es6 Class类的理解
------------恢复内容开始------------
概念:
class类是es6的一种构造函数语法糖写法。
创建一个class类
class myClass{
//构造器,默认为空的构造器 //当class在被new时就会调用构造器 //相当于function //function myClass(name,age){ // this.name=name // this.age=age //}
////name : string; //类的属性
//age:string
constructor(name,age){ //这些都是实例属性 //只有实例才能访问 this.name=name this.age=age } }
//类的方法
greeting() {};//定义于 constructor 内的属性和方法,即定义在 this 上,属于实例属性和方法,否则属于原型属性和方法。在TypeScript中,是不允许直接在constructor中定义变量的,需要在constructor上面先声明。
使用 class 定义类,使用 constructor 定义构造函数。通过 new 生成新实例的时候,会自动调用构造函数。
创建类实例对象
var i=new myClass('小明',18)
类的继承
使用 extends 关键字实现继承,子类中使用 super 关键字来调用父类的构造函数和方法(super需要同步父类的参数个数?)
//动物类 class AnimalClass { private name : string; public constructor(theName:string){ this.name = theName; }; public move(movedistance : number = 0){ console.log(`${this.name} 移动的距离是 ${movedistance}`); }; } //蛇继承了动物类 class Shake extends AnimalClass{ constructor(name : string){ super(name); //初始化父类
// 如果在子类中写了构造函数,相当于重写了父类的构造函数。 // 在子类构造函数中必须对父类的构造函数进行调用, // 否则父类的构造函数不会执行 }; move(movedistance:number =5){ console.log("Shake..."); super.move(movedistance); } } //马继承了动物类 class House extends AnimalClass{ constructor(name : string){ super(name); }; move(movedistance:number =10){ console.log("House..."); super.move(movedistance);
// 在类的方法中super就表示调用当前类的父类方法 } } let shake = new Shake("蛇"); let house : AnimalClass = new House("马"); shake.move(); // 多态 house.move(50); // 多态
修饰符
typeScript 可以使用三种访问修饰符(Access Modifiers),分别是 public、private 和 protected。
public 修饰的属性或方法是公有的,可以在任何地方被访问到,默认所有的属性和方法都是 public 的
private 修饰的属性或方法是私有的,不能在声明它的类的外部访问
protected 修饰的属性或方法是受保护的,它和 private 类似,区别是它在子类中也是允许被访问的
class AnimalClass { //只有当前类可以访问 private _animalName : string; public constructor(theName:string){ this._animalName = theName; }; //子类可以访问 protected move(movedistance : number = 0){ console.log(`${this._animalName} 移动的距离是 ${movedistance}`); }; private jump(distance : number = 0){ console.log(`${this._animalName} jummp ${distance}`); } // getter setter存取器 set animalName(aName : string){ this._animalName = aName; } get animalName(){ return this._animalName; } }
静态方法、静态属性
使用 static 修饰符修饰的方法称为静态方法,它们不需要实例化,而是直接通过类来调用
class Animal { //静态属性 static num = 42; //静态方法 static isAnimal(a) { return a instanceof Animal; } } let a = new Animal('Jack'); Animal.isAnimal(a); // true a.isAnimal(a); // TypeError: a.isAnimal is not a function console.log(Animal.num); // 42
实例方法和属性
ES6 中实例的属性只能通过构造函数中的 this.xxx 来定义,ES7 提案中可以直接在类里面定义
class Animal { //实例属性 name = 'zibin'; constructor() { // ... } } //实例方法 run() {}; let a = new Animal(); console.log(a.name); // zibin
类的类型
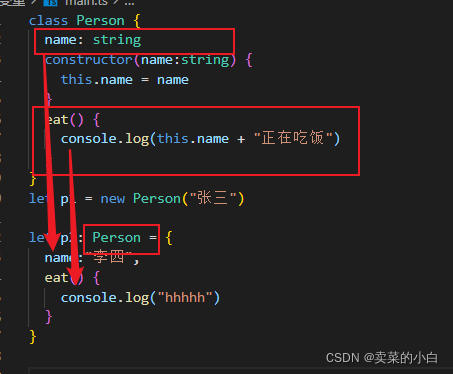
类可以作为数据类型的,如上图所示,我们将Person作为p1的类型,此时p1必须完全按照Person的类型来进行约束。
------------恢复内容结束------------






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构