TreeSet

TreeSet 底层数据结构是二叉树。添加的元素必须进行比较。
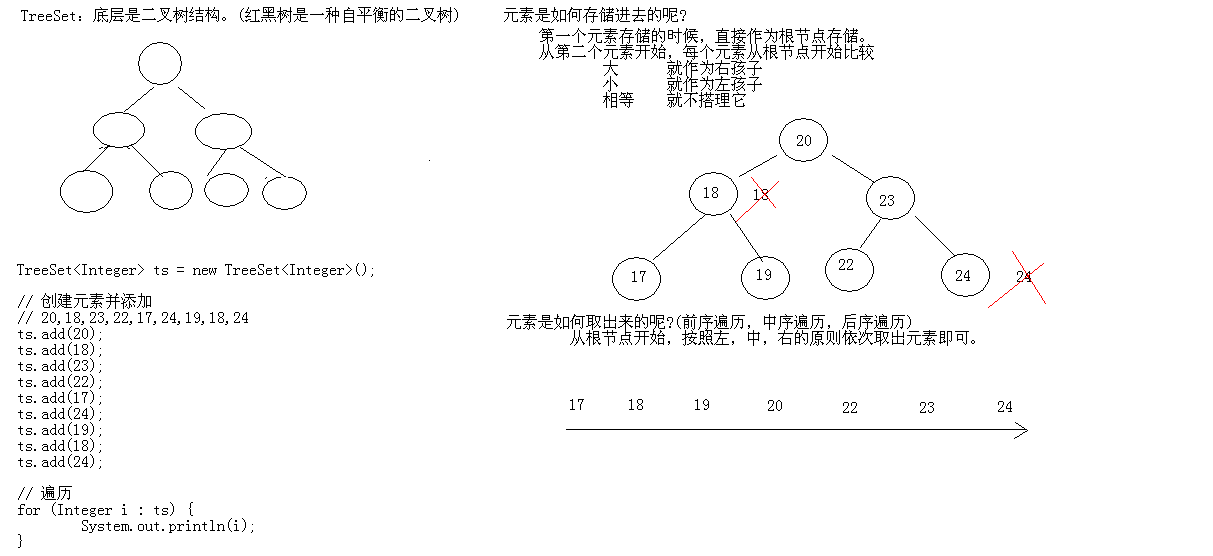
有两种对象比较方式,
一种是自然排序:即元素具备比较性,实现其comparable接口
package treeSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/*按名字的长短排序;
* */
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
public String name;
public int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "名字: " + name + "\t\n年龄: " + age + "\t\n--------";
}
public int compareTo(Student o) {
int num = this.name.length() - o.name.length();
// 姓名的长度相同,不代表姓名的内容相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(o.name) : num;
// 姓名的长度和内容相同,不代表年龄相同,所以还得继续判断年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - o.age : num2;
return num3;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Student> t=new TreeSet<Student>();
t.add(new Student("jacke",20));
t.add(new Student("jack",20));
t.add(new Student("jacken",10));
t.add(new Student("jacke",20));
t.add(new Student("tom",10));
for(Student s:t){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
第二种则是比较器排序 实现comparator接口
package treeSet;
/*TreeSet 底层结构为二叉树
*
*
*
*
*
*
* */
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Studentl {
public String name;
public int No;
public int stu;
public Studentl() {
}
public Studentl(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Studentl(String name, int No) {
this.name = name;
this.No = No;
}
public Studentl(String name, int No, int stu) {
this.name = name;
this.No = No;
this.stu = stu;
}
//重写了toString方法
public String toString() {
return "名字: " + name + "\t\n学号: " + No+"\t\n--------";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getNo() {
return No;
}
/* public int compareTo(Studentl o) {
/*if (this.No > o.No) {
return 1;
} else if (this.No < o.No) {
return -1;
}
return 0;*/
/* int num = this.No - o.No;
// 次要条件
// 年龄相同的时候,还得去看姓名是否也相同
// 如果年龄和姓名都相同,才是同一个元素
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(o.name) : num;
return num2;
}*/
public static void main(String[]args){
TreeSet<Studentl> t3=new TreeSet<Studentl>(new StudentComparator());
//t2.add(new Studentl("a3",12));
///t3.add(new Studentl());
t3.add(new Studentl("a6",16));
t3.add(new Studentl("a7",10));
t3.add(new Studentl("a4",14));
t3.add(new Studentl("a2",12));
t3.add(new Studentl("a1",15));
t3.add(new Studentl("a3",19));
for(Studentl a:t3){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
package treeSet;
import java.util.Comparator;
//比较器比较
public class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Studentl> {
public int compare(Studentl o1, Studentl o2) {
// String o1Name= o1.getName();
// String o2Name= o2.getName();
// if(o1.name==null||o2.name==null) throw new NullPointerException();
int num = o1.getNo() - o2.getNo();
// 次要条件
// 年龄相同的时候,还得去看姓名是否也相同
// 如果年龄和姓名都相同,才是同一个元素
int num2 = num == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : num;
return num2;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号