚拟实现
如果不想渲染可以返回null或者false,这种场景下,React渲染一个<noscript>标签,当返回null或者false时,ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this)返回null render()方法是很纯净的,这就意味着不要在这个方法里初始化组件的state,每次执行时返回相同的值,不会读写DOM或者与服务器交互,如果必须如服务器交互,在componentDidMount()方法中实现或者其他生命周期的方法中实现,保持render()方法纯净使得服务器更准确,组件更简单
componentDidMount
void componentDidMount()
在初始化render之后只执行一次,在这个方法内,可以访问任何组件,componentDidMount()方法中的子组件在父组件之前执行
从这个函数开始,就可以和 JS 其他框架交互了,例如设置计时 setTimeout 或者 setInterval,或者发起网络请求
shouldComponentUpdate
boolean shouldComponentUpdate( object nextProps, object nextState )
这个方法在初始化render时不会执行,当props或者state发生变化时执行,并且是在render之前,当新的props或者state不需要更新组件时,返回false
shouldComponentUpdate: function(nextProps, nextState) { return nextProps.id !== this.props.id; }
当shouldComponentUpdate方法返回false时,讲不会执行render()方法,componentWillUpdate和componentDidUpdate方法也不会被调用
默认情况下,shouldComponentUpdate方法返回true防止state快速变化时的问题,但是如果·state不变,props只读,可以直接覆盖shouldComponentUpdate用于比较props和state的变化,决定UI是否更新,当组件比较多时,使用这个方法能有效提高应用性能
componentWillUpdate
void componentWillUpdate( object nextProps, object nextState )
当props和state发生变化时执行,并且在render方法之前执行,当然初始化render时不执行该方法,需要特别注意的是,在这个函数里面,你就不能使用this.setState来修改状态。这个函数调用之后,就会把nextProps和nextState分别设置到this.props和this.state中。紧接着这个函数,就会调用render()来更新界面了
componentDidUpdate
void componentDidUpdate( object prevProps, object prevState )
组件更新结束之后执行,在初始化render时不执行
componentWillReceiveProps
void componentWillReceiveProps( object nextProps )
当props发生变化时执行,初始化render时不执行,在这个回调函数里面,你可以根据属性的变化,通过调用this.setState()来更新你的组件状态,旧的属性还是可以通过this.props来获取,这里调用更新状态是安全的,并不会触发额外的render调用
componentWillReceiveProps: function(nextProps) { this.setState({ likesIncreasing: nextProps.likeCount > this.props.likeCount }); }
componentWillUnmount
void componentWillUnmount()
当组件要被从界面上移除的时候,就会调用componentWillUnmount(),在这个函数中,可以做一些组件相关的清理工作,例如取消计时器、网络请求等
总结
React Native的生命周期,其中最上面的虚线框和右下角的虚线框的方法一定会执行,左下角的方法根据props state是否变化去执行,其中建议只有在componentWillMount,componentDidMount,componentWillReceiveProps方法中可以修改state值
五、其他API
与上面的生命周期方法(React为您调用)不同,下面的方法是您可以从组件调用的方法。
5.1、setState(updater[, callback])
setState()将对组件状态的更改排队,并告诉React该组件及其子组需要使用更新的状态重新呈现。这是您用来更新用户界面以响应事件处理程序和服务器响应的主要方法。
setState()并不总是立即更新组件。它可能会批处理或推迟更新,直到稍后。
第一个参数是带签名的更新函数:
其中只有两个:setState()和forceUpdate()。
(prevState, props) => stateChange
prevState是对之前状态的引用。它不应该直接变异。相反,应该通过建立一个基于prevState和道具输入的新对象来表示更改。例如,假设我们想通过props.step来增加状态值:
this.setState((prevState, props) => {
return {counter: prevState.counter + props.step};
});
setState()的第二个参数是一个可选的回调函数,一旦setState完成并且组件被重新渲染,该函数将被执行。通常我们建议使用componentDidUpdate()代替这种逻辑。
更多详细:
https://reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html#setstate
5.2、component.forceUpdate(callback)
默认情况下,当你的组件的状态或道具改变时,你的组件将重新渲染。如果你的render()方法依赖于其他的数据,你可以通过调用forceUpdate()来告诉React组件需要重新渲染。
调用forceUpdate()将导致在组件上调用render(),跳过shouldComponentUpdate()。这将触发子组件的正常生命周期方法,包括每个子组件的shouldComponentUpdate()方法。如果标记更改,React仍然只会更新DOM。
通常你应该尽量避免使用forceUpdate(),只能从render.props和this.state中读取render()。
六、类属性
6.1、默认属性
class CustomButton extends React.Component {
// ...
}
CustomButton.defaultProps = {
color: 'blue'
};
6.2、displayName
字符串用于调试消息。通常,您不需要明确设置它,因为它是根据定义组件的函数或类的名称推断出来的。如果要为调试目的显示不同的名称或创建高阶组件时,可能需要显式设置它,
七、实例属性
7.1、props
不能被修改
7.2、state
状态包含特定于此组件的数据,这些数据可能随时间而改变。状态是用户定义的,它应该是一个普通的JavaScript对象。
posted on 2021-06-02 16:56 UnmatchedSelf 阅读(203) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



